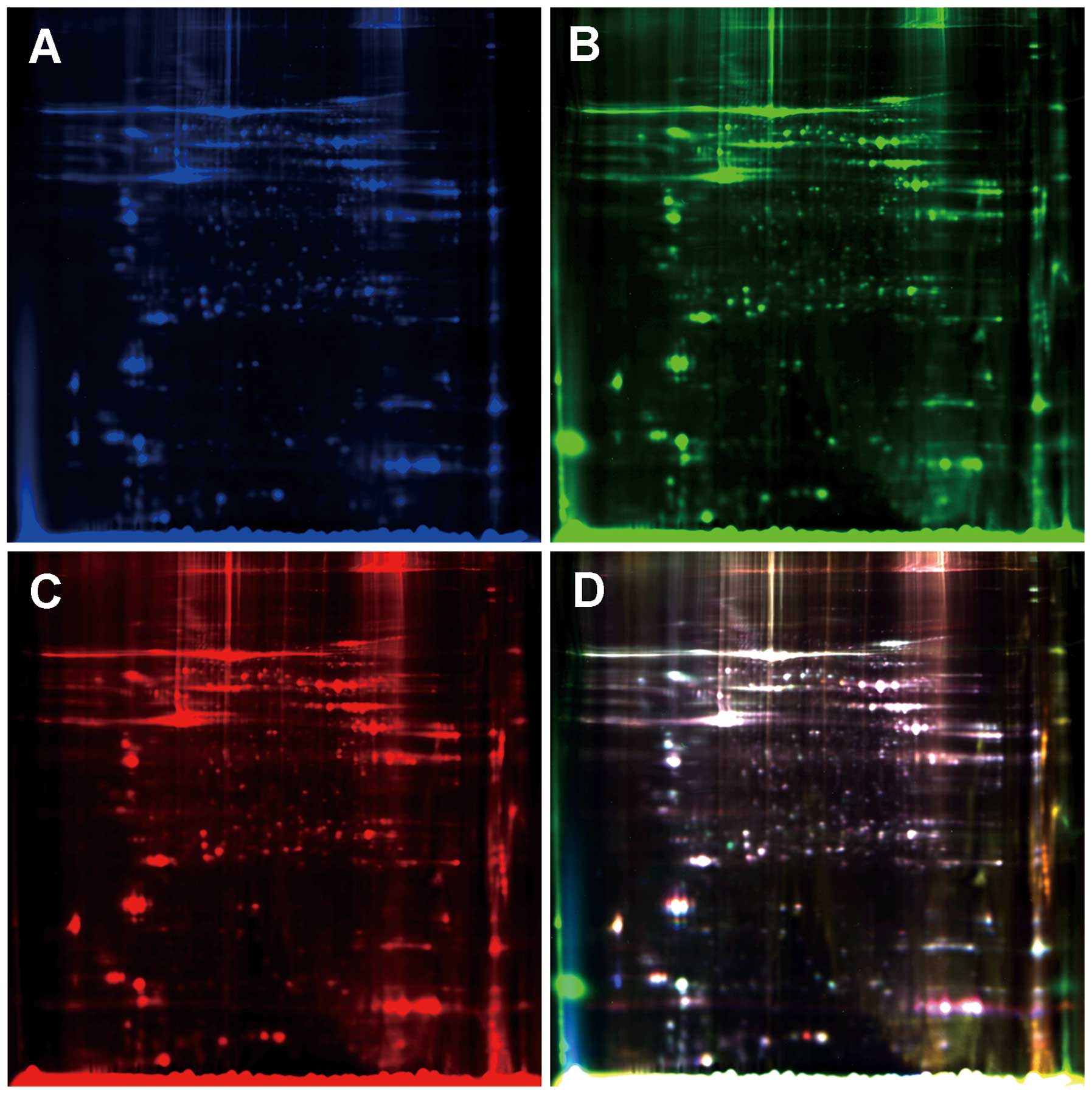
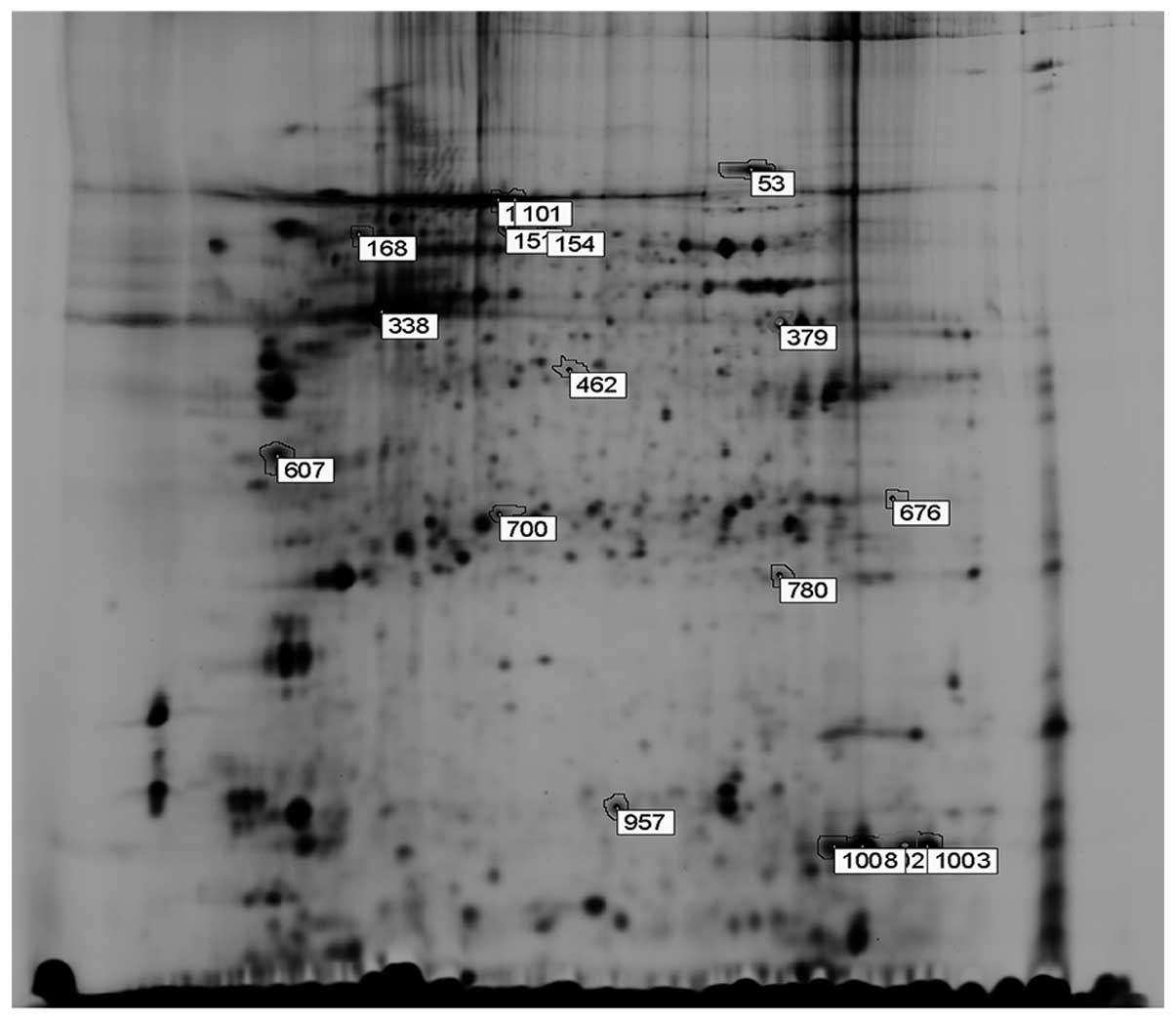
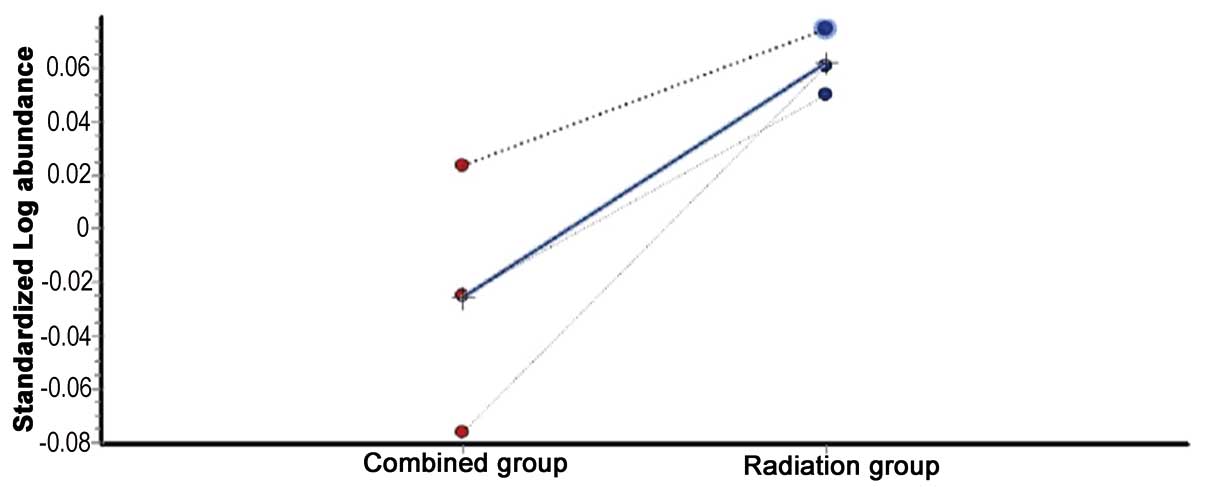
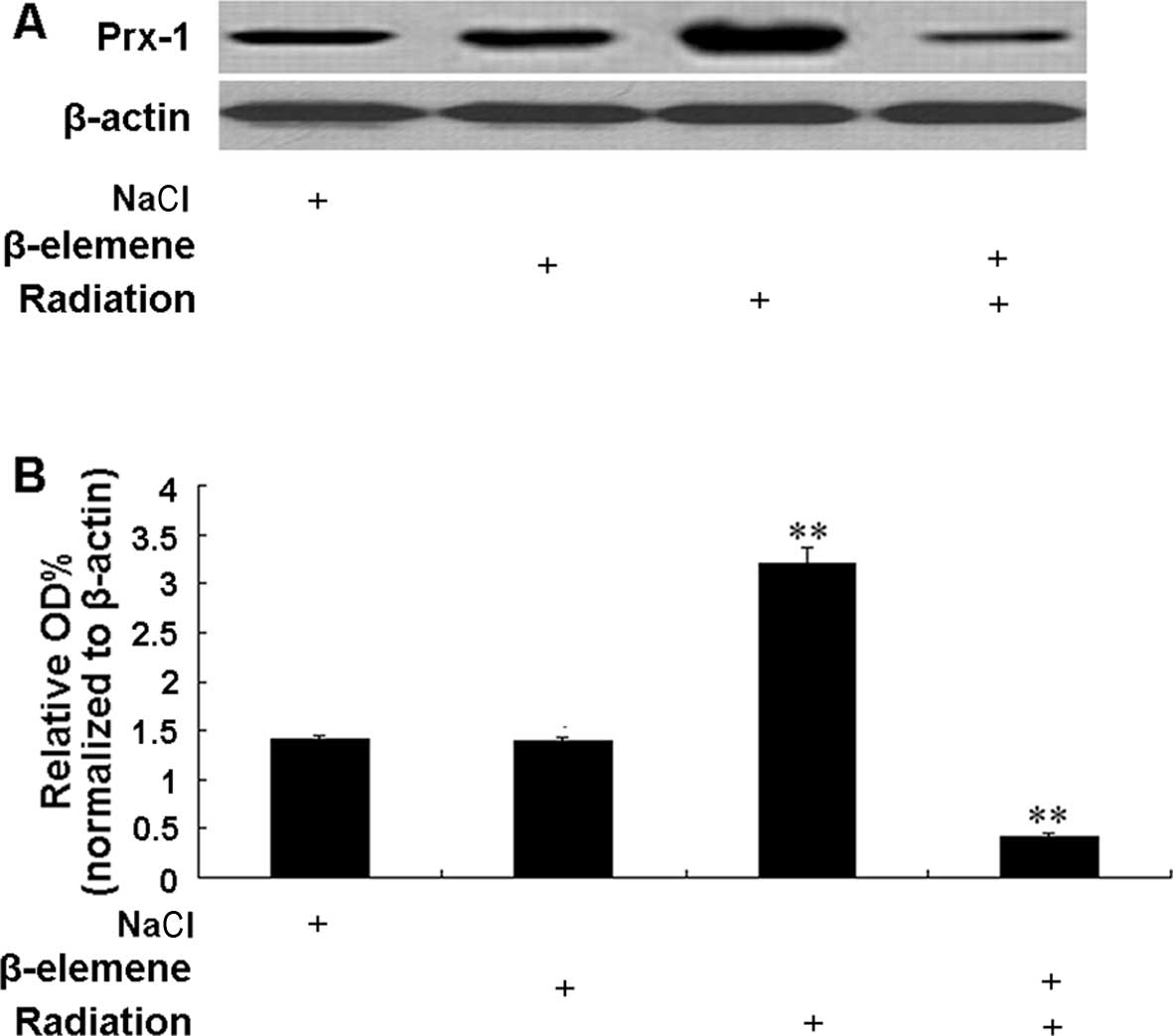
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang H, Ma S and Feng J: In vitro study
of radiosensitization by β-Elemene in A549 cell line from
adenocarcinoma of lung. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol. 8:12–15. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cheng W, Qiao Z, Shi T, Huang C and Wang
Y: In vitro study on increase in radio sensitivity of renal cell
carcinoma induced by β-Elemene. J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ: Med Sci
(Chinese). 25:182–185. 2004.
|
|
4
|
Wu D, Li X, Zhao J, Wang H and Zhao D: A
study of radio-sensitivity of β-elemene to squamous cell carcinoma
of tongue Tca-8113 cell line in vitro. Zhong Liu Ji Chu Yu Lin
Chuang. 19:116–117. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
She J, Wang Z, Che X and Pan C:
Radiosensitization of β-elemene on VX2 carcinoma transplanted on
kidney in rabbits in vivo. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 4:392–396.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu DP, Jiang RB and Zhao DQ: Effects of
β-elemene on radiosensitivity, cell cycle, apoptosis, Bcl2 and Bax
expression of Tca8113 cells in vitro. Zheng Zou Da Xue Xue Bao.
44:414–417. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
She J, Wang Z and Che X: Expressions of
caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in radiosensitization of β-elemene on rabbit
VX2 renal carcinoma. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 27:2285–2287.
2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Li LJ, Zhong LF, Jiang LP, Geng CY and Zou
LJ: β-Elemene radiosensitizes lung cancer A549 cells by enhancing
DNA damage and inhibiting DNA repair. Phytother Res. 25:1095–1097.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li G, Xie B, Li X, et al: Down-regulation
of survivin and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by β-elemene enhances
the radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma xenograft. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 27:56–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang T, Diaz AJ and Yen Y: The role of
peroxiredoxin II in chemoresistance of breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer. 6:73–80. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matés JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ and Márquez
J: Intracellular redox status and oxidative stress: implications
for cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis. Arch
Toxicol. 82:273–299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Woo HA, Yim SH, Shin DH, Kang D, Yu DY and
Rhee SG: Inactivation of peroxiredoxin I by phosphorylation allows
localized H2O2 accumulation for cell
signaling. Cell. 140:517–528. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Herbert BR, Harry JL, Packer NH, Gooley
AA, Pedersen SK and Williams KL: What place for polyacrylamide in
proteomics? Trends Biotechnol. 19(Suppl 10): S3–S9. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tonge R, Shaw J, Middleton B, et al:
Validation and development of fluorescence two-dimensional
differential gel electrophoresis proteomics technology. Proteomics.
1:377–396. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gharbi S, Gaffney P, Yang A, et al:
Evaluation of two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis for
proteomic expression analysis of a model breast cancer cell system.
Molecular Cell Proteomics. 1:91–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yan JX, Devenish AT, Wait R, Stone T,
Lewis S and Fowler S: Fluorescence two-dimensional difference gel
electrophoresis and mass spectrometry based proteomic analysis of
Escherichia coli. Proteomics. 2:1682–1698. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang JW, Jeon HB, Lee JH, et al:
Augmented expression of peroxiredoxin I in lung cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 289:507–512. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim HJ, Chae HZ, Kim YJ, et al:
Preferential elevation of Prx I and Trx expression in lung cancer
cells following hypoxia and in human lung cancer tissues. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 19:285–298. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lehtonen ST, Svensk AM, Soini Y, et al:
Peroxiredoxins, a novel protein family in lung cancer. Int J
Cancer. 111:514–521. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alfonso P, Catalá M, Rico-Morales ML, et
al: Proteomic analysis of lung biopsies: differential protein
expression profile between peritumoral and tumoral tissue.
Proteomics. 4:442–447. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park JH, Kim YS, Lee HL, et al: Expression
of peroxiredoxin and thioredoxin in human lung cancer and paired
normal lung. Respirology. 11:269–275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim JH, Bogner PN, Ramnath N, Park Y, Yu J
and Park YM: Elevated peroxiredoxin 1, but not NF-E2-related factor
2, is an independent prognostic factor for disease recurrence and
reduced survival in stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:3875–3882. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim JH, Bogner PN, Baek SH, et al:
Up-regulation of peroxiredoxin 1 in lung cancer and its implication
as a prognostic and therapeutic target. Clin Cancer Res.
14:2326–2333. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rostila A, Puustinen A, Toljamo T, et al:
Peroxiredoxins and tropomyosins as plasma biomarkers for lung
cancer and asbestos exposure. Lung Cancer. 77:450–459. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen WC, McBride WH, Iwamoto KS, et al:
Induction of radio-protective peroxiredoxin-I by ionizing
irradiation. J Neurosci Res. 70:794–798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang B, Su Y, Ai G, Wang Y, Wang T and
Wang F: Involvement of peroxiredoxin I in protecting cells from
radiation-induced death. J Radiat Res. 46:305–312. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen MF, Keng PC, Shau H, et al:
Inhibition of lung tumor growth and augmentation of
radiosensitivity by decreasing peroxiredoxin I expression. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 64:581–591. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang B, Wang Y, Liu K, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against peroxiredoxin I
enhances the radiosensitivity of human intestinal cancer. Biochem
Pharmacol. 75:660–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gao MC, Jia XD, Wu QF, Cheng Y, Chen FR
and Zhang J: Silencing Prx1 and/or Prx5 sensitizes human esophageal
cancer cells to ionizing radiation and increases apoptosis via
intracellular ROS accumulation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:528–536.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dittmann LM, Danner A, Gronych J, et al:
Downregulation of PRDX1 by promoter hypermethylation is frequent in
1p/19q-deleted oligodendroglial tumours and increases radio- and
chemosensitivity of Hs683 glioma cells in vitro. Oncogene.
31:3409–3418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Guo Q, Huang X, Zhang J, Luo Y, Peng Z and
Li S: Down-regulation of peroxiredoxin I by a novel fully human
phage display recombinant antibody induces apoptosis and enhances
radiation sensitization in A549 lung carcinoma cells. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 27:307–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Milas L, Fujii T, Hunter N, et al:
Enhancement of tumor radioresponse in vivo by gemcitabine. Cancer
Res. 59:107–114. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li LJ, Zhong LF, Jiang LP, et al:
Lysosomal membrane permea-bilization contributes to elemene
emulsion-induced apoptosis in A549 cells. Free Radic Res.
45:1232–1240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|