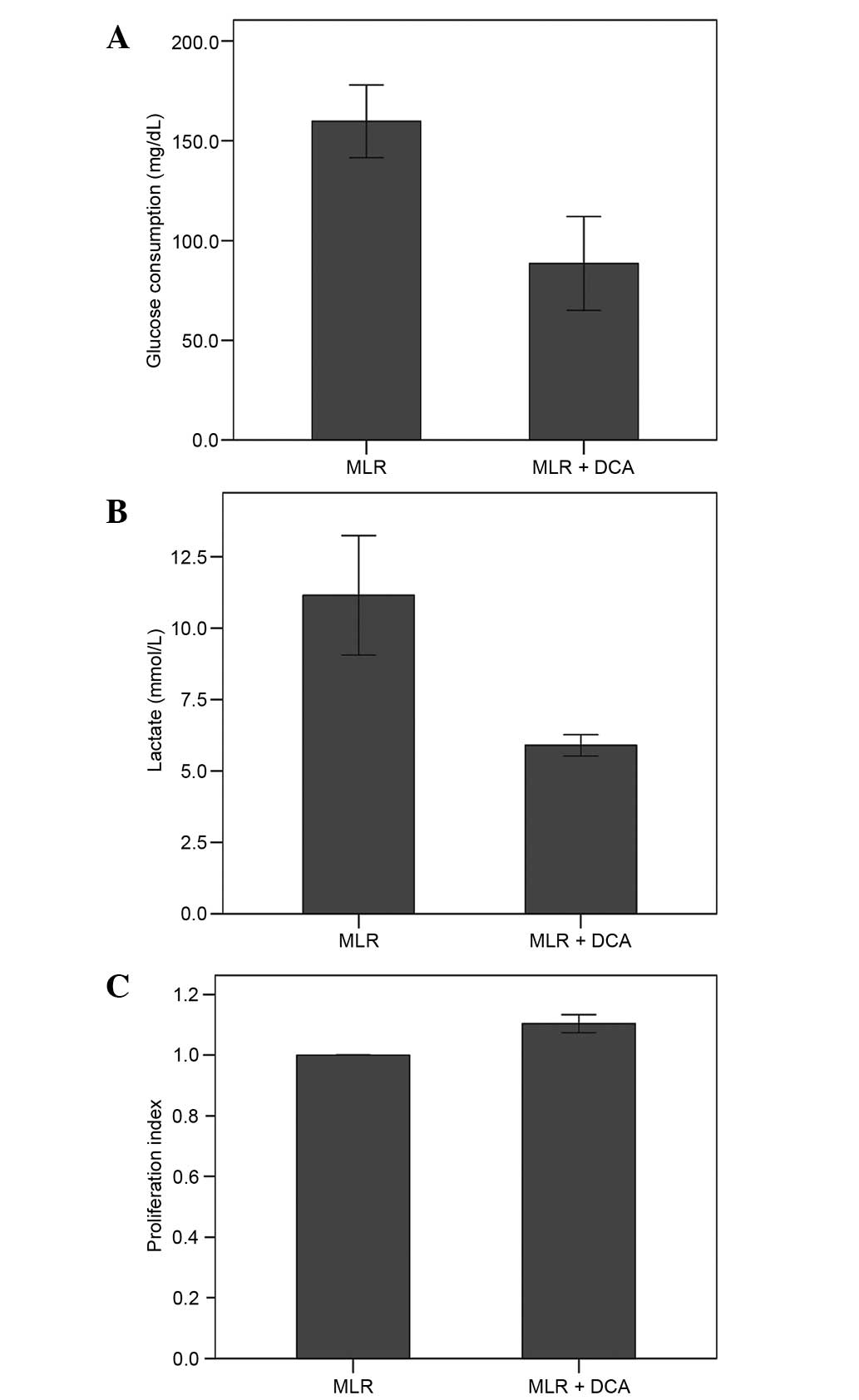
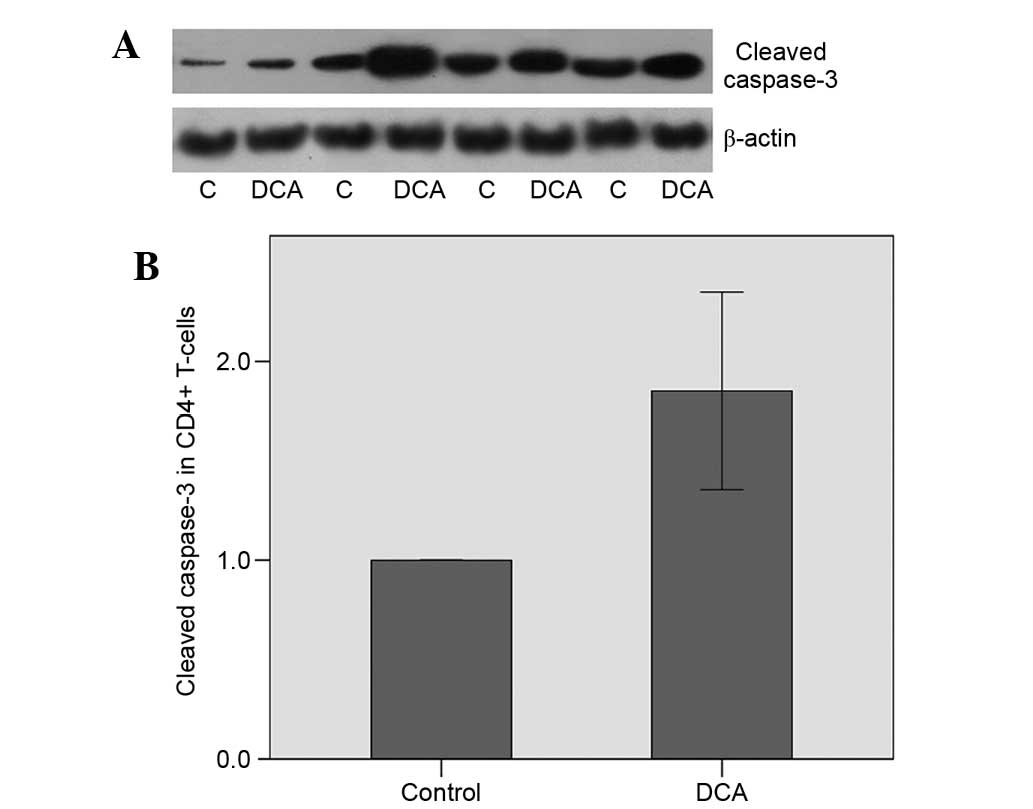
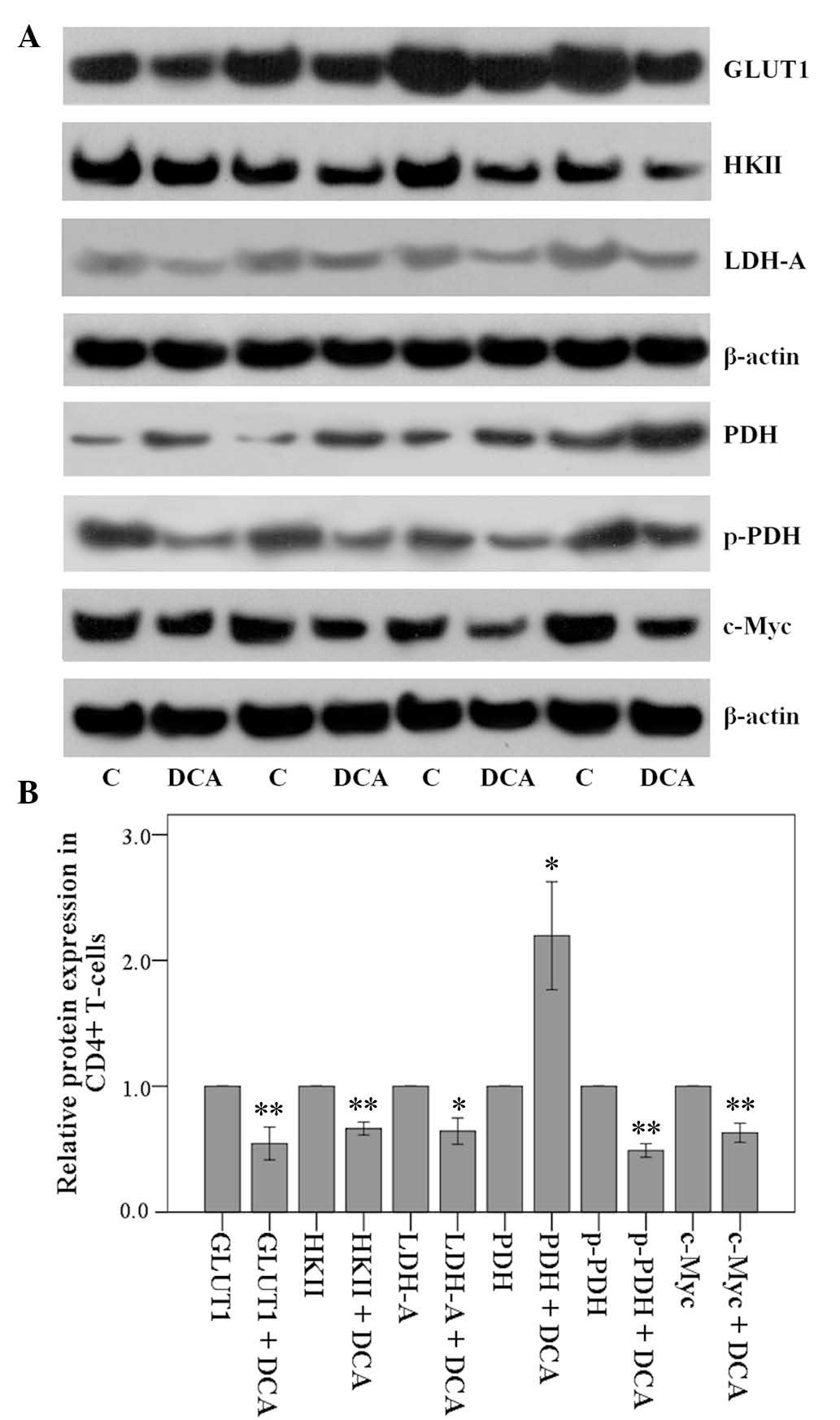
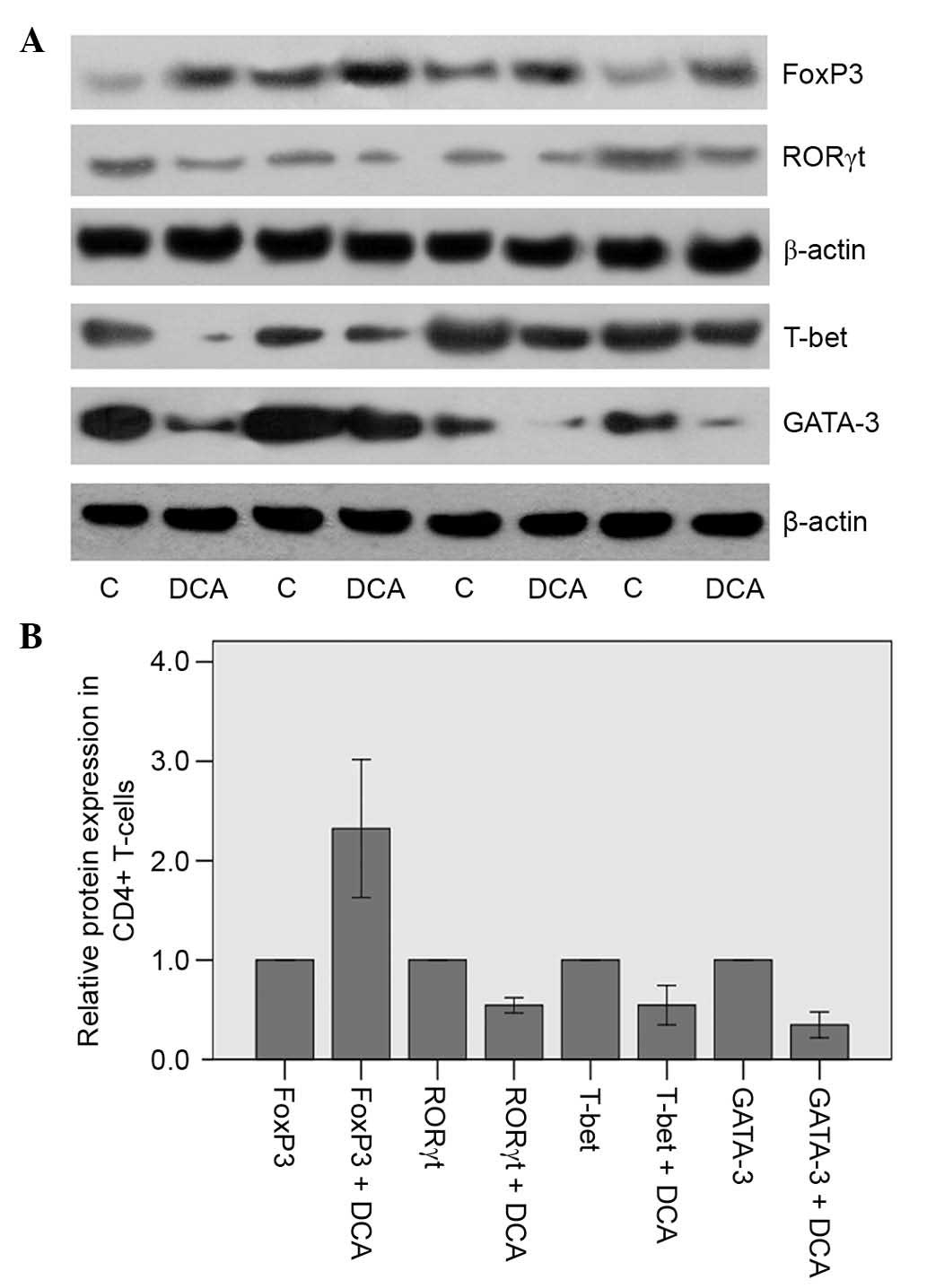
|
1
|
Arend SM, Mallat MJ, Westendorp RJ, van
der Woude FJ and van Es LA: Patient survival after renal
transplantation; more than 25 years follow-up. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 12:1672–1679. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Russell JD, Beecroft ML, Ludwin D and
Churchill DN: The quality of life in renal transplantation-a
prospective study. Transplantation. 54:656–660. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kalluri HV and Hardinger KL: Current state
of renal transplant immunosuppression: Present and future. World J
Transplant. 2:51–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fox CJ, Hammerman PS and Thompson CB: Fuel
feeds function: Energy metabolism and the T-cell response. Nat Rev
Immunol. 5:844–852. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pollizzi KN and Powell JD: Integrating
canonical and metabolic signalling programmes in the regulation of
T cell responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:435–446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Michalek RD, Gerriets VA, Jacobs SR,
Macintyre AN, MacIver NJ, Mason EF, Sullivan SA, Nichols AG and
Rathmell JC: Cutting edge: Distinct glycolytic and lipid oxidative
metabolic programs are essential for effector and regulatory
CD4+ T cell subsets. J Immunol. 186:3299–3303. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Yiannaki E,
Markala D, Arampatzis S, Antoniadi G, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis
I: Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in mixed lymphocyte
reaction affects glucose influx and enzymes involved in aerobic
glycolysis and glutaminolysis in alloreactive T-cells. Hum Immunol.
74:1501–1509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Antoniadi G,
Spanoulis A, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase increases p53 levels in alloreactive human T cells
and both indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and p53 suppress glucose
uptake, glycolysis and proliferation. Int Immunol. 26:673–684.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stacpoole PW: The pharmacology of
dichloroacetate. Metabolism. 38:1124–1144. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bian L, Josefsson E, Jonsson IM, Verdrengh
M, Ohlsson C, Bokarewa M, Tarkowski A and Magnusson M:
Dichloroacetate alleviates development of collagen II-induced
arthritis in female DBA/1 mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:R1322009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ostroukhova M, Goplen N, Karim MZ,
Michalec L, Guo L, Liang Q and Alam R: The role of low-level
lactate production in airway inflammation in asthma. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L300–L307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Abdelmalak M, Lew A, Ramezani R, Shroads
AL, Coats BS, Langaee T, Shankar MN, Neiberger RE, Subramony SH and
Stacpoole PW: Long-term safety of dichloroacetate in congenital
lactic acidosis. Mol Genet Metab. 109:139–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stacpoole PW, Kurtz TL, Han Z and Langaee
T: Role of dichloroacetate in the treatment of genetic
mitochondrial diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 60:1478–1487. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kankotia S and Stacpoole PW:
Dichloroacetate and cancer: New home for an orphan drug? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1846:617–629. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sato T, Deiwick A, Raddatz G, Koyama K and
Schlitt HJ: Interactions of allogeneic human mononuclear cells in
the two-way mixed leucocyte culture (MLC): Influence of cell
numbers, subpopulations and cyclosporin. Clin Exp Immunol.
115:301–308. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Karioti A,
Antoniadi G, Antoniadis N, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I:
Dichloroacetate at therapeutic concentration alters glucose
metabolism and induces regulatory T-cell differentiation in
alloreactive human lymphocytes. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.
24:271–276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Dawar S and Kumar S:
Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ.
22:526–539. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang R, Dillon CP, Shi LZ, Milasta S,
Carter R, Finkelstein D, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Chi H, Munger
J and Green DR: The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic
reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 35:871–882.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Shea JJ and Paul WE: Mechanisms
underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of helper
CD4+ T cells. Science. 327:1098–1102. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Heshe D, Hoogestraat S, Brauckmann C,
Karst U, Boos J and Lanvers-Kaminsky C: Dichloroacetate
metabolically targeted therapy defeats cytotoxicity of standard
anticancer drugs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:647–655. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Macintyre AN, Gerriets VA, Nichols AG,
Michalek RD, Rudolph MC, Deoliveira D, Anderson SM, Abel ED, Chen
BJ, Hale LP and Rathmell JC: The glucose transporter Glut1 is
selectively essential for CD4 T cell activation and effector
function. Cell Metab. 20:61–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Evans OB and Stacpoole PW: Prolonged
hypolactatemia and increased total pyruvate dehydrogenase activity
by dichloroacetate. Biochem Pharmacol. 31:1295–1300. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dummer CD, Carpio VN, Goncalves LF, Manfro
RC and Veronese FV: FOXP3+ regulatory T cells: From
suppression of rejection to induction of renal allograft tolerance.
Transpl Immunol. 26:1–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Edozie FC, Nova-Lamperti EA, Povoleri GA,
Scottà C, John S, Lombardi G and Afzali B: Regulatory T-cell
therapy in the induction of transplant tolerance: The issue of
subpopulations. Transplantation. 98:370–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|