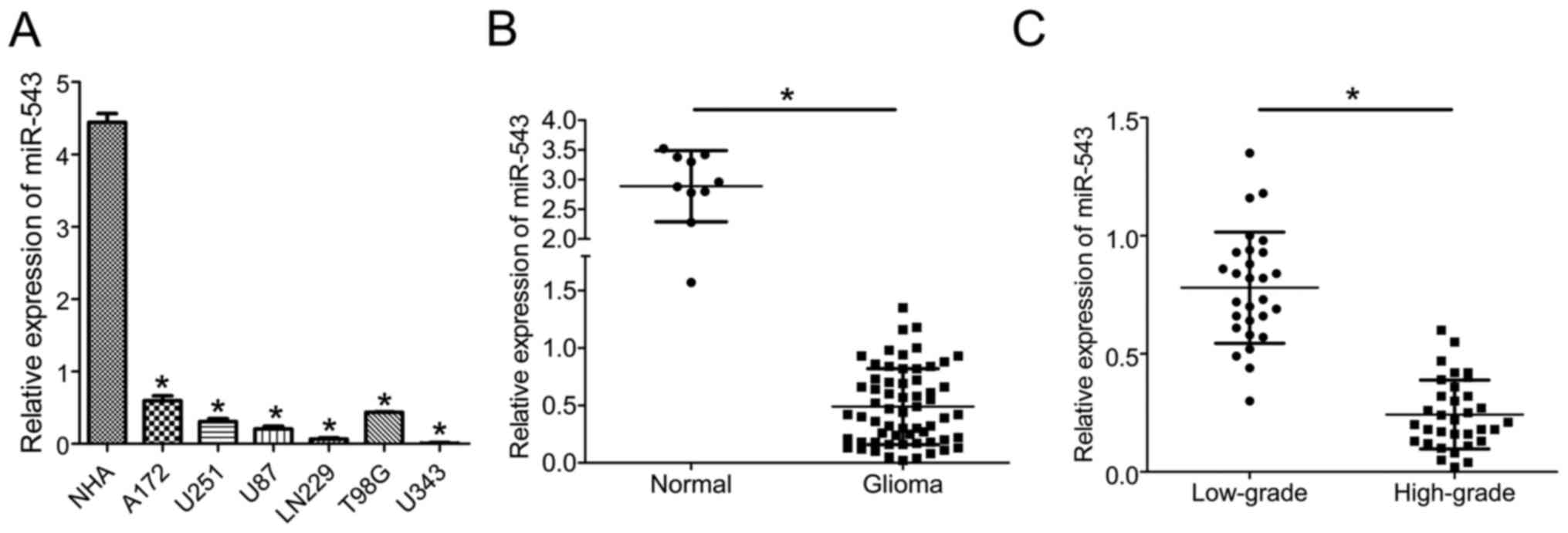
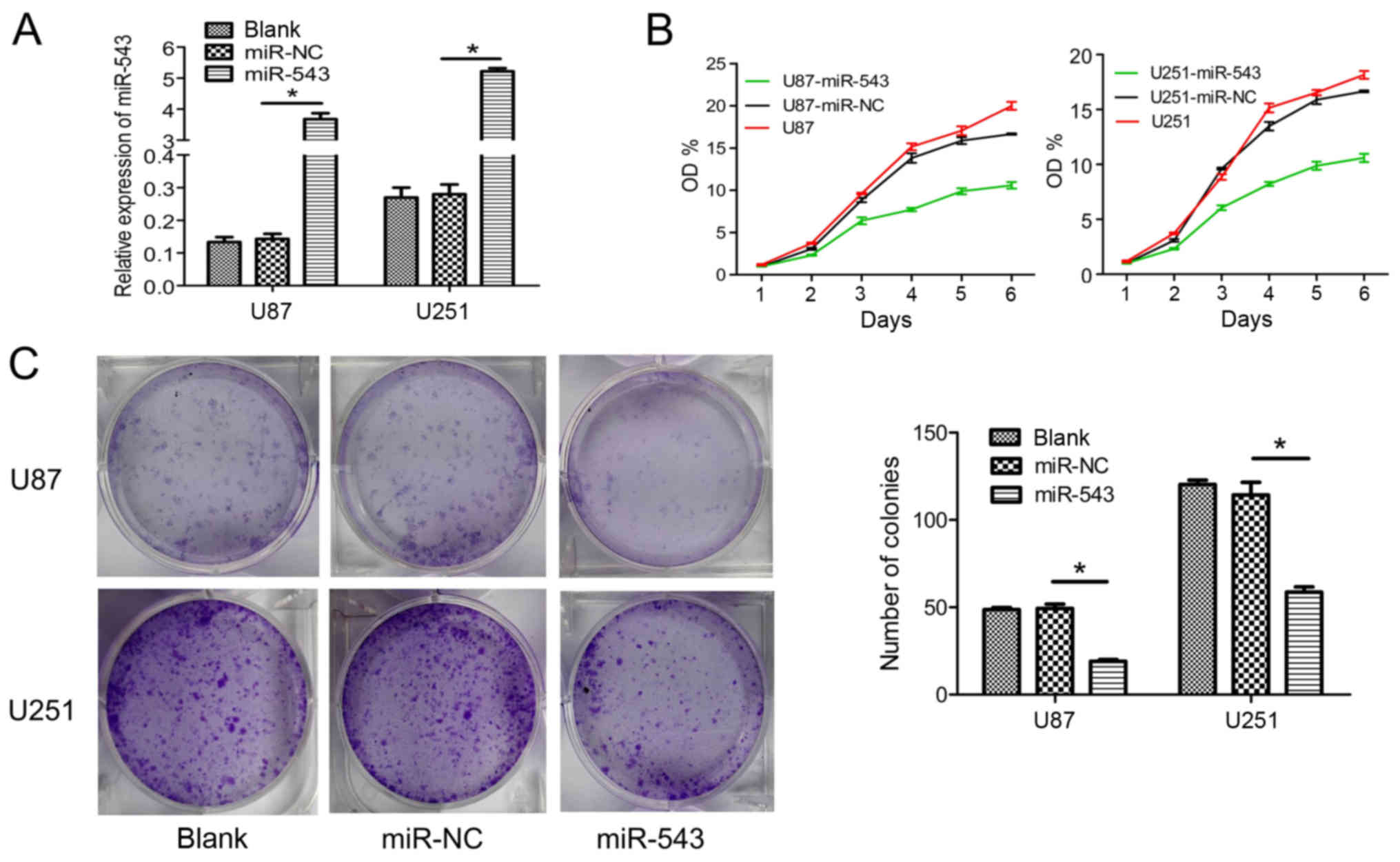
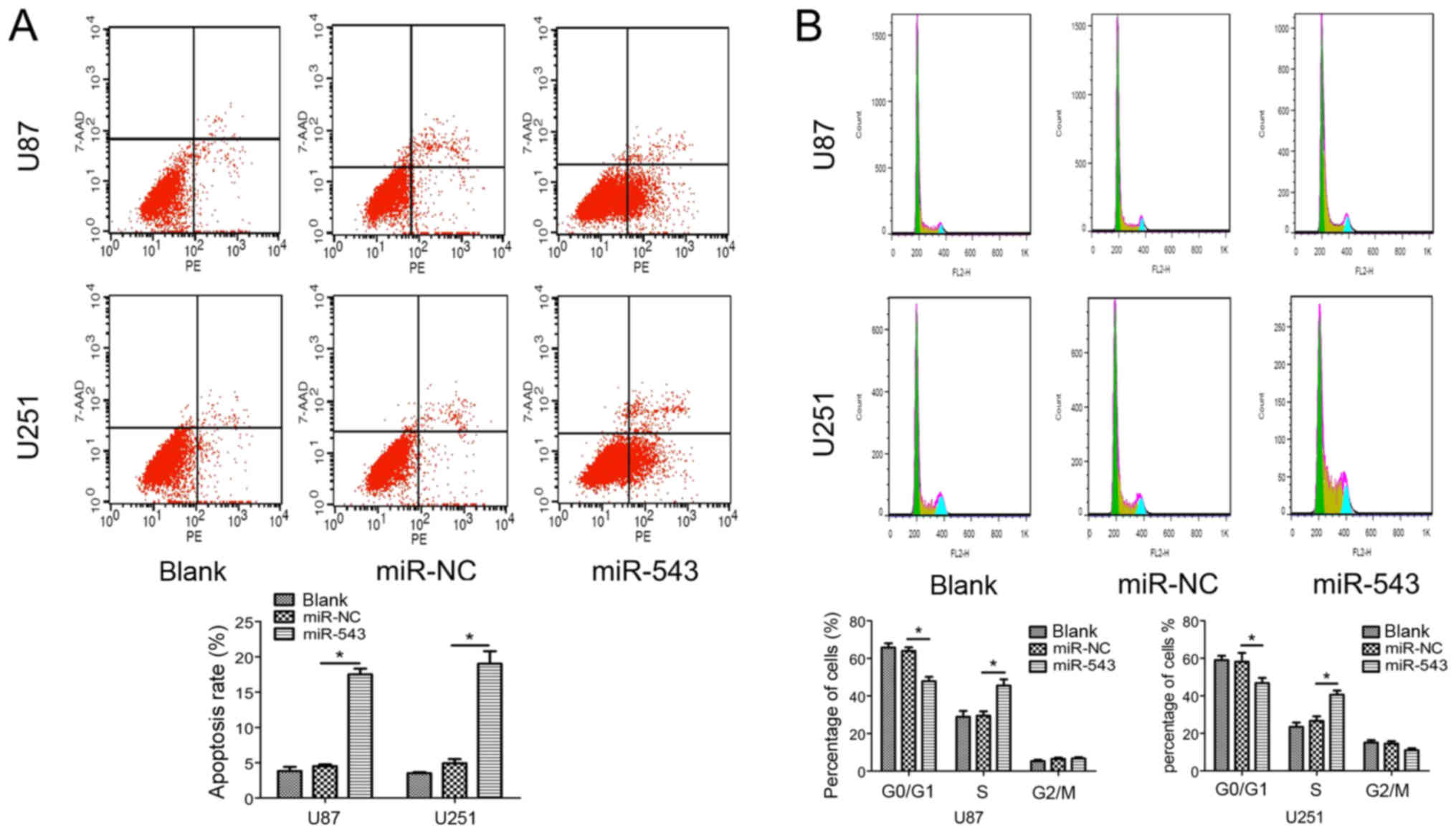
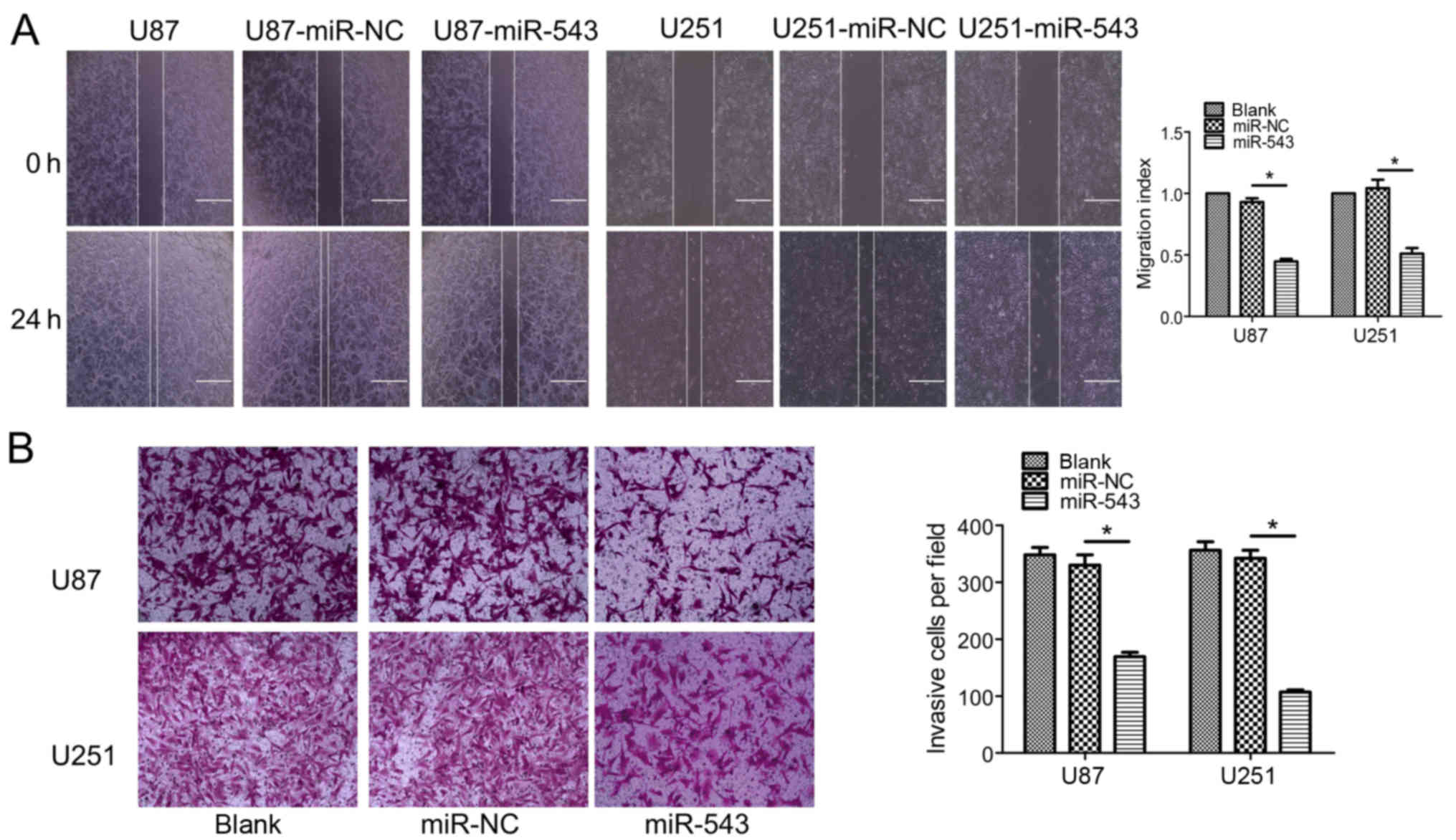
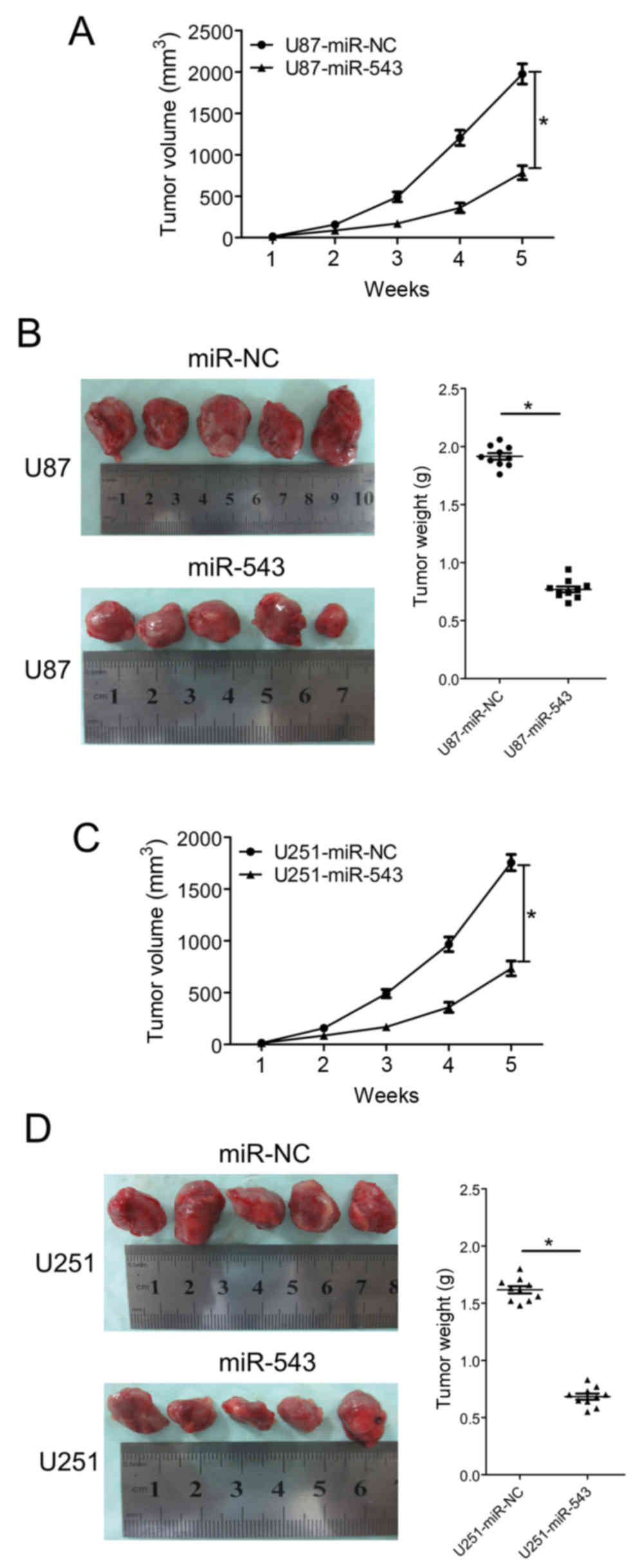
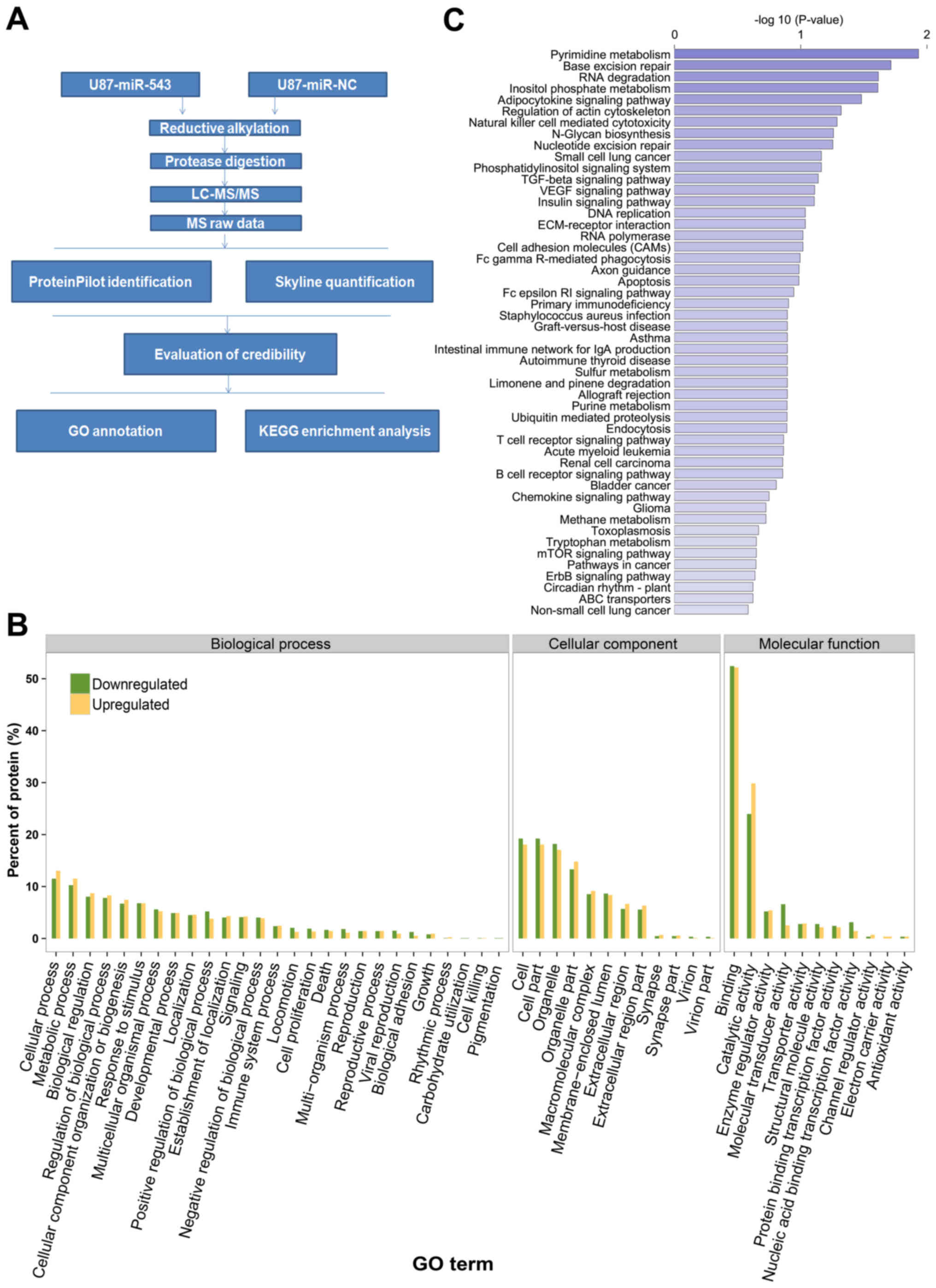
|
1
|
Ohgaki H: Epidemiology of brain tumors.
Methods Mol Biol. 472:323–342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huse JT, Holland E and DeAngelis LM:
Glioblastoma: Molecular analysis and clinical implications. Annu
Rev Med. 64:59–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Orang Valinezhad A, Safaralizadeh R and
Kazemzadeh-Bavili M: Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene regulation
from common downregulation to mRNA-specific upregulation. Int J
Genomics. 2014:9706072014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei Y, Schober A and Weber C: Pathogenic
arterial remodeling: The good and bad of microRNAs. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H1050–H1059. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang S, Hao J, Xie F, Hu X, Liu C, Tong
J, Zhou J, Wu J and Shao C: Downregulation of miR-132 by promoter
methylation contributes to pancreatic cancer development.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1183–1189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Zhou X and Wei M: MicroRNA-144
suppresses osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by targeting ROCK1
and ROCK2. Oncotarget. 6:10297–10308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weiner-Gorzel K, Dempsey E, Milewska M,
McGoldrick A, Toh V, Walsh A, Lindsay S, Gubbins L, Cannon A,
Sharpe D, et al: Overexpression of the microRNA miR-433 promotes
resistance to paclitaxel through the induction of cellular
senescence in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Med. 4:745–758. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu Y, Zhao H, Feng L and Xu S:
MicroRNA-217 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting
Runx2 in human glioma. Am J Transl Res. 8:1482–1491.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng Z, Wang HZ, Li X, Wu Z, Han Y, Li Y,
Chen G, Xie X, Huang Y, Du Z, et al: MicroRNA-184 inhibits cell
proliferation and invasion, and specifically targets TNFAIP2 in
Glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang H, Lu Y, Luo L, Li W, Liang C, He H
and Ba Y: MicroRNA-195 inhibits the proliferation of human glioma
cells by directly targeting cyclin D1 and cyclin E1. PLoS One.
8:e549322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Haga CL and Phinney DG: MicroRNAs in the
imprinted DLK1-DIO3 region repress the epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by targeting the TWIST1 protein signaling network. J
Biol Chem. 287:42695–42707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu L, Zhou L, Cheng Y, Sun L, Fan J, Liang
J, Guo M, Liu N and Zhu L: MicroRNA-543 acts as an oncogene by
targeting PAQR3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res.
4:897–906. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan C, Lin Y, Mao Y, Huang Z, Liu AY, Ma
H, Yu D, Maitikabili A, Xiao H, Zhang C, et al: MicroRNA-543
suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by targeting
KRAS, MTA1 and HMGA2. Oncotarget. 7:21825–21839. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shilov IV, Seymour SL, Patel AA, Loboda A,
Tang WH, Keating SP, Hunter CL, Nuwaysir LM and Schaeffer DA: The
Paragon Algorithm, a next generation search engine that uses
sequence temperature values and feature probabilities to identify
peptides from tandem mass spectra. Mol Cell Proteomics.
6:1638–1655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Conesa A and Götz S: Blast2GO: A
comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int
J Plant Genomics. 2008:6198322008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu WG, Shang YL, Cong XR, Bian X and Yuan
Z: MicroRNA-135b promotes proliferation, invasion and migration of
osteosarcoma cells by degrading myocardin. Int J Oncol.
45:2024–2032. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu SH, Zhang CL, Dong FS and Zhang YM:
miR-99a suppresses the metastasis of human non-small cell lung
cancer cells by targeting AKT1 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
116:268–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai MM, Wang CS, Tsai CY, Chen CY, Chi
HC, Tseng YH, Chung PJ, Lin YH, Chung IH, Chen CY, et al:
MicroRNA-196a/−196b promote cell metastasis via negative regulation
of radixin in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 351:222–231. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang QQ, Xu H, Huang MB, Ma LM, Huang QJ,
Yao Q, Zhou H and Qu LH: MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role
in human glioblastoma cells by targeting signaling pathways
involved in cellular proliferation and invasion. Neuro Oncol.
14:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao X and Jin W: The emerging role of
tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 in targeting glioblastoma stemness.
Cancer Lett. 353:25–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Che S, Sun T, Wang J, Jiao Y, Wang C, Meng
Q, Qi W and Yan Z: miR-30 overexpression promotes glioma stem cells
by regulating Jak/STAT3 signaling pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:6805–6811. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Dong G, Wang B, Gao W and Yang Q:
miR-543 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting
SIRT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:15–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bing L, Hong C, Li-Xin S and Wei G:
MicroRNA-543 suppresses endometrial cancer oncogenicity via
targeting FAK and TWIST1 expression. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
290:533–541. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang W, Luo J, Sheng W, Xue J, Li M, Ji J,
Liu P, Zhang X, Cao J and Zhang S: Proteomic profiling of
radiation-induced skin fibrosis in rats: Targeting the
ubiquitin-proteasome system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
95:751–760. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang S, Wang W, Gu Q, Xue J, Cao H, Tang
Y, Xu X, Cao J, Zhou J, Wu J, et al: Protein and miRNA profiling of
radiation-induced skin injury in rats: The protective role of
peroxiredoxin-6 against ionizing radiation. Free Radic Biol Med.
69:96–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan W and Chen SS: Mass spectrometry-based
quantitative proteomic profiling. Brief Funct Genomics Proteomics.
4:27–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hanash S: Disease proteomics. Nature.
422:226–232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fielding AB, Lim S, Montgomery K, Dobreva
I and Dedhar S: A critical role of integrin-linked kinase, ch-TOG
and TACC3 in centrosome clustering in cancer cells. Oncogene.
30:521–534. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Martens-de Kemp SR, Nagel R, Stigter-van
Walsum M, van der Meulen IH, van Beusechem VW, Braakhuis BJ and
Brakenhoff RH: Functional genetic screens identify genes essential
for tumor cell survival in head and neck and lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1994–2003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Schulz R, Edmunds S, Krüger E,
Markert E, Gaedcke J, Cormet-Boyaka E, Ghadimi M, Beissbarth T,
Levine AJ, et al: MicroRNA-101 suppresses tumor cell proliferation
by acting as an endogenous proteasome inhibitor via targeting the
proteasome assembly factor POMP. Mol Cell. 59:243–257. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sang MM, Du WQ, Zhang RY, Zheng JN and Pei
DS: Suppression of CSN5 promotes the apoptosis of gastric cancer
cells through regulating p53-related apoptotic pathways. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 25:2897–2901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tan J, Yu CY, Wang ZH, Chen HY, Guan J,
Chen YX and Fang JY: Genetic variants in the inositol phosphate
metabolism pathway and risk of different types of cancer. Sci Rep.
5:84732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Wang Z and Gemeinhart RA:
Progress in microRNA delivery. J Control Release. 172:962–974.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|