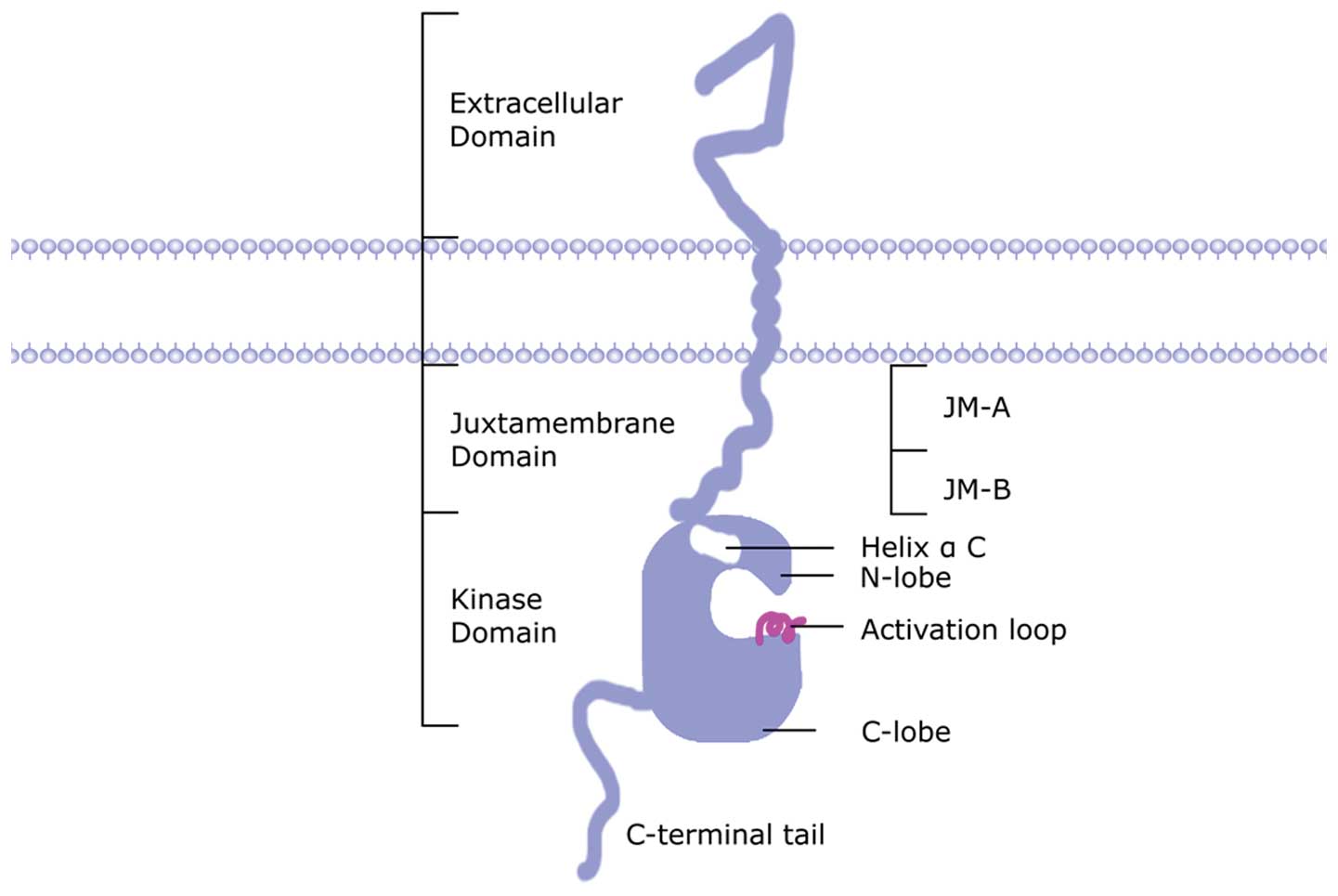
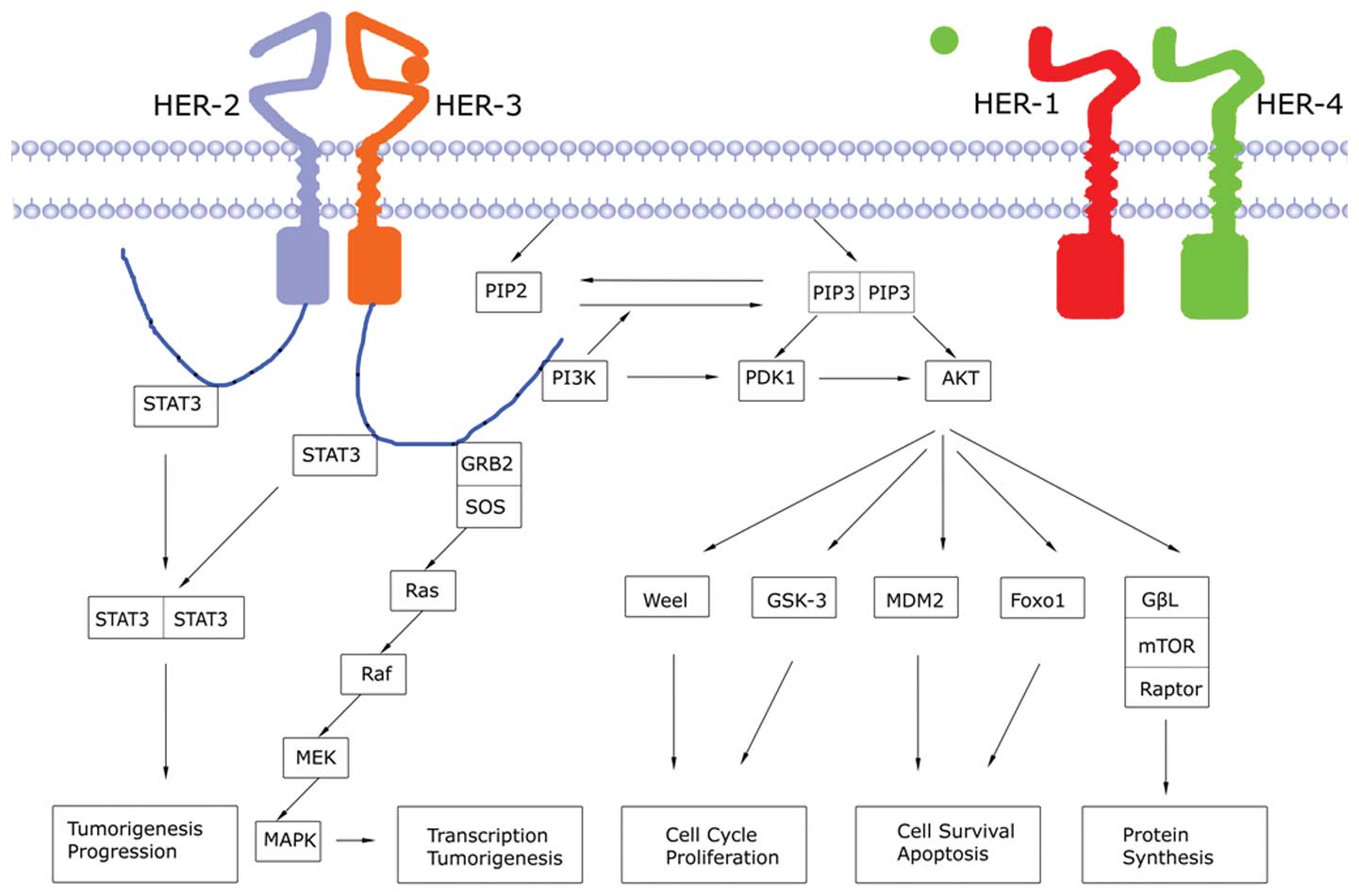
|
1
|
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA and Hynes
NE: The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in
development and cancer. EMBO J. 19:3159–3167. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schlessinger J: Cell signaling by receptor
tyrosine kinases. Cell. 103:211–225. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marmor MD, Skaria KB and Yarden Y: Signal
transduction and oncogenesis by ErbB/HER receptors. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 58:903–913. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shepard HM, Brdlik CM and Schreiber H:
Signal integration: a framework for understanding the efficacy of
therapeutics targeting the human EGFR family. J Clin Invest.
118:3574–3581. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kraus MH, Issing W, Miki T, Popescu NC and
Aaronson SA: Isolation and characterization of ERBB3, a third
member of the ERBB/epidermal growth factor receptor family:
evidence for overexpression in a subset of human mammary tumors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:9193–9197. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Plowman GD, Whitney GS, Neubauer MG, et
al: Molecular cloning and expression of an additional epidermal
growth factor receptor-related gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
87:4905–4909. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick JS, et al:
Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant
expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma
cells. Nature. 309:418–425. 1984. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coussens L, Yang-Feng TL, Liao YC, et al:
Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor
shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science.
230:1132–1139. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cho HS and Leahy DJ: Structure of the
extracellular region of HER3 reveals an interdomain tether.
Science. 297:1330–1333. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen WS, Lazar CS, Lund KA, et al:
Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor
from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and
calcium regulation. Cell. 59:33–43. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yoo J, Wang X, Rishi A, et al: Interaction
of the PA2G4 (EBP1) protein with ErbB-3 and regulation of this
binding by heregulin. Br J Cancer. 82:683–690. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jura N, Shan Y, Cao X, Shaw DE and Kuriyan
J: Structural analysis of the catalytically inactive kinase domain
of the human EGF receptor 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:21608–21613. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Red Brewer M, Choi SH, Alvarado D, et al:
The juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor functions as an
activation domain. Mol Cell. 34:641–651. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jones RB, Gordus A, Krall JA and MacBeath
G: A quantitative protein interaction network for the ErbB
receptors using protein microarrays. Nature. 439:168–174. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sierke SL, Cheng K, Kim HH and Koland JG:
Biochemical characterization of the protein tyrosine kinase
homology domain of the ErbB3 (HER3) receptor protein. Biochem J.
322:757–763. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prigent SA and Gullick WJ: Identification
of c-erbB-3 binding sites for phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and
SHC using an EGF receptor/c-erbB-3 chimera. EMBO J. 13:2831–2841.
1994.
|
|
18
|
Citri A, Skaria KB and Yarden Y: The deaf
and the dumb: the biology of ErbB-2 and ErbB-3. Exp Cell Res.
284:54–65. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T
and Sudarsanam S: The protein kinase complement of the human
genome. Science. 298:1912–1934. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kornev AP and Taylor SS: Pseudokinases:
functional insights gleaned from structure. Structure. 17:5–7.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi F, Telesco SE, Liu Y, Radhakrishnan R
and Lemmon MA: ErbB3/HER3 intracellular domain is competent to bind
ATP and catalyze autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:7692–7697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dawson JP, Berger MB, Lin CC, Schlessinger
J, Lemmon MA and Ferguson KM: Epidermal growth factor receptor
dimerization and activation require ligand-induced conformational
changes in the dimer interface. Mol Cell Biol. 25:7734–7742. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Carrasco-García E, Saceda M, Grasso S, et
al: Small tyrosine kinase inhibitors interrupt EGFR signaling by
interacting with erbB3 and erbB4 in glioblastoma cell lines. Exp
Cell Res. 317:1476–1489. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baselga J and Swain SM: Novel anticancer
targets: revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:463–475. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Opresko L, Shankaran H, Chrisler
WB, Wiley HS and Resat H: HER/ErbB receptor interactions and
signaling patterns in human mammary epithelial cells. BMC Cell
Biol. 10:782009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee D, Yu M, Lee E, et al: Tumor-specific
apoptosis caused by deletion of the ERBB3 pseudo-kinase in mouse
intestinal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 119:2702–2713. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller TW, Pérez-Torres M, Narasanna A, et
al: Loss of Phosphatase and Tensin homologue deleted on chromosome
10 engages ErbB3 and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor
signaling to promote antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 69:4192–4201. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lowenstein EJ, Daly RJ, Batzer AG, et al:
The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor
tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 70:431–442. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Batzer AG, Rotin D, Ureña JM, Skolnik EY
and Schlessinger J: Hierarchy of binding sites for Grb2 and Shc on
the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 14:5192–5201.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hallberg B, Rayter SI and Downward J:
Interaction of Ras and Raf in intact mammalian cells upon
extracellular stimulation. J Biol Chem. 269:3913–3916.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liebmann C: Regulation of MAP kinase
activity by peptide receptor signalling pathway: paradigms of
multiplicity. Cell Signal. 13:777–785. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, et
al: Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and
physiological functions. Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gridelli C, De Marinis F, Di Maio M,
Cortinovis D, Cappuzzo F and Mok T: Gefitinib as first-line
treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
with activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor mutation:
implications for clinical practice and open issues. Lung Cancer.
72:3–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tejani MA, Cohen RB and Mehra R: The
contribution of cetuximab in the treatment of recurrent and/or
metastatic head and neck cancer. Biologics. 4:173–185.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Boige V, et al:
KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in
patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J
Clin Oncol. 26:374–379. 2008.
|
|
37
|
Pirker R, Pereira JR, Szczesna A, et al:
Cetuximab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (FLEX): an open-label randomised phase
III trial. Lancet. 373:1525–1531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, et al:
Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for
metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med.
344:783–792. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et
al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ji XD, Li G, Feng YX, et al: EphB3 is
overexpressed in non-small-cell lung cancer and promotes tumor
metastasis by enhancing cell survival and migration. Cancer Res.
71:1156–1166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Holbro T, Beerli RR, Maurer F, Koziczak M,
Barbas CF III and Hynes NE: The ErbB2/ErbB3 heterodimer functions
as an oncogenic unit: ErbB2 requires ErbB3 to drive breast tumor
cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8933–8938. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Smirnova T, Zhou ZN, Flinn RJ, et al:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling is critical for ErbB3-driven
breast cancer cell motility and metastasis. Oncogene. 31:706–715.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, et al:
Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the
kinase-inactive HER3. Nature. 445:437–441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Erjala K, Sundvall M, Junttila TT, et al:
Signaling via ErbB2 and ErbB3 associates with resistance and
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification with
sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4103–4111. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y, Linn D, Liu Z, et al: EBP1, an
ErbB3-binding protein, is decreased in prostate cancer and
implicated in hormone resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3176–3186.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Desbois-Mouthon C, Baron A, Blivet-Van
Eggelpoël MJ, et al: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
inhibition induces a resistance mechanism via the epidermal growth
factor receptor/HER3/AKT signaling pathway: rational basis for
cotargeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and epidermal
growth factor receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:5445–5456. 2009.
|
|
47
|
Frogne T, Benjaminsen RV, Sonne-Hansen K,
et al: Activation of ErbB3, EGFR and Erk is essential for growth of
human breast cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to
fulvestrant. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 114:263–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et
al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung
cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Grøvdal LM, Kim J, Holst MR, Knudsen SLJ,
Grandal MV and van Deurs B: EGF receptor inhibitors increase ErbB3
mRNA and protein levels in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal.
24:296–301. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
McDonagh CF, Huhalov A, Harms BD, et al:
Antitumor activity of a novel bispecific antibody that targets the
ErbB2/ErbB3 oncogenic unit and inhibits heregulin-induced
activation of ErbB3. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:582–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sithanandam G, Fornwald LW, Fields JR,
Morris NL and Anderson LM: Anti-tumor efficacy of naked siRNAs for
ERBB3 or AKT2 against lung adenocarcinoma cell xenografts. Int J
Cancer. 130:251–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Engelman JA, Jänne PA, Mermel C, et al:
ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in
gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:3788–3793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ogino A, Kitao H, Hirano S, et al:
Emergence of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation during
chronic exposure to gefitinib in a non-small cell lung cancer cell
line. Cancer Res. 67:7807–7814. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers
acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kwak E: The role of irreversible HER
family inhibition in the treatment of patients with non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncologist. 16:1498–1507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ling B, Wang GX, Long G, Qiu JH and Hu ZL:
Tumor suppressor miR-22 suppresses lung cancer cell progression
through post-transcriptional regulation of ErbB3. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 138:1355–1361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kawano O, Sasaki H, Endo K, et al: ErbB3
mRNA expression correlated with specific clinicopathologic features
of Japanese lung cancers. J Surg Res. 146:43–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Vaught DB, Stanford JC, Young C, et al:
HER3 is required for HER2-induced preneoplastic changes to the
breast epithelium and tumor formation. Cancer Res. 72:2672–2682.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee-Hoeflich ST, Crocker L, Yao E, et al:
A central role for HER3 in HER2-amplified breast cancer:
implications for targeted therapy. Cancer Res. 68:5878–5887. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Agus DB, Akita RW, Fox WD, et al:
Targeting ligand-activated ErbB2 signaling inhibits breast and
prostate tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 2:127–137. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Göstring L, Malm M, Höidén-Guthenberg I,
et al: Cellular effects of HER3-specific affibody molecules. PLoS
One. 7:e400232012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Weiner DB, Kokai Y, Wada T, Cohen JA,
Williams WV and Greene MI: Linkage of tyrosine kinase activity with
transforming ability of the p185neu oncoprotein. Oncogene.
4:1175–1183. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R:
Transphosphorylation of kinase-dead HER3 and breast cancer
progression: a new standpoint or an old concept revisited? Breast
Cancer Res. 9:1112007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yao E, Zhou W, Lee-Hoeflich ST, et al:
Suppression of HER2/HER3-mediated growth of breast cancer cells
with combinations of GDC-0941 PI3K inhibitor, trastuzumab, and
pertuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4147–4156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Junttila TT, Akita RW, Parsons K, et al:
Ligand-independent HER2/HER3/PI3K complex is disrupted by
trastuzumab and is effectively inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor
GDC-0941. Cancer Cell. 15:429–440. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chakrabarty A, Sánchez V, Kuba MG,
Rinehart C and Arteaga CL: Feedback upregulation of HER3 (ErbB3)
expression and activity attenuates antitumor effect of PI3K
inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2718–2723. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kim JH, Im KS, Kim NH, Yhee JY, Nho WG and
Sur JH: Expression of HER-2 and nuclear localization of HER-3
protein in canine mammary tumors: histopathological and
immunohistochemical study. Vet J. 189:318–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chiu CG, Masoudi H, Leung S, et al: HER-3
overexpression is prognostic of reduced breast cancer survival: a
study of 4046 patients. Ann Surg. 251:1107–1116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Giltnane JM, Moeder CB, Camp RL and Rimm
DL: Quantitative multiplexed analysis of ErbB family coexpression
for primary breast cancer prognosis in a large retrospective
cohort. Cancer. 115:2400–2409. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Haas S, Gevensleben H, Rabstein S, et al:
Expression of heregulin, phosphorylated HER-2, HER-3 and HER-4 in
HER-2 negative breast cancers. Oncol Rep. 21:299–304.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gori S, Foglietta J, Mameli MG, et al:
HER-3 status by immunohistochemistry in HER-2-positive metastatic
breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab: correlation with
clinical outcome. Tumori. 98:39–44. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yoshioka T, Nishikawa Y, Ito R, et al:
Significance of integrin αvβ5 and erbB3 in enhanced cell migration
and liver metastasis of colon carcinomas stimulated by
hepatocyte-derived heregulin. Cancer Sci. 101:2011–2018. 2010.
|
|
74
|
Scartozzi M, Mandolesi A, Giampieri R, et
al: The role of HER-3 expression in the prediction of clinical
outcome for advanced colorectal cancer patients receiving
irinotecan and cetuximab. Oncologist. 16:53–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang XL, Yang YS, Xu DP, et al:
Comparative study on overexpression of HER2/neu and HER3 in gastric
cancer. World J Surg. 33:2112–2118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhu S, Belkhiri A and El-Rifai W: DARPP-32
increases interactions between epidermal growth factor receptor and
ERBB3 to promote tumor resistance to gefitinib. Gastroenterology.
141:1738–1748. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Moelans CB, van Diest PJ, Milne AN and
Offerhaus GJ: Her-2/neu testing and therapy in gastroesophageal
adenocarcinoma. Patholog Res Int. 2011:6741822010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
te Velde EA, Franke AC, van Hillegersberg
R, et al: HER-family gene amplification and expression in resected
pancreatic cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:1098–1104. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hirakawa T, Nakata B, Amano R, et al: HER3
overexpression as an independent indicator of poor prognosis for
patients with curatively resected pancreatic cancer. Oncology.
81:192–198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Haley JD, Gibson NW,
Cagnoni P and Iwata KK: Inactivation of Akt by the epidermal growth
factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib is mediated by HER-3 in
pancreatic and colorectal tumor cell lines and contributes to
erlotinib sensitivity. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2051–2059. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hsieh SY, He JR, Yu MC, et al: Secreted
ERBB3 isoforms are serum markers for early hepatoma in patients
with chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. J Proteome Res. 10:4715–4724.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Blivet-Van Eggelpoël MJ, Chettouh H,
Fartoux L, et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor and HER-3
restrict cell response to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. J Hepatol. 57:108–115. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sheng Q, Liu X, Fleming E, et al: An
activated ErbB3/NRG1 autocrine loop supports in vivo proliferation
in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 17:298–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tanner B, Hasenclever D, Stern K, et al:
ErbB-3 predicts survival in ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol.
24:4317–4323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Leng J, Lang J, Shen K and Guo L:
Overexpression of p53, EGFR, c-erbB2 and c-erbB3 in endometrioid
carcinoma of the ovary. Chin Med Sci J. 12:67–70. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Soler M, Mancini F, Meca-Cortes O, et al:
HER3 is required for the maintenance of neuregulin-dependent and
-independent attributes of malignant progression in prostate cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 125:2565–2575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Buac K, Xu M, Cronin J, Weeraratna AT,
Hewitt SM and Pavan WJ: NRG1/ERBB3 signaling in melanocyte
development and melanoma: inhibition of differentiation and
promotion of proliferation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 22:773–784.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ueno Y, Sakurai H, Tsunoda S, et al:
Heregulin-induced activation of ErbB3 by EGFR tyrosine kinase
activity promotes tumor growth and metastasis in melanoma cells.
Int J Cancer. 123:340–347. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Belleudi F, Marra E, Mazzetta F, et al:
Monoclonal antibody-induced ErbB3 receptor internalization and
degradation inhibits growth and migration of human melanoma cells.
Cell Cycle. 11:1455–1467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Djerf Severinsson EA, Trinks C, Gréen H,
et al: The pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib
promotes apoptosis of malignant melanoma in vitro and displays
antitumor activity in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
414:563–568. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|