|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, ; Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H,
Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, et
al: The global burden of cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, ; Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H,
Abd-Allah F, Abdel-Rahman O, Abdelalim A, Abdoli A, Abdollahpour I,
et al: Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality,
years of life lost, years lived with disability, and
disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017:
A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA
Oncol. 5:1749–1768. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
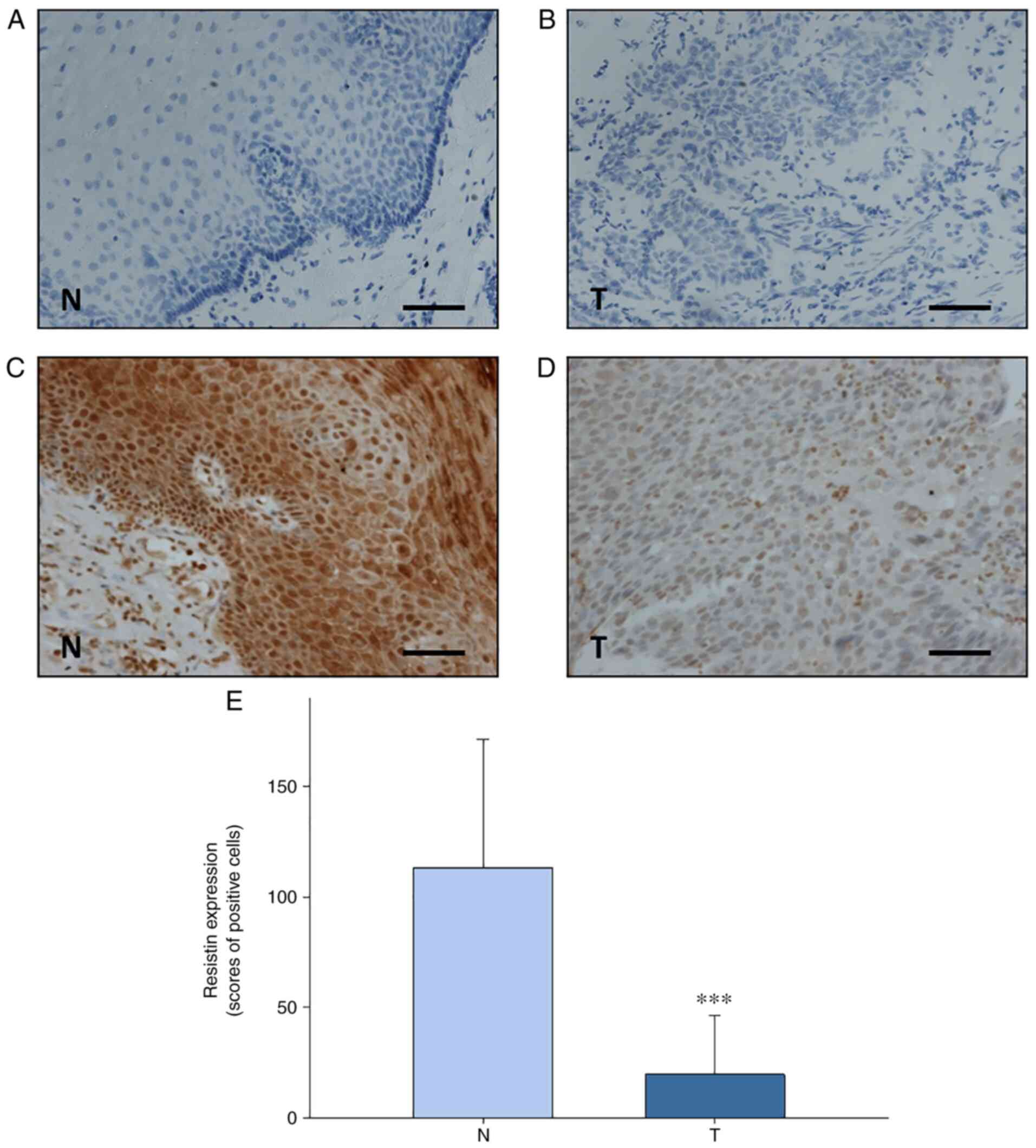
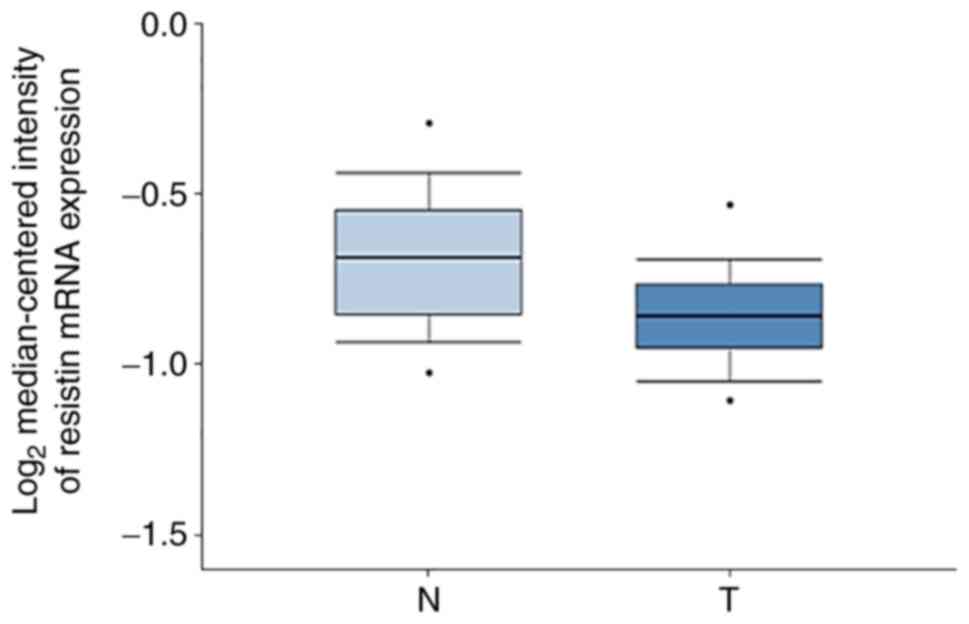
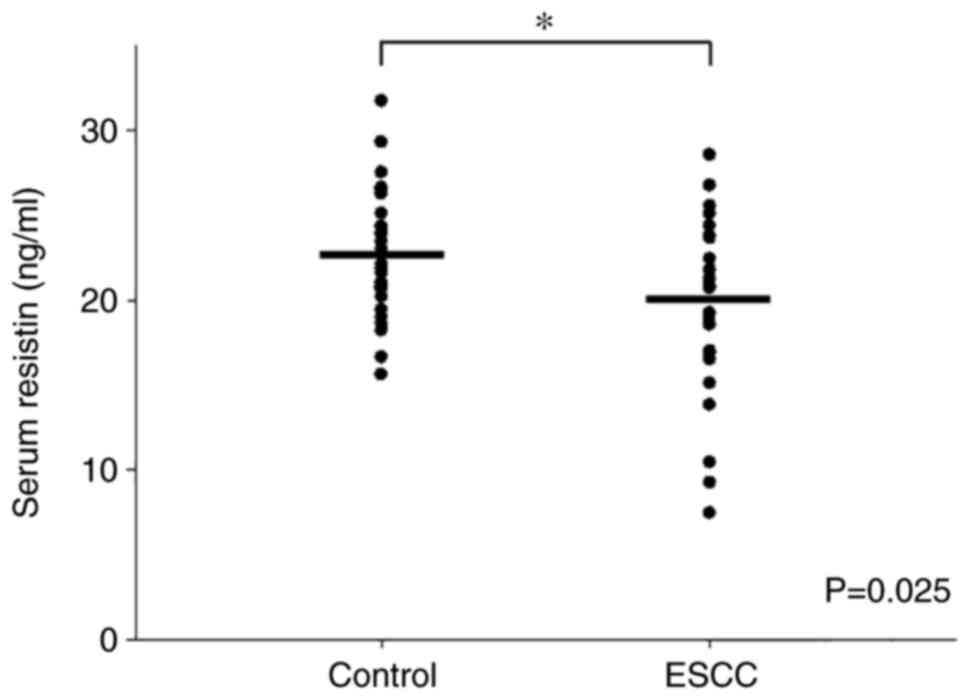
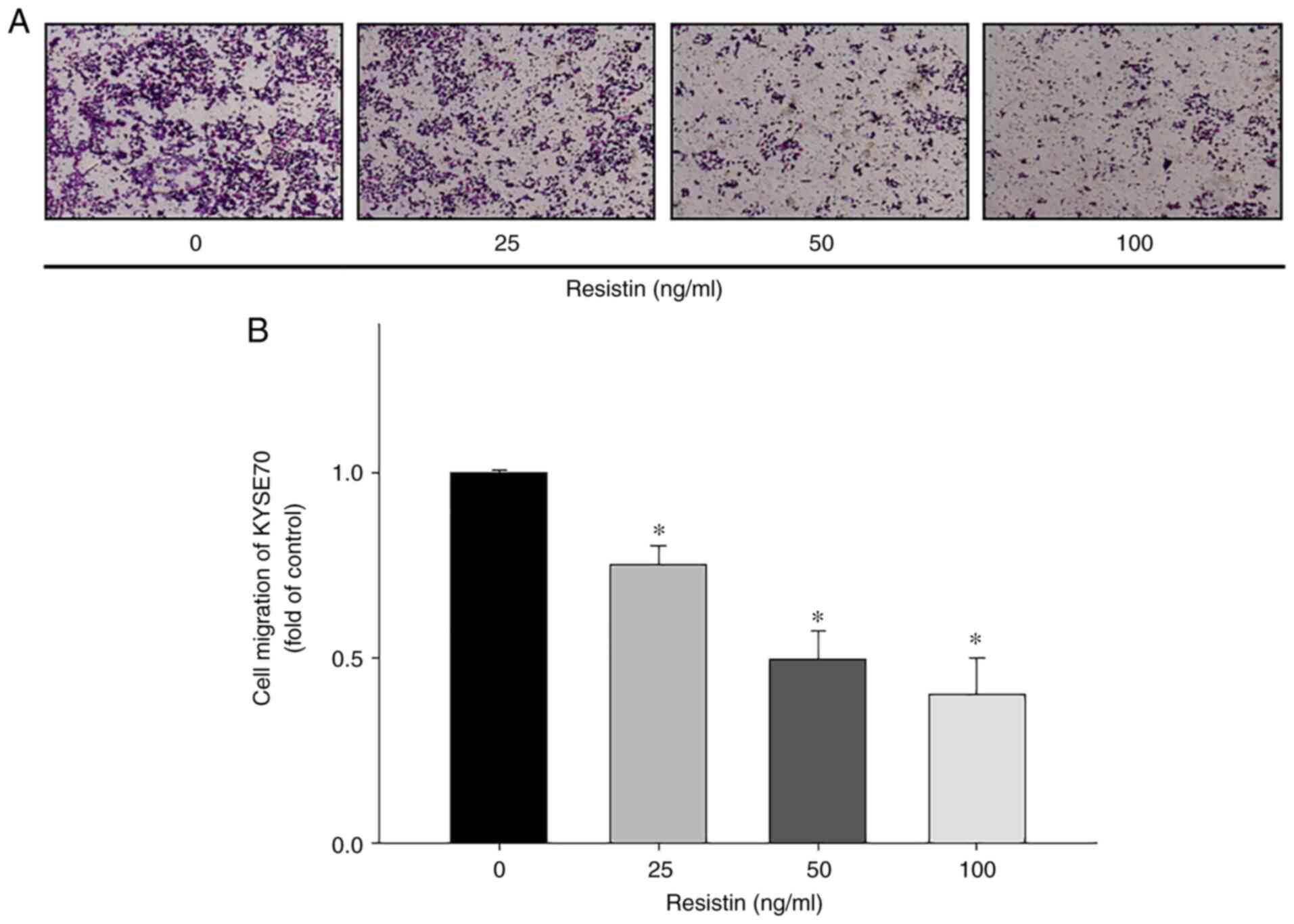
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lao-Sirieix P and Fitzgerald RC: Screening
for oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 9:278–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Edgren G, Adami HO, Weiderpass E and Nyren
O: A global assessment of the oesophageal adenocarcinoma epidemic.
Gut. 62:1406–1414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lagergren J, Smyth E, Cunningham D and
Lagergren P: Oesophageal cancer. Lancet. 390:2383–2396. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hajizadeh B, Jessri M, Moasheri SM, Rad AH
and Rashidkhani B: Fruits and vegetables consumption and esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma: A case-control study. Nutr Cancer.
63:707–713. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Wang J, Leng Y and Lv C: Intake of
fruit and vegetables and risk of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J Cancer.
133:473–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bosetti C, Franceschi S, Levi F, Negri E,
Talamini R and La Vecchia C: Smoking and drinking cessation and the
risk of oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 83:689–691. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ,
Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS and Lazar MA: The
hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 409:307–312.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Steppan CM, Brown EJ, Wright CM, Bhat S,
Banerjee RR, Dai CY, Enders GH, Silberg DG, Wen X, Wu GD and Lazar
MA: A family of tissue-specific resistin-like molecules. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:502–506. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Banerjee RR and Lazar MA: Dimerization of
resistin and resistin-like molecules is determined by a single
cysteine. J Biol Chem. 276:25970–25973. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McTernan PG, McTernan CL, Chetty R, Jenner
K, Fisher FM, Lauer MN, Crocker J, Barnett AH and Kumar S:
Increased resistin gene and protein expression in human abdominal
adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:24072002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patel L, Buckels AC, Kinghorn IJ, Murdock
PR, Holbrook JD, Plumpton C, Macphee CH and Smith SA: Resistin is
expressed in human macrophages and directly regulated by PPAR gamma
activators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 300:472–476. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U
and Tarkowski A: Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory
properties. J Immunol. 174:5789–5795. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Curat CA, Wegner V, Sengenès C, Miranville
A, Tonus C, Busse R and Bouloumié A: Macrophages in human visceral
adipose tissue: Increased accumulation in obesity and a source of
resistin and visfatin. Diabetologia. 49:744–747. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lehrke M, Reilly MP, Millington SC, Iqbal
N, Rader DJ and Lazar MA: An inflammatory cascade leading to
hyperresistinemia in humans. PLoS Med. 1:e452004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reilly MP, Lehrke M, Wolfe ML, Rohatgi A,
Lazar MA and Rader DJ: Resistin is an inflammatory marker of
atherosclerosis in humans. Circulation. 111:932–939. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang YY, Hung AC, Lo S and Yuan SF:
Adipocytokines visfatin and resistin in breast cancer: Clinical
relevance, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Cancer
Lett. 498:229–239. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hlavna M, Kohut L, Lipkova J,
Bienertova-Vasku J, Dostalova Z, Chovanec J and Vasku A:
Relationship of resistin levels with endometrial cancer risk.
Neoplasma. 58:124–128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Danese E, Montagnana M, Minicozzi AM,
Bonafini S, Ruzzenente O, Gelati M, De Manzoni G, Lippi G and Guidi
GC: The role of resistin in colorectal cancer. Clin Chim Acta.
413:760–764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tzanavari T, Tasoulas J, Vakaki C,
Mihailidou C, Tsourouflis G and Theocharis S: The role of
adipokines in the establishment and progression of head and neck
neoplasms. Curr Med Chem. 26:4726–4748. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang CH, Wang PJ, Hsieh YC, Lo S, Lee YC,
Chen YC, Tsai CH, Chiu WC, Chu-Sung Hu S, Lu CW, et al: Resistin
facilitates breast cancer progression via TLR4-mediated induction
of mesenchymal phenotypes and stemness properties. Oncogene.
37:589–600. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Detre S, Saclani Jotti G and Dowsett M: A
‘quickscore’ method for immunohistochemical semiquantitation:
Validation for oestrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. J Clin
Pathol. 48:876–878. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Assiri AM and Kamel HF: Evaluation of
diagnostic and predictive value of serum adipokines: Leptin,
resistin and visfatin in postmenopausal breast cancer. Obes Res
Clin Pract. 10:442–453. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee YC, Chen YJ, Wu CC, Lo S, Hou MF and
Yuan SS: Resistin expression in breast cancer tissue as a marker of
prognosis and hormone therapy stratification. Gynecol Oncol.
125:742–750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karapanagiotou EM, Tsochatzis EA, Dilana
KD, Tourkantonis I, Gratsias I and Syrigos KN: The significance of
leptin, adiponectin, and resistin serum levels in non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 61:391–397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kerem M, Ferahkose Z, Yilmaz UT, Pasaoglu
H, Ofluoglu E, Bedirli A, Salman B, Sahin TT and Akin M: Adipokines
and ghrelin in gastric cancer cachexia. World J Gastroenterol.
14:3633–3641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakajima TE, Yamada Y, Hamano T, Furuta K,
Gotoda T, Katai H, Kato K, Hamaguchi T and Shimada Y: Adipocytokine
levels in gastric cancer patients: Resistin and visfatin as
biomarkers of gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 44:685–690. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gonullu G, Kahraman H, Bedir A, Bektas A
and Yucel I: Association between adiponectin, resistin, insulin
resistance, and colorectal tumors. Int J Colorectal Dis.
25:205–212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tripathi D, Kant S, Pandey S and Ehtesham
NZ: Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease. FEBS J.
287:3141–3149. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nitenberg G and Raynard B: Nutritional
support of the cancer patient: Issues and dilemmas. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 34:137–168. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fahey PP, Mallitt KA, Astell-Burt T, Stone
G and Whiteman DC: Impact of pre-diagnosis behavior on risk of
death from esophageal cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 26:1365–1373. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakajima TE, Yamada Y, Hamano T, Furuta K,
Oda I, Kato H, Kato K, Hamaguchi T and Shimada Y: Adipocytokines
and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 136:261–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Diakowska D, Markocka-Maczka K,
Nienartowicz M, Rosinczuk J and Krzystek-Korpacka M: Assessment of
apelin, apelin receptor, resistin, and adiponectin levels in the
primary tumor and serum of patients with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Adv Clin Exp Med. 28:671–678. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aeffner F, Wilson K, Martin NT, Black JC,
Hendriks CLL, Bolon B, Rudmann DG, Gianani R, Koegler SR, Krueger J
and Young GD: The gold standard paradox in digital image analysis:
Manual versus automated scoring as ground truth. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 141:1267–1275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bankhead P, Fernández JA, McArt DG, Boyle
DP, Li G, Loughrey MB, Irwin GW, Harkin DP, James JA, McQuaid S, et
al: Integrated tumor identification and automated scoring minimizes
pathologist involvement and provides new insights to key biomarkers
in breast cancer. Lab Invest. 98:15–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Adipocytokines:
Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat
Rev Immunol. 6:772–783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Codoner-Franch P and Alonso-Iglesias E:
Resistin: Insulin resistance to malignancy. Clin Chim Acta.
438:46–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee S, Lee HC, Kwon YW, Lee SE, Cho Y, Kim
J, Lee S, Kim JY, Lee J, Yang HM, et al: Adenylyl
cyclase-associated protein 1 is a receptor for human resistin and
mediates inflammatory actions of human monocytes. Cell Metab.
19:484–497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rosendahl AH, Bergqvist M, Lettiero B,
Kimbung S and Borgquist S: Adipocytes and obesity-related
conditions jointly promote breast cancer cell growth and motility:
Associations with CAP1 for prognosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9:6892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Daquinag AC, Zhang Y, Amaya-Manzanares F,
Simmons PJ and Kolonin MG: An isoform of decorin is a resistin
receptor on the surface of adipose progenitor cells. Cell Stem
Cell. 9:74–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sanchez-Solana B, Laborda J and Baladron
V: Mouse resistin modulates adipogenesis and glucose uptake in
3T3-L1 preadipocytes through the ROR1 receptor. Mol Endocrinol.
26:110–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Banerjee AG, Bhattacharyya I, Lydiatt WM
and Vishwanatha JK: Aberrant expression and localization of decorin
in human oral dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res.
63:7769–7776. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sudan SK, Deshmukh SK, Poosarla T,
Holliday NP, Dyess DL, Singh AP and Singh S: Resistin: An
inflammatory cytokine with multi-faceted roles in cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1874:1884192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wysocka MB, Pietraszek-Gremplewicz K and
Nowak D: The role of apelin in cardiovascular diseases, obesity and
cancer. Front Physiol. 9:5572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|