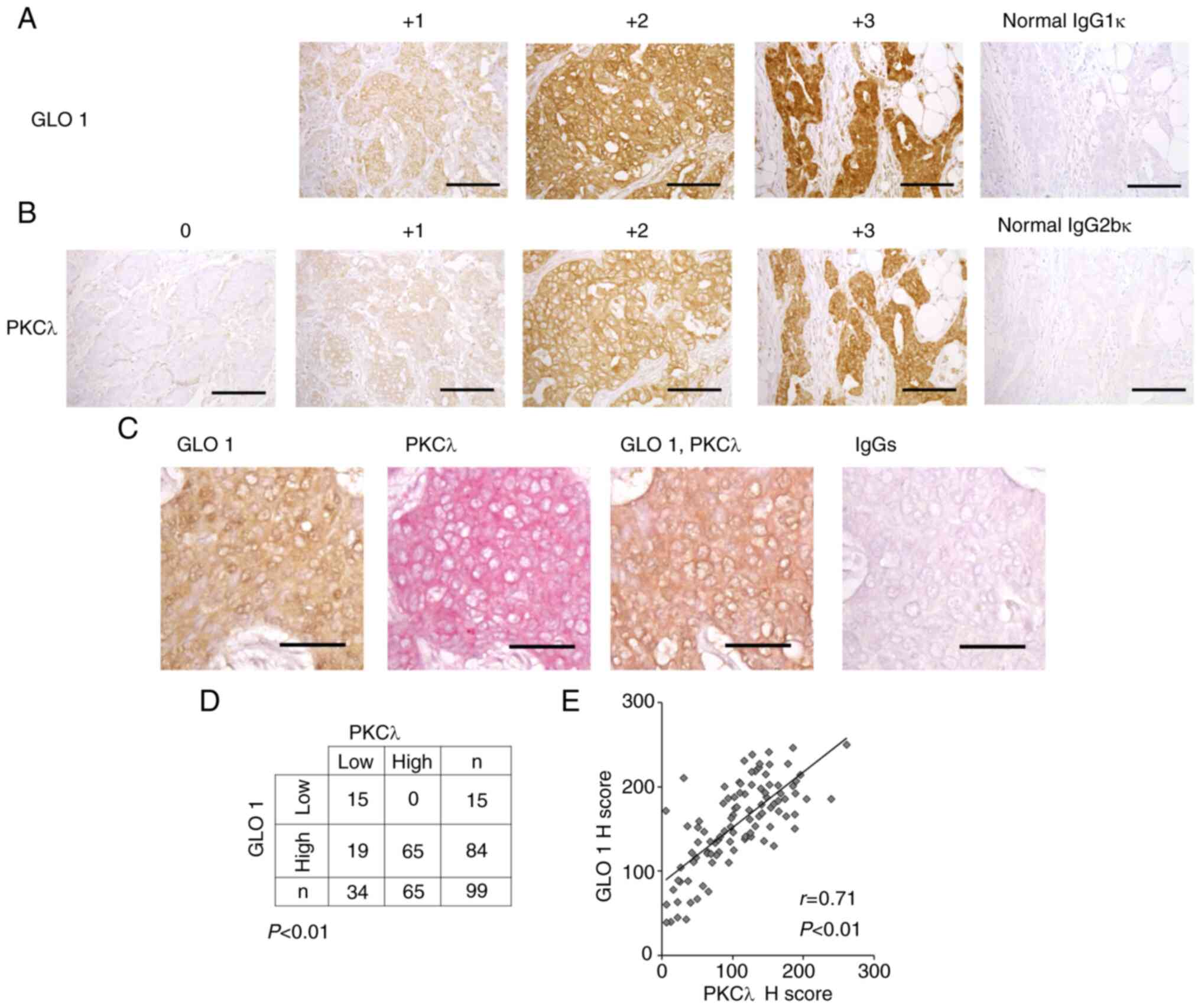
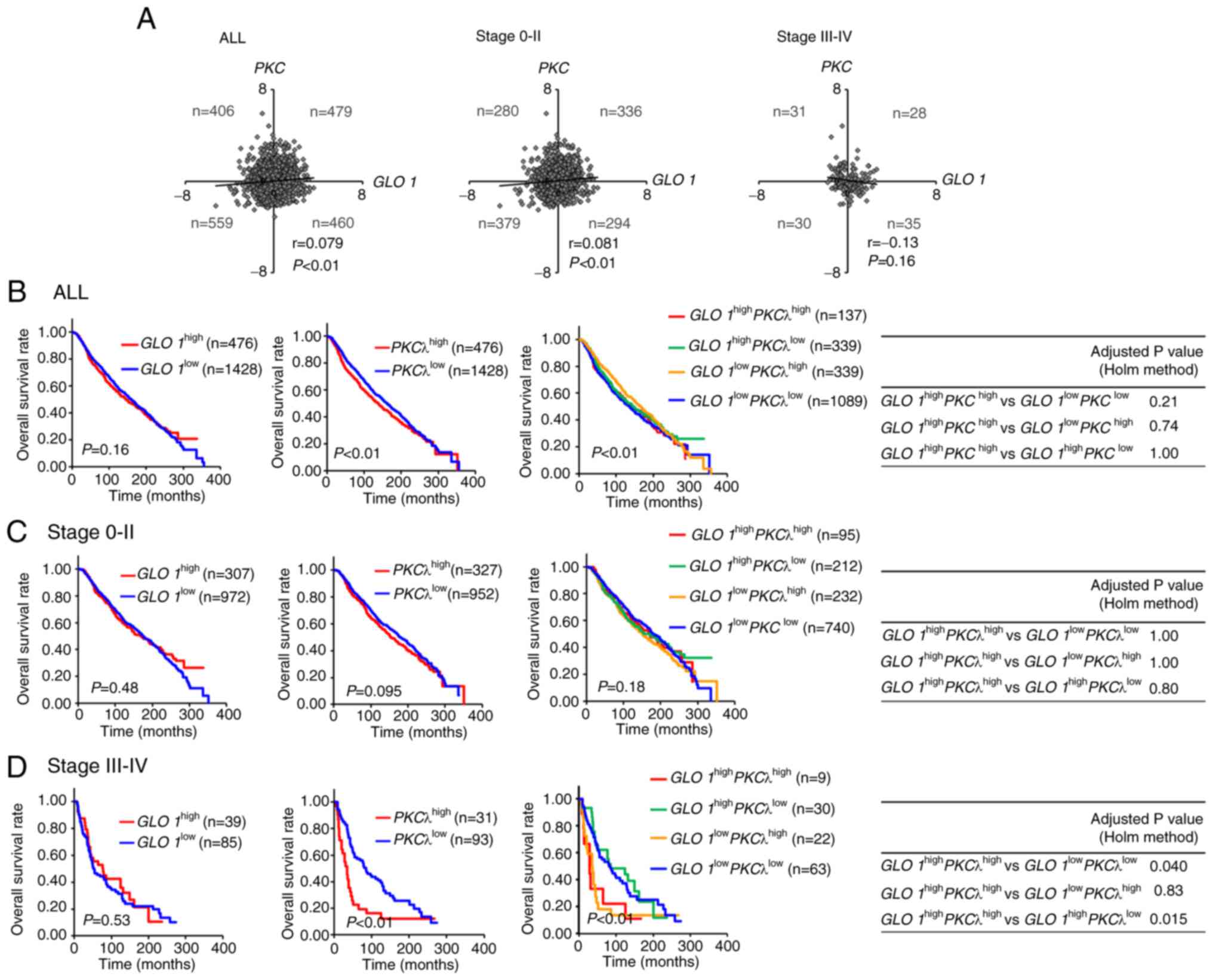
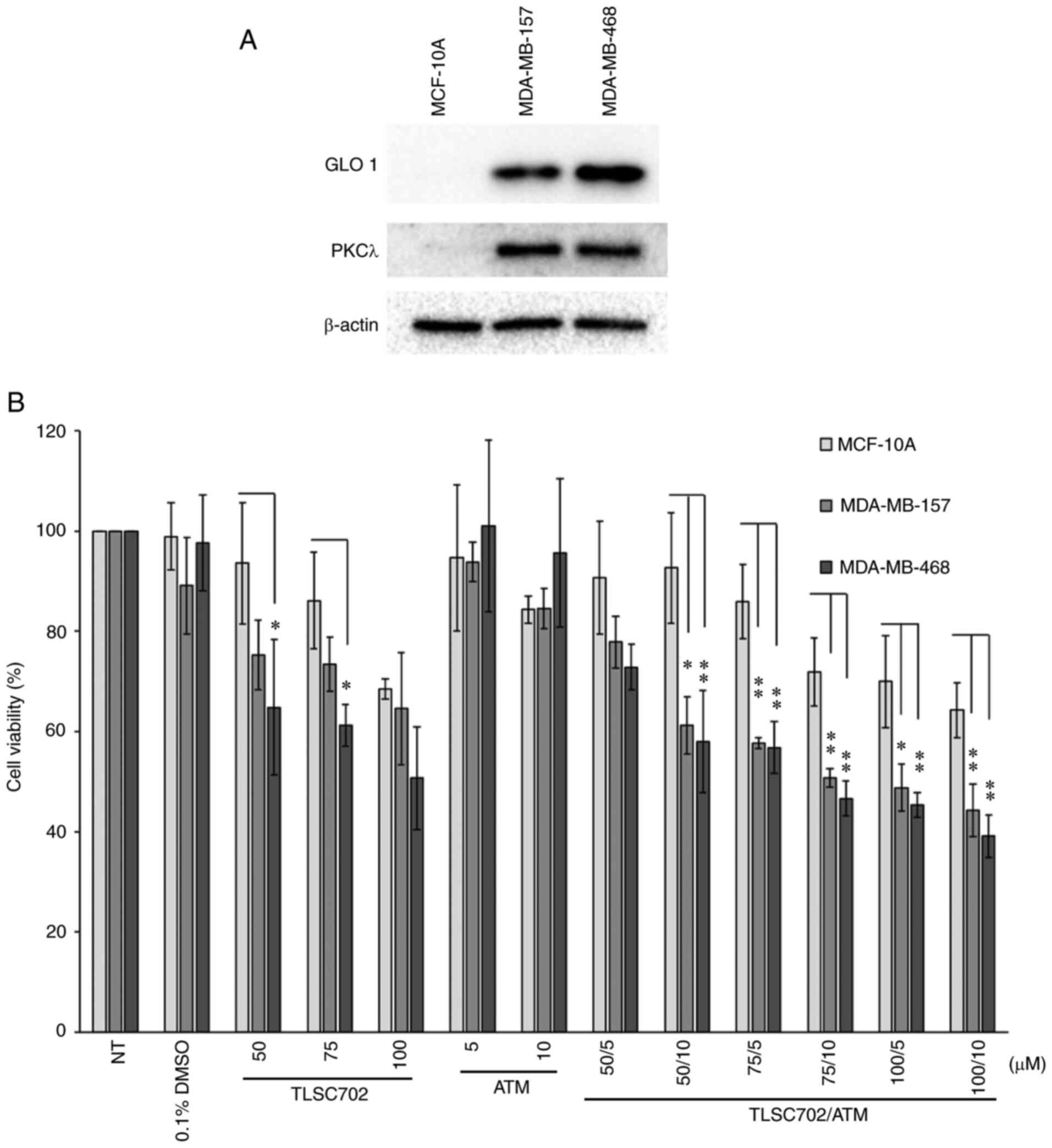
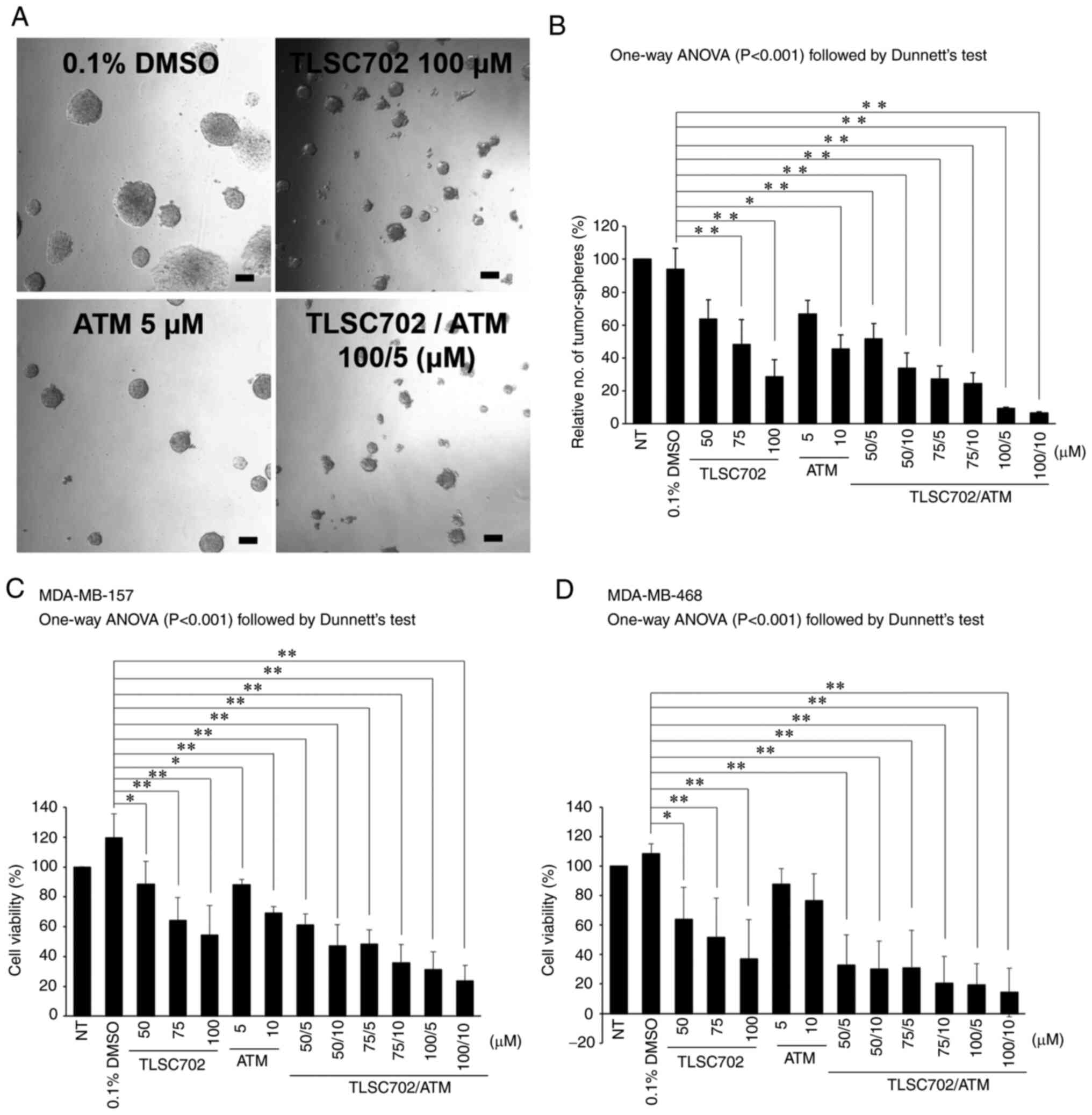
|
1
|
World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF), .
Breast cancer statistics. Breast cancer is the most common cancer
in women worldwide. WCRF, London. 2018.https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/breast-cancer-statistics
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maughan KL, Lutterbie MA and Ham PS:
Treatment of breast cancer. Am Fam Physician. 81:1339–1346.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van't Veer LJ,
Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, Schreiber GJ, Peterse JL, Roberts C,
Marton MJ, et al: A gene-expression signature as a predictor of
survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 347:1999–2009. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ,
Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z, Rasmussen KE, Jones LP, Assefnia S,
Chandrasekharan S, et al: Identification of conserved gene
expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and
human breast tumors. Genome Biol. 8:R762007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Badve S, Dabbs DJ, Schnitt SJ, Baehner FL,
Decker T, Eusebi V, Fox SB, Ichihara S, Jacquemier J, Lakhani SR,
et al: Basal-like and triple-negative breast cancers: A critical
review with an emphasis on the implications for pathologists and
oncologists. Mod Pathol. 24:157–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Warburg O, Wind F and Negelein E: The
metabolism of tumors in the body. J Gen Physiol. 8:519–530. 1927.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gatenby RA and Gillies RJ: Why do cancers
have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 4:891–899. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sakamoto H, Mashima T, Sato S, Hashimoto
Y, Yamori T and Tsuruo T: Selective activation of apoptosis program
by S-p-bromobenzylglutathione cyclopentyl diester in glyoxalase
I-overexpressing human lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
7:2513–2518. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng WL, Tsai MM, Tsai CY, Huang YH, Chen
CY, Chi HC, Tseng YH, Chao IW, Lin WC, Wu SM, et al: Glyoxalase-I
is a novel prognosis factor associated with gastric cancer
progression. PLoS One. 7:e343522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ranganathan S and Tew KD: Analysis of
glyoxalase-I from normal and tumor tissue from human colon. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1182:311–316. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang S, Liang X, Zheng X, Huang H, Chen
X, Wu K, Wang B and Ma S: Glo1 genetic amplification as a potential
therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:2079–2090. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baunacke M, Horn LC, Trettner S, Engel KM,
Hemdan NY, Wiechmann V, Stolzenburg JU, Bigl M and Birkenmeier G:
Exploring glyoxalase 1 expression in prostate cancer tissues:
Targeting the enzyme by ethyl pyruvate defangs some
malignancy-associated properties. Prostate. 74:48–60. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kreycy N, Gotzian C, Fleming T,
Flechtenmacher C, Grabe N, Plinkert P, Hess J and Zaoui K:
Glyoxalase 1 expression is associated with an unfavorable prognosis
of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 17:3822017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zou XY, Ding D, Zhan N, Liu XM, Pan C and
Xia YM: Glyoxalase I is differentially expressed in cutaneous
neoplasms and contributes to the progression of squamous cell
carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol. 135:589–598. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bair WB III, Cabello CM, Uchida K, Bause
AS and Wondrak GT: GLO1 overexpression in human malignant melanoma.
Melanoma Res. 20:85–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rulli A, Carli L, Romani R, Baroni T,
Giovannini E, Rosi G and Talesa V: Expression of glyoxalase I and
II in normal and breast cancer tissues. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
66:67–72. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng HT, Chen J, Liu TY, Wu YQ, Lin XH,
Lai YH and Huang YF: Up-regulation of the tumor promoter
Glyoxalase-1 indicates poor prognosis in breast cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 10:10852–10862. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tamori S, Nozaki Y, Motomura H, Nakane H,
Katayama R, Onaga C, Kikuchi E, Shimada N, Suzuki Y, Noike M, et
al: Glyoxalase 1 gene is highly expressed in basal-like human
breast cancers and contributes to survival of ALDH1-positive breast
cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 9:36515–36529. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang D, Tai LK, Wong LL, Chiu LL, Sethi
SK and Koay ES: Proteomic study reveals that proteins involved in
metabolic and detoxification pathways are highly expressed in
HER-2/neu-positive breast cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics. 4:1686–1696.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gandalovičová A, Vomastek T, Rosel D and
Brábek J: Cell polarity signaling in the plasticity of cancer cell
invasiveness. Oncotarget. 7:25022–25049. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Akimoto K, Mizuno K, Osada S, Hirai S,
Tanuma S, Suzuki K and Ohno S: A new member of the third class in
the protein kinase C family, PKC lambda, expressed dominantly in an
undifferentiated mouse embryonal carcinoma cell line and also in
many tissues and cells. J Biol Chem. 269:12677–12683. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suzuki A, Akimoto K and Ohno S: Protein
kinase C lambda/iota (PKClambda/iota): A PKC isotype essential for
the development of multicellular organisms. J Biochem. 133:9–16.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ohno S: Intercellular junctions and
cellular polarity: The PAR-aPKC complex, a conserved core cassette
playing fundamental roles in cell polarity. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
13:641–648. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parker PJ, Justilien V, Riou P, Linch M
and Fields AP: Atypical protein kinase Cι as a human oncogene and
therapeutic target. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:1–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murray NR, Jamieson L, Yu W, Zhang J,
Gökmen-Polar Y, Sier D, Anastasiadis P, Gatalica Z, Thompson EA and
Fields AP: Protein kinase Ciota is required for Ras transformation
and colon carcinogenesis in vivo. J Cell Biol. 164:797–802. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kojima Y, Akimoto K, Nagashima Y, Ishiguro
H, Shirai S, Chishima T, Ichikawa Y, Ishikawa T, Sasaki T, Kubota
Y, et al: The overexpression and altered localization of the
atypical protein kinase C lambda/iota in breast cancer correlates
with the pathologic type of these tumors. Hum Pathol. 39:824–831.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Paul A, Gunewardena S, Stecklein SR, Saha
B, Parelkar N, Danley M, Rajendran G, Home P, Ray S, Jokar I, et
al: PKCλ/ι signaling promotes triple-negative breast cancer growth
and metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 21:1469–1481. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mizushima T, Asai-Sato M, Akimoto K,
Nagashima Y, Taguri M, Sasaki K, Nakaya MA, Asano R, Tokinaga A,
Kiyono T, et al: Aberrant expression of the cell polarity regulator
aPKCλ/ι is associated with disease progression in cervical
intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN): A possible marker for predicting
CIN prognosis. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 35:106–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tokinaga-Uchiyama A, Mizushima T, Akimoto
K, Nagashima Y, Sasaki K, Nakaya MA, Ohashi K, Kubota K, Maruyama
Y, Kato H, et al: Aberrant nuclear localization of aPKCλ/ι is
associated with poorer prognosis in uterine cervical cancer.
Gynecol Pathol. 38:301–309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baba J, Kioi M, Akimoto K, Nagashima Y,
Taguri M, Inayama Y, Aoki I, Ohno S, Mitsudo K and Tohnai I:
Atypical protein kinase Cλ/ι expression is associated with
malignancy of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
38:6291–6297. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ishiguro H, Akimoto K, Nagashima Y, Kagawa
E, Sasaki T, Sano JY, Takagawa R, Fujinami K, Sasaki K, Aoki I, et
al: Coexpression of aPKCλ/ι and IL-6 in prostate cancer tissue
correlates with biochemical recurrence. Cancer Sci. 102:1576–1581.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ishiguro H, Akimoto K, Nagashima Y, Kojima
Y, Sasaki T, Ishiguro-Imagawa Y, Nakaigawa N, Ohno S, Kubota Y and
Uemura H: aPKClambda/iota promotes growth of prostate cancer cells
in an autocrine manner through transcriptional activation of
interleukin-6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:16369–16374. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Regala RP, Weems C, Jamieson L, Khoor A,
Edell ES, Lohse CM and Fields AP: Atypical protein kinase C iota is
an oncogene in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
65:8905–8911. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eder AM, Sui X, Rosen DG, Nolden LK, Cheng
KW, Lahad JP, Kango-Singh M, Lu KH, Warneke CL, Atkinson EN, et al:
Atypical PKCiota contributes to poor prognosis through loss of
apical-basal polarity and cyclin E overexpression in ovarian
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:12519–12524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Scotti ML, Bamlet WR, Smyrk TC, Fields AP
and Murray NR: Protein kinase Ciota is required for pancreatic
cancer cell transformed growth and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
70:2064–2074. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kato S, Akimoto K, Nagashima Y, Ishiguro
H, Kubota K, Kobayashi N, Hosono K, Watanabe S, Sekino Y, Sato T,
et al: aPKCλ/ι is a beneficial prognostic marker for pancreatic
neoplasms. Pancreatology. 13:360–368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Takagawa R, Akimoto K, Ichikawa Y, Akiyama
H, Kojima Y, Ishiguro H, Inayama Y, Aoki I, Kunisaki C, Endo I, et
al: High expression of atypical protein kinase C lambda/iota in
gastric cancer as a prognostic factor for recurrence. Ann Surg
Oncol. 17:81–88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nozaki Y, Motomura H, Tamori S, Kimura Y,
Onaga C, Kanai S, Ishihara Y, Ozaki A, Hara Y, Harada Y, et al:
High PKCλ expression is required for ALDH1-positive cancer
stem cell function and indicates a poor clinical outcome in
late-stage breast cancer patients. PLoS One. 15:e02357472020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Motomura H, Nozaki Y, Onaga C, Ozaki A,
Tamori S, Shiina TA, Kanai S, Ohira C, Hara Y, Harada Y, et al:
High expression of c-Met, PKCλ and ALDH1A3 predicts a poor
prognosis in late-stage breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 40:35–52.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Akimoto K, Takahashi R, Moriya S, Nishioka
N, Takayanagi J, Kimura K, Fukui Y, Osada SI, Mizuno K, Hirai SI,
et al: EGF or PDGF receptors activate atypical PKClambda through
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO J. 15:788–798. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kotani K, Ogawa W, Matsumoto M, Kitamura
T, Sakaue H, Hino Y, Miyake K, Sano W, Akimoto K, Ohno S and Kasuga
M: Requirement of atypical protein kinase clambda for insulin
stimulation of glucose uptake but not for Akt activation in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 18:6971–6982. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Farese RV: Function and dysfunction of
aPKC isoforms for glucose transport in insulin-sensitive and
insulin-resistant states. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
283:E1–E11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Akimoto K, Nakaya M, Yamanaka T, Tanaka J,
Matsuda S, Weng QP, Avruch J and Ohno S: Atypical protein kinase
Clambda binds and regulates p70 S6 kinase. Biochem J. 335:417–424.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Regala RP, Weems C, Jamieson L, Copland
JA, Thompson EA and Fields AP: Atypical protein kinase Ciota plays
a critical role in human lung cancer cell growth and
tumorigenicity. J Biol Chem. 280:31109–31115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Riddell M, Nakayama A, Hikita T,
Mirzapourshafiyi F, Kawamura T and Pasha A: aPKC controls
endothelial growth by modulating c-Myc via FoxO1 DNA-binding
ability. Nat Commun. 9:53572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Szablewski L: Expression of glucose
transporters in cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1835:164–169.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hussein YR, Bandyopadhyay S, Semaan A,
Ahmed Q, Albashiti B, Jazaerly T, Nahleh Z and Ali-Fehmi R: Glut-1
expression correlates with basal-like breast cancer. Transl Oncol.
4:321–327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bosch RR, Bazuine M, Span PN, Willems PH,
Olthaar AJ, van Rennes H, Maassen JA, Tack CJ, Hermus AR and Sweep
CG: Regulation of GLUT1-mediated glucose uptake by
PKClambda-PKCbeta(II) interactions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem J.
384:349–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Varghese F, Bukhari AB, Malhotra R and De
A: IHC Profiler: An open source plugin for the quantitative
evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of
human tissue samples. PLoS One. 9:e968012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nozaki Y, Tamori S, Inada M, Katayama R,
Nakane H, Minamishima O, Onodera Y, Abe M, Shiina S, Tamura K, et
al: Correlation between c-Met and ALDH1 contributes to the survival
and tumor-sphere formation of ALDH1 positive breast cancer stem
cells and predicts poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. Genes
Cancer. 8:628–639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sato K and Akimoto K: Expression levels of
KMT2C and SLC20A1 identified by information-theoretical analysis
are powerful prognostic biomarkers in estrogen receptor-positive
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 17:e135–e142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast
tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pereira B, Chin SF, Rueda OM, Vollan HK,
Provenzano E, Bardwell HA, Pugh M, Jones L, Russell R, Sammut SJ,
et al: The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refine
their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat Commun.
7:114792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Dicov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
490:61–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Takasawa R, Tao A, Saeki K, Shionozaki N,
Tanaka R, Uchiro H, Takahashi S, Yoshimori A and Tanuma S:
Discovery of a new type inhibitor of human glyoxalase I by
myricetin-based 4-point pharmacophore. Bioorg. Med Chem Lett.
21:4337–4342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Stallings-Mann M, Jamieson L, Regala RP,
Weems C, Murray NR and Fields AP: A novel small-molecule inhibitor
of protein kinase Ciota blocks transformed growth of non-small-cell
lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:1767–1774. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Trani M, Sorrentino A, Busch C and
Landström M: Pro-apoptotic effect of aurothiomalate in prostate
cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 8:306–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chiavarina B, Nokin MJ, Durieux F, Bianchi
E, Turtoi A, Peulen O, Peixoto P, Irigaray P, Uchida K, Belpomme D,
et al: Triple negative tumors accumulate significantly less
methylglyoxal specific adducts than other human breast cancer
subtypes. Oncotarget. 5:5472–5482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Justilien V and Fields AP: Ect2 links the
PKCiota-Par6alpha complex to Rac1 activation and cellular
transformation. Oncogene. 28:3597–3607. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Yang X, Lu P, Yan X, Xiao
F, Zhou H, Wen C, Shi M, Lu J and Meng QH: Effects of methylglyoxal
and glyoxalase I inhibition on breast cancer cells proliferation,
invasion, and apoptosis through modulation of MAPKs, MMP9, and
Bcl-2. Cancer Biol Ther. 17:169–180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Singh S, Brocker C, Koppaka V, Chen Y,
Jackson BC and Matsumoto A: Aldehyde dehydrogenases in cellular
responses to oxidative/electrophilic stress. Free Radic Biol Med.
56:89–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kang Y, Edwards LG and Thornalley PJ:
Effect of methylglyoxal on human leukaemia 60 cell growth:
Modification of DNA G1 growth arrest and induction of apoptosis.
Leuk Res. 20:97–405. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Liu L, Lei B, Wang L, Chang C, Yang H, Liu
J, Huang G and Xie W: Protein kinase C-iota-mediated glycolysis
promotes non-small-cell lung cancer progression. Onco Targets Ther.
12:5835–5848. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tisdale EJ: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase is phosphorylated by protein kinase Ciota/lambda and
plays a role in microtubule dynamics in the early secretory
pathway. J Biol Chem. 277:3334–3341. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tisdale EJ: Rab2 interacts directly with
atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) iota/lambda and inhibits
aPKCiota/lambda-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 278:52524–52530. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kim JY, Valencia T, Abu-Baker S, Linares
J, Lee SJ, Yajima T, Chen J, Eroshkin A, Castilla EA, Brill LM, et
al: c-Myc phosphorylation by PKCζ represses prostate tumorigenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6418–6423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Osthus RC, Shim H, Kim S, Li Q, Reddy R,
Mukherjee M, Xu Y, Wonsey D, Lee LA and Dang CV: Deregulation of
glucose transporter 1 and glycolytic gene expression by c-Myc. J
Biol Chem. 275:21797–21800. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gjyshi O, Bottero V, Veettil MV, Dutta S,
Singh VV and Chikoti L: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
induces Nrf2 during de novo infection of endothelial cells to
create a microenvironment conducive to infection. PLoS Pathog.
10:e10044602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ma L, Tao Y, Duran A, Llado V, Galvez A,
Barger JF, Castilla EA, Chen J, Yajima T, Porollo A, et al: Control
of nutrient stress-induced metabolic reprogramming by PKCζ in
tumorigenesis. Cell. 152:599–611. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Franchet C, Duprez-Paumier R and
Lacroix-Triki M: Molecular taxonomy of luminal breast cancer in
2015. Bull Cancer. 102 (6 Suppl 1):S34–S46. 2015.(In French).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu Z, Zhang XS and Zhang S: Breast tumor
subgroups reveal diverse clinical prognostic power. Sci Rep.
4:40022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|