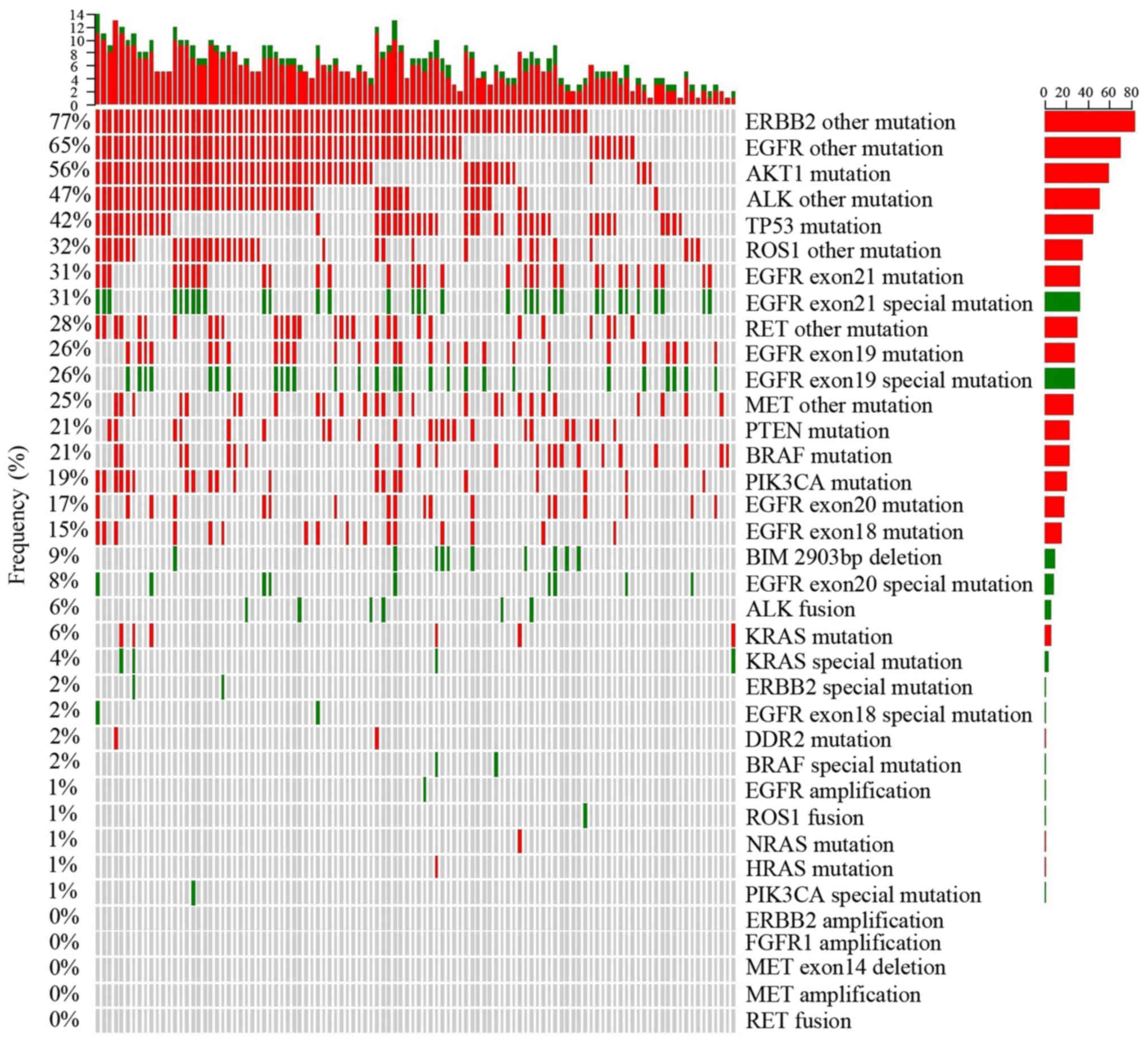
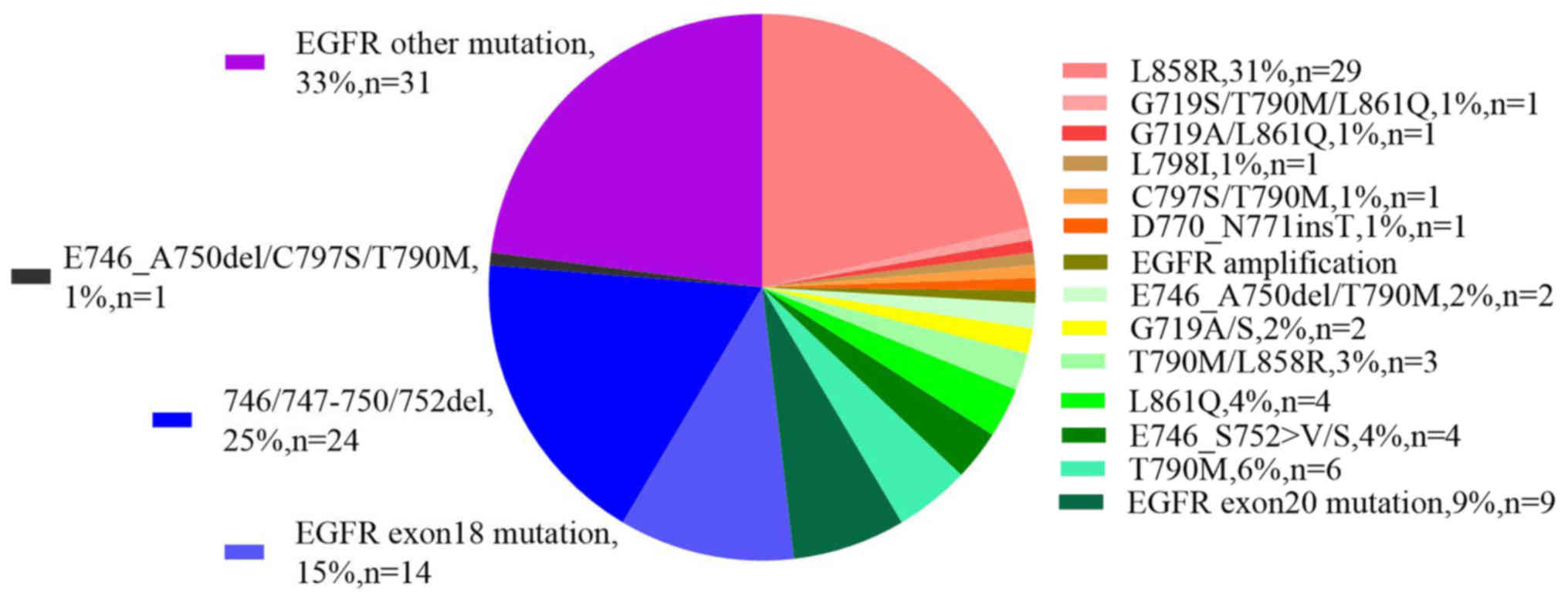
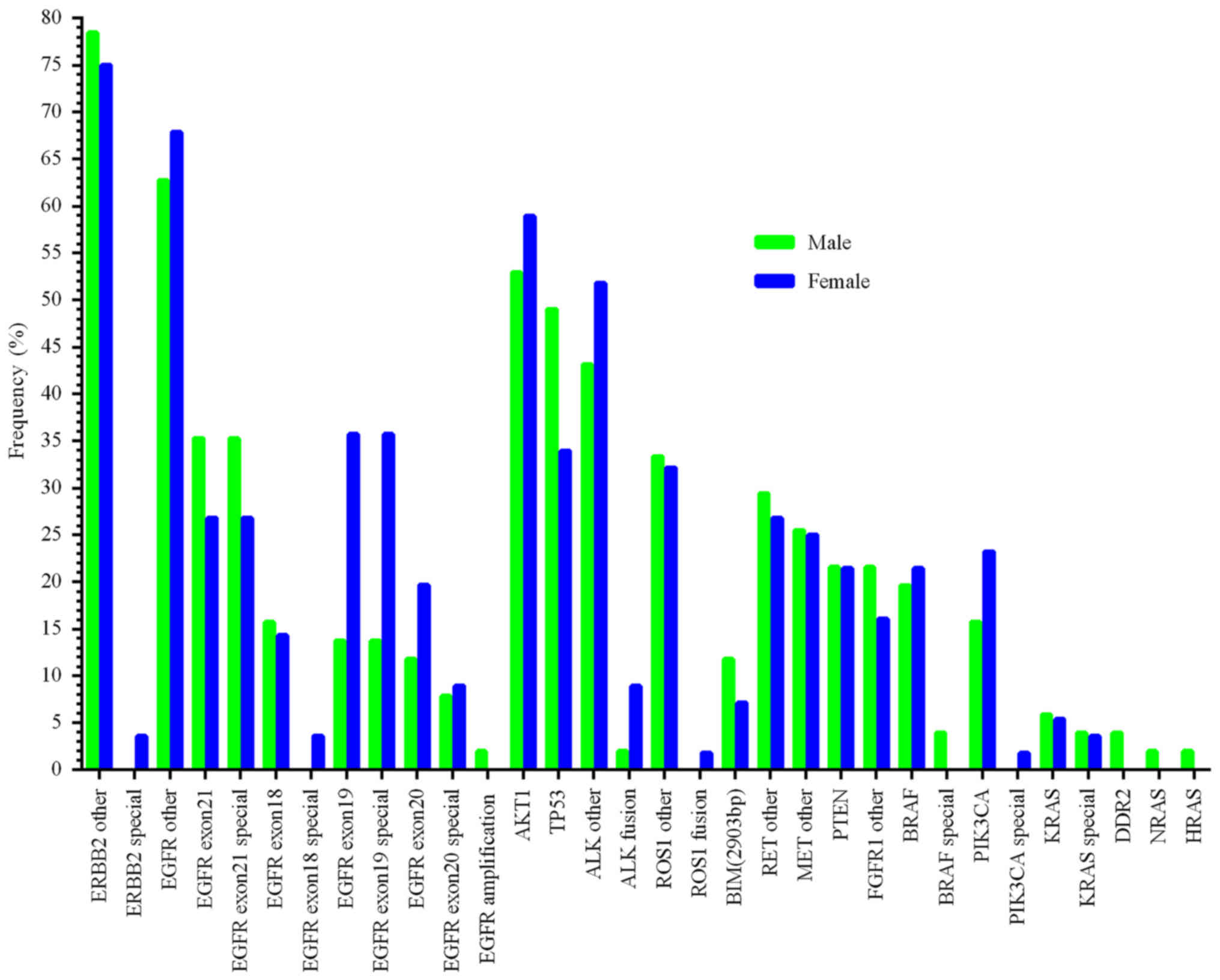
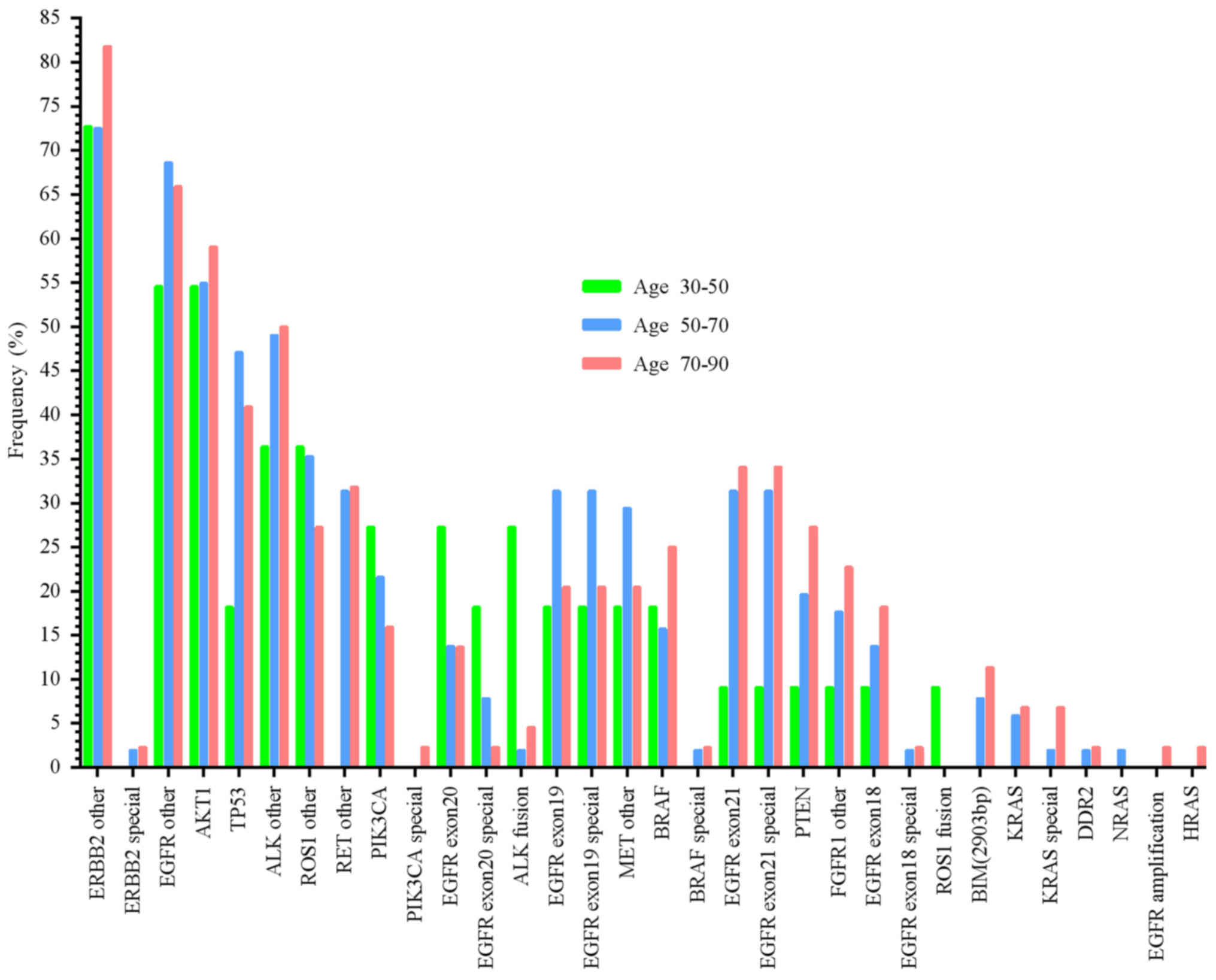
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Spiro SG and Silvestri GA: One hundred
years of lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 172:523–529. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung
cancers. Nature. 489:519–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Imielinski M, Berger AH, Hammerman PS,
Hernandez B, Pugh TJ, Hodis E, Cho J, Suh J, Capelletti M,
Sivachenko A, et al: Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma
with massively parallel sequencing. Cell. 150:1107–1120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Govindan R, Ding L, Griffith M,
Subramanian J, Dees ND, Kanchi KL, Maher CA, Fulton R, Fulton L,
Wallis J, et al: Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in
smokers and never-smokers. Cell. 150:1121–1134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Campbell JD, Alexandrov A, Kim J, Wala J,
Berger AH, Pedamallu CS, Shukla SA, Guo G, Brooks AN, Murray BA, et
al: Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung
adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Nat Genet.
48:607–616. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weinstein IB and Joe A: Oncogene
addiction. Cancer Res. 68:3077–3080; discussion 3080. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Inamura K: Lung Cancer: Understanding its
molecular pathology and the 2015 WHO classification. Front Oncol.
7:1932017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kohno T, Nakaoku T, Tsuta K, Tsuchihara K,
Matsumoto S, Yoh K and Goto K: Beyond ALK-RET, ROS1 and other
oncogene fusions in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 4:156–164.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tan L, Alexander M, Officer A, MacManus M,
Mileshkin L, Jennens R, Herath D, de Boer R, Fox SB, Ball D and
Solomon B: Survival difference according to mutation status in a
prospective cohort study of Australian patients with metastatic
non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Intern Med J. 48:37–44. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han Y and Li J: Sample types applied for
molecular diagnosis of therapeutic management of advanced non-small
cell lung cancer in the precision medicine. Clin Chem Lab Med.
55:1817–1833. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Diaz LA Jr and Bardelli A: Liquid
biopsies: Genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J Clin Oncol.
32:579–586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heitzer E, Ulz P and Geigl JB: Circulating
tumor DNA as a liquid biopsy for cancer. Clin Chem. 61:112–123.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Masters GA, Krilov L, Bailey HH, Brose MS,
Burstein H, Diller LR, Dizon DS, Fine HA, Kalemkerian GP, Moasser
M, et al: Clinical cancer advances 2015: Annual report on progress
against cancer from the American society of clinical oncology. J
Clin Oncol. 33:786–809. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Froudarakis ME: Pleural effusion in lung
cancer: More questions than answers. Respiration. 83:367–376. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roberts ME, Neville E, Berrisford RG,
Antunes G and Ali NJ; BTS Pleural Disease Guideline Group, :
Management of a malignant pleural effusion: British thoracic
society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax. 65 (Suppl
2):ii32–ii40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YL, Lee CT, Lu CC, Yang SC, Chen WL,
Lee YC, Yang CH, Peng SL, Su WC, Chow NH and Ho CL: Epidermal
growth factor receptor mutation and anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene
fusion: Detection in malignant pleural effusion by RNA or PNA
analysis. PLoS One. 11:e01581252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zarogoulidis K, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche
K, Tsakiridis K, Machairiotis N, Kougioumtzi I, Courcoutsakis N,
Terzi E, Zaric B, Huang H, et al: Malignant pleural effusion and
algorithm management. J Thorac Dis. 5 (Suppl 4):S413–S419.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Akamatsu H, Koh Y, Kenmotsu H, Naito T,
Serizawa M, Kimura M, Mori K, Imai H, Ono A, Shukuya T, et al:
Multiplexed molecular profiling of lung cancer using pleural
effusion. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1048–1052. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Agalioti T, Giannou AD and Stathopoulos
GT: Pleural involvement in lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 7:1021–1030.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsai TH, Wu SG, Hsieh MS, Yu CJ, Yang JC
and Shih JY: Clinical and prognostic implications of RET
rearrangements in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma patients with
malignant pleural effusion. Lung Cancer. 88:208–214. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tiran V, Stanzer S, Heitzer E, Meilinger
M, Rossmann C, Lax S, Tsybrovskyy O, Dandachi N and Balic M:
Genetic profiling of putative breast cancer stem cells from
malignant pleural effusions. PLoS One. 12:e01752232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jian G, Songwen Z, Ling Z, Qinfang D, Jie
Z, Liang T and Caicun Z: Prediction of epidermal growth factor
receptor mutations in the plasma/pleural effusion to efficacy of
gefitinib treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1341–1347. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han HS, Eom DW, Kim JH, Kim KH, Shin HM,
An JY, Lee KM, Choe KH, Lee KH, Kim ST, et al: EGFR mutation status
in primary lung adenocarcinomas and corresponding metastatic
lesions: Discordance in pleural metastases. Clin Lung Cancer.
12:380–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu SG, Gow CH, Yu CJ, Chang YL, Yang CH,
Hsu YC, Shih JY, Lee YC and Yang PC: Frequent epidermal growth
factor receptor gene mutations in malignant pleural effusion of
lung adenocarcinoma. Eur Respir J. 32:924–930. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Wang M, Yap WS and Chang
AY: Detection and comparison of epidermal growth factor receptor
mutations in cells and fluid of malignant pleural effusion in
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 60:175–182. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kimura H, Fujiwara Y, Sone T, Kunitoh H,
Tamura T, Kasahara K and Nishio K: EGFR mutation status in
tumour-derived DNA from pleural effusion fluid is a practical basis
for predicting the response to gefitinib. Br J Cancer.
95:1390–1395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu SG, Yu CJ, Tsai MF, Liao WY, Yang CH,
Jan IS, Yang PC and Shih JY: Survival of lung adenocarcinoma
patients with malignant pleural effusion. Eur Respir J.
41:1409–1418. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carter J, Miller JA, Feller-Kopman D,
Ettinger D, Sidransky D and Maleki Z: Molecular profiling of
malignant pleural effusion in metastatic non-small-cell lung
carcinoma. The effect of preanalytical factors. Ann Am Thorac Soc.
14:1169–1176. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin J, Gu Y, Du R, Deng M, Lu Y and Ding
Y: Detection of EGFR mutation in supernatant, cell pellets of
pleural effusion and tumor tissues from non-small cell lung cancer
patients by high resolution melting analysis and sequencing. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8813–8822. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang J, Lee OJ, Son SM, Woo CG, Jeong Y,
Yang Y, Kwon J, Lee KH and Han HS: EGFR mutation status in lung
adenocarcinoma-associated malignant pleural effusion and efficacy
of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res Treat. 50:908–916.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yeo CD, Kim JW, Kim KH, Ha JH, Rhee CK,
Kim SJ, Kim YK, Park CK, Lee SH, Park MS and Yim HW: Detection and
comparison of EGFR mutations in matched tumor tissues, cell blocks,
pleural effusions, and sera from patients with NSCLC with malignant
pleural effusion, by PNA clamping and direct sequencing. Lung
Cancer. 81:207–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han HS, Lim SN, An JY, Lee KM, Choe KH,
Lee KH, Kim ST, Son SM, Choi SY, Lee HC and Lee OJ: Detection of
EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma specimens with
different proportions of tumor cells using two methods of
differential sensitivity. J Thorac Oncol. 7:355–364. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Buttitta F, Felicioni L, Del Grammastro M,
Filice G, Di Lorito A, Malatesta S, Viola P, Centi I, D'Antuono T,
Zappacosta R, et al: Effective assessment of egfr mutation status
in bronchoalveolar lavage and pleural fluids by next-generation
sequencing. Clin Cancer Res. 19:691–698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Biankin AV, Piantadosi S and Hollingsworth
SJ: Patient-centric trials for therapeutic development in precision
oncology. Nature. 526:361–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Celesti F, Celesti A, Wan J and Villari M:
Why deep learning is changing the way to approach NGS data
processing: A review. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 11:68–76. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kamps R, Brandão RD, Bosch BJ, Paulussen
AD, Xanthoulea S, Blok MJ and Romano A: Next-generation sequencing
in oncology: Genetic diagnosis, risk prediction and cancer
classification. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E3082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu YC, Zhou YF, Wang WX, Xu CW, Zhuang W,
Du KQ and Chen G: CEP72-ROS1: A novel ROS1 oncogenic fusion variant
in lung adenocarcinoma identified by next-generation sequencing.
Thorac Cancer. 9:652–655. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Li Y, Liu C, Wang W, Li M, Lv D,
Sun G, Chen H, Dong X, Miao Z, et al: Identification of a novel
KIF13A-RET fusion in lung adenocarcinoma by next-generation
sequencing. Lung Cancer. 118:27–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu L, Shao D, Deng Q, Tang H, Wang J, Liu
J, Guo F, Lin Y, Peng Z, Mao M, et al: Next generation
sequencing-based molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma using
pleural effusion specimens. J Thorac Dis. 10:2631–2637. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
R Core Team, . A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing;
Vienna, Austria: 2014, http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
47
|
RStudio Team, . RStudio: Integrated
Development for R. RStudio, Inc., Boston, MA, 2015. http://www.rstudio.com/
|
|
48
|
Bai H, Xia J, Zhao X, Gong Z, Zhang D and
Xiong L: Detection of EGFR mutations using target capture
sequencing in plasma of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J
Clin Pathol. 72:379–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chmielecki J, Ross JS, Wang K, Frampton
GM, Palmer GA, Ali SM, Palma N, Morosini D, Miller VA, Yelensky R,
et al: Oncogenic alterations in ERBB2/HER2 represent potential
therapeutic targets across tumors from diverse anatomic sites of
origin. Oncologist. 20:7–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J,
Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, et al:
EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never
smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib
and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:13306–13311. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hyman DM, Smyth LM, Donoghue MTA, Westin
SN, Bedard PL, Dean EJ, Bando H, El-Khoueiry AB, Pérez-Fidalgo JA,
Mita A, et al: AKT Inhibition in Solid Tumors With AKT1 Mutations.
J Clin Oncol. 35:2251–2259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim J, Yu L, Chen W, Xu Y, Wu M, Todorova
D, Tang Q, Feng B, Jiang L, He J, et al: Wild-type p53 promotes
cancer metabolic switch by inducing PUMA-dependent suppression of
oxidative phosphorylation. Cancer Cell. 35:191–203.e8. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ng KP, Hillmer AM, Chuah CT, Juan WC, Ko
TK, Teo AS, Ariyaratne PN, Takahashi N, Sawada K, Fei Y, et al: A
common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and
inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat
Med. 18:521–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
BRAF fusions in clinically advanced
non-small cell lung cancer, . An emerging target for anti-BRAF
therapies. J Clin Oncol. 35 (Suppl. 15):S90722017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Caris Life Sciences, . BRAF mutations are
potentially targetable alterations in a wide variety of solid
cancers. https://www.carislifesciences.com/documents/braf-mutations-are-potentially-targetable-alterations-in-a-wide-variety-of-solid-cancers/December
2–2016
|
|
58
|
Samuels Y and Waldman T: Oncogenic
mutations of PIK3CA in human cancers. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
347:21–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ng PK, Li J, Jeong KJ, Shao S, Chen H,
Tsang YH, Sengupta S, Wang Z, Bhavana VH, Tran R, et al: Systematic
functional annotation of somatic mutations in cancer. Cancer Cell.
33:450–462.e10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang LH, Wu CF, Rajasekaran N and Shin YK:
Loss of tumor suppressor gene function in human cancer: An
overview. Cell Physiol Biochem. 51:2647–2693. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hammerman PS, Sos ML, Ramos AH, Xu C, Dutt
A, Zhou W, Brace LE, Woods BA, Lin W, Zhang J, et al: Mutations in
the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic target in
squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 1:78–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lui MMS, et al: Malignant pleural effusion
from lung cancers with driver mutations. Curr Pulmonol Rep.
7:13–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Davies HE, Mishra EK, Kahan BC, Wrightson
JM, Stanton AE, Guhan A, Davies CW, Grayez J, Harrison R, Prasad A,
et al: Effect of an indwelling pleural catheter vs. chest tube and
talc pleurodesis for relieving dyspnea in patients with malignant
pleural effusion: The TIME2 randomized controlled trial. JAMA.
307:2383–2389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sahn SA and Good JT Jr: Pleural fluid pH
in malignant effusions. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic
implications. Ann Intern Med. 108:345–349. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Heffner JE, Nietert PJ and Barbieri C:
Pleural fluid pH as a predictor of survival for patients with
malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 117:79–86. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Heffner JE, Heffner JN and Brown LK:
Multilevel and continuous pleural fluid pH likelihood ratios for
evaluating malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 123:1887–1894. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Stathopoulos GT, Sherrill TP, Karabela SP,
Goleniewska K, Kalomenidis I, Roussos C, Fingleton B, Yull FE,
Peebles RS Jr and Blackwell TS: Host-derived interleukin-5 promotes
adenocarcinoma-induced malignant pleural effusion. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 182:1273–1281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Stathopoulos GT, Zhu Z, Everhart MB,
Kalomenidis I, Lawson WE, Bilaceroglu S, Peterson TE, Mitchell D,
Yull FE, Light RW and Blackwell TS: Nuclear factor-kappaB affects
tumor progression in a mouse model of malignant pleural effusion.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 34:142–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Stathopoulos GT, Psallidas I, Moustaki A,
Moschos C, Kollintza A, Karabela S, Porfyridis I, Vassiliou S,
Karatza M, Zhou Z, et al: A central role for tumor-derived monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 in malignant pleural effusion. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 100:1464–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Giannou AD, Marazioti A, Spella M,
Kanellakis NI, Apostolopoulou H, Psallidas I, Prijovich ZM, Vreka
M, Zazara DE, Lilis I, et al: Mast cells mediate malignant pleural
effusion formation. J Clin Invest. 125:2317–2334. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen Y, Mathy NW and Lu H: The role of
VEGF in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural effusion
in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer (Review). Mol Med Rep.
17:8019–8030. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wu XZ, Zhou Q, Lin H, Zhai K, Wang XJ,
Yang WB and Shi HZ: Immune regulation of toll-like receptor 2
engagement on CD4+ T cells in murine models of malignant
pleural effusion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 56:342–352. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Stathopoulos GT and Kalomenidis I:
Malignant pleural effusion: Tumor-host interactions unleashed. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 186:487–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Psallidas I, Stathopoulos GT, Maniatis NA,
Magkouta S, Moschos C, Karabela SP, Kollintza A, Simoes DC, Kardara
M, Vassiliou S, et al: Secreted phosphoprotein-1 directly provokes
vascular leakage to foster malignant pleural effusion. Oncogene.
32:528–535. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cui R, Takahashi F, Ohashi R, Yoshioka M,
Gu T, Tajima K, Unnoura T, Iwakami S, Hirama M, Ishiwata T, et al:
Osteopontin is involved in the formation of malignant pleural
effusion in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 63:368–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Thomas R, Cheah HM, Creaney J, Turlach BA
and Lee YC: Longitudinal measurement of pleural fluid biochemistry
and cytokines in malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 149:1494–1500.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ho CC, Liao WY, Wang CY, Lu YH, Huang HY,
Chen HY, Chan WK, Chen HW and Yang PC: TREM-1 expression in
tumor-associated macrophages and clinical outcome in lung cancer.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 177:763–770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gopinathan G, Milagre C, Pearce OM,
Reynolds LE, Hodivala-Dilke K, Leinster DA, Zhong H, Hollingsworth
RE, Thompson R, Whiteford JR and Balkwill F: Interleukin-6
stimulates defective angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 75:3098–3107. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yeh HH, Lai WW, Chen HH, Liu HS and Su WC:
Autocrine IL-6-induced Stat3 activation contributes to the
pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and malignant pleural effusion.
Oncogene. 25:4300–4309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu Q, Yu YX, Wang XJ and Wang Z and Wang
Z: Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-27 between tuberculous
pleural effusion and malignant pleural effusion: A meta-analysis.
Respiration. 95:469–477. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ye ZJ, Zhou Q, Yin W, Yuan ML, Yang WB,
Xiang F, Zhang JC, Xin JB, Xiong XZ and Shi HZ: Interleukin
22-producing CD4+ T cells in malignant pleural effusion. Cancer
Lett. 326:23–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sriram KB, Relan V, Clarke BE, Duhig EE,
Yang IA, Bowman RV, Lee YC and Fong KM: Diagnostic molecular
biomarkers for malignant pleural effusions. Future Oncol.
7:737–752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Palaoro LA, Blanco AM, Gamboni M, Rocher
AE and Rotenberg RG: Usefulness of ploidy, AgNOR and
immunocytochemistry for differentiating benign and malignant cells
in serous effusions. Cytopathology. 18:33–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Nam HS: Malignant pleural effusion:
Medical approaches for diagnosis and management. Tuberc Respir Dis
(Seoul). 76:211–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Light RW: Pleural effusions. Med Clin
North Am. 95:1055–1070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Jiang B, Wu GP, Zhao YJ and Wang SC:
Transcription expression and clinical significance of TTF-1 mRNA in
pleural effusion of patients with lung cancer. Diagn Cytopathol.
36:849–854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Woo CG, Son SM, Han HS, Lee KH, Choe KH,
An JY, Man Lee K, Lim YH, Lee HC and Lee OJ: Diagnostic benefits of
the combined use of liquid-based cytology, cell block, and
carcinoembryonic antigen immunocytochemistry in malignant pleural
effusion. J Thorac Dis. 10:4931–4939. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhang F, Wang J, Zheng X, Hu L, Chen J,
Jiang F and Wang Y: Clinical value of jointly detection pleural
fluid Midkine, pleural fluid adenosine deaminase, and pleural fluid
carbohydrate antigen 125 in the identification of nonsmall cell
lung cancer-associated malignant pleural effusion. J Clin Lab Anal.
32:e225762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Han L, Jiang Q, Yao W, Fu T and Zeng Q:
Thoracic injection of low-dose interleukin-2 as an adjuvant therapy
improves the control of the malignant pleural effusions: A
systematic review and meta-analysis base on Chinese patients. BMC
Cancer. 18:7252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Xu L, Wang B, Gao M, Zhang Y, Qi Q, Li T,
Li C, Wang A and Li Y: Intrapleural combination therapy with
lobaplatin and erythromycin for non-small cell lung cancer-mediated
malignant pleural effusion. Thorac Cancer. 9:950–955. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Tseng YH, Ho HL, Lai CR, Luo YH, Tseng YC,
Whang-Peng J, Lin YH, Chou TY and Chen YM: PD-L1 expression of
tumor cells, macrophages, and immune cells in non-small cell lung
cancer patients with malignant pleural effusion. J Thorac Oncol.
13:447–453. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li Y, Li X, Ma W and Dong Z:
Conformational transition pathways of epidermal growth factor
receptor kinase domain from multiple molecular dynamics simulations
and bayesian clustering. J Chem Theory Comput. 10:3503–3511. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Pan AC, Weinreich TM, Shan Y, Scarpazza DP
and Shaw DE: Assessing the accuracy of two enhanced sampling
methods using EGFR kinase transition pathways: The influence of
collective variable choice. J Chem Theory Comput. 10:2860–2865.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Sutto L and Gervasio FL: Effects of
oncogenic mutations on the conformational free-energy landscape of
EGFR kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:10616–10621. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ruan Z and Kannan N: Altered
conformational landscape and dimerization dependency underpins the
activation of EGFR by αC-β4 loop insertion mutations. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 115:E8162–E8171. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sims D, Sudbery I, Ilott NE, Heger A and
Ponting CP: Sequencing depth and coverage: Key considerations in
genomic analyses. Nat Rev Genet. 15:121–132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara
S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I,
et al: Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer
with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ,
Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al: Erlotinib versus
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced
EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL,
CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS,
Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M and Riely GJ:
Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to
EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:2240–2247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yang M, Topaloglu U, Petty WJ, Pagni M,
Foley KL, Grant SC, Robinson M, Bitting RL, Thomas A, Alistar AT,
et al: Circulating mutational portrait of cancer: Manifestation of
aggressive clonal events in both early and late stages. J Hematol
Oncol. 10:1002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang Z, Yang JJ, Huang J, Ye JY, Zhang XC,
Tu HY, Han-Zhang H and Wu YL: Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR
T790M and in trans C797S responds to combination therapy of first-
and third-generation EGFR TKIs and shifts allelic configuration at
resistance. J Thorac Oncol. 12:1723–1727. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lin YT, Liu YN, Wu SG, Yang JC and Shih
JY: Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-sensitive exon 19 insertion and exon 20 insertion in
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung
Cancer. 18:324–332.e1. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ibrahim U, Saqib A and Atallah JP: EGFR
exon 18 delE709_T710insD mutated stage IV lung adenocarcinoma with
response to afatinib. Lung Cancer. 108:45–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R,
Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M,
et al: Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 361:958–967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chic N, Mayo-de-Las-Casas C and Reguart N:
Successful treatment with gefitinib in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer after acquired resistance to osimertinib. J Thorac Oncol.
12:e78–e80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ganesan P, Ali SM, Wang K, Blumenschein
GR, Esmaeli B, Wolff RA, Miller VA, Stephens PJ, Ross JS, Palmer GA
and Janku F: Epidermal growth factor receptor P753S mutation in
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma responsive to cetuximab-based
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 34:e34–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Costa DB: Kinase inhibitor-responsive
genotypes in EGFR mutated lung adenocarcinomas: Moving past common
point mutations or indels into uncommon kinase domain duplications
and rearrangements. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 5:331–337. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Thress KS, Paweletz CP, Felip E, Cho BC,
Stetson D, Dougherty B, Lai Z, Markovets A, Vivancos A, Kuang Y, et
al: Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in
non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat Med.
21:560–562. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zou J, Bella AE, Chen Z, Han X, Su C, Lei
Y and Luo H: Frequency of EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma
with malignant pleural effusion: Implication of cancer biological
behaviour regulated by EGFR mutation. J Int Med Res. 42:1110–1117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Tsai MF, Chang TH, Wu SG, Yang HY, Hsu YC,
Yang PC and Shih JY: EGFR-L858R mutant enhances lung adenocarcinoma
cell invasive ability and promotes malignant pleural effusion
formation through activation of the CXCL12-CXCR4 pathway. Sci Rep.
5:135742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Lee JG and Wu R: Erlotinib-cisplatin
combination inhibits growth and angiogenesis through c-MYC and
HIF-1α in EGFR-mutated lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
17:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Mertens F and Tayebwa J: Evolving
techniques for gene fusion detection in soft tissue tumours.
Histopathology. 64:151–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Martinengo C, Poggio T, Menotti M, Scalzo
MS, Mastini C, Ambrogio C, Pellegrino E, Riera L, Piva R, Ribatti
D, et al: ALK-dependent control of hypoxia-inducible factors
mediates tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 74:6094–6106.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wang Z, Wu X, Han X, Cheng G, Mu X, Zhang
Y, Cui D, Liu C, Liu D and Shi Y: ALK gene expression status in
pleural effusion predicts tumor responsiveness to crizotinib in
Chinese patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res.
28:606–616. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Liu L, Zhan P, Zhou X, Song Y, Zhou X, Yu
L and Wang J: Detection of EML4-ALK in lung adenocarcinoma using
pleural effusion with FISH, IHC, and RT-PCR methods. PLoS One.
10:e01170322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zhong J, Li X, Bai H, Zhao J, Wang Z, Duan
J, An T, Wu M, Wang Y, Wang S and Wang J: Malignant pleural
effusion cell blocks are substitutes for tissue in EML4-ALK
rearrangement detection in patients with advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer. Cytopathology. 27:433–443. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Raparia K, Villa C, Raj R and Cagle PT:
Peripheral lung adenocarcinomas with KRAS mutations are more likely
to invade visceral pleura. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 139:189–193. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Renaud S, Seitlinger J, Falcoz PE,
Schaeffer M, Voegeli AC, Legrain M, Beau-Faller M and Massard G:
Specific KRAS amino acid substitutions and EGFR mutations predict
site-specific recurrence and metastasis following non-small-cell
lung cancer surgery. Br J Cancer. 115:346–353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Agalioti T, Giannou AD, Krontira AC,
Kanellakis NI, Kati D, Vreka M, Pepe M, Spella M, Lilis I, Zazara
DE, et al: Mutant KRAS promotes malignant pleural effusion
formation. Nat Commun. 8:152052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wu SG, Liu YN, Yu CJ, Yang PC and Shih JY:
Association of BIM deletion polymorphism with intrinsic resistance
to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2:826–828. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Lee JH, Lin YL, Hsu WH, Chen HY, Chang YC,
Yu CJ, Shih JY, Lin CC, Chen KY, Ho CC, et al: Bcl-2-like protein
11 deletion polymorphism predicts survival in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1385–1392. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Cardona AF, Rojas L, Wills B, Arrieta O,
Carranza H, Vargas C, Otero J, Corrales-Rodriguez L, Martín C,
Reguart N, et al: BIM deletion polymorphisms in Hispanic patients
with non-small cell lung cancer carriers of EGFR mutations.
Oncotarget. 7:68933–68942. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Xia J, Bai H, Yan B, Li R, Shao M, Xiong L
and Han B: Mimicking the BIM BH3 domain overcomes resistance to
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:108522–108533. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Cai W, Li J, Zhou F,
Cheng N, Ren R, Zhao C, Li X, Ren S, et al: The Bim deletion
polymorphism clinical profile and its relation with tyrosine kinase
inhibitor resistance in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer. 120:2299–2307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lee JK, Shin JY, Kim S, Lee S, Park C, Kim
JY, Koh Y, Keam B, Min HS, Kim TM, et al: Primary resistance to
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(TKIs) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring
TKI-sensitive EGFR mutations: An exploratory study. Ann Oncol.
24:2080–2087. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Isobe K, Hata Y, Tochigi N, Kaburaki K,
Kobayashi H, Makino T, Otsuka H, Sato F, Ishida F, Kikuchi N, et
al: Clinical significance of BIM deletion polymorphism in
non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor
mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 9:483–487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Wu SG, Chang YL, Yu CJ, Yang PC and Shih
JY: Lung adenocarcinoma patients of young age have lower EGFR
mutation rate and poorer efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. ERJ Open Res. 3:00092–2016. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Wu M, Pan X, Xu Y, Wu S, Wu X and Chen B:
Methodological comparison of the allele refractory mutation system
and direct sequencing for detecting EGFR mutations in NSCLC, and
the association of EGFR mutations with patient characteristics.
Oncol Lett. 16:1087–1094. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan
S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G and Yang PC: A
prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in
Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of
adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 9:154–162.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Tseng CH, Chiang CJ, Tseng JS, Yang TY,
Hsu KH, Chen KC, Wang CL, Chen CY, Yen SH, Tsai CM, et al: EGFR
mutation, smoking, and gender in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:98384–98393. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kota R, Gundeti S, Gullipalli M, Linga VG,
Maddali LS and Digumarti R: Prevalence and outcome of epidermal
growth factor receptor mutations in non-squamous non-small cell
lung cancer patients. Lung India. 32:561–565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Aunan JR, Cho WC and Soreide K: The
biology of aging and cancer: A brief overview of shared and
divergent molecular hallmarks. Aging Dis. 8:628–642. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|