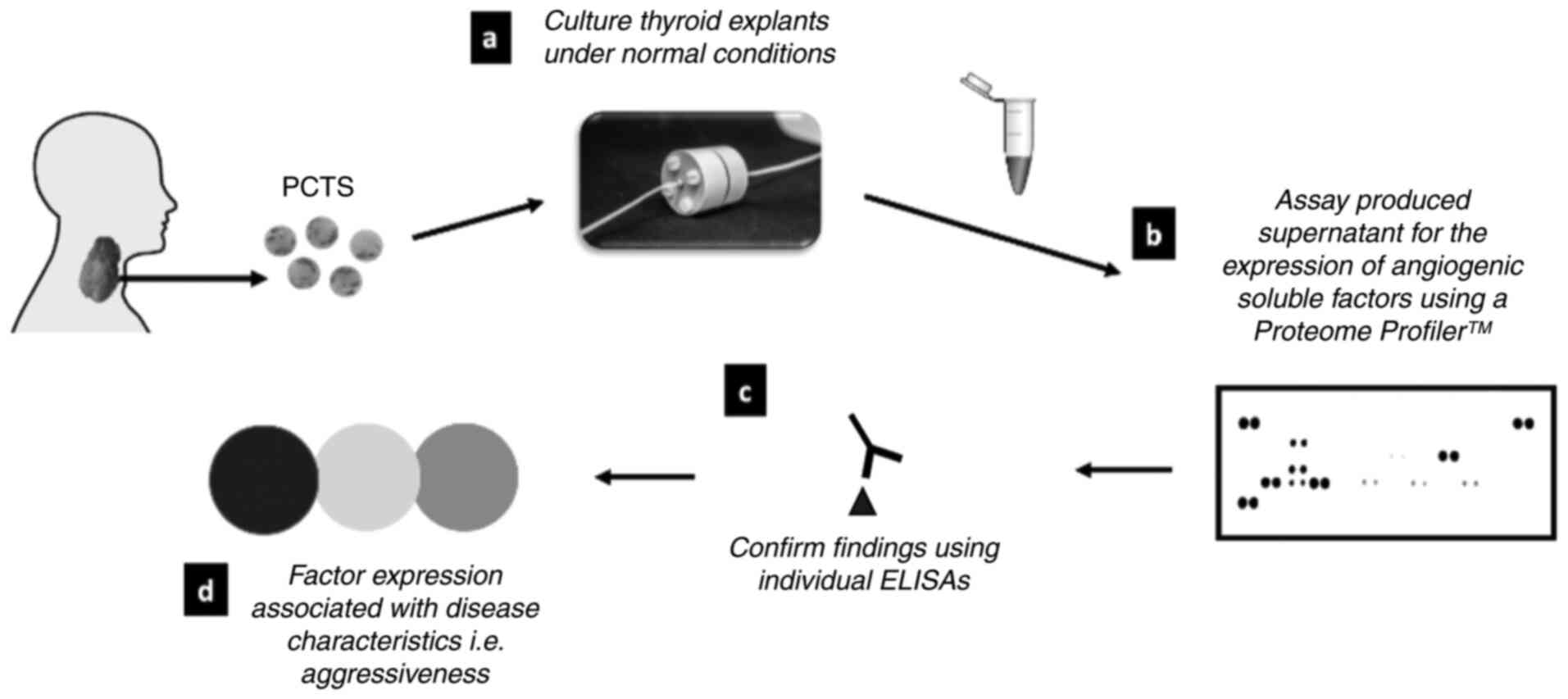
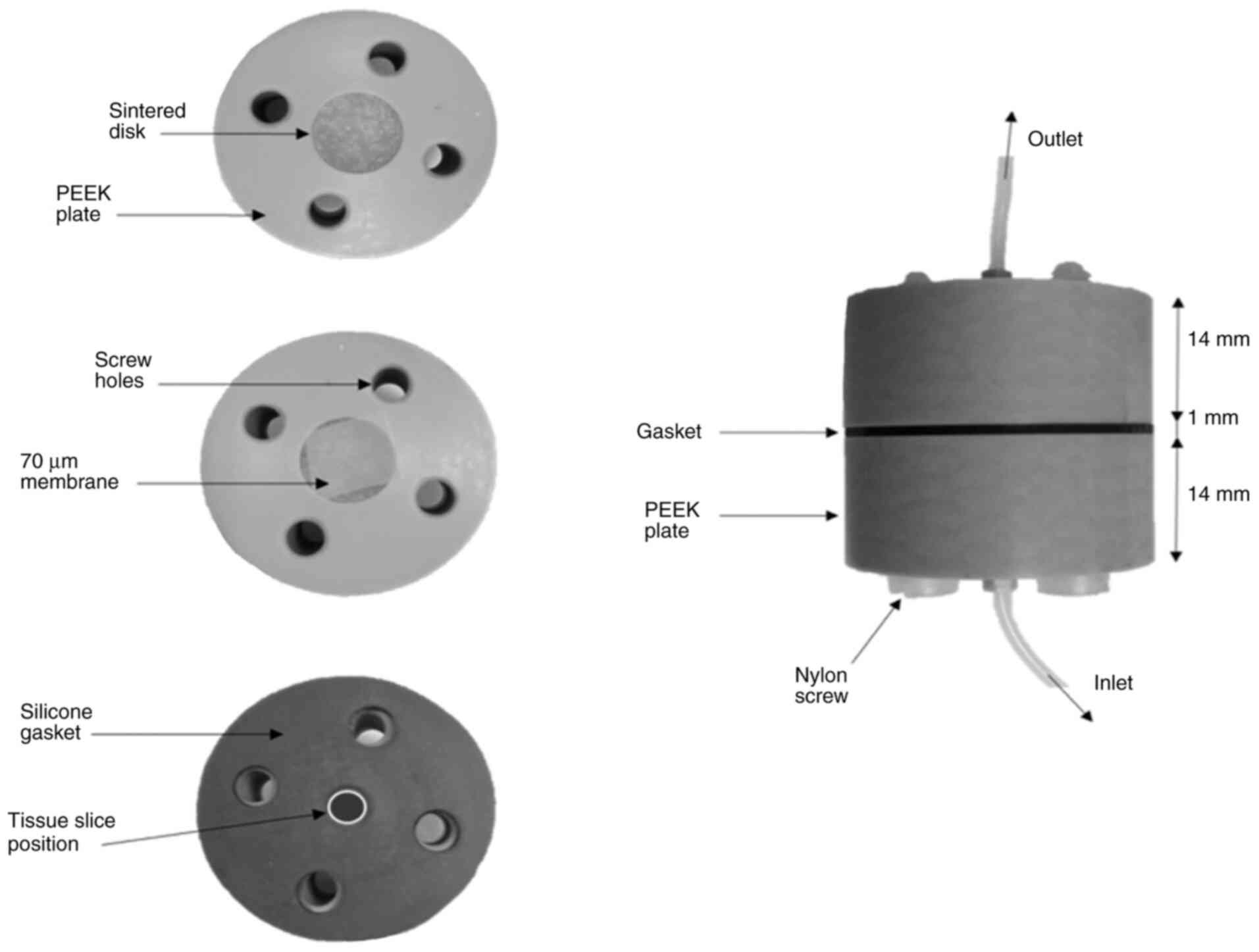
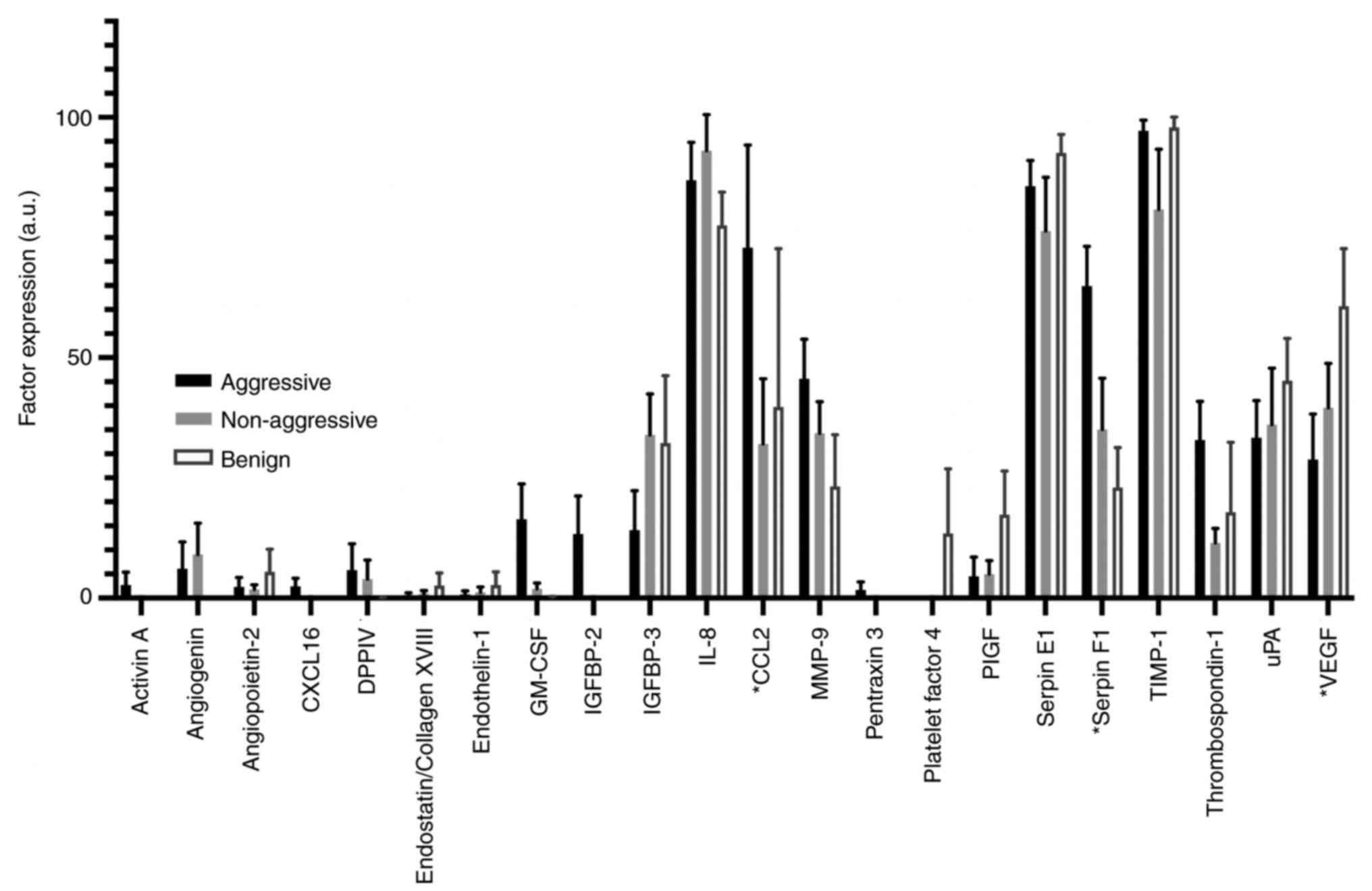
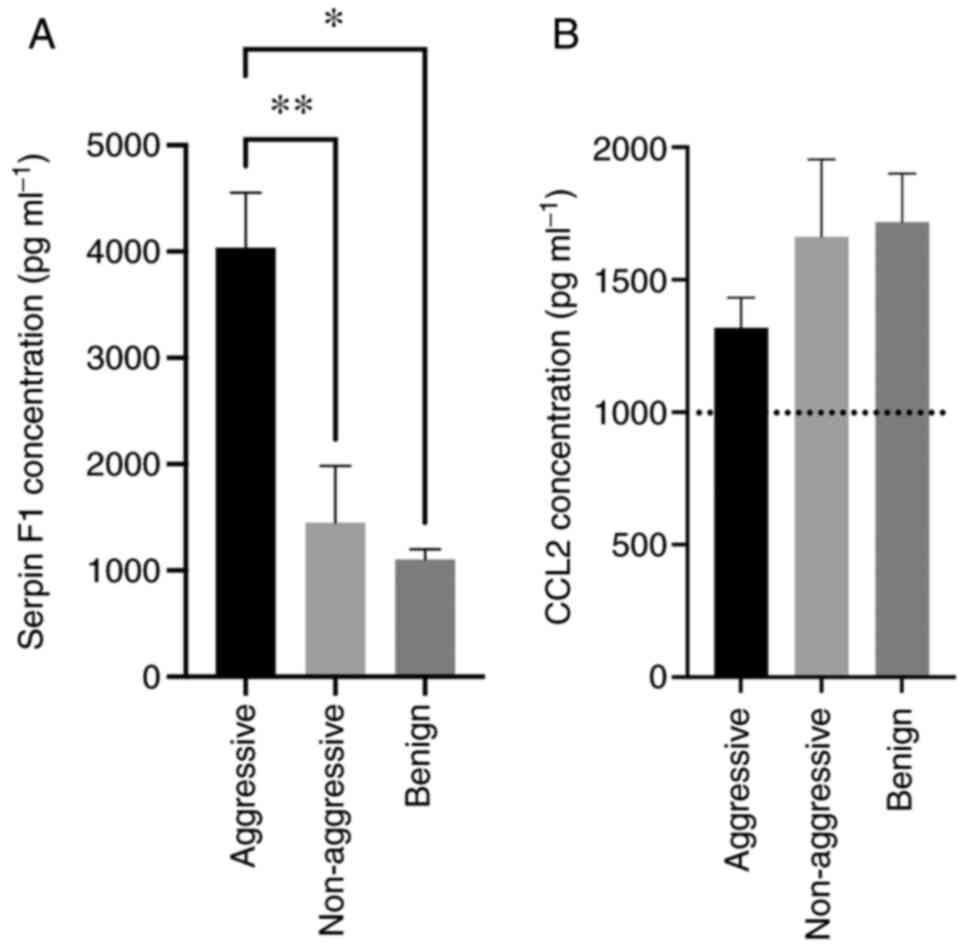
|
1
|
Wang LY and Ganly I: Nodal metastases in
thyroid cancer: Prognostic implications and management. Future
Oncol. 12:981–994. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty
GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM and
Schlumberger M: 2015 American thyroid association management
guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer: The American thyroid association
guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid
cancer. Thyroid. 26:1–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Indrasena BSH: Use of thyroglobulin as a
tumour marker. World J Biol Chem. 8:81–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim SJ, Lee KE, Myong JP, Park JH, Jeon
YK, Min HS, Park SY, Jung KC, Koo DH and Youn YK: BRAF V600E
mutation is associated with tumor aggressiveness in papillary
thyroid cancer. World J Surg. 36:310–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kato MA and Fahey TJ 3rd: Molecular
markers in thyroid cancer diagnostics. Surg Clin North Am.
89:1139–1155. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yip L, Kelly L, Shuai Y, Armstrong MJ,
Nikiforov YE, Carty SE and Nikiforova MN: MicroRNA signature
distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2035–2041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Acibucu F, Dökmetaş HS, Tutar Y, Elagoz S
and Kilicli F: Correlations between the expression levels of
micro-RNA146b, 221, 222 and p27Kip1 protein mRNA and the
clinicopathologic parameters in papillary thyroid cancers. Exp Clin
Endocrinol Diabetes. 122:137–143. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cookson VJ, Bentley MA, Hogan BV, Horgan
K, Hayward BE, Hazelwood LD and Hughes TA: Circulating microRNA
profiles reflect the presence of breast tumours but not the
profiles of microRNAs within the tumours. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
35:301–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang H, Zhong Y, Luo Z, Huang Y, Lin H,
Zhan S, Xie K and Li QQ: Diagnostic value of 16 cellular tumor
markers for metastatic thyroid cancer: An immunohistochemical
study. Anticancer Res. 31:3433–3440. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Šelemetjev S, Ðoric I, Paunovic I, Tatic S
and Cvejic D: Coexpressed high levels of VEGF-C and active MMP-9
are associated with lymphatic spreading and local invasiveness of
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 146:594–602. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jang JY, Kim DS, Park HY, Shin SC, Cha W,
Lee JC, Wang SG and Lee BJ: Preoperative serum VEGF-C but not
VEGF-A level is correlated with lateral neck metastasis in
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Head Neck. 41:2602–2609. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi Y, Su C, Hu H, Yan H, Li W, Chen G, Xu
D, Du X and Zhang P: Serum MMP-2 as a potential predictive marker
for papillary thyroid carcinoma. PLoS One. 13:e01988962018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riley A, Green V, Cheah R, McKenzie G,
Karsai L, England J and Greenman J: A novel microfluidic device
capable of maintaining functional thyroid carcinoma specimens ex
vivo provides a new drug screening platform. BMC Cancer.
22:2592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Folkman J: Role of angiogenesis in tumor
growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 29 (Suppl 16):S15–S18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kohn EC and Liotta LA: Molecular insights
into cancer invasion: Strategies for prevention and intervention.
Cancer Res. 55:1856–1862. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Kihara M, Fukushima M,
Higashiyama T and Miya A: Overall survival of papillary thyroid
carcinoma patients: A single-institution long-term follow-up of
5897 patients. World J Surg. 42:615–622. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tombran-Tink J, Chader GG and Johnson LV:
PEDF: A pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal
differentiative activity. Exp Eye Res. 53:411–414. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bilak MM, Corse AM, Bilak SR, Lehar M,
Tombran-Tink J and Kuncl RW: Pigment epithelium-derived factor
(PEDF) protects motor neurons from chronic glutamate-mediated
neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 58:719–728. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Chen J, Ke Y, Mansel RE and Jiang
WG: Expression of pigment epithelial derived factor is reduced in
non-small cell lung cancer and is linked to clinical outcome. Int J
Mol Med. 17:937–944. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Gillis P, Crawford
SE, Xu H, Benedict W and Bouck NP: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor: A potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science. 285:245–248.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Han J, Yang X, Shao C, Xu Z,
Cheng R, Cai W, Ma J, Yang Z and Gao G: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor inhibits angiogenesis and growth of gastric carcinoma by
down-regulation of VEGF. Oncol Rep. 26:681–686. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Crawford SE, Stellmach V, Ranalli M, Huang
X, Huang L, Volpert O, De Vries GH, Abramson LP and Bouck N:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in neuroblastoma: A
multifunctional mediator of schwann cell antitumor activity. J Cell
Sci. 114((Pt 24)): 4421–4428. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Filleur S, Volz K, Nelius T, Mirochnik Y,
Huang H, Zaichuk TA, Aymerich MS, Becerra SP, Yap R, Veliceasa D,
et al: Two functional epitopes of pigment epithelial-derived factor
block angiogenesis and induce differentiation in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:5144–5152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheung LW, Au SC, Cheung AN, Ngan HY,
Tombran-Tink J, Auersperg N and Wong AST: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor is estrogen sensitive and inhibits the
growth of human ovarian cancer and ovarian surface epithelial
cells. Endocrinology. 147:4179–4191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guan M, Pang CP, Yam HF, Cheung KF, Liu WW
and Lu Y: Inhibition of glioma invasion by overexpression of
pigment epithelium-derived factor. Cancer Gene Ther. 11:325–332.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lv Y, Sun Y, Shi T, Shi C, Qin H and Li Z:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor has a role in the progression of
papillary thyroid carcinoma by affecting the HIF1α-VEGF signaling
pathway. Oncol Lett. 12:5217–5222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Graves DT, Barnhill R, Galanopoulos T and
Antoniades HN: Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in
human melanoma in vivo. Am J Pathol. 140:9–14. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Negus RP, Stamp GW, Relf MG, Burke F,
Malik ST, Bernasconi S, Allavena P, Sozzani S, Mantovani A and
Balkwill FR: The detection and localization of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in human ovarian cancer. J Clin
Invest. 95:2391–2396. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saji H, Koike M, Yamori T, Saji S, Seiki
M, Matsushima K and Toi M: Significant correlation of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 expression with neovascularization and
progression of breast carcinoma. Cancer. 92:1085–1091. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohta M, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M,
Yasui W, Mukaida N, Haruma K and Chayama K: Monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 expression correlates with macrophage
infiltration and tumor vascularity in human esophageal squamous
cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 102:220–224. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Koide N, Nishio A, Sato T, Sugiyama A and
Miyagawa S: Significance of macrophage chemoattractant protein-1
expression and macrophage infiltration in squamous cell carcinoma
of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 99:1667–1674. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu Y, Cai Z, Galson DL, Xiao G, Liu Y,
George DE, Melhem MF, Yao Z and Zhang J: Monocyte chemotactic
protein-1 (MCP-1) acts as a paracrine and autocrine factor for
prostate cancer growth and invasion. Prostate. 66:1311–1318. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ueno T, Toi M, Saji H, Muta M, Bando H,
Kuroi K, Koike M, Inadera H and Matsushima K: Significance of
macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 in macrophage recruitment,
angiogenesis, and survival in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
6:3282–3289. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanaka K, Kurebayashi J, Sohda M, Nomura
T, Prabhakar U, Yan L and Sonoo H: The expression of monocyte
chemotactic protein-1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma is correlated
with lymph node metastasis and tumor recurrence. Thyroid. 19:21–25.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ryder M, Gild M, Hohl TM, Pamer E, Knauf
J, Ghossein R, Joyce JA and Fagin JA: Genetic and pharmacological
targeting of CSF-1/CSF-1R inhibits tumor-associated macrophages and
impairs BRAF-induced thyroid cancer progression. PLoS One.
8:e543022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dawes J, Pratt DA, Dewar MS and Preston
FE: Do extra-platelet sources contribute to the plasma level of
thrombospondin? Thromb Haemost. 59:273–276. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen H, Herndon ME and Lawler J: The cell
biology of thrombospondin-1. Matrix Biol. 19:597–614. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nucera C, Porrello A, Antonello ZA, Mekel
M, Nehs MA, Giordano TJ, Gerald D, Benjamin LE, Priolo C, Puxeddu
E, et al: B-Raf(V600E) and thrombospondin-1 promote thyroid cancer
progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:10649–10654. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Soula-Rothhut M, Coissard C, Sartelet H,
Boudot C, Bellon G, Martiny L and Rothhut B: The tumor suppressor
PTEN inhibits EGF-induced TSP-1 and TIMP-1 expression in FTC-133
thyroid carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 304:187–201. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bienes-Martínez R, Ordóñez A,
Feijoo-Cuaresma M, Corral-Escariz M, Mateo G, Stenina O, Jiménez B
and Calzada MJ: Autocrine stimulation of clear-cell renal carcinoma
cell migration in hypoxia via HIF-independent suppression of
thrombospondin-1. Sci Rep. 2:7882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tzeng HT, Tsai CH, Yen YT, Cheng HC, Chen
YC, Pu SW, Wang YS, Shan YS, Tseng YL, Su WC, et al: Dysregulation
of Rab37-mediated cross-talk between cancer cells and endothelial
cells via thrombospondin-1 promotes tumor neovasculature and
metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2335–2345. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang T, Sun L, Yuan X and Qiu H:
Thrombospondin-1 is a multifaceted player in tumor progression.
Oncotarget. 8:84546–84558. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schlaeppi JM and Wood JM: Targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) for anti-tumor therapy,
by anti-VEGF neutralizing monoclonal antibodies or by VEGF receptor
tyrosine-kinase inhibitors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 18:473–481.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D and Keshet E:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate
hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 359:843–845. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Soh EY, Duh QY, Sobhi SA, Young DM,
Epstein HD, Wong MG, Garcia YK, Min YD, Grossman RF, Siperstein AE
and Clark OH: Vascular endothelial growth factor expression is
higher in differentiated thyroid cancer than in normal or benign
thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82:3741–3747. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tuttle RM, Fleisher M, Francis GL and
Robbins RJ: Serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels are
elevated in metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer but not
increased by short-term TSH stimulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
87:1737–1742. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xie J, Liu Y, Du X and Wu Y: TGF-β1
promotes the invasion and migration of papillary thyroid carcinoma
cells by inhibiting the expression of lncRNA-NEF. Oncol Lett.
17:3125–3132. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang W, van Weerden WM, de Ridder CMA,
Erkens-Schulze S, Schönfeld E, Meijer TG, Kanaar R, van Gent DC and
Nonnekens J: Ex vivo treatment of prostate tumor tissue
recapitulates in vivo therapy response. Prostate. 79:390–402. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu X, Su C, Xu J, Zhou D, Yan H, Li W,
Chen G, Zhang N, Xu D and Hu H: Immunohistochemical analysis of
matrix metalloproteinase-9 predicts papillary thyroid carcinoma
prognosis. Oncol Lett. 17:2308–2316. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Selemetjev S, Savin S, Paunovic I, Tatic S
and Cvejic D: Concomitant high expression of survivin and vascular
endothelial growth factor-C is strongly associated with metastatic
status of lymph nodes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Cancer Res
Ther. 14 (Suppl):S114–S119. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guan H, Guo Y, Liu L, Ye R, Liang W, Li H,
Xiao H and Li Y: INAVA promotes aggressiveness of papillary thyroid
cancer by upregulating MMP9 expression. Cell Biosci. 8:262018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cui M, Chang Y, Du W, Liu S, Qi J, Luo R
and Luo S: Upregulation of lncRNA-ATB by transforming growth factor
β1 (TGF-β1) promotes migration and invasion of papillary thyroid
carcinoma cells. Med Sci Monit. 24:5152–5158. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lu ZL, Chen YJ, Jing XY, Wang NN, Zhang T
and Hu CJ: Detection and identification of serum peptides biomarker
in papillary thyroid cancer. Med Sci Monit. 24:1581–1587. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang N, Jiang R, Yang JY, Tang C, Yang L,
Xu M, Jiang QF and Liu ZM: Expression of TGF-β1, SNAI1 and MMP-9 is
associated with lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. J Mol Histol. 45:391–399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Makki FM, Taylor SM, Shahnavaz A, Leslie
A, Gallant J, Douglas S, Teh E, Trites J, Bullock M, Inglis K, et
al: Serum biomarkers of papillary thyroid cancer. J Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 42:162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou ZH, Cui XN, Xing HG, Yan RH, Yao DK
and Wang LX: Changes and prognostic value of serum vascular
endothelial growth factor in patients with differentiated thyroid
cancer. Med Princ Pract. 22:24–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liang H, Zhong Y, Luo Z, Huang Y, Lin H,
Luo M, Zhan S, Xie K, Ma Y and Li QQ: Assessment of biomarkers for
clinical diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma with distant
metastasis. Int J Biol Markers. 25:38–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang T, Jiang CX, Li Y and Liu X:
Pathologic study of expression and significance of matrix
metalloproteinases-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1,
vascular endothelial growth factor and transforming growth factor
beta-1 in papillary carcinoma and follicular carcinoma of thyroid.
Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 38:824–828. 2009.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang JX, Dong R, Liu QL, Yang SB, Fan YX,
Zhang Q, Yang FQ, Wu P, Yu JK and Zheng S: Detection and
identification of specific serum biomarkers in papillary thyroid
cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 31:265–268. 2009.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|