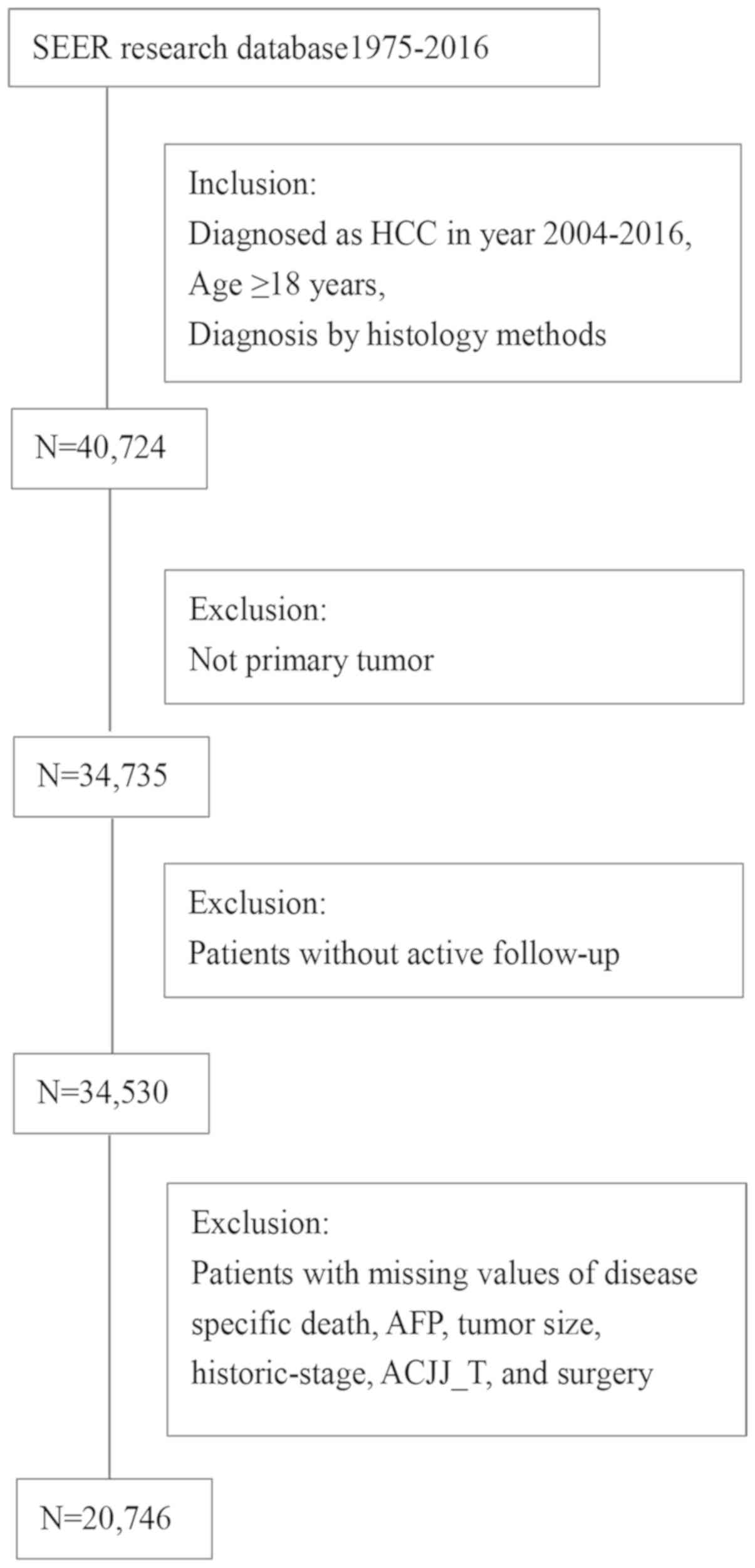
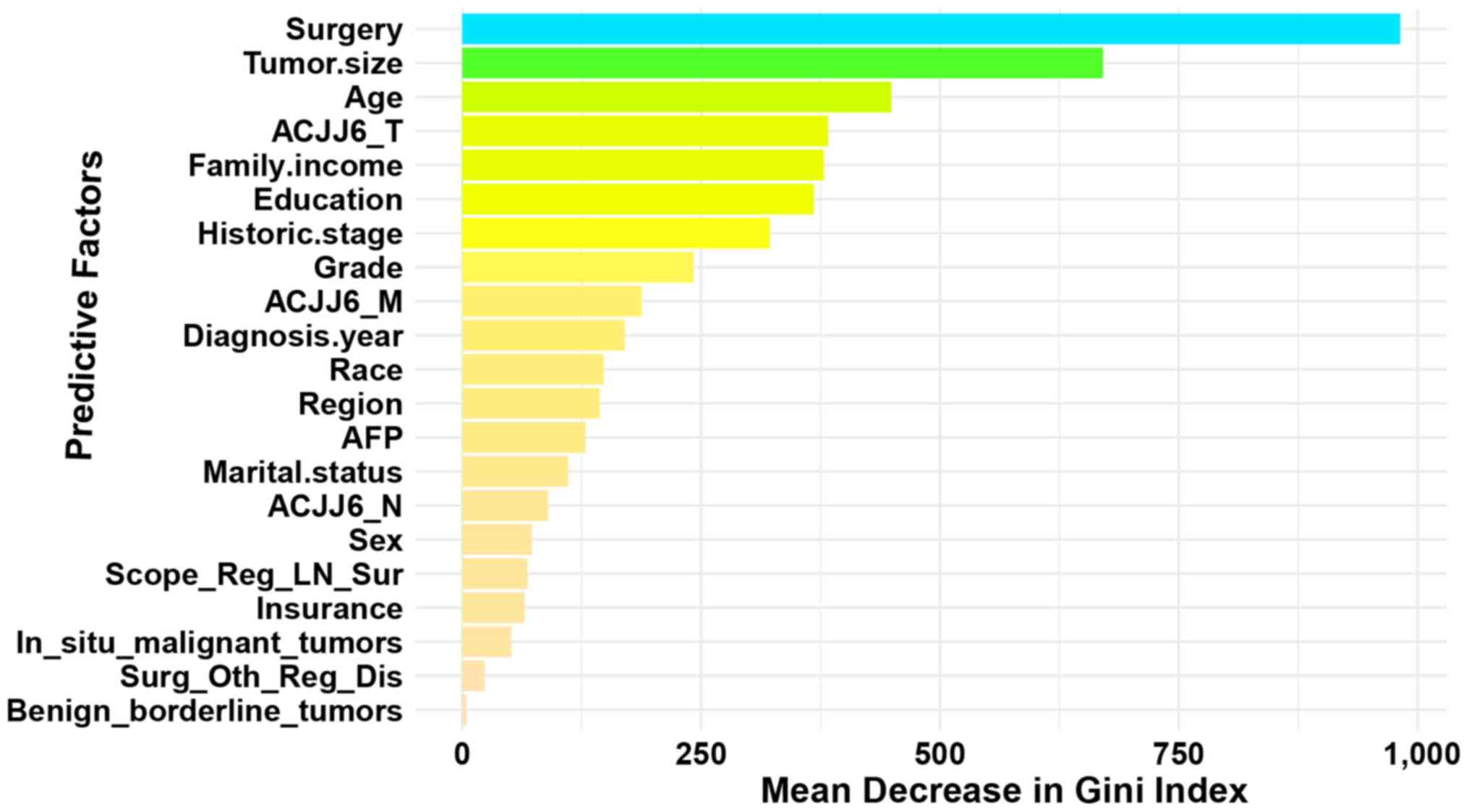
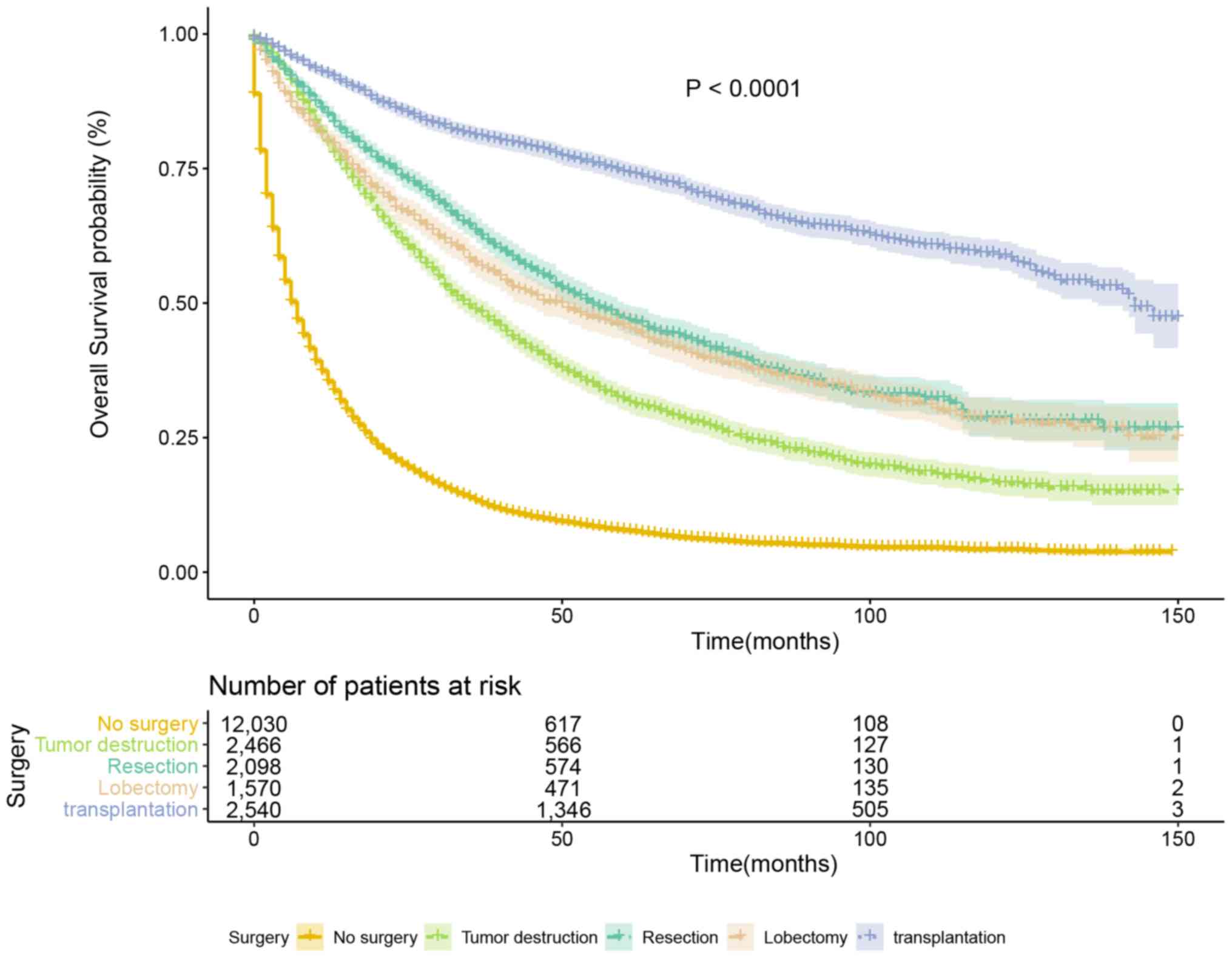
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Labgaa I, Demartines N and Melloul E:
Surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for
intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma (BCLC-B): An unsolved
question. Hepatology. 69:9232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baddour HM Jr, Fedewa SA and Chen AY:
Five- and 10-year cause-specific survival rates in carcinoma of the
minor salivary gland. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 142:67–73.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lexe G, Monaco J, Doyle S, Basavanhally A,
Reddy A, Seiler M, Ganesan S, Bhanot G and Madabhushi A: Towards
improved cancer diagnosis and prognosis using analysis of gene
expression data and computer aided imaging. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
234:860–879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, : Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
European Association For The Study of The
Liver and European Organisation For Research and Treatment of
Cancer, . EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:908–943. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hyun MH, Lee YS, Kim JH, Lee CU, Jung YK,
Seo YS, Yim HJ, Yeon JE and Byun KS: Hepatic resection compared to
chemoembolization in intermediate- to advanced-stage hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis of high-quality studies. Hepatology.
68:977–993. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kutlu OC, Chan JA, Aloia TA, Chun YS,
Kaseb AO, Passot G, Yamashita S, Vauthey JN and Conrad C:
Comparative effectiveness of first-line radiofrequency ablation
versus surgical resection and transplantation for patients with
early hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 123:1817–1827. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shimose S, Tanaka M, Iwamoto H, Niizeki T,
Shirono T, Aino H, Noda Y, Kamachi N, Okamura S, Nakano M, et al:
Prognostic impact of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization
(TACE) combined with radiofrequency ablation in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with TACE alone
using decision-tree analysis after propensity score matching.
Hepatol Res. 49:919–928. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R, Chen PJ,
Lin SM, Yoshida H, Kudo M, Lee JM, Choi BI, Poon RT, et al: Asian
pacific association for the study of the liver consensus
recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology Int.
4:439–474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jarnagin W, Chapman WC, Curley S,
D'Angelica M, Rosen C, Dixon E and Nagorney D; American
Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association, Society of Surgical Oncology
and Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract, : Surgical
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Expert consensus statement.
HPB (Oxford). 12:302–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Korean Liver Cancer Study Group (KLCSG)
and National Cancer Center, Korea (NCC), . 2014 KLCSG-NCC Korea
practice guideline for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gut Liver. 9:267–317. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kudo M, Matsui O, Izumi N, Iijima H,
Kadoya M, Imai Y, Okusaka T, Miyayama S, Tsuchiya K, Ueshima K, et
al: JSH consensus-based clinical practice guidelines for the
management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2014 update by the liver
cancer study group of Japan. Liver Cancer. 3:458–468. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kaibori M, Yoshii K, Yokota I, Hasegawa K,
Nagashima F, Kubo S, Kon M, Izumi N, Kadoya M, Kudo M, et al:
Impact of advanced age on survival in patients undergoing resection
of hepatocellular carcinoma: Report of a Japanese nationwide
survey. Annals Surg. 269:692–699. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang A, Xiao W, Chen D, Wei X, Huang S,
Lin Y, Zhang C, Lin J, Deng F, Wu C and He X: The power of tumor
sizes in predicting the survival of solitary hepatocellular
carcinoma patients. Cancer Med. 7:6040–6050. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shinkawa H, Tanaka S, Takemura S, Ishihara
T, Yamamoto K and Kubo S: Tumor size drives the prognosis after
hepatic resection of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma without
vascular invasion. J Gastrointest Surg. June 13–2019.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wu W, Fang D, Shi D, Bian X and Li L:
Effects of marital status on survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
by race/ethnicity and gender. Cancer Manag Res. 10:23–32. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bai DS, Zhang C, Chen P, Jin SJ and Jiang
GQ: The prognostic correlation of AFP level at diagnosis with
pathological grade, progression, and survival of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:128702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sarveazad A, Agah S, Babahajian A, Amini N
and Bahardoust M: Predictors of 5 year survival rate in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Res Med Sci. 24:862019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song Q, Chen X, Hu W, Mei G, Yang X and Wu
H: Downregulation of Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 is
associated with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after
curative resection. Oncol Lett. 15:7751–7759. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Noda Y, Kawaguchi T, Korenaga M, Yoshio S,
Komukai S, Nakano M, Niizeki T, Koga H, Kawaguchi A, Kanto T and
Torimura T: High serum interleukin-34 level is a predictor of poor
prognosis in patients with non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatol Res. 49:1046–1053. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pang W, Jiang H and Li S: Sparse
contribution feature selection and classifiers optimized by
concave-convex variation for HCC image recognition. Biomed Res Int.
2017:97183862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi GH, Han S, Shim JH, Ryu MH, Ryoo BY,
Kang YK, Kim KM, Lim YS and Lee HC: Prognostic scoring models for
patients undergoing sorafenib treatment for advanced stage
hepatocellular carcinoma in real-life practice. Am J Clin Oncol.
40:167–174. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He Y, Wu W, Zheng HM, Li P, McDonald D,
Sheng HF, Chen MX, Chen ZH, Ji GY, Zheng ZD, et al: Regional
variation limits applications of healthy gut microbiome reference
ranges and disease models. Nat Med. 24:1532–1535. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song Y, Gao S, Tan W, Qiu Z, Zhou H and
Zhao Y: Multiple machine learnings revealed similar predictive
accuracy for prognosis of PNETs from the surveillance,
epidemiology, and end result database. J Cancer. 9:3971–3978. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X and Ishwaran H: Random forests for
genomic data analysis. Genomics. 99:323–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu C, Ackerman HH and Carulli JP: A
genome-wide screen of gene-gene interactions for rheumatoid
arthritis susceptibility. Hum Genet. 129:473–485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Briggs FB, Ramsay PP, Madden E, Norris JM,
Holers VM, Mikuls TR, Sokka T, Seldin MF, Gregersen PK, Criswell LA
and Barcellos LF: Supervised machine learning and logistic
regression identifies novel epistatic risk factors with PTPN22 for
rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 11:199–208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Degenhardt F, Seifert S and Szymczak S:
Evaluation of variable selection methods for random forests and
omics data sets. Brief Bioinform. 20:492–503. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu C, Ren X and Zhang Q: Incidence, risk
factors, and prognosis in patients with primary hepatocellular
carcinoma and lung metastasis: A population-based study. Cancer
Manag Res. 11:2759–2768. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ryu SM, Lee SH, Kim ES and Eoh W:
Predicting survival of spinal ependymoma patients using machine
learning algorithms with SEER database. World Neurosurg. Dec
28–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
32
|
Shukla N, Hagenbuchner M, Win KT and Yang
J: Breast cancer data analysis for survivability studies and
prediction. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 155:199–208. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lynch CM, Abdollahi B, Fuqua JD, de Carlo
AR, Bartholomai JA, Balgemann RN, van Berkel VH and Frieboes HB:
Prediction of lung cancer patient survival via supervised machine
learning classification techniques. Int J Med Inform. 108:1–8.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Adamo MB, Johnson CH, Ruhl JL and Dickie
LA: SEER Program Coding and Staging Manual. National Cancer
Institute, NIH Publication no. 12-5581. (Bethesda, MD). 2012.
|
|
35
|
Raghu G, Chen SY, Yeh WS, Maroni B, Li Q,
Lee YC and Collard HR: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US medicare
beneficiaries aged 65 years and older: Incidence, prevalence, and
survival, 2001-11. Lancet Respir Med. 2:566–572. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen Y, Guo H, Wu T, Lu Q, Nan KJ, Lv Y
and Zhang XF: Lower education and household income contribute to
advanced disease, less treatment received and poorer prognosis in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 8:3070–3077.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jones PD, Diaz C, Wang D, Gonzalez-Diaz J,
Martin P and Kobetz E: The impact of race on survival after
hepatocellular carcinoma in a diverse American population.
digestive diseases and sciences. Dig Dis Sci. 63:515–528. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lai MW, Chu YD, Lin CL, Chien RN, Yeh TS,
Pan TL, Ke PY, Lin KH and Yeh CT: Is there a sex difference in
postoperative prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma? BMC Cancer.
19:2502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee GC, Ferrone CR, Vagefi PA, Uppot RN,
Tanabe KK, Lillemoe KD, Blaszkowsky LS and Qadan M: Surgical
resection versus ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma:
A retrospective cohort analysis. Am J Surg. 218:157–163. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu B, Ding Y, Liao X, Wang C, Wang B and
Chen X: Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection in
elderly patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in the
era of organ shortage. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 24:317–325. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mills A, Thayer D, Noda C, Salter A, Tao
Y, Xing M, Martin R, Ramaswamy R and Akinwande O: Thermal ablation
versus surgical resection for localized hepatocellular carcinoma: A
population study using the SEER database. Future Oncol. 14:631–645.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yim SY, Seo YS, Jung CH, Kim TH, Lee JM,
Kim ES, Keum B, Jong YK, An H, Kim JH, et al: The management and
prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: What has
changed in 20 years? Liver Int. 36:445–453. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shen J, Liu J, Li C, Wen T, Yan L and Yang
J: The impact of tumor differentiation on the prognosis of
HBV-associated solitary hepatocellular carcinoma following
hepatectomy: A propensity score matching analysis. Dig Dis Sci.
63:1962–1969. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang JF, Shu ZJ, Xie CY, Li Q, Jin XH, Gu
W, Jiang FJ and Ling CQ: Prognosis of unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma: Comparison of seven staging systems (TNM, Okuda, BCLC,
CLIP, CUPI, JIS, CIS) in a Chinese cohort. PLoS One. 9:e881822014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoshizumi T, Ikegami T, Yoshiya S,
Motomura T, Mano Y, Muto J, Ikeda T, Soejima Y, Shirabe K and
Maehara Y: Impact of tumor size, number of tumors and
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in liver transplantation for
recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 43:709–716. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jain SS, Sarkar IN, Stey PC, Anand RS,
Biron DR and Chen ES: Using demographic factors and comorbidities
to develop a predictive model for ICU mortality in patients with
acute exacerbation COPD. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018:1319–1328.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Touw WG, Bayjanov JR, Overmars L, Backus
L, Boekhorst J, Wels M and van Hijum SA: Data mining in the life
sciences with random forest: A walk in the park or lost in the
jungle? Brief Bioinform. 14:315–326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu G, Dong C, Wang X, Hou G, Zheng Y, Xu
H, Zhan X and Liu L: Regulatory activity based risk model
identifies survival of stage II and III colorectal carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:98360–98370. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kawaguchi T, Tokushige K, Hyogo H, Aikata
H, Nakajima T, Ono M, Kawanaka M, Sawada K, Imajo K, Honda K, et
al: A data mining-based prognostic algorithm for NAFLD-related
hepatoma patients: A nationwide study by the Japan study group of
NAFLD. Sci Rep. 8:104342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cheong JY, Lee KM, Cho SW, Won JH, Kim JK,
Wang HJ, Hahm KB and Kim JH: Survival benefits of intra-arterial
infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Hepatol Res.
32:127–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|