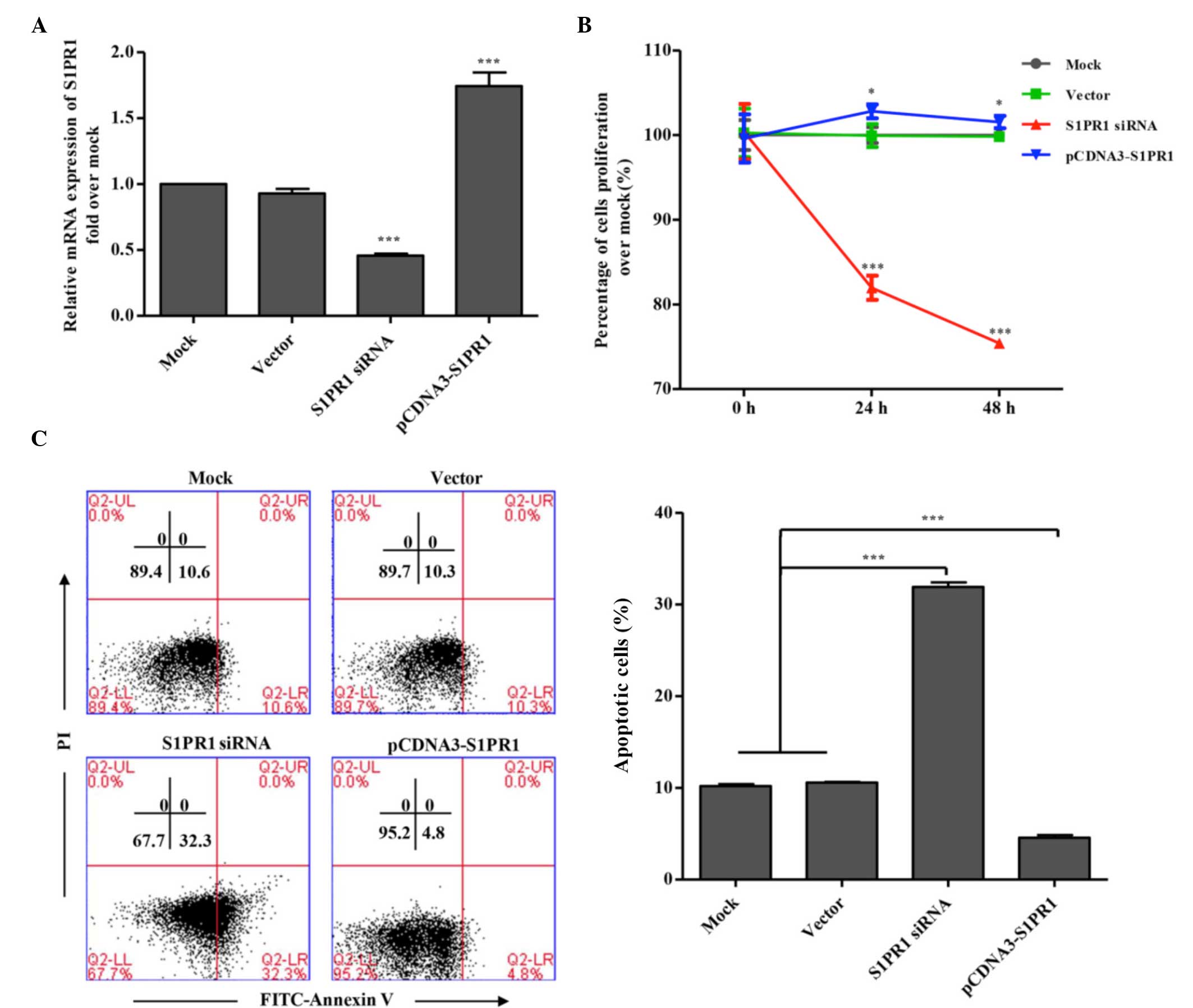
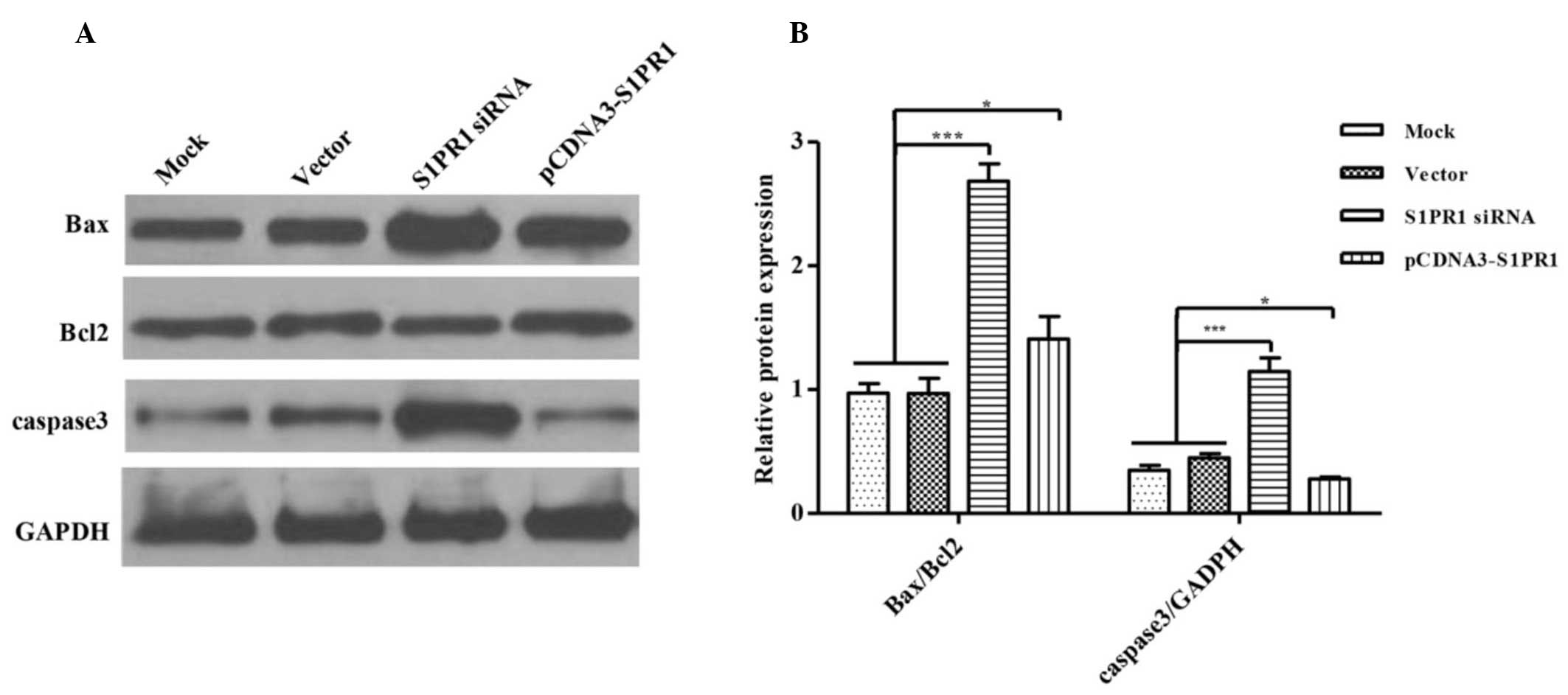
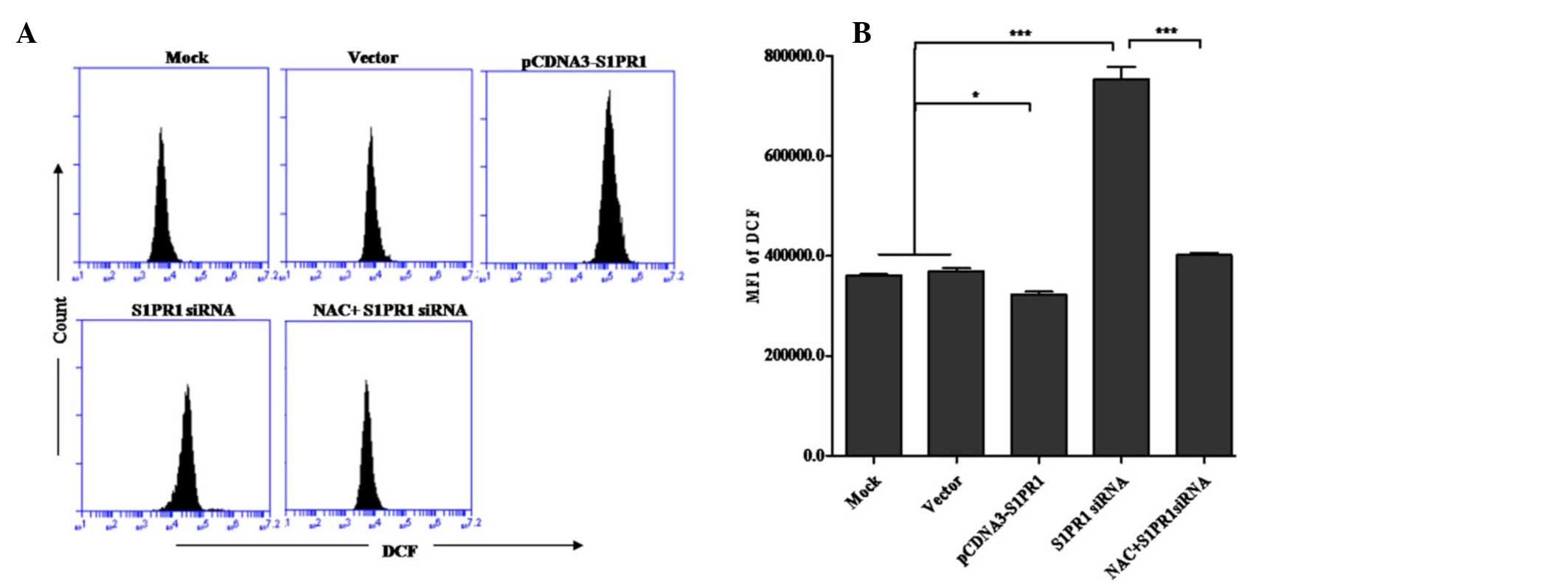
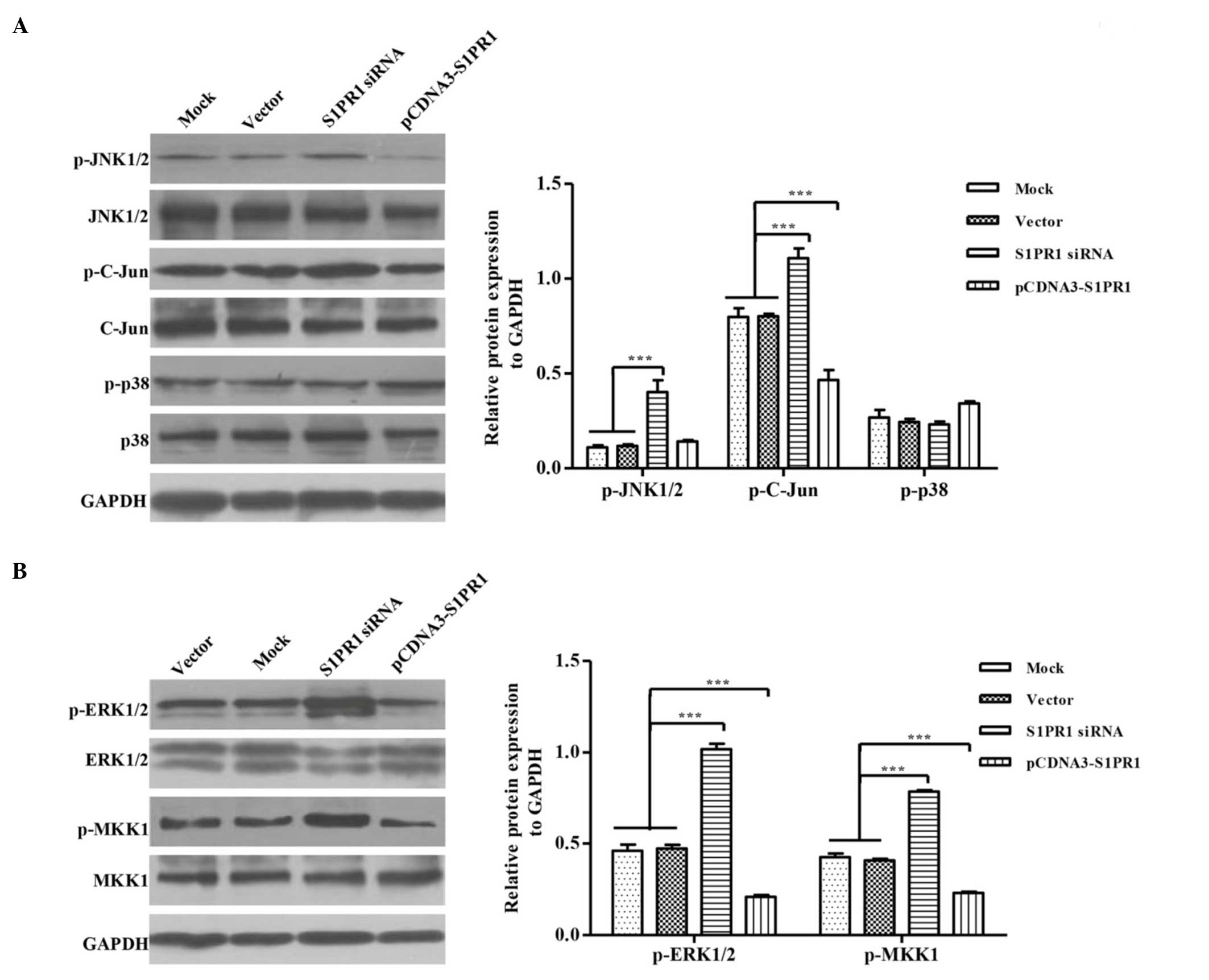
|
1
|
Pyne NJ and Pyne S: Sphingosine
1-phosphate and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:489–503. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee H, Deng J, Kujawski M, Yang C, Liu Y,
Herrmann A, Kortylewski M, Horne D, Somlo G, Forman S, et al:
STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3
activation in tumors. Nat Med. 16:1421–1428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chae SS, Paik JH, Furneaux H and Hla T:
Requirement for sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 in tumor
angiogenesis demonstrated by in vivo RNA interference. J Clin
Invest. 114:1082–1089. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deng J, Liu Y, Lee H, Herrmann A, Zhang W,
Zhang C, Shen S, Priceman SJ, Kujawski M, Pal SK, et al:
S1PR1-STAT3 signaling is crucial for myeloid cell colonization at
future metastatic sites. Cancer Cell. 21:642–654. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoshida Y, Nakada M, Harada T, Tanaka S,
Furuta T, Hayashi Y, Kita D, Uchiyama N, Hayashi Y and Hamada J:
The expression level of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 is
related to MIB-1 labeling index and predicts survival of
glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol. 98:41–47. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Matsuoka Y, Nagahara Y, Ikekita M and
Shinomiya T: A novel immunosuppressive agent FTY720 induced Akt
dephosphorylation in leukemia cells. Br J Pharmacol. 138:1303–1312.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang JD, Takahara S, Nonomura N, Ichimaru
N, Toki K, Azuma H, Matsumiya K, Okuyama A and Suzuki S: Early
induction of apoptosis in androgen-independent prostate cancer cell
line by FTY720 requires caspase-3 activation. Prostate. 40:50–55.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hung JH, Lu YS, Wang YC, Ma YH, Wang DS,
Kulp SK, Muthusamy N, Byrd JC, Cheng AL and Chen CS: FTY720 induces
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activation of
protein kinase C delta signaling. Cancer Res. 68:1204–1212. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adams JM: Ways of dying: Multiple pathways
to apoptosis. Genes Dev. 17:2481–2495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fiers W, Beyaert R, Declercq W and
Vandenabeele P: More than one way to die: Apoptosis, necrosis and
reactive oxygen damage. Oncogene. 18:7719–7730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fiers W, Beyaert R, Declercq W and
Vandenabeele P: More than one way to die: Apoptosis, necrosis and
reactive oxygen damage. Oncogene. 18:7719–7730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen YR, Shrivastava A and Tan TH:
Down-regulation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphatase
M3/6 and activation of JNK by hydrogen peroxide and pyrrolidine
dithiocarbamate. Oncogene. 20:367–374. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sakon S, Xue X, Takekawa M, Sasazuki T,
Okazaki T, Kojima Y, Piao JH, Yagita H, Okumura K, Doi T and Nakano
H: NF-kappaB inhibits TNF-induced accumulation of ROS that mediate
prolonged MAPK activation and necrotic cell death. EMBO J.
22:3898–3909. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kamata H, Honda S, Maeda S, Chang L,
Hirata H and Karin M: Reactive oxygen species promote
TNFalpha-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting
MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell. 120:649–661. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grigoryev S, Salzberg A, Berg A,
Harris-Becker A, Loughran T and Claxton D: Genome-wide mapping of
large organized heterochromatin domains reveals hotspots of
epigenetic and transcriptional changes associated with myeloid
differentiation and acute myeloid leukemia (565.1). The FASEB
Journal. 28:565.5612014.
|
|
17
|
Sarkisyan G, Gay LJ, Nguyen N, Felding BH
and Rosen H: Host endothelial S1PR1 regulation of vascular
permeability modulates tumor growth. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
307:C14–C24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hamidi S, Schäfer-Korting M and Weindl G:
TLR2/1 and sphingosine 1-phosphate modulate inflammation,
myofibroblast differentiation and cell migration in fibroblasts.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:484–494. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang T, Chen F, Chen Z, Wu YF, Xu XL,
Zheng S and He X: Honokiol induces apoptosis through
p53-independent pathway in human colorectal cell line RKO. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:2205–2208. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jabs T: Reactive oxygen intermediates as
mediators of programmed cell death in plants and animals. Biochem
Pharmacol. 57:231–245. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai J and Jones DP: Mitochondrial redox
signaling during apoptosis. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 31:327–334. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cristóbal I, Blanco FJ, Garcia-Orti L,
Marcotegui N, Vicente C, Rifon J, Novo FJ, Bandres E, Calasanz MJ,
Bernabeu C and Odero MD: SETBP1 overexpression is a novel
leukemogenic mechanism that predicts adverse outcome in elderly
patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 115:615–625. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Adams J and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pagès G, Lenormand P, L'Allemain G,
Chambard JC, Meloche S and Pouysségur J: Mitogen-activated protein
kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast
proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:8319–8323. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rubinfeld H and Seger R: The ERK cascade:
A prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol. 31:151–174. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chalah A and Khosravi-Far R: The
mitochondrial death pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 615:25–45. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|