|
1
|
Li Z, Sang M, Tian Z, Liu Z, Lv J, Zhang F
and Shan B: Identification of key biomarkers and potential
molecular mechanisms in lung cancer by bioinformatics analysis.
Oncol Lett. 18:4429–4440. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giuliano CJ, Lin A, Smith JC, Palladino AC
and Sheltzer JM: MELK expression correlates with tumor mitotic
activity but is not required for cancer growth. Elife. 7:2018.
|
|
5
|
Luo J, Solimini NL and Elledge SJ:
Principles of cancer therapy: Oncogene and non-oncogene addiction.
Cell. 136:823–837. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang P and Zhang D: Maternal embryonic
leucine zipper kinase (MELK): A novel regulator in cell cycle
control, embryonic development, and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
14:21551–21560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Speers C, Zhao SG, Kothari V, Santola A,
Liu M, Wilder-Romans K, Evans J, Batra N, Bartelink H, Hayes DF, et
al: Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) as a novel
mediator and biomarker of radioresistance in human breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 22:5864–5875. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Li Y, Xu Y, Lu K, Li P
and Wang X: Inhibition of maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase
with OTSSP167 displays potent anti-leukemic effects in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Oncogene. 37:5520–5533. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kohler RS, Kettelhack H,
Knipprath-Mészaros AM, Fedier A, Schoetzau A, Jacob F and
Heinzelmann-Schwarz V: MELK expression in ovarian cancer correlates
with poor outcome and its inhibition by OTSSP167 abrogates
proliferation and viability of ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol.
145:159–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xia H, Kong SN, Chen J, Shi M, Sekar K,
Seshachalam VP, Rajasekaran M, Goh BKP, Ooi LL and Hui KM: MELK is
an oncogenic kinase essential for early hepatocellular carcinoma
recurrence. Cancer Lett. 383:85–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ganguly R, Hong CS, Smith LGF, Kornblum HI
and Nakano I: Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase: Key kinase
for stem cell phenotype in glioma and other cancers. Mol Cancer
Ther. 13:1393–1398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chung S and Nakamura Y: MELK inhibitor,
novel molecular targeted therapeutics for human cancer stem cells.
Cell Cycle. 12:1655–1656. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chung S, Suzuki H, Miyamoto T, Takamatsu
N, Tatsuguchi A, Ueda K, Kijima K, Nakamura Y and Matsuo Y:
Development of an orally-administrative MELK-targeting inhibitor
that suppresses the growth of various types of human cancer.
Oncotarget. 3:1629–1640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
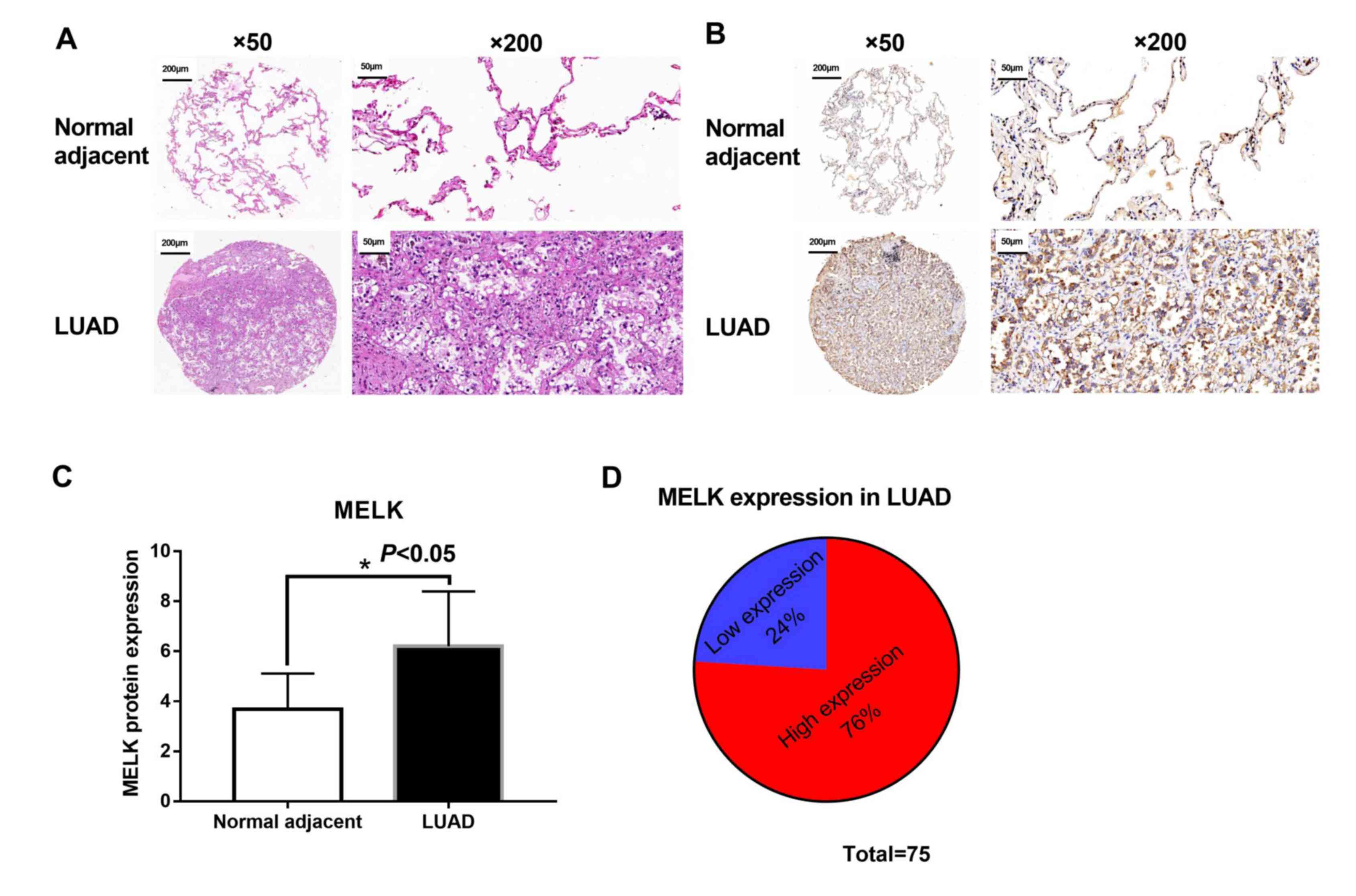
Li Y, Tang H, Sun Z, Bungum AO, Edell ES,
Lingle WL, Stoddard SM, Zhang M, Jen J, Yang P and Wang L:
Network-based approach identified cell cycle genes as predictor of
overall survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer.
80:91–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zang X, Qian C, Ruan Y, Xie J, Luo T, Xu B
and Jiang J: Higher maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase mRNA
expression level is a poor prognostic factor in non-small-cell lung
carcinoma patients. Biomark Med. 13:1349–1361. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
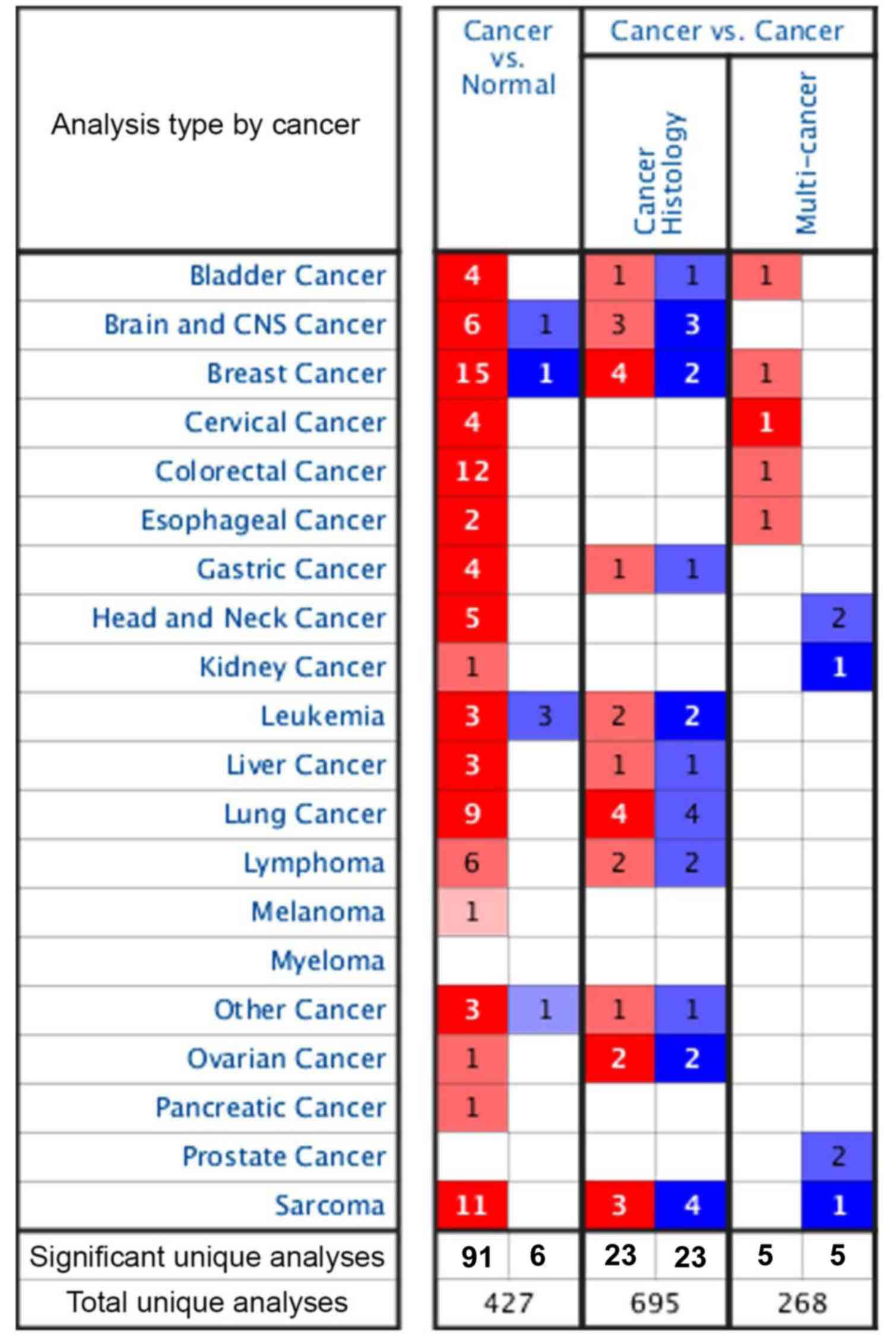
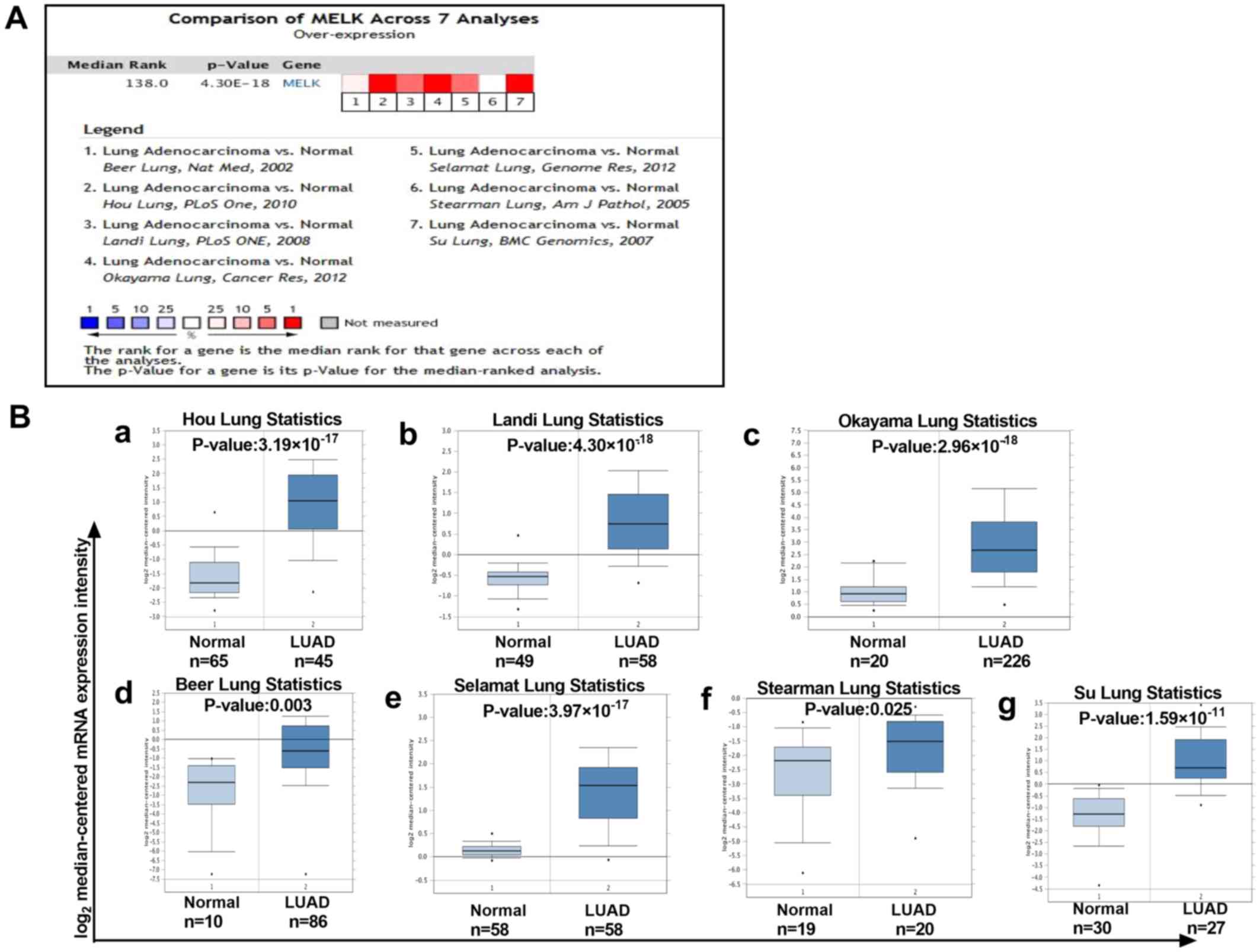
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bornstein S, Schmidt M, Choonoo G, Levin
T, Gray J, Thomas CJ Jr, Wong M and McWeeney S: IL-10 and integrin
signaling pathways are associated with head and neck cancer
progression. BMC Genomics. 17:382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dastsooz H, Cereda M, Donna D and Oliviero
S: A comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of UBE2C in cancers. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:22282019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
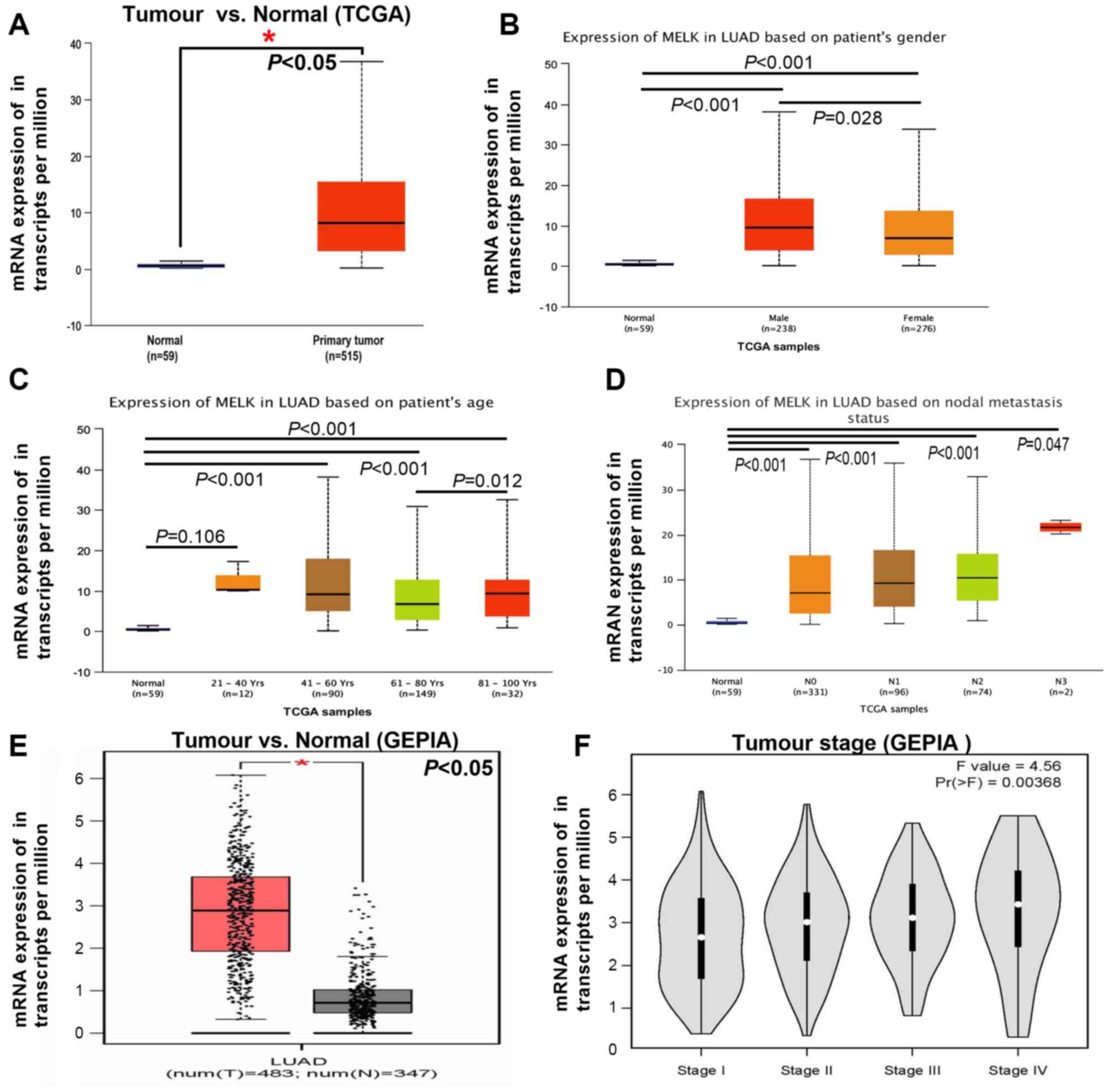
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu L, Chen S, Bao H, Zhang W, Liao M,
Liang Q and Cheng X: The role of lncRNA CASC2 on prognosis of
malignant tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:4355–4365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Detterbeck FC, Chansky K, Groome P,
Bolejack V, Crowley J, Shemanski L, Kennedy C, Krasnik M, Peake M
and Rami-Porta R; IASLC Staging and Prognostic Factors Committee,
Advisory Boards, Participating Institutions, : The IASLC Lung
Cancer Staging Project: Methodology and validation used in the
development of proposals for revision of the stage classification
of NSCLC in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the tnm
classification of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 11:1433–1446. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dadhania V, Zhang M, Zhang L, Bondaruk J,
Majewski T, Siefker-Radtke A, Guo CC, Dinney C, Cogdell DE, Zhang
S, et al: Meta-analysis of the luminal and basal subtypes of
bladder cancer and the identification of signature
immunohistochemical markers for clinical use. EBioMedicine.
12:105–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu DD, Li PC, He YF, Jia W and Hu B:
Overexpression of coiled-coil domain-containing protein 34 (CCDC34)
and its correlation with angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 24:698–705. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Inoue H, Kato T, Olugbile S, Tamura K,
Chung S, Miyamoto T, Matsuo Y, Salgia R, Nakamura Y and Park JH:
Effective growth-suppressive activity of maternal embryonic
leucine-zipper kinase (MELK) inhibitor against small cell lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:13621–13633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hiwatashi K, Ueno S, Sakoda M, Iino S,
Minami K, Yonemori K, Nishizono Y, Kurahara H, Mataki Y, Maemura K,
et al: Expression of maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase
(MELK) correlates to malignant potentials in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 36:5183–5188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu S, Chen X, Hu C, Wang J, Shen Y and
Zhong Z: Up-regulated maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase
predicts poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients in a
Chinese Han population. Med Sci Monit. 23:5705–5713. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin ML, Park JH, Nishidate T, Nakamura Y
and Katagiri T: Involvement of maternal embryonic leucine zipper
kinase (MELK) in mammary carcinogenesis through interaction with
Bcl-G, a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. Breast Cancer
Res. 9:R172007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gu C, Banasavadi-Siddegowda YK, Joshi K,
Nakamura Y, Kurt H, Gupta S and Nakano I: Tumor-specific activation
of the C-JUN/MELK pathway regulates glioma stem cell growth in a
p53-dependent manner. Stem Cells. 31:870–881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|