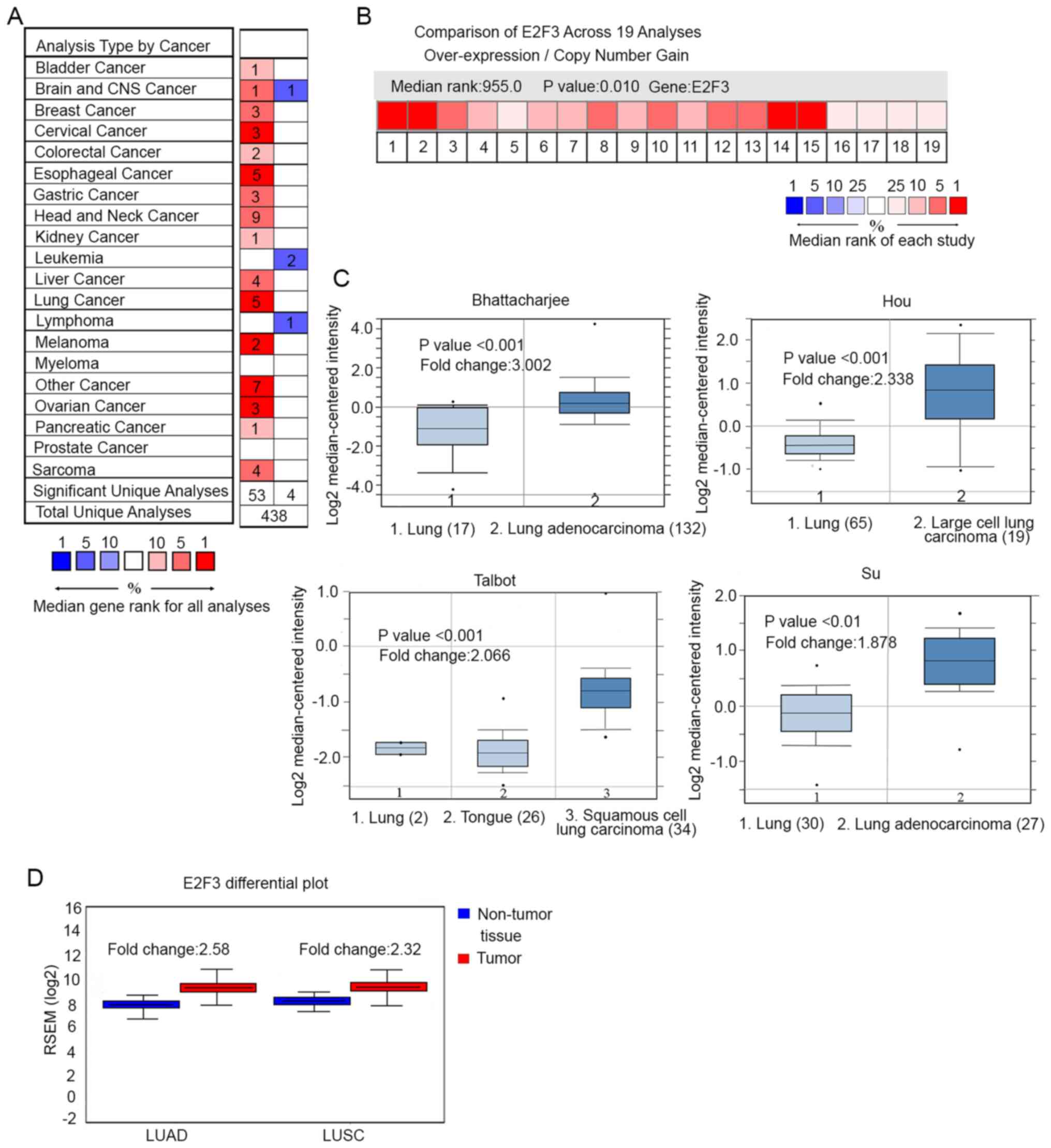
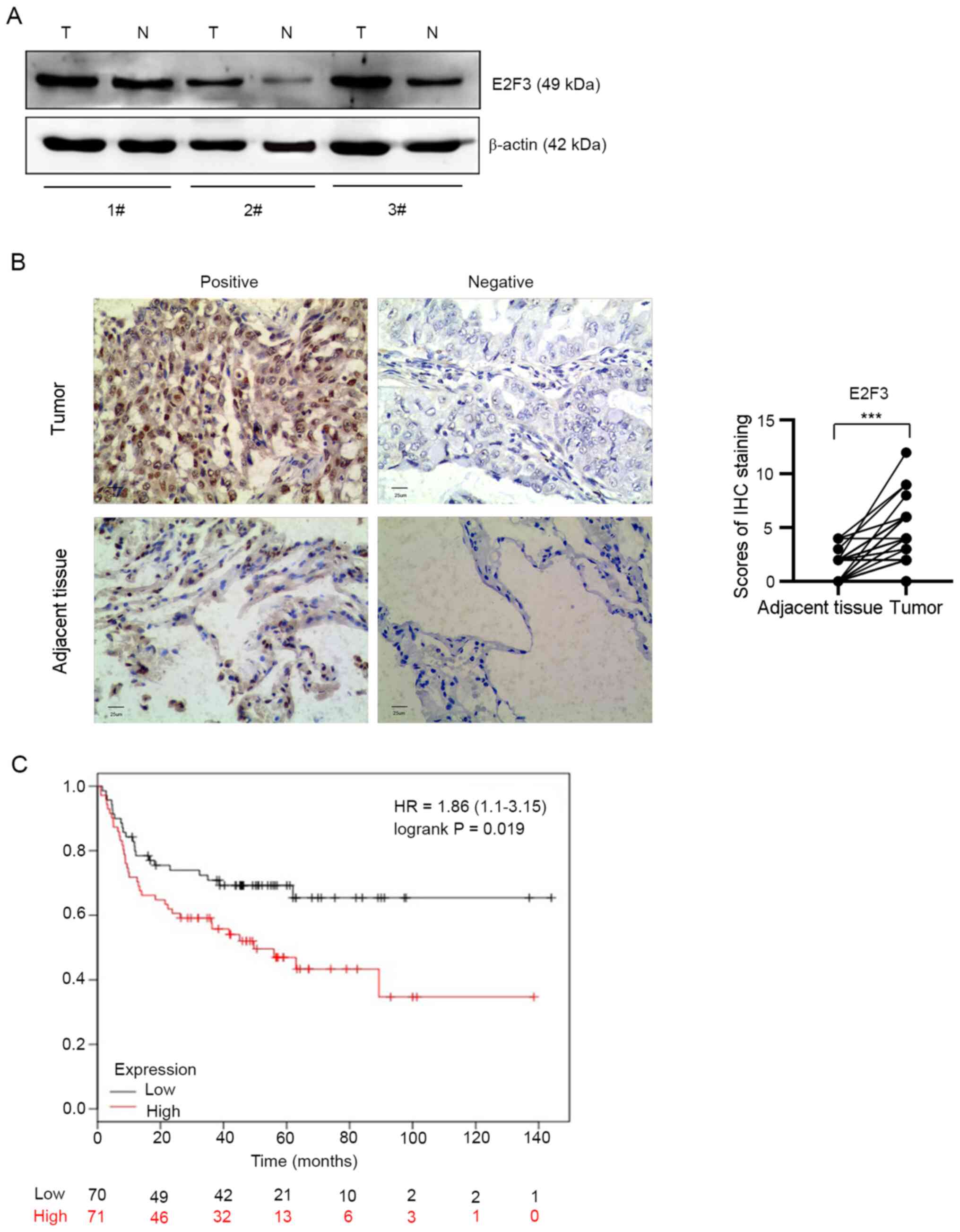
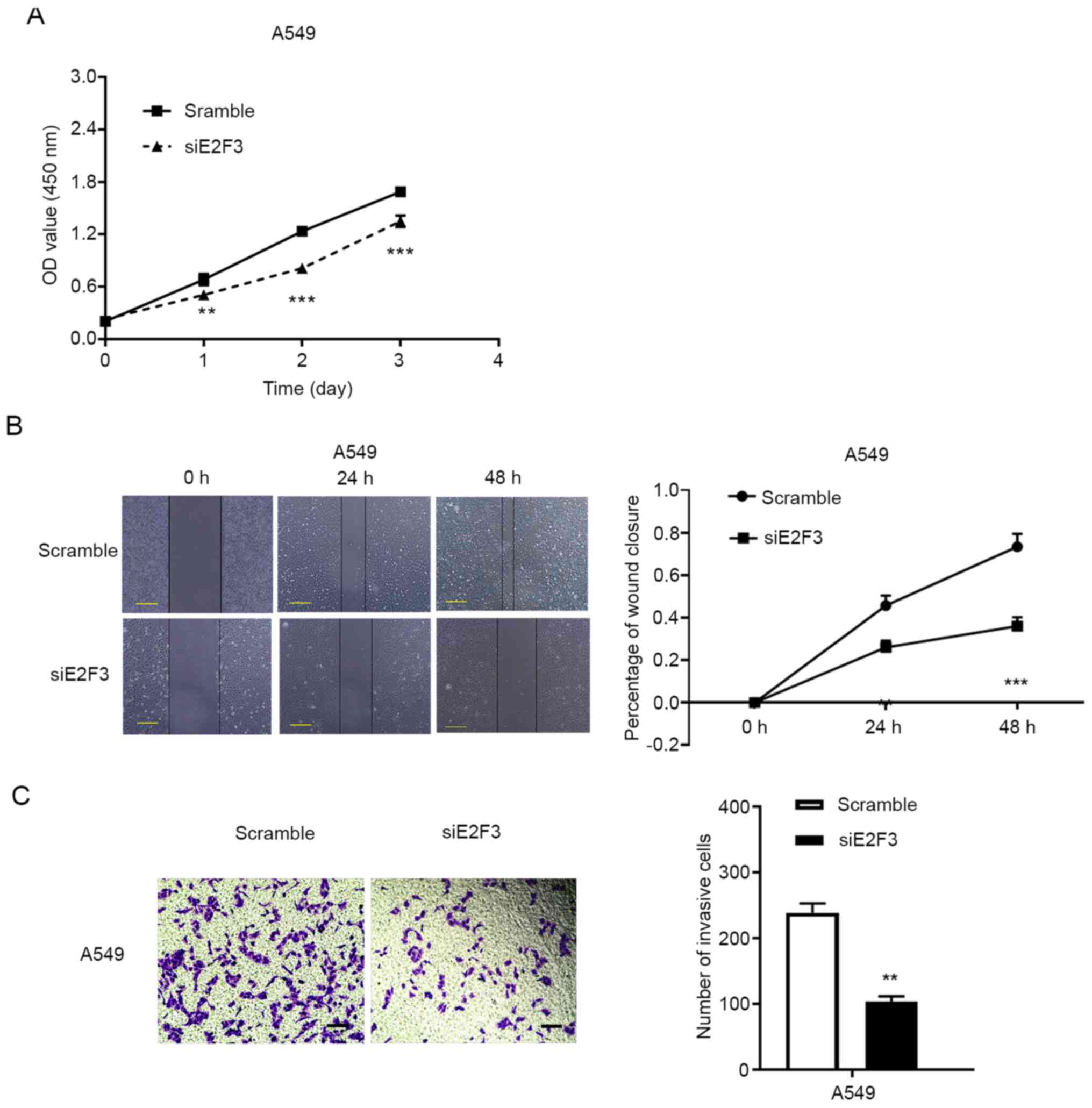
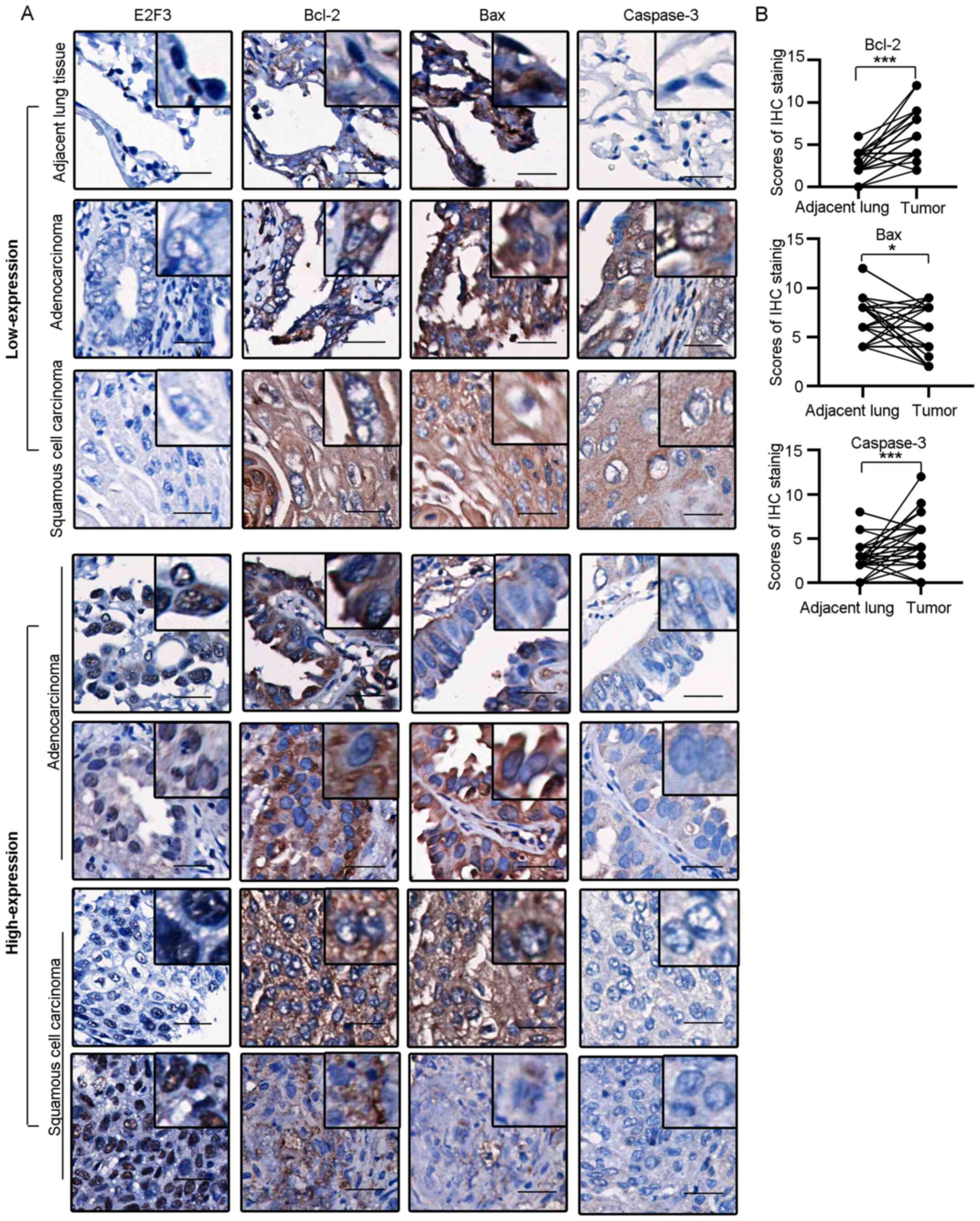
|
1
|
Chen WQ, Li H, Sun KX, Zheng RS, Zhang SW,
Zeng HM, Zou XN, Gu XY and He J: Report of cancer incidence and
mortality in China, 2014. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 40:5–13.
2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oliver TG, Patel J and Akerley W: Squamous
non-small cell lung cancer as a distinct clinical entity. Am J Clin
Oncol. 38:220–226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E and Li QK:
Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical
markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma
(NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 52:103–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Segundo-Val IS and Sanz-Lozano CS:
Introduction to the gene expression analysis. Methods Mol Biol.
1434:29–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lánczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e822412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lánczky A, Nagy A, Bottai G, Munkácsy G,
Szabó A, Santarpia L and Győrffy B: MiRpower: A web-tool to
validate survival-associated miRNAs utilizing expression data from
2178 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 160:439–446.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu Y, Peng Q, Lin Y, Zou L, Shen P, Chen
F, Min M, Shen L, Chen J and Shen B: Identification of biomarker
microRNAs for predicting the response of colorectal cancer to
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy based on microRNA regulatory network.
Oncotarget. 8:2233–2248. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sarver AL, Sarver AE, Yuan C and
Subramanian S: OMCD: OncomiR cancer database. BMC Cancer.
18:12232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhan L, Zhang Y, Wang W, Song E, Fan Y and
Wei B: E2F1: A promising regulator in ovarian carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 37:2823–2831. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park SA, Platt J, Lee JW, López-Giráldez
F, Herbst RS and Koo JS: E2F8 as a novel therapeutic target for
lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 107:1512015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kurtyka CA, Chen L and Cress WD: E2F
inhibition synergizes with paclitaxel in lung cancer cell lines.
PLoS One. 9:e963572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rotgers E, Rivero-Müller A, Nurmio M,
Parvinen M, Guillou F, Huhtaniemi I, Kotaja N, Bourguiba-Hachemi S
and Toppari J: Retinoblastoma protein (RB) interacts with E2F3 to
control terminal differentiation of sertoli cells. Cell Death Dis.
5:e12742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Danielian PS, Friesenhahn LB, Faust AM,
West JC, Caron AM, Bronson RT and Lees JA: E2f3a and E2f3b make
overlapping but different contributions to total E2f3 activity.
Oncogene. 27:6561–6570. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lou X, Fu J, Zhao X, Zhuansun X, Rong C,
Sun M, Niu H, Wu L, Zhang Y, An L, et al: MiR-7e-5p downregulation
promotes transformation of low-grade follicular lymphoma to
aggressive lymphoma by modulating an immunosuppressive stroma
through the upregulation of FasL in M1 macrophages. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 39:2372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Montojo J, Zuberi K, Rodriguez H, Bader GD
and Morris Q: GeneMANIA: Fast gene network construction and
function prediction for cytoscape. F1000Res. 3:1532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Liu J, Jin N, Zhang G, Xi Y and
Liu H: SiRNA targeting mTOR effectively prevents the proliferation
and migration of human lens epithelial cells. PLoS One.
11:e01673492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Collins TJ: ImageJ for microscopy.
Biotechniques. 43:25–30. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meyers DE, Bryan PM, Banerji S and Morris
DG: Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis for the treatment of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol. 25:e324–e334. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guinde J, Frankel D, Perrin S, Delecourt
V, Lévy N, Barlesi F, Astoul P, Roll P and Kaspi E: Lamins in lung
cancer: Biomarkers and key factors for disease progression through
miR-9 regulation? Cells. 7:782018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Suzuki T, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Naka K,
Ishikawa T and Tahara E: Expression of the E2F family in human
gastrointestinal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 81:535–538. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oliveira A, Beyer G, Chugh R, Skube SJ,
Majumder K, Banerjee S, Sangwan V, Li L, Dawra R, Subramanian S, et
al: Triptolide abrogates growth of colon cancer and induces cell
cycle arrest by inhibiting transcriptional activation of E2F. Lab
Invest. 95:648–659. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Salon C, Merdzhanova G, Brambilla C,
Brambilla E, Gazzeri S and Eymin B: E2F-1, Skp2 and cyclin E
oncoproteins are upregulated and directly correlated in high-grade
neuroendocrine lung tumors. Oncogene. 26:6927–6936. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Li H, Zhang R and Liu J and Liu J:
MicroRNA-449a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by
directly repressing E2F3 in gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem.
35:2033–2042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sherlock G and Ball CA: Storage and
retrieval of microarray data and open source microarray database
software. Mol Biotechnol. 30:239–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Frank DK, Liu TJ, Frederick MJ and Clayman
GL: Combination E2F-1 and p53 gene transfer does not enhance growth
inhibition in human squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Clin Cancer Res. 4:2265–2272. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou X, Ji G, Ke X, Gu H, Jin W and Zhang
G: MiR-141 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation by interacting
with long noncoding RNA MEG3 and down-regulating E2F3 expression.
Dig Dis Sci. 60:3271–3282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xue J, Niu YF, Huang J, Peng G, Wang LX,
Yang YH and Li YQ: MiR-141 suppresses the growth and metastasis of
HCC cells by targeting E2F3. Tumour Biol. 35:12103–12107. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Naeini MM, Tavassoli M and Ghaedi K:
Systematic bioinformatic approaches reveal novel gene expression
signatures associated with acquired resistance to EGFR targeted
therapy in lung cancer. Gene. 667:62–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|