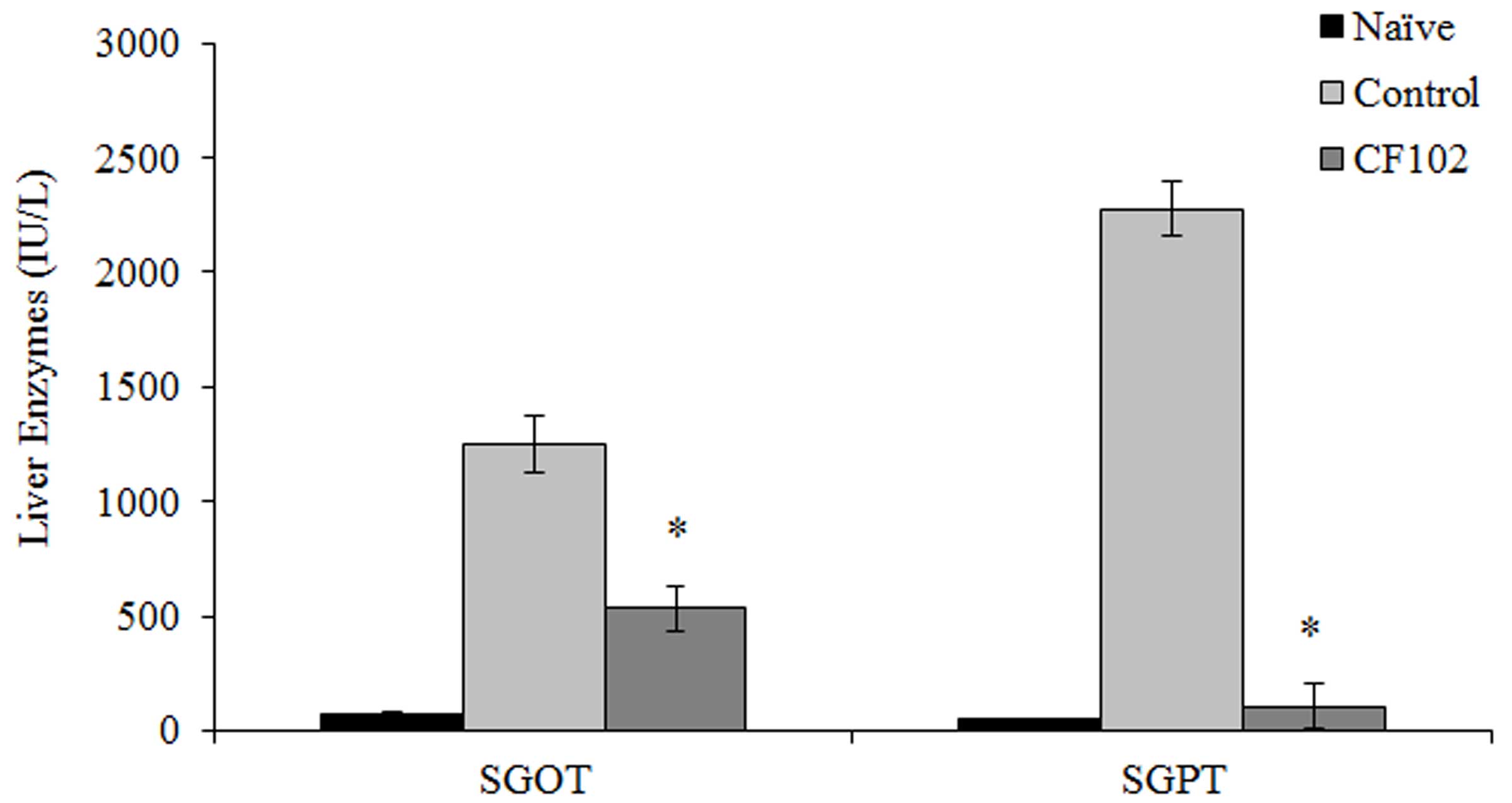
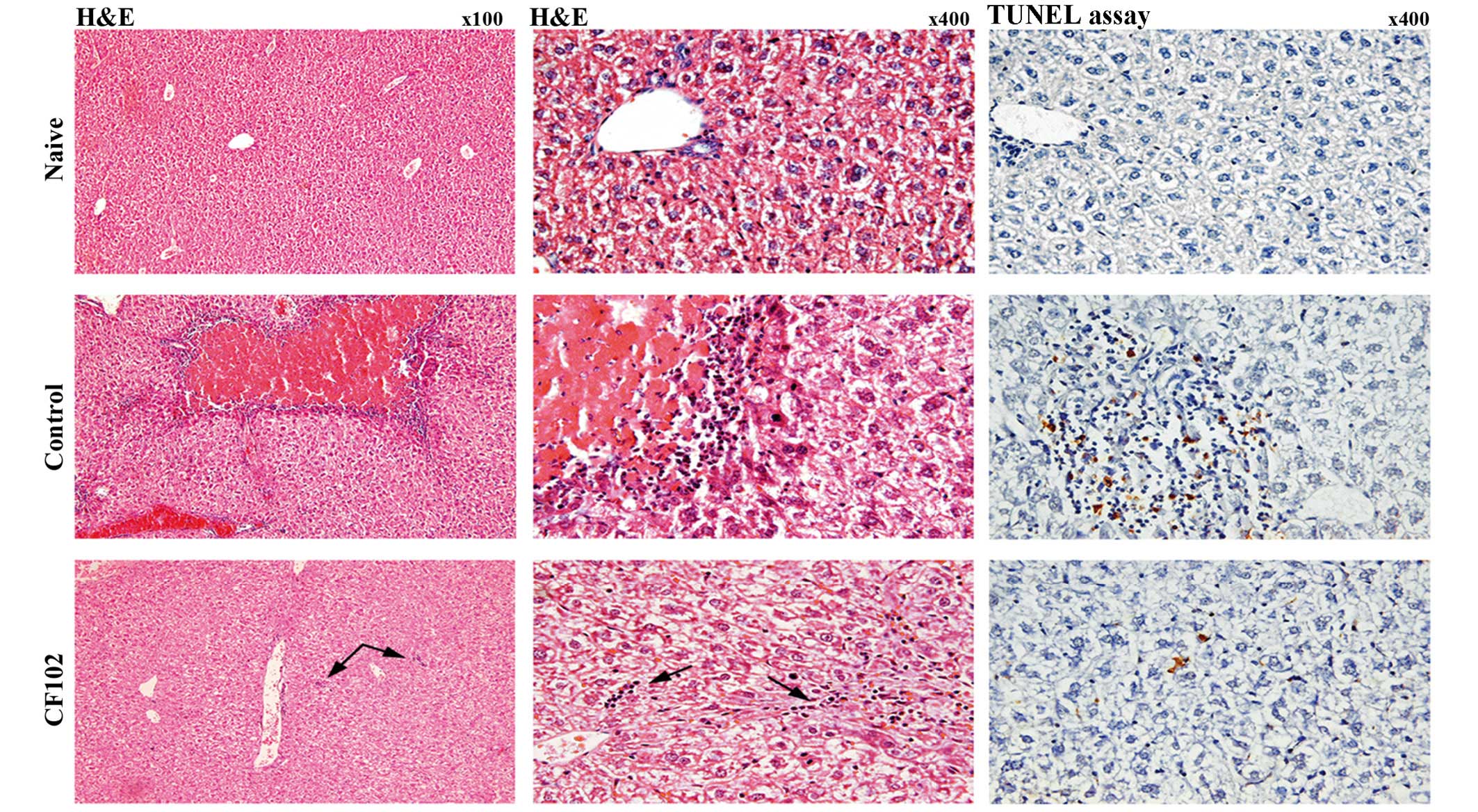
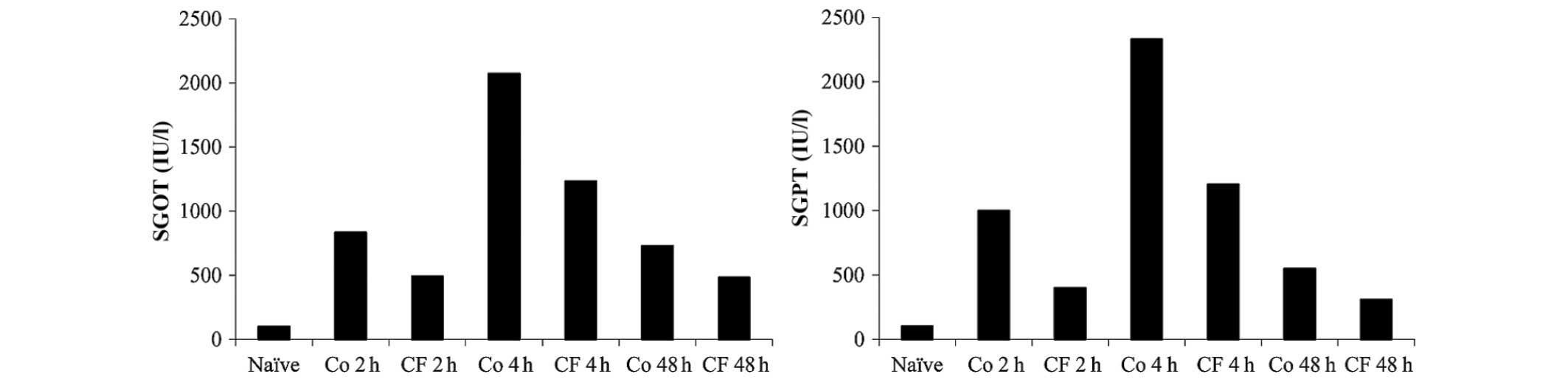
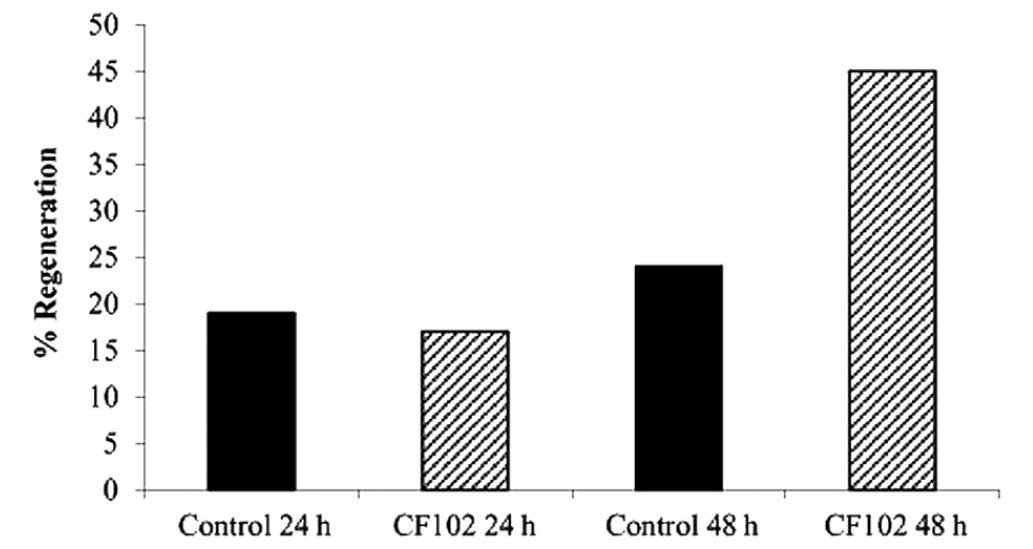
|
1
|
Lentsch AB, Atsushi K, Yoshidome H,
MacMasters KM and Edwards MJ: Inflammatory mechanisms and
therapeutic strategies for warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Hepatology. 32:169–173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Mediator of
physiological and pathophysiological response to hypoxia. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 88:1474–1480. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li C and Jackson RM: Reactive species
mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 282:C227–C241. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jaeschke H: Mechanisms of reperfusion
injury after warm ischemia of the liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Surg. 5:402–408. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okuaki Y, Miyazaki H, Zeniya M, Ishikawa
T, Ohkawa Y, Teuno S, Sakaguchi M, Hara M, Takahashi H and Toda G:
Splenectomy-reduced hepatic injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion
in the rat. Liver. 16:188–194. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zwacka RM, Zhang Y, Halldorson J,
Schlossberg H, Dudus L and Ehgelhardt JF: CD4(+)
T-lymphocytes mediate ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory
responses in mouse liver. J Clin Invest. 100:279–289. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu P, McGuire GM, Fischer MA, Farhood A,
Smith CW and Jaeschke H: Activation of Kupffer cells and
neutrophils for reactive oxygen formation is responsible for
endotoxin-enhanced liver injury after hepatic ischemia. Shock.
3:56–62. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao W, Bentely RC, Madden JF and Clavien
PA: Apoptosis of sinusoidal endothelial cells is a critical
mechanism of prevention of injury in rat liver transplantation.
Hepatology. 27:1652–1660. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cursio R, Gugenheim J, Ricci JE, Crenesse
D, Rostagno P, Maulon L, Saint-Paul MC, Ferrua B and Auberger AP: A
caspase inhibitor fully protects rats against lethal normothermic
liver ischemia by inhibition of liver apoptosis. FASEB J.
13:253–261. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kohli V, Selzner M, Madden JF, Bentley RC
and Clavien PA: Endothelial cell and hepatocyte deaths occur by
apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat liver.
Transplantation. 67:1099–1105. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murry CE, Jenning RB and Reimer KA:
Preconditioning with ischemia: A delay of lethal cell injury in
ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 74:1124–1136. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Teoh NC and Farrell GC: Hepatic ischemia
reperfusion injury: Pathogenic mechanisms and basis for
hepatoprotection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:891–902. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peralta C, Closa D, Xaus C, Gelpi E,
Roselló-Catafau J and Hotter G: Hepatic preconditioning in rats is
defined by a balance of adenosine and xanthine. Hepatology.
28:768–773. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Teoh N, Pena A Dela and Farrel G: Hepatic
ischemia preconditioning in mice is associated with activation of
NF-kappaB, p38 kinase, and cell cycle entry. Hepatology. 36:94–102.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gross ER, Hsu AK and Gross GJ:
Opioid-induced cardioprotection occurs via glycogen synthase kinase
beta inhibition during reperfusion in intact rat hearts. Circ Res.
94:960–966. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vaughn BP, Robson SC and Longhi MS:
Purinergic signaling in liver disease. Dig Dis. 32:516–24. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun X, Imai M, Nowak-Machen M,
Guckelberger O, Enjyoj K, Wu Y, Khalpey Z, Berberat P, Munasinghe J
and Robson SC: Liver damage and systemic inflammatory responses are
exacerbated by the genetic deletion of CD39 in total hepatic
ischemia. Purinergic Signal. 7:427–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Black RG Jr, Guo Y, Ge ZD, Murphree SS,
Prabhu SD, Jones WK, Bolli R and Auchampach JA: Gene
dosage-dependent effects of cardiac-specific overexpression of the
A3 adenosine receptor. Circ Res. 91:165–172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cross HR, Murphy E, Black RG, Auchampach J
and Steenbergen C: Overexpression of A(3) adenosine receptors
decreases heart rate, preserves energetics, and protects ischemic
hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 283:H1562–H1568. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matot I, Weiniger CF, Zeira E, Galun E,
Joshi BV and Jacobson KA: A3 adenosine receptors and
mitogen-activated protein kinases in lung injury following in vivo
reperfusion. Crit Care. 10:R652006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen GJ, Harvey BK, Shen H, Chou J, Victor
A and Wang Y: Activation of A3 adenosine receptors reduces ischemic
brain injury in rodents. J Neurosci Res. 84:1848–1855. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Borea PA, Varani K, Vincenzi F, Baraldi
PG, Tabrizi MA, Merighi S and Gessi S: The A3 adenosine receptor:
History and perspectives. Pharmacol Rev. 67:74–102. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fishman P, Bar-Yehuda S, Ohana G, Barer F,
Ochaion A, Erlanger A and Madi L: An agonist to the A3 adenosine
receptor inhibits colon carcinoma growth in mice via modulation of
GSK-3 beta and NF-kappa B. Oncogene. 23:2465–2471. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fishman P, Madi L, Bar-Yehuda S, Barer F,
Del Valle L and Khalili K: Evidence for involvement of Wnt
signaling pathway in IB-MECA mediated suppression of melanoma
cells. Oncogene. 21:4060–4064. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hanada T and Yoshimura A: Regulation of
cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
13:413–421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fishman P, Bar-Yehuda S, Madi L,
Rath-Wolfson L, Ochaion A, Cohen S and Baharav E: The PI3K-NF-kappa
B signal transduction pathway is involved in mediating the
anti-inflammatory effect of IB-MECA in adjuvant-induced arthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 8:R332006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shackelford RE, Alford BP, Xue Y, Thai SF,
Adams DO and Pizzo S: Aspirin inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha
gene expression in murine tissue macrophages. Mol Pharmacol.
52:421–429. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ohana G, Bar-Yehuda S, Barer F and Fishman
P: Differential effect of adenosine on tumor and normal cell
growth: Focus on the A3 adenosine receptor. J Cell Physiol.
186:19–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cohen S, Stemmer SM, Zozulya G, Ochaion A,
Patoka R, Barer F, Bar-Yehuda S, Rath-Wolfson L, Jacobson KA and
Fishman P: CF102 an A3 adenosine receptor agonist mediates
anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory effects in the liver. J Cell
Physiol. 226:2438–2447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Higgins G and Anderson R: Experimental
pathology of the liver: restoration of the liver of the white rat
following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol. 12:186–202.
1931.
|
|
31
|
Kogure K, Zhang YQ, Shibata H and Kojima
I: Immediate onset of DNA synthesis in remnant rat liver after 90%
hepatectomy by administration of follistatin. J Hepatol.
29:977–984. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Selzner M and Clavien PA: Failure of
regeneration of the steatotic rat liver: Disruption at two
different levels in the regeneration pathway. Hepatology. 31:35–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Auchampach JA, Ge ZD, Wan TC, Moore J and
Gross GJ: A3 adenosine receptor agonist IB-MECA reduces myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in dogs. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 285:H607–H613. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fishman P, Bar-Yehuda S, Barer F, Madi L,
Multani AS and Pathak S: The A3 adenosine receptor as a new target
for cancer therapy and chemoprotection. Exp Cell Res. 269:230–236.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maddock HL, Mocanu MM and Yellon DM:
Adenosine A(3) receptor activation protects the myocardium from
reperfusion/reoxygenation injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
283:H1307–H1313. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rivo J, Zeira E, Galun E and Matot I:
Activation of A3 adenosine receptors provides lung protection
against ischemia reperfusion injury associated with reduction in
apoptosis. Am J Transplant. 4:1941–1948. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacobson KA, Hoffmann C, Cattabeni F and
Abbracchio MP: Adenosine-induced cell death: Evidence for
receptor-mediated signaling. Apoptosis. 4:197–211. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abbracchio MP, Ceruti S, Brambilla R,
Franceschi C, Malorni W, Jacobson KA, von Lubitz DK and Cattabeni
F: Modulation of apoptsis by adenosine in the central nervous
system: A possible role for the A3 adenosine receptor.
Pathophysiological significance and therapeutic implications for
neurodegenerative disorders. Ann NY Acad Sci. 825:11–22. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Borghi-Scoazec G, Scoazec JY, Durand F,
Bernuau J, Belghiti J, Feldmann G, Henin D and Degott C: Apoptosis
after ischemia-reperfusion in human liver allografts. Liver Transpl
Surg. 3:407–415. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang BH, Gong DZ and Mei MH: Protection
of regenerating liver after partial hepatectomy from carbon
tetrachloride hepatotoxicity in rats: Role of hepatic stimulator
substance. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:1010–1017. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|