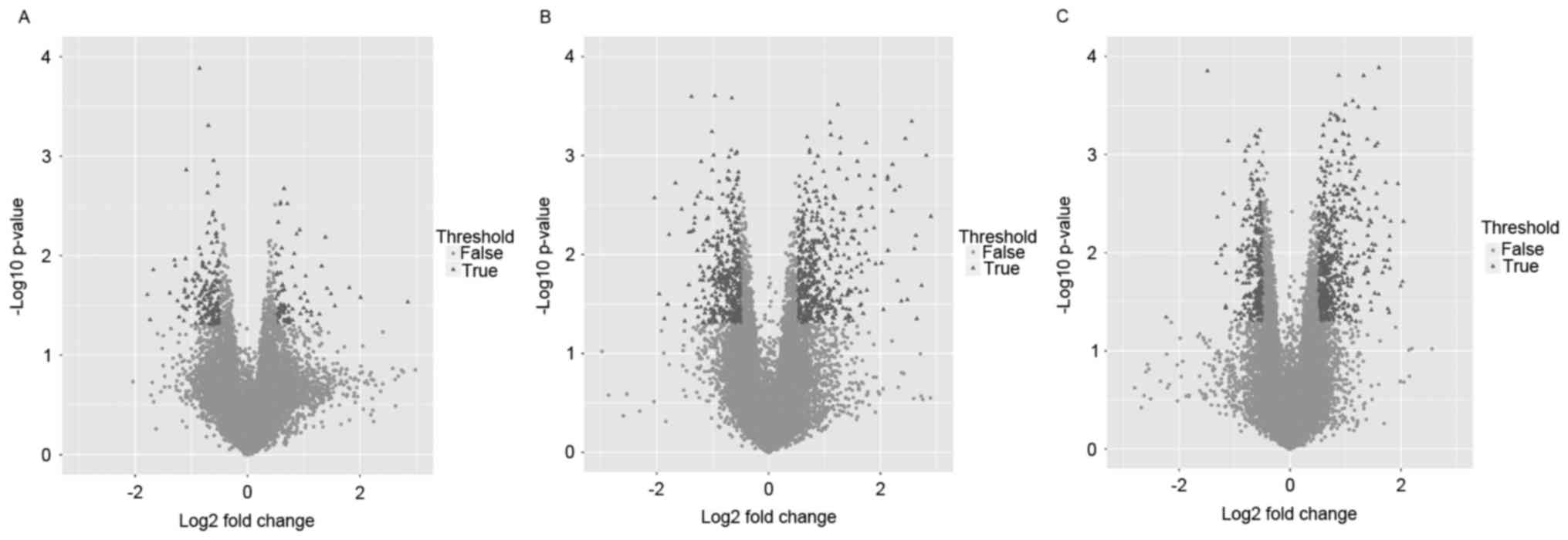
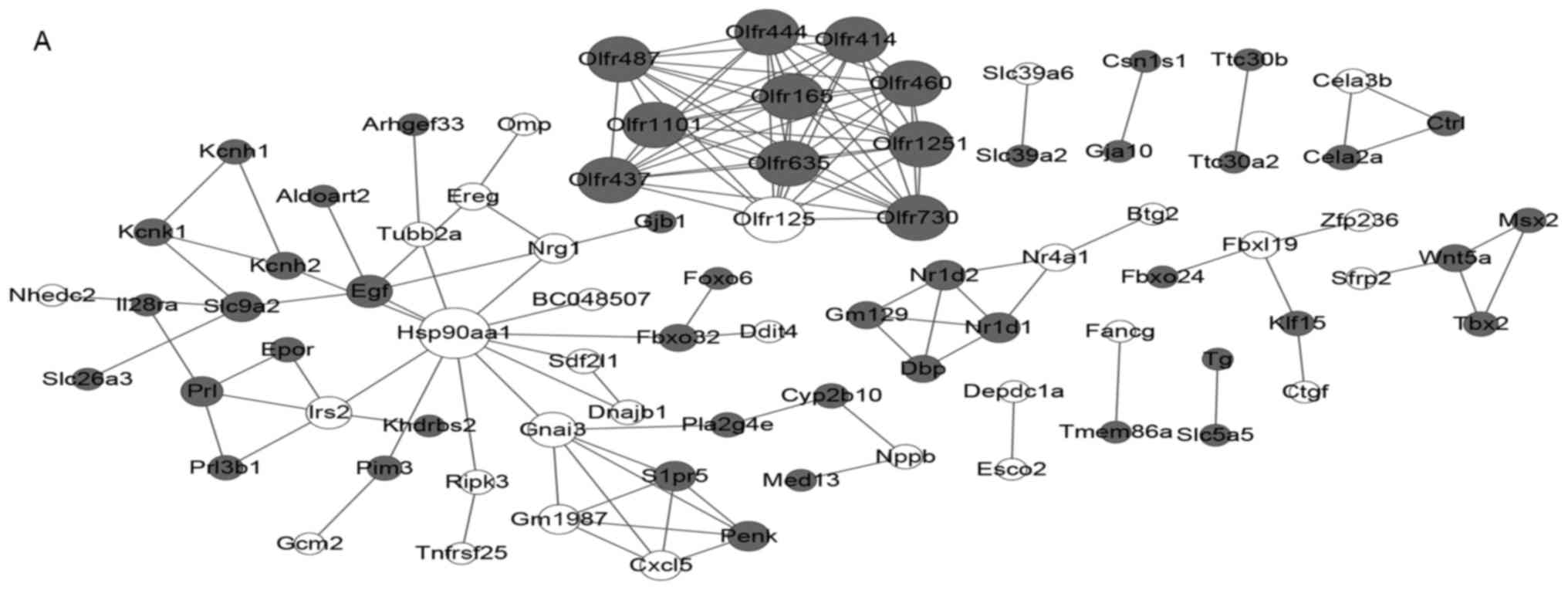
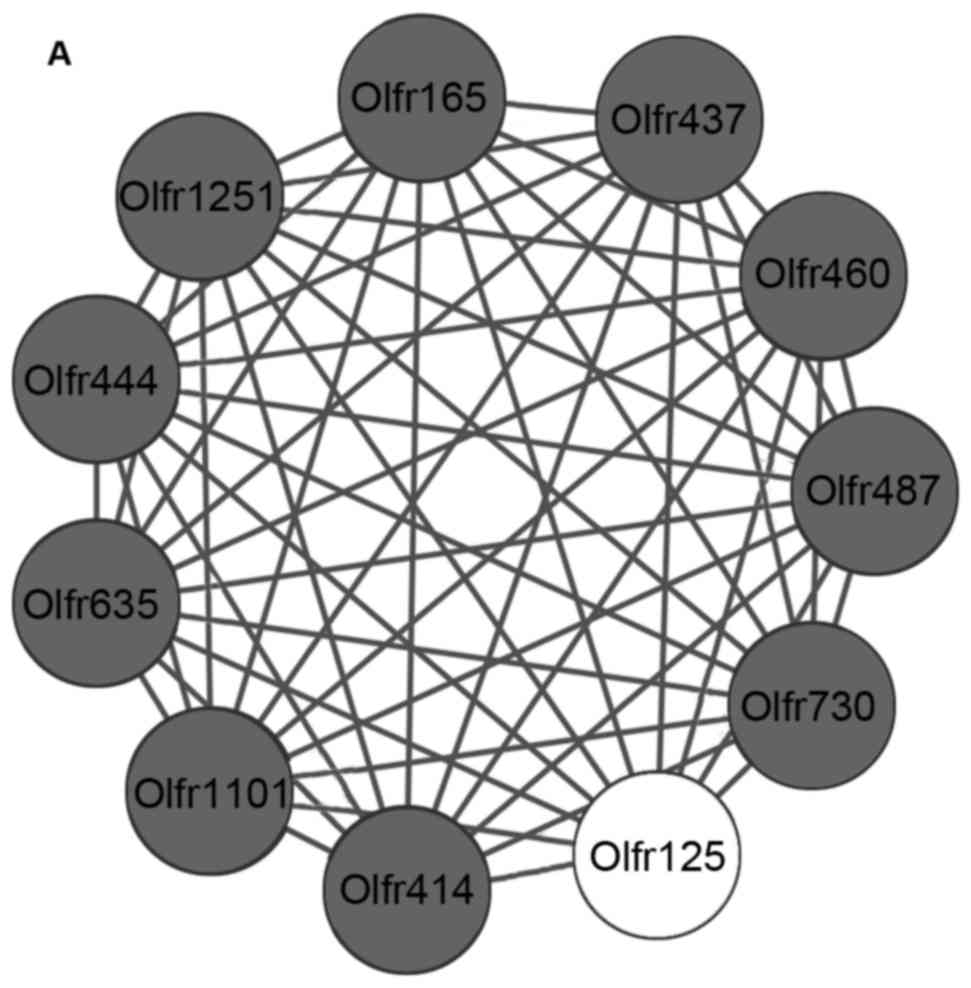
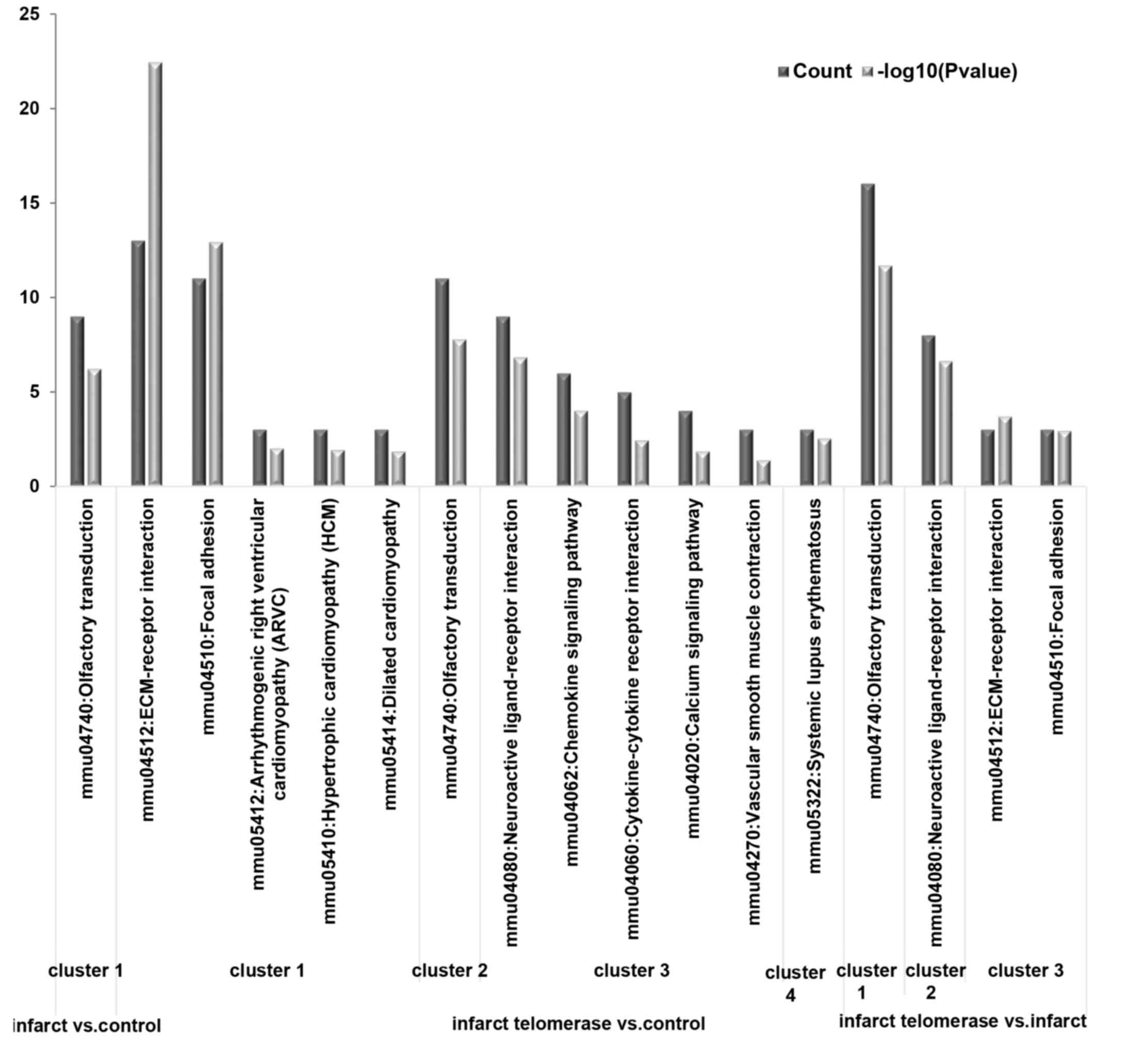
|
1
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, et al:
Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Redefinition of
Myocardial Infarction: Universal definition of myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 50:2173–2195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons
ML, Chaitman BR and White HD: JointESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for
Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction, Authors/Task Force
Members Chairpersons. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, et al: Third universal
definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol.
60:1581–1598. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vos T, Barber RM, Bell B, Bertozzi-Villa
A, Biryukov S, Bolliger I, Charlson F, Davis A, Degenhardt L,
Dicker D, et al: Global, regional, and national incidence,
prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and
chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A
systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013.
Lancet. 386:743–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/heartattack/
|
|
5
|
Task Force on the management of ST-segment
elevation acute myocardial infarction of the European Society of
Cardiology (ESC), . Steg PG, James SK, Atar D, Badano LP,
Blömstrom-Lundqvist C, Borger MA, Di Mario C, Dickstein K, Ducrocq
G, et al: ESC guidelines for the management of acute myocardial
infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur
Heart J. 33:2569–2619. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Doyle F, McGee H, Conroy R, Conradi HJ,
Meijer A, Steeds R, Sato H, Stewart DE, Parakh K, Carney R, et al:
Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of sex
differences in depression and prognosis in persons with myocardial
infarction: A MINDMAPS study. Psychosom Med. 77:419–428. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mehta PK, Wei J and Wenger NK: Ischemic
heart disease in women: A focus on risk factors. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 25:140–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
World Health Organization (WHΟ): Global
atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control. WHO;
Geneva: 2011
|
|
9
|
Dominguez LJ, Galioto A, Ferlisi A, Pineo
A, Putignano E, Belvedere M, Costanza G and Barbagallo M: Ageing,
lifestyle modifications, and cardiovascular disease in developing
countries. J Nutr Health Aging. 10:143–149. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liew CC and Dzau VJ: Molecular genetics
and genomics of heart failure. Nat Rev Genet. 5:811–825. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cohn JN, Ferrari R and Sharpe N: Cardiac
remodeling-concepts and clinical implications: A consensus paper
from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an
international forum on cardiac remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol.
35:569–582. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boonekamp JJ, Simons MJ, Hemerik L and
Verhulst S: Telomere length behaves as biomarker of somatic
redundancy rather than biological age. Aging Cell. 12:330–332.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bär C, de Bernardes Jesus B, Serrano R,
Tejera A, Ayuso E, Jimenez V, Formentini I, Bobadilla M, Mizrahi J,
de Martino A, et al: Telomerase expression confers cardioprotection
in the adult mouse heart after acute myocardial infarction. Nat
Commun. 5:58632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Soonpaa MH, Koh GY, Klug MG and Field LJ:
Formation of nascent intercalated disks between grafted fetal
cardiomyocytes and host myocardium. Science. 264:98–101. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Senyo SE, Steinhauser ML, Pizzimenti CL,
Yang VK, Cai L, Wang M, Wu TD, Guerquin-Kern JL, Lechene CP and Lee
RT: Mammalian heart renewal by pre-existing cardiomyocytes. Nature.
493:433–436. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weischer M, Bojesen SE, Cawthon RM,
Freiberg JJ, Tybjærg-Hansen A and Nordestgaard BG: Short telomere
length, myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and early
death. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:822–829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Buechner N, Drose S, Jakob S, Brandt U,
Altschmied J and Haendeler J: Mitochondrial TERT enhances
mitochondria functions in vivo by protecting mitochondrial DNA
integrity from oxidative damage. Cell Circulation Signaling.
7:(Suppl 1). A572009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cohen H: Forced TERT expression in mice.
Scientist. 15:222001.
|
|
19
|
Harrington M: Telomerase limits damage
after heart attack. Lab Anim (NY). 44:462015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor Springer. 397–420. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Berkeley C: Linear models and empirical
Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray
experiments. http://www.bepress.com/sagmb/vol3/iss1/art3.2004
|
|
22
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Altermann E and Klaenhammer TR:
PathwayVoyager: Pathway mapping using the Kyoto encyclopedia of
genes and genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genomics. 6:602005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
da Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nepusz T, Yu H and Paccanaro A: Detecting
overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction
networks. Nat Methods. 9:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weis S, Shintani S, Weber A, Kirchmair R,
Wood M, Cravens A, McSharry H, Iwakura A, Yoon YS, Himes N, et al:
Src blockade stabilizes a Flk/cadherin complex, reducing edema and
tissue injury following myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest.
113:885–894. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rutledge CA, Ng FS, Sulkin MS, Greener ID,
Sergeyenko AM, Liu H, Gemel J, Beyer EC, Sovari AA, Efimov IR and
Dudley SC: c-Src kinase inhibition reduces arrhythmia inducibility
and connexin43 dysregulation after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 63:928–934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dawn B, Takano H, Tang XL, Kodani E,
Banerjee S, Rezazadeh A, Qiu Y and Bolli R: Role of Src protein
tyrosine kinases in late preconditioning against myocardial
infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 283:H549–H556. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miao L, Xin X, Xin H, Shen X and Zhu YZ:
Hydrogen sulfide recruits macrophage migration by integrin
β1-Src-FAK/Pyk2-Rac pathway in myocardial infarction. Sci Rep.
6:223632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xin Y, Bai Y, Jiang X, Zhou S, Wang Y,
Wintergerst KA, Tan Y, Cui T and Cai L: Activation of Nrf2 by
Sulforaphane via the AKT/GSK-3β/Fyn pathway prevents angiotensin
ii-induced cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 117:A802015.
|
|
33
|
Yu L, Lin Q, Feng J, Dong X, Chen W, Liu Q
and Ye J: Inhibition of nephrin activation by c-mip through
Csk-Cbp-Fyn axis plays a critical role in Angiotensin II-induced
podocyte damage. Cell Signal. 25:581–588. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Y, Tsuchida A, Cohen MV and Downey JM:
Pretreatment with angiotensin II activates protein kinase C and
limits myocardial infarction in isolated rabbit hearts. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 27:883–892. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yano H, Hibi K, Nozawa N, Ozaki H, Kusama
I, Ebina T, Kosuge M, Tsukahara K, Okuda J, Morita S, et al:
Effects of valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker, on
coronary atherosclerosis in patients with acute myocardial
infarction who receive an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor.
Circ J. 76:1442–1451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim SH, Yoon YC, Lee AS, Kang N, Koo J,
Rhyu MR and Park JH: Expression of human olfactory receptor 10J5 in
heart aorta, coronary artery, and endothelial cells and its
functional role in angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
460:404–408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Drutel G, Arrang JM, Diaz J, Wisnewsky C,
Schwartz K and Schwartz JC: Cloning of OL1, a putative olfactory
receptor and its expression in the developing rat heart. Receptors
Channels. 3:33–40. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Griffin CA, Kafadar KA and Pavlath GK:
MOR23 promotes muscle regeneration and regulates cell adhesion and
migration. Dev Cell. 17:649–661. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kang N and Koo J: Olfactory receptors in
non-chemosensory tissues. BMB Rep. 45:612–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li H, Zhong X, Li C, Peng L, Liu W, Ye M
and Tuo B: Analysis of pathways and networks influencing the
differential expression of genes in coronary artery disease. Arch
Biol Sci Belgrade. 66:983–988. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|