Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most
frequently occurring malignancies in Asia, due to the endemic
status of chronic hepatitis B and C virus infection (1). The onset of HCC is insidious, and no
symptoms occur in the early stages. Surgical removal is not
suitable for most patients with HCC; therefore, transcatheter
arterial chemoembolization (TACE) has become the mainstay of
treatment (2). However, hepatoma
cells are known to be highly resistant to chemotherapeutic drugs
(3). This severely reduces the
effects of TACE. Thus, there is an urgent need to determine the
drug resistance mechanism in HCC.
Lin28, a well-known cancer stem cell marker
(4), has become a popular target of
researchers in recent years. Several studies have demonstrated that
high expression of Lin28 correlates with resistance to chemotherapy
in breast and gastric cancer (5,6). Since
Lin28 is also highly expressed in HCC (7), we investigated whether high Lin28
expression is also related to drug resistance in HCC. Lin28 is an
RNA binding protein that blocks the biogenesis of let-7 by inducing
terminal uridylation and degradation of let-7 precursors (8,9).
Downregulation of let-7 promotes the expression of Bcl-xL, an
anti-apoptotic gene; overexpression of Bcl-xL always induces
apoptosis resistance and reduces the sensitivity of tumor cells to
drugs (10). Here, we examined
whether Lin28-mediated dysregulation of the Lin28/let-7/Bcl-xL
pathway is involved in the drug resistance of HCC.
In the present study, we established a
drug-resistant Hep3B cell line (Hep3B/TAX) by stepwise sequential
exposure to increasing concentrations of paclitaxel to analyze the
relationship between Lin28, the let-7 family, Bcl-xL and the drug
resistance in HCC. The aim of the present study was to gain insight
into the molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance and to provide a
potential target to overcome chemoresistance in HCC.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
Paclitaxel was purchased from Tianjin YiFang Science
and Technology, Ltd. (Tianjin, China). 5-Fluorouracil injection,
cisplatin and cytoxan were obtained from Zhejiang Chinese Medical
University Second Clinical Medical College. Antibodies against
Lin28 and β-actin, and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary
antibodies were purchased from Boster Biological Technology, Ltd.
(Wuhan, China). Antibodies against caspase-3 and -9, BAX,
cytochrome c, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL were purchased from Hangzhou
HuaAn Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). Dulbecco’s
modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS), and other
tissue culture reagents were purchased from Beijing Dingguo
Changsheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). TRIzol reagent
was purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). HiFi-MMLV cDNA
kits and UltraSYBR Mixture were obtained from Beijing Kang Century
Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
Cell culture
The human hepatoma cell line Hep3B was obtained from
Boster Biological Technology, Ltd., and was routinely cultured in
DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, penicillin (100 U/ml) and
streptomycin (100 mg/ml) at 37°C and 5% CO2.
Development of a paclitaxel-resistant
cell line (Hep3B/TAX)
To develop a paclitaxel-resistant HCC cell line,
Hep3B cells were exposed to gradually increasing concentrations of
paclitaxel (0.01–0.2 μM) in complete medium. Briefly, Hep3B cells
were seeded in culture flasks at a density of 4–5×105
cells/ml and allowed to grow. After 24 h incubation, paclitaxel
(0.01 μM) was added, and the cells were incubated for another 24 h.
Then, the cells were washed 3 times with D-Hanks solution and the
medium was changed to paclitaxel-free medium. The cells were
incubated and allowed to grow until confluent. Then, the cells were
subcultured and re-exposed to double the dose of drug. This process
was repeated until the cells were resistant to 0.2 μM paclitaxel.
After successful development, Hep3B/TAX cells were maintained in
complete medium containing a low concentration of paclitaxel (0.01
μM).
Morphological examination of the
drug-resistant Hep3B/TAX cells
Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cells were seeded in 35 mm petri
plates at a density of 1×105 cells/ml. After 24 h
incubation, cells were visualized and photographed under a Nikon
Eclipse 80i microscope connected to a DS-5M-L1 camera.
Cell viability assay
A previously described
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)
uptake method (11) was used to
determine the effect of drugs on the proliferation and viability of
Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cells. Experiments were repeated three times
with 6 wells for each treatment to ensure the reproducibility of
results. The IC50 value was defined as the dose of the
drug required to inhibit cell growth by 50% and was calculated
using the improved Karber’s method.
Flow cytometry analysis (FCM)
To determine whether Hep3B/TAX cells were more
resistant to paclitaxel than the parental Hep3B cells, Hep3B/TAX
and Hep3B cells were seeded in 35 mm petri plates at a density of
1×105 cells/ml. After 24 h incubation, cells were
treated with paclitaxel for another 24 h, and untreated cells
served as control. Next, the cells were washed twice with PBS and
resuspended in 100 μl incubation buffer (PBS buffer containing 2%
BSA and 2% FBS), and 100 μl of Guava Nexin reagent was added. After
incubation for 20 min at RT in the dark, all the samples were
filtered sequentially through 200 μm mesh sieves and analyzed using
Guava EasyCyte 8 flow cytometer (EMD Millipore, USA). Annexin
V-PE-negative and 7-AAD-negative cells were considered alive.
Quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent
according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was synthesized
using a HiFi-MMLV cDNA kit. To synthesize let-7 family cDNAs,
specific RT-primers were used that were based on the sequence of
each family member, and the RT-primer for U6 was the same as the
reverse primer (Table I). Real-time
PCR was conducted using UltraSYBR Mixture. All primers were
synthesized by GenScript Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). All samples
were run in triplicate, and changes in gene expression were
calculated using the ΔΔCt method.
 | Table IPrimer pairs used for quantitative
real-time PCR. |
Table I
Primer pairs used for quantitative
real-time PCR.
| Gene | Primer name | Sequences
(5′-3′) |
|---|
| Let-7a | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACTAT |
| Forward primer |
CGGTGAGGTAGTAGGTTGT |
| Let-7b | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACCAC |
| Forward primer |
CGGTGAGGTAGTAGGTTGT |
| Let-7c | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACCAT |
| Forward primer |
CGGTGAGGTAGTAGGTTGT |
| Let-7d | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACTAT |
| Forward primer |
CGCCGAGAGGTAGTAGGTTGC |
| Let-7e | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACTAT |
| Forward primer |
CGGTGAGGTAGGAGGTTGT |
| Let-7f | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACTAT |
| Forward primer |
CGGTGAGGTAGTAGATTGT |
| Let-7g | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACTGT |
| Forward primer |
CGCCGTGAGGTAGTAGTTTGT |
| Let-7i | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACAGC |
| Forward primer |
CGCCGTGAGGTAGTAGTTTGT |
| Mir-98 | RT-primer |
GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACAAT |
| Forward primer |
CGGTGAGGTAGTAAGTTGT |
| Universal | Reverse primer | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
| U6 | Forward primer |
CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| Reverse primer |
AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| Lin28 | Forward primer |
CGGCCAAAAGGAAAGAGCAT |
| Reverse primer |
GTTGGCTTTCCCTGTGCACT |
| Bcl-2 | Forward primer |
CCAAGAATGCAAAGCACATCCA |
| Reverse primer |
GGTTATCGTACCCTGTTCTCCC |
| Bax | Forward primer |
CAGCTGACATGTTTTCTGACGG |
| Reverse primer |
AATGTCCAGCCCATGATGGTT |
| β-actin | Forward primer |
GGCACCACACCTTCTACAAT |
| Reverse primer |
GTGGTGGTGAAGCTGTAGCC |
Western blot analysis
Total protein was extracted from cells using Protein
Extraction Reagent (Boster Bioengineering, Wuhan, China) containing
1 mM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Roche Molecular
Biochemicals, Indianapolis, IN, USA). Protein concentrations were
determined by the BCA protein assay (Nanjing KeyGen Biotech Co.
Ltd., Nanjing, China). The proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE
and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane
(Pall Gelman Laboratory Corporation, Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Then, the
western blot analyses were probed with antibodies against Lin28,
caspase-3 and -9, BAX, cytochrome c, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and
β-actin. The protein bands were detected by enhanced
chemiluminescence.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as means ± SD of experiments
performed in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed using
one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for multiple comparisons and
t-tests for comparisons between groups. A P-value of <0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Establishment of the Hep3B/TAX cell
line
A human hepatoma paclitaxel-resistant model system
was established, as described in the Materials and methods section,
to study the molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. After 9
months of development, we obtained Hep3B/TAX cells that grew stably
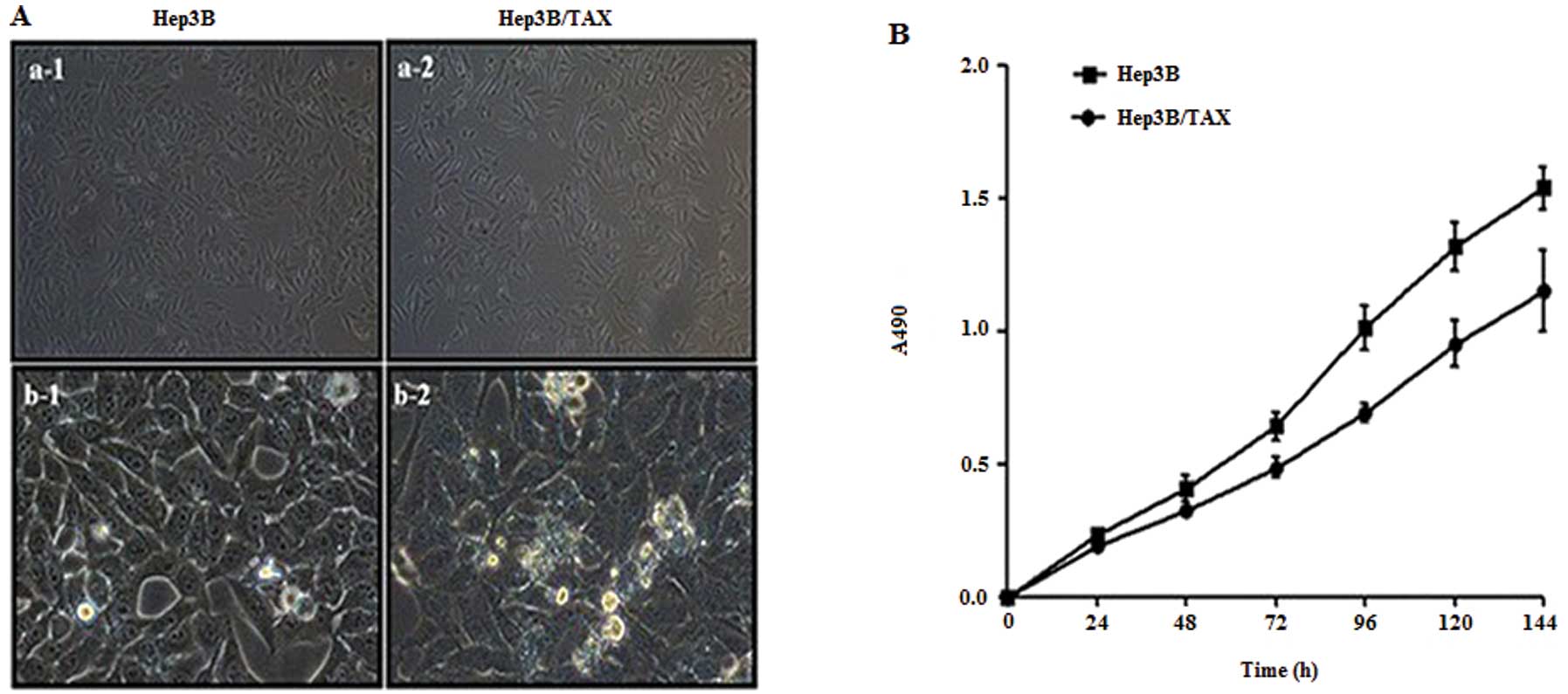
in DMEM containing 0.2 μM paclitaxel. Microscopic observation
showed that the Hep3B/TAX cells were elongated compared with their
parental cells, especially at low cell density (Fig. 1A, a-1 and a-2), and the number of
black particles in cytoplasm of Hep3B/TAX cells increased (Fig. 1A, b-1 and b-2). The doubling time
for Hep3B was 44.21±1.47 h and that of Hep3B/TAX cells was
49.16±1.89 h, therefore the growth rate of paclitaxel-resistant
cells was significantly lower than that of the parental cells
(Fig. 1B, P<0.01). Next, to
determine the IC50 value of paclitaxel, Hep3B and
Hep3B/TAX cells were treated with various doses of paclitaxel for
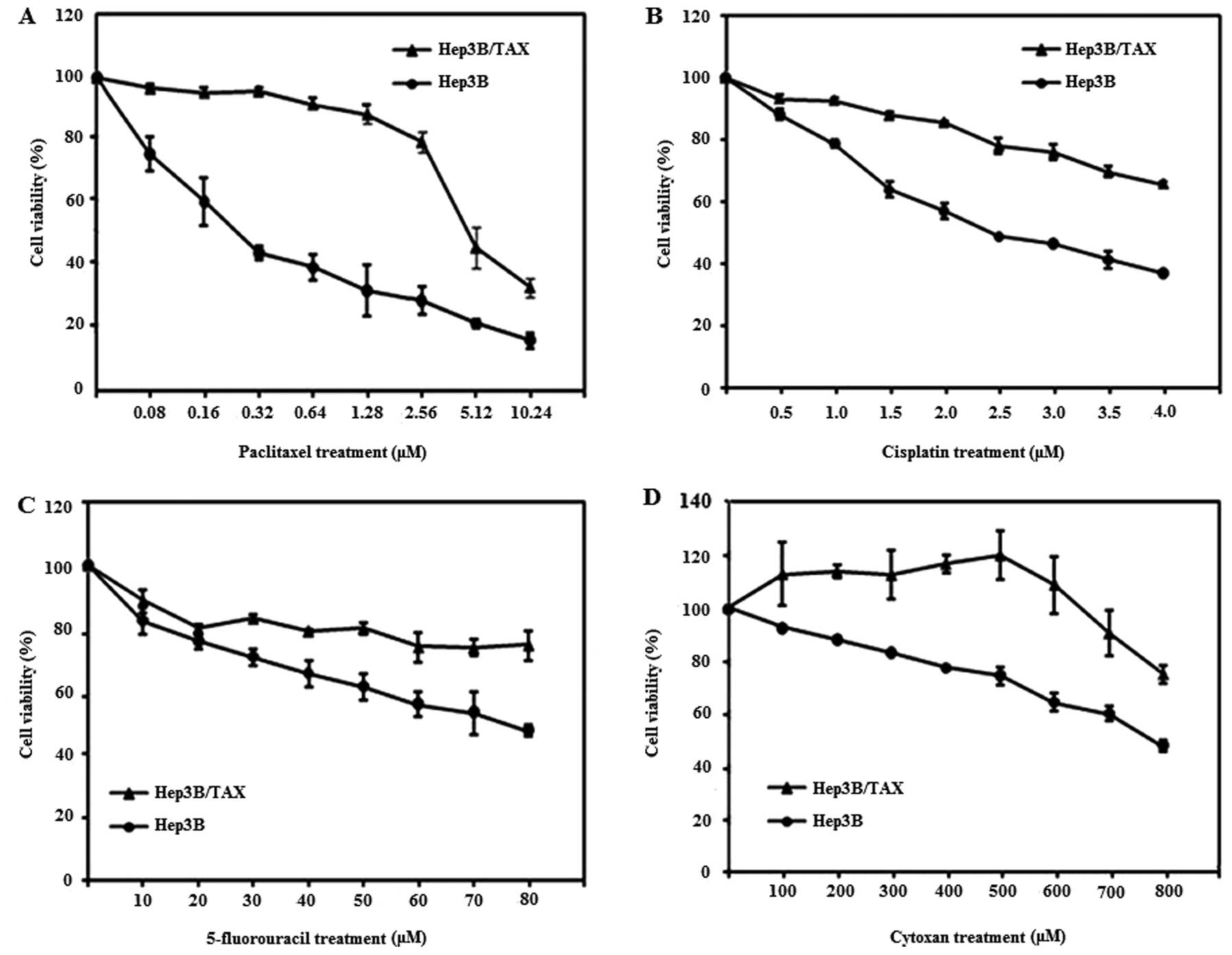
48 h and then cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay. As
shown in Fig. 2A, we found that the
survival rate of Hep3B/TAX cells was much higher than that of their
parental cells after treatment with the same dose of paclitaxel.
The IC50 values were 0.2 μM for Hep3B cells and 5.65 μM
for Hep3B/TAX cells at 48 h, and the drug resistance index was
28.25 (Table II). These data
suggest that Hep3B cells are more sensitive to paclitaxel than
Hep3B/TAX cells. We also assessed the response of Hep3B and
Hep3B/TAX cells to other chemical drugs besides paclitaxel, and we
found that Hep3B/TAX cells exhibited cross-resistance to cisplatin,
5-fluorouracil and cytoxan (Fig.
2B–D and Table II).
 | Table IIResponse of Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cell
lines to various anticancer drugs. |
Table II
Response of Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cell
lines to various anticancer drugs.
| Anticancer drug | IC50
(μg/ml) | Resistance index |
|---|
|
|---|
| Hep3B | Hep3B/TAX |
|---|
| Paclitaxel | 0.2 | 5.65 | 28.250 |
| Cisplatin | 2.976 | 6.591 | 2.215 |
| 5-Fluorouracil | 64.874 | 148.431 | 2.288 |
| Cytoxan | 712.582 | 2407.008 | 3.378 |
Apoptosis resistance of Hep3B/TAX cells
and expression of apoptosis-related genes
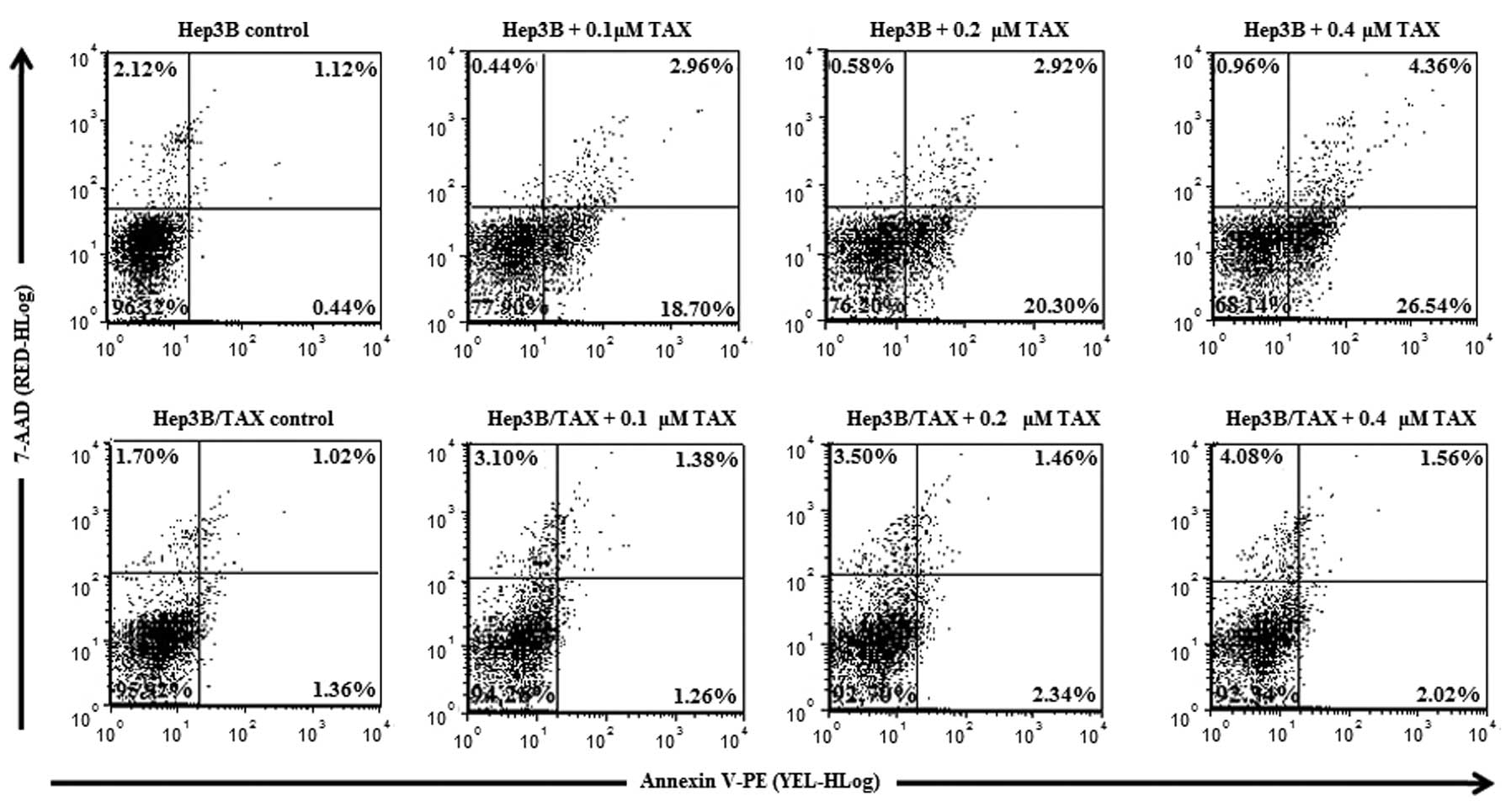
After 24 h exposure to paclitaxel in DMEM, Hep3B and
Hep3B/TAX cells were harvested, and their apoptosis rates were
determined. As shown in Fig. 3, we
observed that untreated Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cells both showed very
low apoptosis rates (1.55±0.55 and 2.41±0.69%, respectively;
Table III). After treatment with
paclitaxel, the percentage of apoptotic Hep3B cells markedly
increased to 21.65±2.28% (0.1 μM) and 30.57±4.74% (0.4 μM), whereas
the apoptosis rate in Hep3B/TAX cells was still very low, only
2.63±0.87, 3.82±0.99 and 3.55±0.57% following treatment with 0.1,
0.2 and 0.4 μM paclitaxel. Therefore, compared with Hep3B cells,
Hep3B/TAX cells were much less sensitive to paclitaxel.
 | Table IIIRate of apoptosis in Hep3B and
Hep3B/TAX cells induced by paclitaxel. |
Table III
Rate of apoptosis in Hep3B and
Hep3B/TAX cells induced by paclitaxel.
| Dose of paclitaxel
(μM) |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| Cell type | 0 (%) | 0.1 (%) | 0.2 (%) | 0.4 (%) |
|---|
| Hep3B | 1.55±0.55 | 21.65±2.28a | 23.39±4.24a | 30.57±4.74a |
| Hep3B/TAX | 2.41±0.69 | 2.63±0.87b | 3.82±0.99b | 3.55±0.57b |
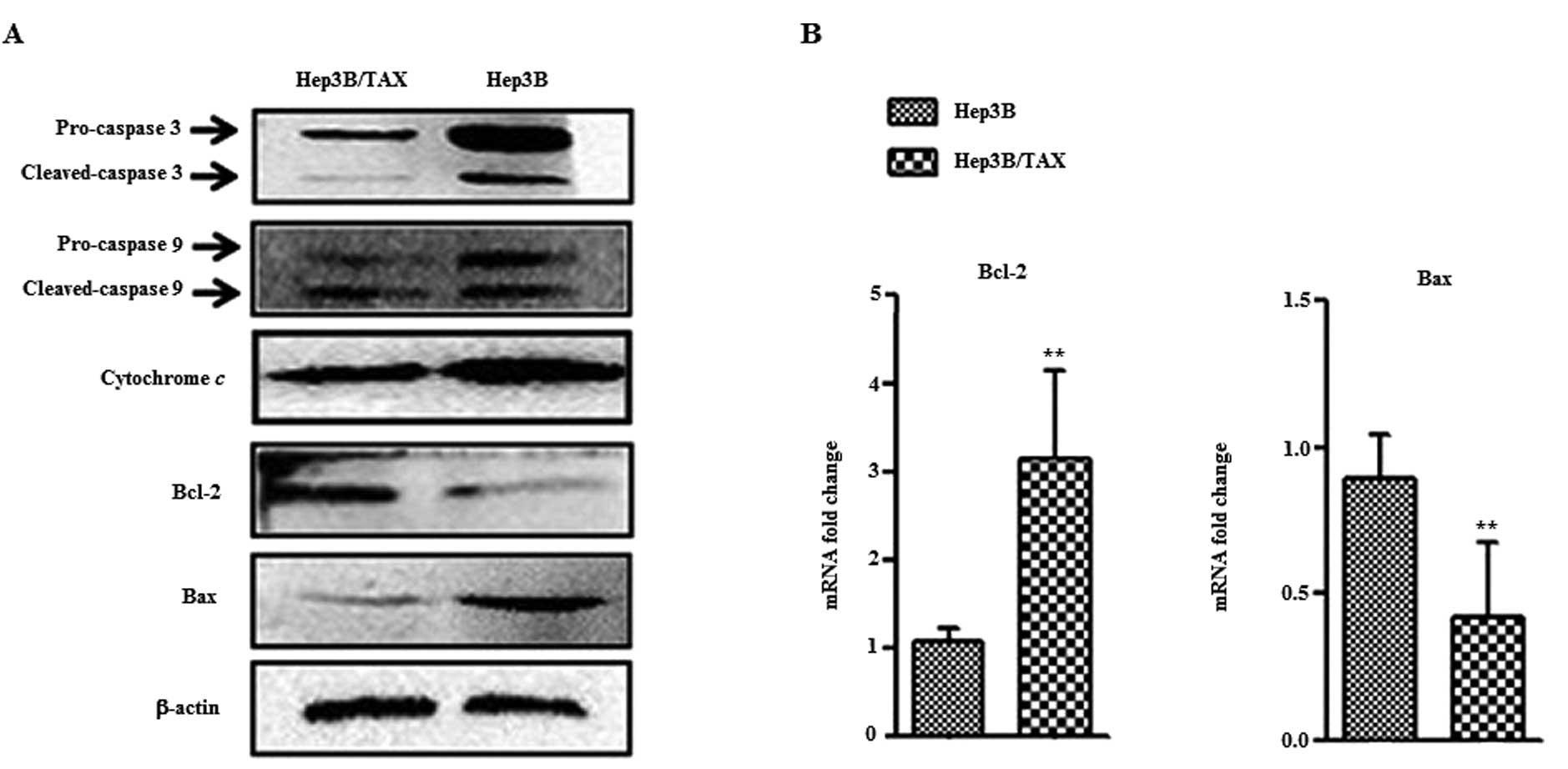
Activation of caspases is a hallmark of apoptosis;
to measure this, Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cells were treated with 0.2 μM
paclitaxel for 24 h, and whole cell extracts were prepared and
caspase-9 and -3 activation was assessed. Western blot analysis
showed that cleavage of caspase-9 and -3 in Hep3B/TAX was reduced
(Fig. 4A). Furthermore, we found
that in Hep3B/TAX cells, the expression of Bax was reduced whereas
the expression of anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2 was enhanced
(Fig. 4A), and real-time PCR
analysis confirmed these findings (Fig.
4B). These results indicated that Hep3B/TAX cells are resistant
to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Although this phenotype may be
related to drug resistance, it nevertheless confirmed the
successful development of a drug-resistant cell line.
Lin28/let-7/Bcl-xL is associated with
drug resistance in Hep3B cells
To determine whether Lin28 expression is associated
with the drug resistance observed in HCC, we examined the
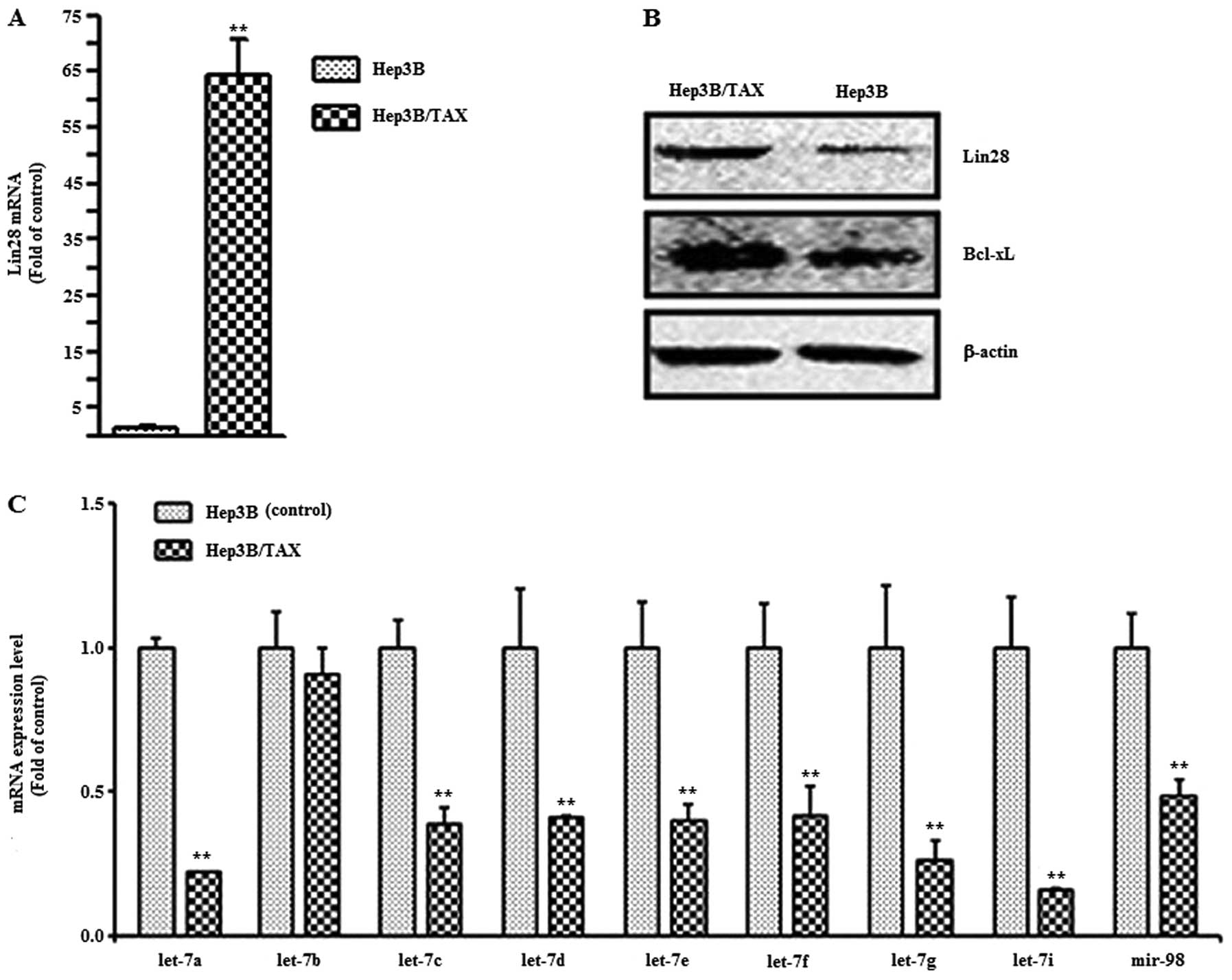
expression of Lin28 in Hep3B and paclitaxel-resistant Hep3B/TAX
cells by qPCR. We found that the mRNA level of Lin28 in the
paclitaxel-resistant cell line was 75-fold higher than that in the
parental Hep3B cells (Fig. 5A) and
the Lin28 protein level in Hep3B/TAX cells was also much higher
than that in Hep3B cells (Fig. 5B).
Then, we measured the expression of let-7 family miRNAs, which are
regulated by Lin28. The results showed that the expression of all
the let-7 family members tested was reduced except let-7b (Fig. 5C). The anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL
plays a transcendental role in chemoresistance in tumor cells, and
Bcl-xL is regulated by let-7. Therefore, we examined the expression
of Bcl-xL both in Hep3B and Hep3B/TAX cells by western blotting. We
observed that the level of Bcl-xL protein was much higher in
Hep3B/TAX cells than in Hep3B cells. All the data suggest that the
Lin28/let-7/Bcl-xL pathway is associated with drug resistance in
Hep3B cells.
Discussion
Human cancer exhibits differential sensitivities to
chemotherapeutic drugs, which is associated with the inherent
sensitivity of their tissues of origin. Solid tumors, such as
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), show a high degree of drug
resistance due to poor drug uptake as well as intrinsic factors
which regulate the cellular response to different drugs. Although a
considerable research has been carried out, particularly on the
overexpression of the P-glycoproteins which are encoded by the MDR1
class of genes (12–14), the micro-mechanism has not yet been
fully elucidated. Therefore, in the present study, we established a
drug-resistant cell line, Hep3B/TAX, using stepwise selection to
explore the underlying mechanism of drug resistance in HCC
cells.
We confirmed the drug-resistant phenotype by
assessing the growth properties of Hep3B/TAX cells in comparison to
the parental Hep3B cells. Although Hep3B/TAX cells doubled more
slowly than Hep3B cells, the survival rate of Hep3B/TAX cells in
the presence of paclitaxel was much higher than that of Hep3B
cells. The IC50 value of paclitaxel for Hep3B/TAX was
5.65 μM, whereas that for Hep3B was only 0.2 μM (the drug
resistance index was 28.25). Additionally, Hep3B/TAX cells also
exhibited resistance to cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and cytoxan. This
cross-resistance phenotype was also reported by other groups
(15,16). Next, we confirmed the drug
resistance phenotype by measuring the induction of apoptosis in
Hep3B/TAX cells following treatment with paclitaxel. The apoptosis
rate in Hep3B/TAX cells was clearly lower than that in Hep3B cells
after same dose paclitaxel treatment. Since caspases are situated
at pivotal junctions in apoptosis, we examined the expression and
cleavage of caspase-9 and -3 in these two cell lines. The data
suggest that the resistance of Hep3B/TAX cells to apoptosis
associated with drug resistance and the caspases dependent
mitochondrial intrinsic pathway since we observed a reduction in
cytochrome c release and cleavage of caspase-9 and -3, which
act on the death substrates (17).
In addition, the anti-apoptosis gene Bcl-2 and the pro-apoptosis
gene BAX were also involved (Bcl-2 was downregulated and BAX was
upregulated in Hep3B/TAX cells).
Recently, the cancer stem cell marker Lin28 has
emerged as a contributor to drug resistance. It has been reported
that Lin28 expression is a possible mechanism of chemoresistance in
breast cancer by targeting p21, Rb and let-7 miRNA (5). Teng et al (6) demonstrated the role of Lin28 in
predicting the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer patients. In this
study, we also found much higher Lin28 mRNA and protein expression
in the drug-resistant Hep3B/TAX cell line than in the parental cell
line. Furthermore, the expression of let-7 family miRNAs, which are
regulated by Lin28, were all reduced in Hep3B/TAX cells except
let-7b, and let-7i had the lowest expression. Liu et al also
found that decreased expression of microRNA let-7i was associated
with chemotherapeutic response in human gastric cancer (18). On the other hand, our results of the
let-7 family showed a preference for interaction of let-7 microRNAs
with Lin28.
Previous studies demonstrated that Bcl-xL was
overexpressed in one-third of human HCC and that it was associated
with drug resistance in hepatoma cells (19). Notably, it is negatively regulated
by the let-7 family. Therefore, we measured the expression of
Bcl-xL in Hep3B/TAX and Hep3B cells. Western blotting showed that
the expression of Bcl-xL was significantly higher in Hep3B/TAX
cells than in the parental Hep3B cells, suggesting its association
with drug resistance in Hep3B cells. Bcl-xL is a well-known
anti-apoptotic gene of the Bcl-2 family. Cancer cells frequently
overexpress one or more members of this family to acquire a
survival advantage (20).
Therefore, we considered that overexpression of Lin28 induced
downregulation of let-7 family microRNAs, which induced the
overexpression of Bcl-xL. The overexpression of Bcl-xL allowed
Hep3B/TAX cells to escape from apoptosis and acquire a survival
advantage when treated with chemotherapeutic drugs.
In summary, the Lin28/let-7/Bcl-xL pathway may be an
underlying mechanism of drug resistance of Hep3B cells. Our study
provides valuable information for the improvement of chemotherapy
in patients with HCC.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by research grants
from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, Youth
Fund Project (no. LQ12C07001), and research fund for the Doctoral
Program of Higher Education of China (no. 20133322120002).
Abbreviations:
|
DMEM
|
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
|
|
FBS
|
fetal bovine serum
|
|
FCM
|
flow cytometry analysis
|
|
HCC
|
hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
MTT
|
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-
diphenyltetrazolium bromide
|
|
TACE
|
transcatheter arterial
chemo-embolization
|
References
|
1
|
Poon D, Anderson BO, Chen LT, et al:
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia: consensus statement
from the Asian Oncology Summit 2009. Lancet Oncol. 10:1111–1118.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cammà C, Schepis F, Orlando A, Albanese M,
Shahied L, Trevisani F, Andreone P, Craxì A and Cottone M:
Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Radiology. 224:47–54. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin HL, Lui WY, Liu TY and Chi CW:
Reversal of Taxol resistance in hepatoma by cyclosporine A:
involvement of the PI-3 kinase-AKT 1 pathway. Br J Cancer.
88:973–980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang X, Lin X, Zhong X, et al:
Double-negative feedback loop between reprogramming factor LIN28
and microRNA let-7 regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase
1-positive cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 70:9463–9472. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lv K1, Liu L, Wang L, et al: Lin28
mediates paclitaxel resistance by modulating p21, Rb and Let-7a
miRNA in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e 400082012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Teng RY, Zhou JC, Jiang ZN, Xu CY, Li ZD,
Wang QC, Xu CP, Guo JF, Shen JG and Wang LB: The relationship
between Lin28 and the chemotherapy response of gastric cancer. Onco
Targets Ther. 6:1341–1345. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Viswanathan SR, Powers JT, Einhorn W,
Hoshida Y, Ng TL, Toffanin S, et al: Lin28 promotes transformation
and is associated with advanced human malignancies. Nat Genet.
41:843–848. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Viswanathan SR, Daley GQ and Gregory RI:
Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science.
320:97–100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heo I, Joo C, Cho J, Ha M, Han J and Kim
VN: Lin28 mediates the terminal uridylation of let-7 precursor
microRNA. Mol Cell. 32:276–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shimizu S, Takehara T, Hikita H, et al:
The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and
potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 52:698–704. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Tian N, Li X, Luo Y, Han Z, Li Z and Fan
C: Curcumin regulates the metabolism of low density lipoproteins by
improving the C-to-U RNA editing efficiency of apolipoprotein B in
primary rat hepatocytes. Mol Med Rep. 9:132–136. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cavalieri EL, Stack DE, Devanesan PD, et
al: Molecular origin of cancer: catechol estrogen-3,4-quinones as
endogenous tumor initiators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:10937–10942. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kool M1, de Haas M, Scheffer GL, Scheper
RJ, van Eijk MJ, Juijn JA, Baas F and Borst P: Analysis of
expression of cMOAT (MRP2), MRP3, MRP4, and
MRP5, homologues of the multidrug resistance-associated
protein gene (MRP1), in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res.
57:3537–3547. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin HL, Liu TY, Lui WY and Chi CW:
Up-regulation of multidrug resistance transporter expression by
berberine in human and murine hepatoma cells. Cancer. 85:1937–1942.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Zhao J, Zhang W, Liu G, Yin D, Li
J, Zhang S and Li H: Establishment of paclitaxel-resistant cell
line and the underlying mechanism on drug resistance. Int J Cynecol
Cancer. 22:1450–1456. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Işeri OD, Kars MD, Eroglu S and Gündüz U:
Drug resistant MCF-7 cell lines also developed cross-resistance to
structurally unrelated anticancer agents. UHOD. 19:1–8. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Andersen MH, Becker JC and Straten Pt:
Regulators of apoptosis: suitable targets for immune therapy of
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:399–409. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu K, Qian T, Tang L, Wang J, Yang H and
Ren J: Decreased expression of microRNA let-7i and its association
with chemotherapeutic response in human gastric cancer. World J
Surg Oncol. 10:2252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takehara T, Liu X, Fujimoto J, Friedman SL
and Takahashi H: Expression and role of Bcl-xL in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 34:55–61. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lessene G, Czabotar PE and Colman PM:
BCL-2 family antagonists for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
7:989–1000. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|