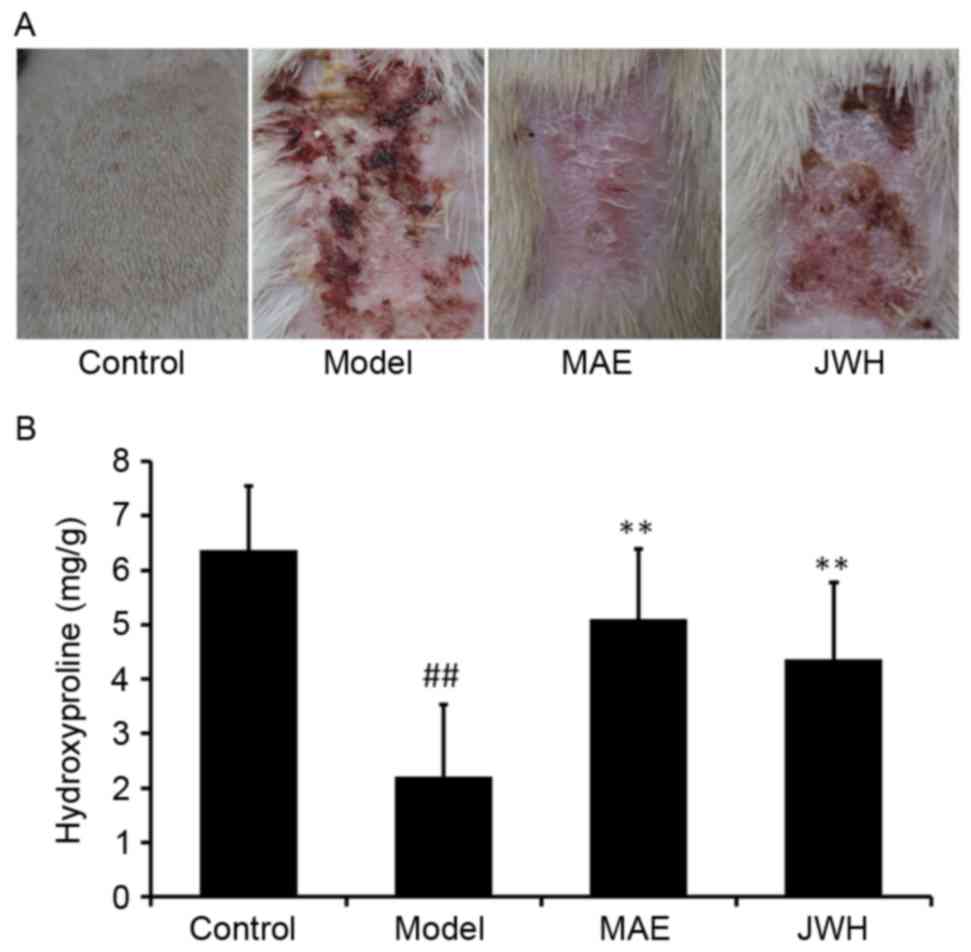
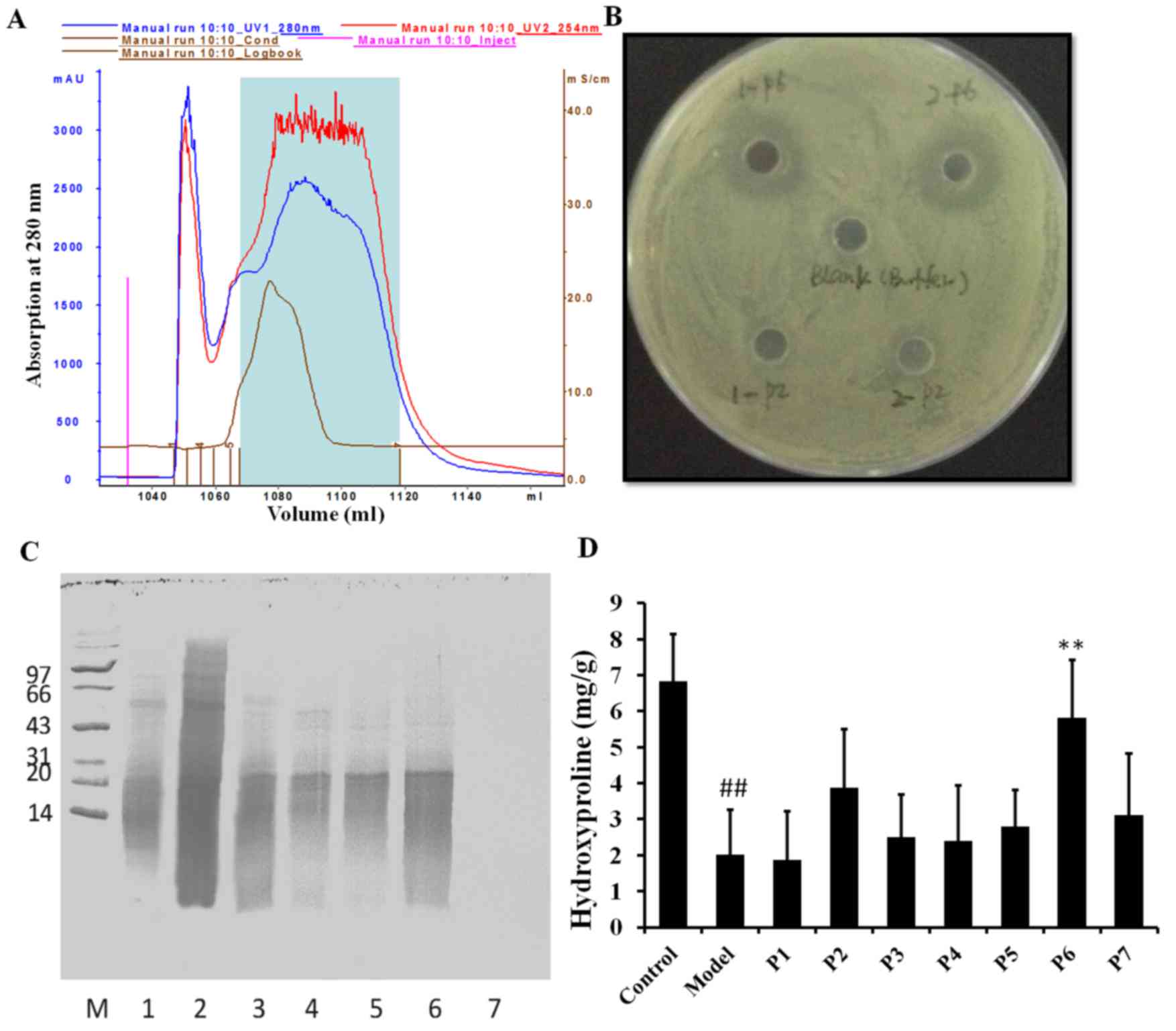
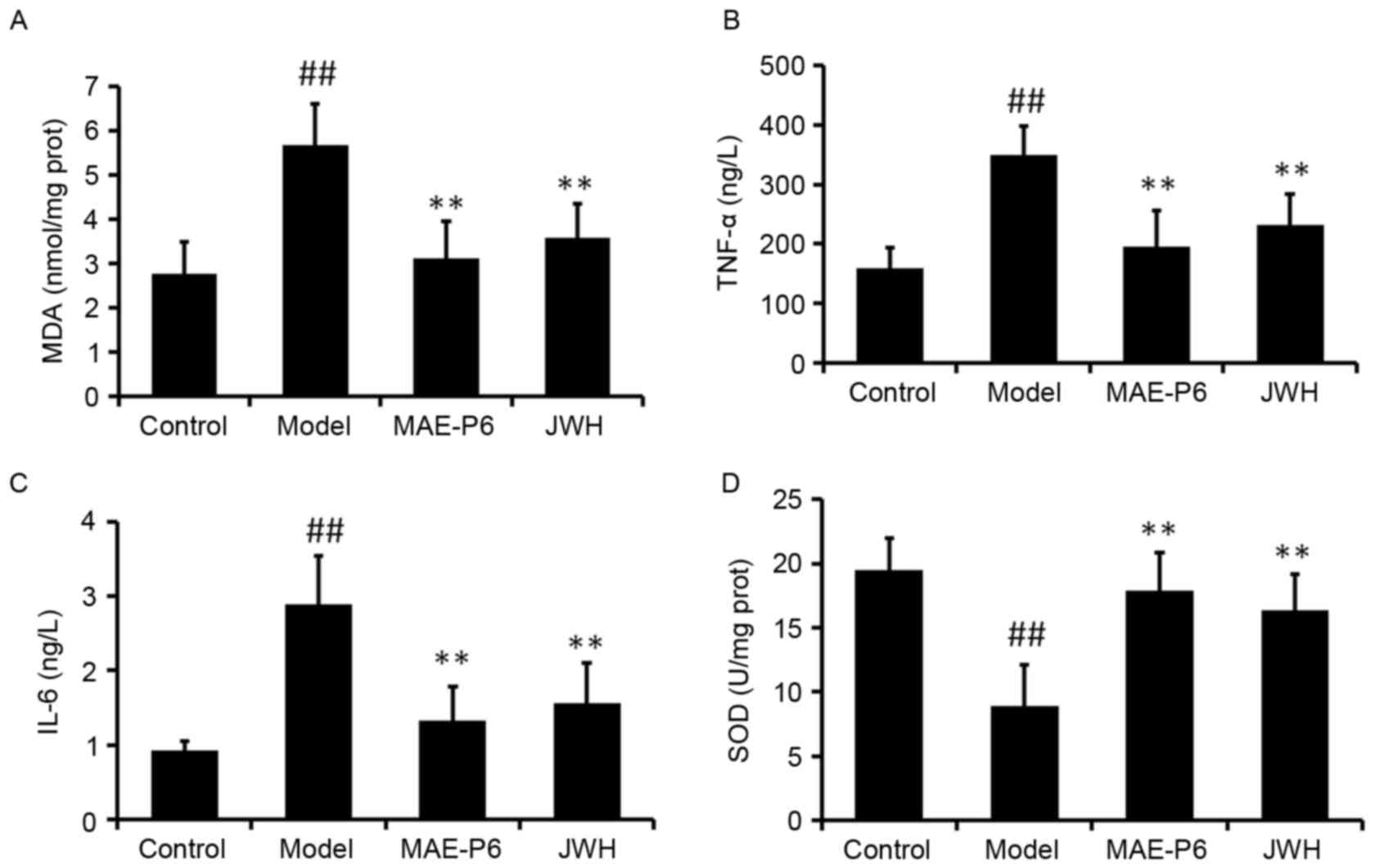
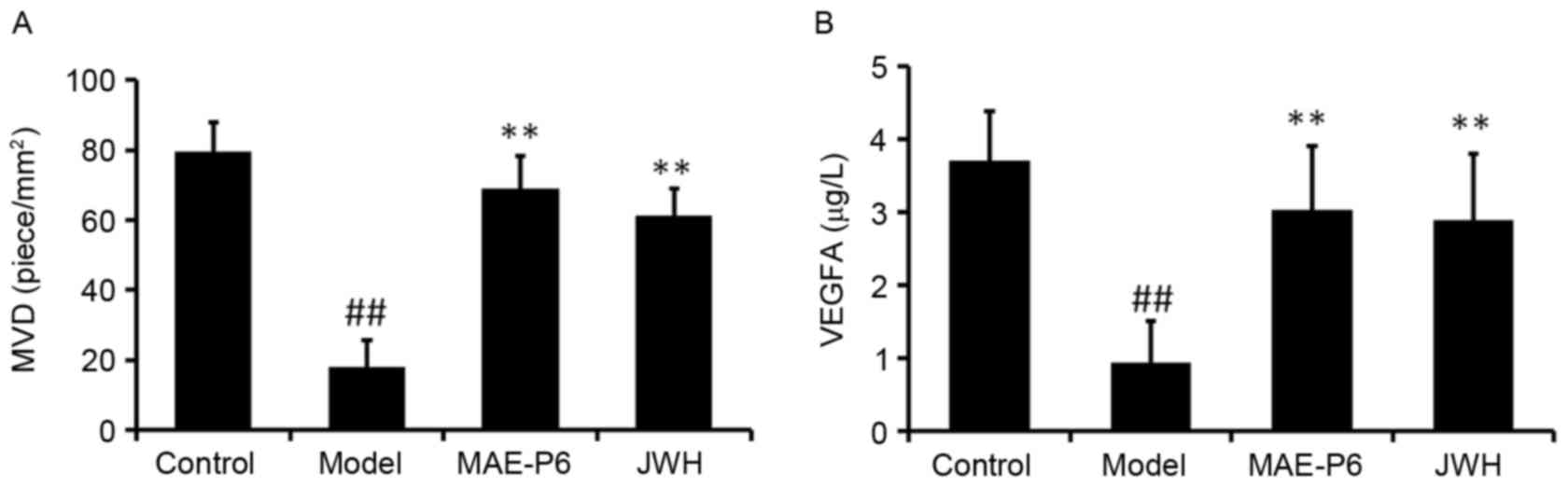
|
1
|
Mogoşanu GD and Grumezescu AM: Natural and
synthetic polymers for wounds and burns dressing. Int J Pharm.
463:127–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lay-flurrie K: Honey in wound care:
Effects, clinical application and patient benefit. Br J Nurs.
17:S30–S36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Riedel K, Ryssel H, Koellensperger E,
Germann G and Kremer T: Pathogenesis of chronic wounds. Chirurg.
79:526–534. 2008.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ghasemi Pirbalouti A: Medicinal plants
used in Chaharmahal and Bakhtyari districts. Iran Herba Pol.
55:34–38. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Nayak BS, Isitor G, Davis EM and Pillai
GK: The evidence-based wound healing activity of Lawsonia inermis
Linn. Phytother Res. 21:827–831. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bahramsoltani R, Farzaei MH and Rahimi R:
Medicinal plants and their natural components as future drugs for
the treatment of burn wounds: An integrative review. Arch Dermatol
Res. 306:601–617. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hou L, Shi Y, Zhai P and Le G:
Antibacterial activity and in vitro anti-tumor activity of the
extract of the larvae of the housefly (Musca domestica). J
Ethnopharmacol. 111:227–231. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sherman RA: Maggot versus conservative
debridement therapy for the treatment of pressure ulcers. Wound
Repair Regen. 4:208–214. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dumville JC, Worthy G, Bland JM, Cullum N,
Dowson C, Iglesias C, Mitchell JL, Nelson EA, Soares MO and
Torgerson DJ: VenUS II team: Larval therapy for leg ulcers (VenUS
II): Randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 338:b7732009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Paul AG, Ahmad NW, Lee HL, Ariff AM,
Saranum M, Naicker AS and Osman Z: Maggot debridement therapy with
Lucilia cuprina: A comparison with conventional debridement in
diabetic foot ulcers. Inter Wound J. 6:39–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wollina U, Liebold K, Schmidt WD, Hartmann
M and Fassler D: Biosurgery supports granulation and debridement in
chronic wounds-clinical data and remittance spectroscopy
measurement. Int J Dermatol. 41:635–639. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huberman L, Gollop N, Mumcuoglu KY, Block
C and Galun R: Antibacterial properties of whole body extracts and
haemolymph of Lucilia sericata maggots. J Wound Care. 16:123–127.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pinheiro MA, Ferraz JB, Junior MA, Moura
AD, da Costa ME, Costa FJ, Neto VF, Neto RM and Gama RA: Use of
maggot therapy for treating a diabetic foot ulcer colonized by
multidrug resistant bacteria in Brazil. Indian J Med Res.
141:340–342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nigam Y and Morgan C: Does maggot therapy
promote wound healing? The clinical and cellular evidence. J Eur
Acad Dermatol. 30:776–782. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Vilcinskas A: From traditional maggot
therapy to modern biosurgeryInsect Biotechnology. Vilcinskas A:
Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer; pp. 67–755. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bohova J, Majtan J, Majtan V and Takac P:
Selective antibiofilm effects of Lucilia sericata larvae
secretions/excretions against wound pathogens. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2014:8573602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hultmark D: Techniques in Insect
Immunology. Weisner A, Dunphy GB, Marmaras VJ, Morishima I,
Sugumaran M and Yamakawa M: SOS Publications; New Jersey: pp.
103–1075. 1998
|
|
18
|
Mumcuoglu KY, Ingber A, Gilead L, Stessman
J, Friedmann R, Schulman H, Bichucher H, Ioffe-Uspensky I, Miller
J, Galun R and Raz I: Maggot therapy for the treatment of
intractable wounds. Int J Dermatol. 8:623–627. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huberman L, Gollop N, Mumcuoglu KY, Block
C and Galun R: Antibacterial properties of whole body extracts and
haemolymph of Lucilia sericata maggots. J Wound Care. 16:123–127.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morellini NM, Giles NL, Rea S, Adcroft KF,
Falder S, King CE, Dunlop SA, Beazley LD, West AK, Wood FM and Fear
MW: Exogenous metallothionein-IIA promotes accelerated healing
after a burn wound. Wound Repair Regen. 16:682–690. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu J and Chen ZW: Isolation,
characterization and anti-cancer activity of SK84, a novel
glycine-rich antimicrobial peptide from Drosophila virilis.
Peptides. 31:44–50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sen CK: The general case for redox control
of wound repair. Wound Repair Regen. 11:431–438. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo S and Dipietro LA: Factors affecting
wound healing. J Dent Res. 89:219–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hassan B, Akcakanat A, Holder AM and
Meric-Bernstam F: Targeting the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 22:641–664. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hettiaratchy S and Dziewulski P: ABC of
burns. BMJ. 328:1366–1368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Church D, Elsayed S, Reid O, Winston B and
Lindsay R: Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 19:403–434.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
DeSanti L: Pathophysiology and current
management of burn injury. Adv Skin Wound Care. 18:323–332. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rowan MP, Cancio LC, Elster EA, Burmeister
DM, Rose LF, Natesan S, Chan RK, Christy RJ and Chung KK: Burn
wound healing and treatment: Review and advancements. Critical
Care. 19:2432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hinz B: The myofibroblast: Paradigm for a
mechanically active cell. J Biomech. 43:146–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Werner S, Krieg T and Smola H:
Keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J Invest
Dermatol. 127:998–1008. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo S and Dipietro LA: Factors affecting
wound healing. J Dent Res. 89:219–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Macri L and Clark RA: Tissue engineering
for cutaneous wounds: Selecting the proper time and space for
growth factors, cells and the extracellular matrix. Skin Pharmacol
Physiol. 22:83–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Richelle M, Sabatier M, Steiling H and
Williamson G: Skin bioavailability of dietary vitamin E,
carotenoids, polyphenols, vitamin C, zinc and selenium. Br J Nutr.
96:227–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta A, Singh RL and Raghubir R:
Antioxidant status during cutaneous wound healing in
immunocompromised rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 241:1–7. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mast BA and Schultz GS: Interactions of
cytokines, growth factors and proteases in acute, and chronic
wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 4:411–420. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Distler JH, Hirth A, Kurowska-Stolarska M,
Gay RE, Gay S and Distler O: Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in
the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 41:149–161.
2003.
|
|
37
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sarkar S: Regulation of autophagy by
mTOR-dependent and mTOR-independent pathways: Autophagy dysfunction
in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic application of
autophagy enhancers. Biochem Soc Trans. 41:1103–1130. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|