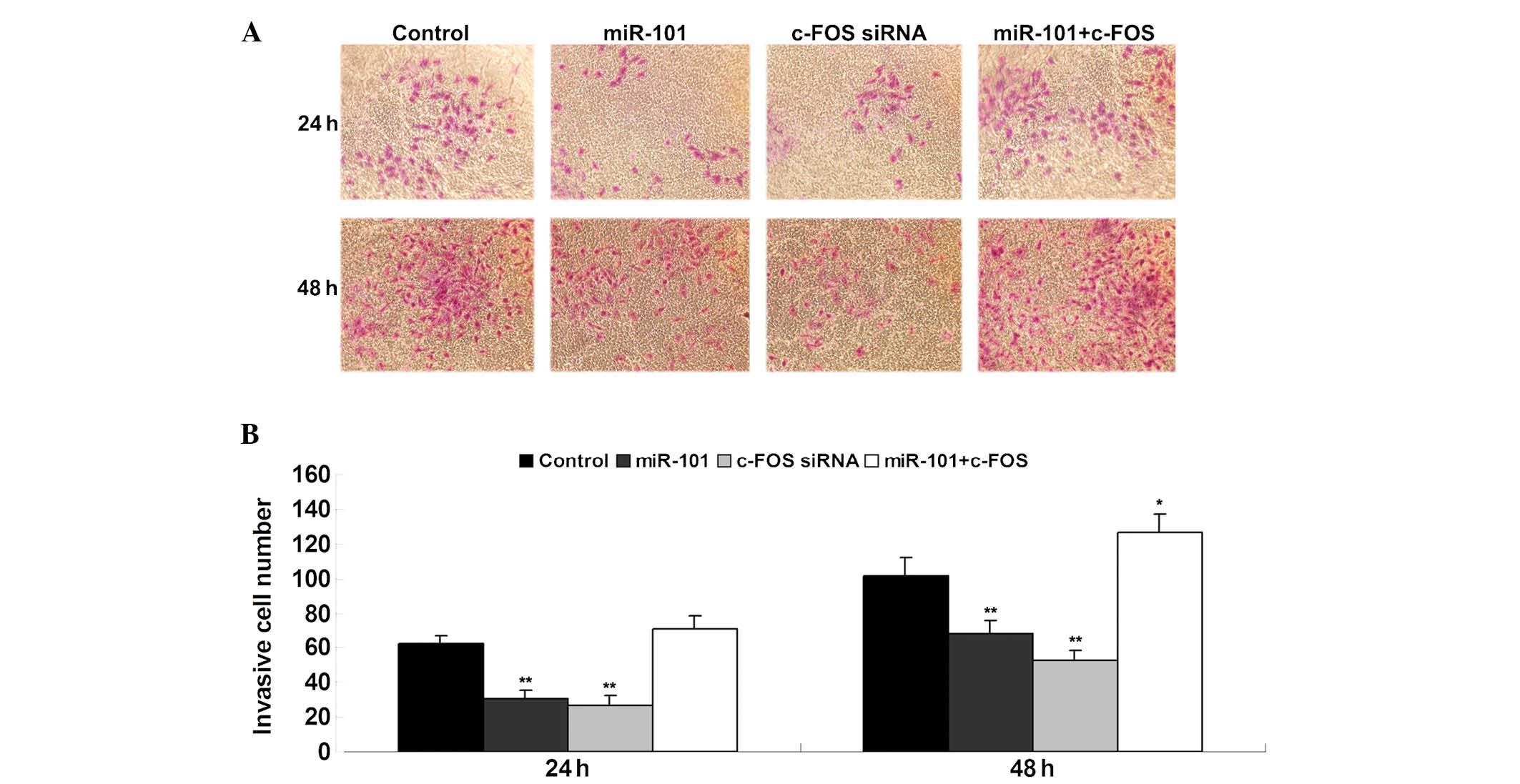
|
1
|
Liang Z, Li S, Xu X, Wang X, Wu J, Zhu Y,
Hu Z, Lin Y, Mao Y, Chen H, et al: MicroRNA-576-3p inhibits
proliferation in bladder cancer cells by targeting cyclin D1. Mol
Cells. 38:130–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Nekoohesh L and
Motevaseli E: Bladder Cancer biomarkers: Review and update. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2395–2403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoshino H, Seki N, Itesako T, Chiyomaru T,
Nakagawa M and Enokida H: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in
bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 10:396–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Friedman JM, Liang G, Liu CC, Wolff EM,
Tsai YC, Ye W, Zhou X and Jones PA: The putative tumor suppressor
microRNA-101 modulates the cancer epigenome by repressing the
polycomb group protein EZH2. Cancer Res. 69:2623–2629. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang H, Qi F, Cao Y, Chen M and Zu X:
Down-regulated microRNA-101 in bladder transitional cell carcinoma
is associated with poor prognosis. Med Sci Monit. 20:812–817. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bu Q, Fang Y, Cao Y, Chen Q and Liu Y:
Enforced expression of miR-101 enhances cisplatin sensitivity in
human bladder cancer cells by modulating the cyclooxygenase-2
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 10:2203–2209. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lei Y, Li B, Tong S, Qi L, Hu X, Cui Y, Li
Z, He W, Zu X, Wang Z and Chen M: miR-101 suppresses vascular
endothelial growth factor C that inhibits migration and invasion
and enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity of bladder cancer cells.
PLoS One. 10:e01178092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu Z, Lin Y, Chen H, Mao Y, Wu J, Zhu Y,
Xu X, Xu X, Li S, Zheng X and Xie L: MicroRNA-101 suppresses
motility of bladder cancer cells by targeting c-Met. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 435:82–87. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang JG, Guo JF, Liu DL, Liu Q and Wang
JJ: MicroRNA-101 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in non-small
cell lung cancer through directly targeting enhancer of zeste
homolog 2. J Thorac Oncol. 6:671–678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J, Han C, Zhu H, Song K and Wu T:
miR-101 inhibits cholangiocarcinoma angiogenesis through targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Am J Pathol.
182:1629–1639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Li L, Guo R, Li X, Lu Y, Guan X,
Gitau SC, Wang L, Xu C, Yang B and Shan H: miR-101 promotes breast
cancer cell apoptosis by targeting janus kinase 2. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:413–422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y
and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular
carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer
Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Guo X, Xiong L, Kong X, Xu Y, Liu
C, Zou L, Li Z, Zhao J and Lin N: MicroRNA-101 suppresses
SOX9-dependent tumorigenicity and promotes favorable prognosis of
human hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 586:4362–4370. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Ren K, Zhao G, Yan K and
Ma B: MicroRNA-101 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
downregulation of EZH2 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:2143–2149.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barsotti AM, Ryskin M, Zhong W, Zhang WG,
Giannakou A, Loreth C, Diesl V, Follettie M, Golas J, Lee M, et al:
Epigenetic reprogramming by tumor-derived EZH2 gain-of-function
mutations promotes aggressive 3D cell morphologies and enhances
melanoma tumor growth. Oncotarget. 6:2928–2938. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koumangoye RB, Andl T, Taubenslag KJ,
Zilberman ST, Taylor CJ, Loomans HA and Andl CD: SOX4 interacts
with EZH2 and HDAC3 to suppress microRNA-31 in invasive esophageal
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 14:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Geng J, Li X, Zhou Z, Wu CL, Dai M and Bai
X: EZH2 promotes tumor progression via regulating VEGF-A/AKT
signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 359:275–287.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Shahryari V, Deng G,
Nakajima K, Tabatabai ZL, Ishii N and Dahiya R: Long noncoding RNA
MALAT1 promotes aggressive renal cell carcinoma through Ezh2 and
interacts with miR-205. Cancer Res. 75:1322–1331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kottakis F, Polytarchou C, Foltopoulou P,
Sanidas I, Kampranis SC and Tsichlis PN: FGF-2 regulates cell
proliferation, migration and angiogenesis through an
NDY1/KDM2B-miR-101-EZH2 pathway. Mol Cell. 43:285–298. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Xiang W, Wang M, Huang T, Xiao X,
Wang L, Tao D, Dong L, Zeng F and Jiang G: Methyl jasmonate
sensitizes human bladder cancer cells to gambogic acid-induced
apoptosis through down-regulation of EZH2 expression by miR-101. Br
J Pharmacol. 171:618–635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caputto BL, Cardozo Gizzi AM and Gil GA:
c-Fos: An AP-1 transcription factor with an additional cytoplasmic,
non-genomic lipid synthesis activation capacity. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1841:1241–1246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao HQ, Peng Y, Zhong ZZ, He HX and Li ZH:
Association of the expressions of platelet-derived growth factor
receptor and c-Fos with the biological characteristics of bladder
cancer. Acad J First Med Coll PLA. 24:177–179. 2004.
|
|
26
|
Li S, Xu X, Xu X, Hu Z, Wu J, Zhu Y, Chen
H, Mao Y, Lin Y, Luo J, et al: MicroRNA-490-5p inhibits
proliferation of bladder cancer by targeting c-Fos. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 441:976–981. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|