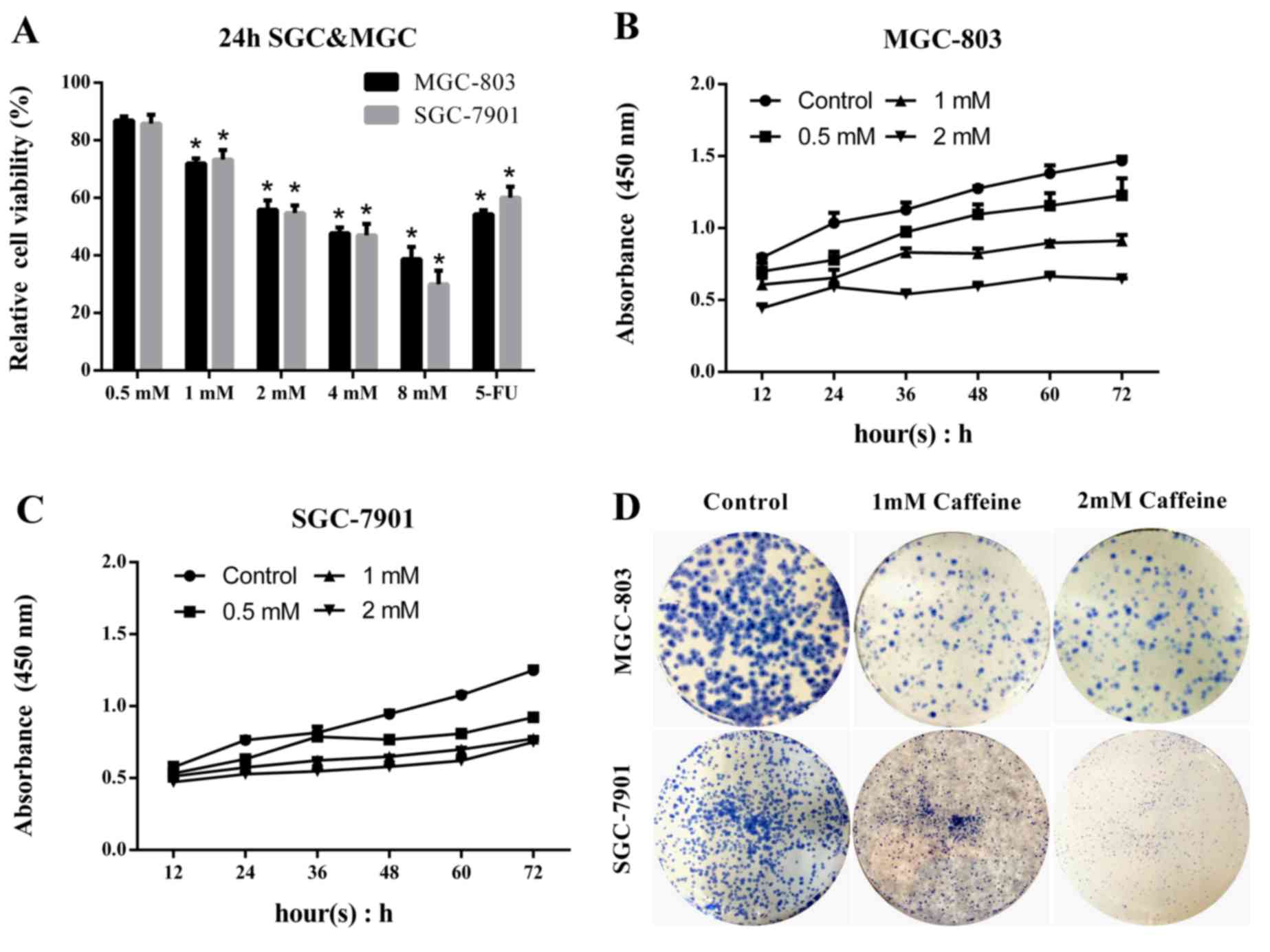
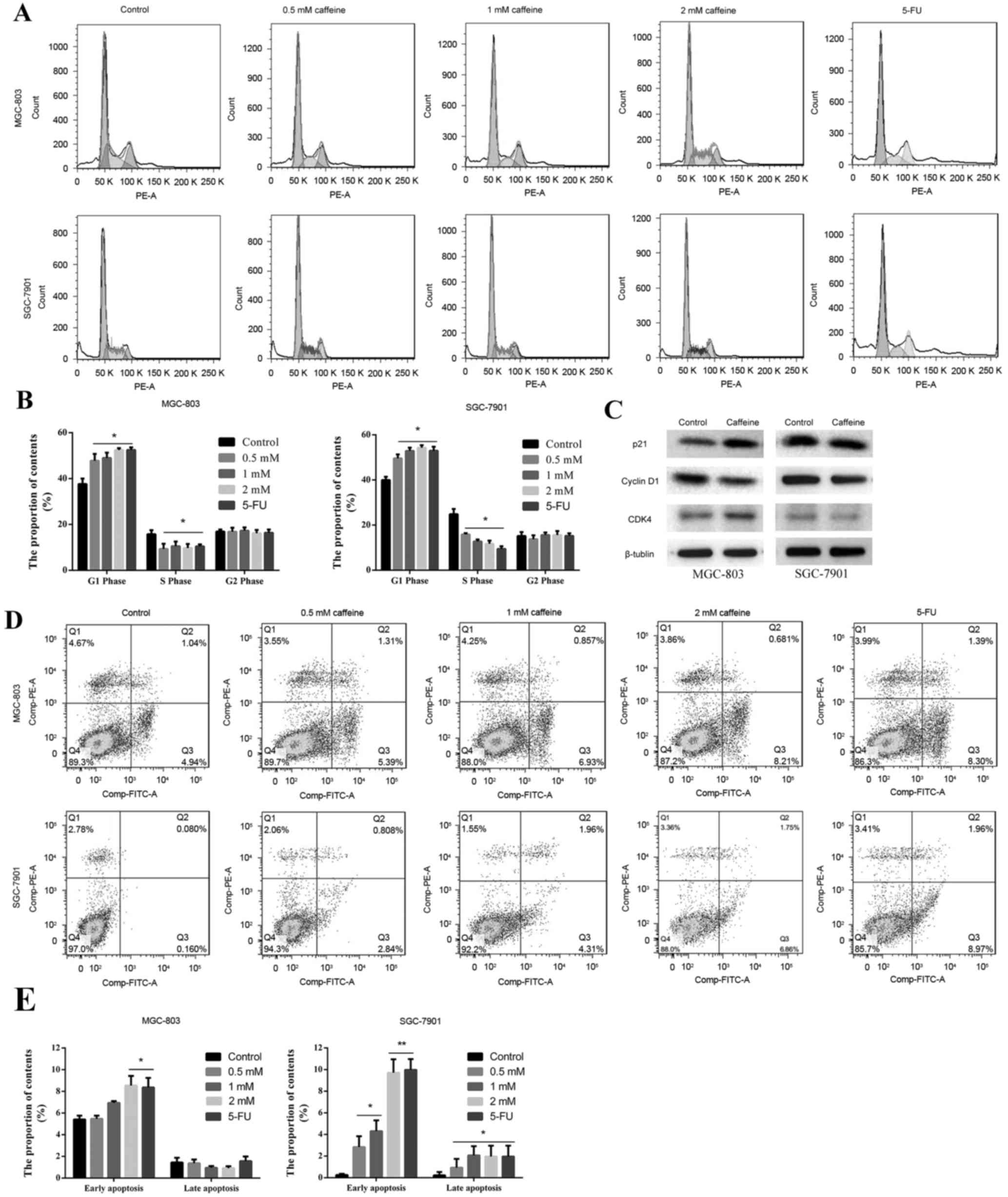
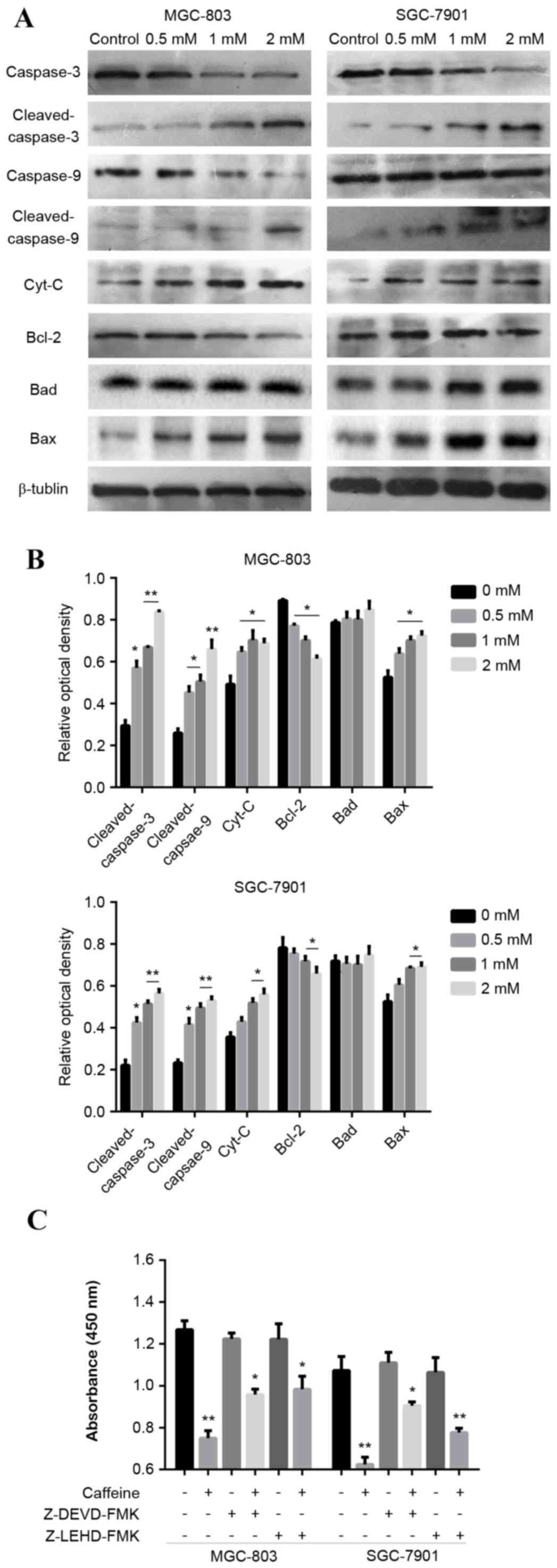
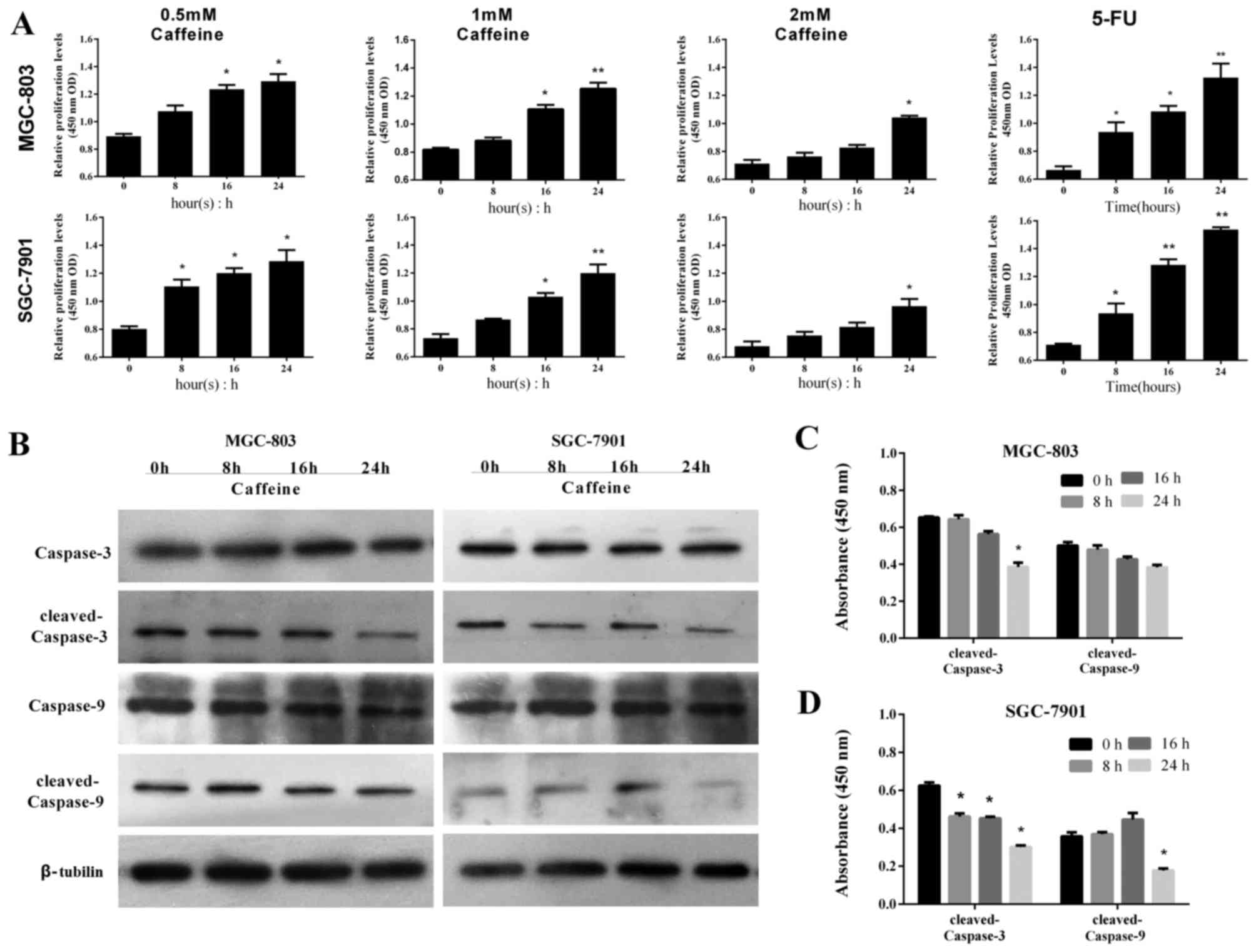
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Danaei G, Vander Hoorn S, Lopez AD, Murray
CJ, Ezzati M, et al: Comparative Risk Assessment collaborating
group (Cancers): Causes of cancer in the world: Comparative risk
assessment of nine behavioural and environmental risk factors.
Lancet. 366:1784–1793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olefson S and Moss SF: Obesity and related
risk factors in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Gastric Cancer.
18:23–32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura
N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N and Schlemper RJ:
Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric
cancer. N Engl J Med. 345:784–789. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi J, Qu YP and Hou P: Pathogenetic
mechanisms in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 20:13804–1319.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim B, Srivastava SK and Kim SH: Caspase-9
as a therapeutic target for treating cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 19:113–127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goldstein A, Kaizer S and Warren R:
Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. II. Alertness, psychomotor
coordination, and mood. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 150:146–151.
1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arnaud MJ: The pharmacology of caffeine.
Prog Drug Res. 31:273–313. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dunwiddie TV: Interactions between the
effects of adenosine and calcium on synaptic responses in rat
hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 350:545–559. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Keefe JH, Bhatti SK, Patil HR,
DiNicolantonio JJ, Lucan SC and Lavie CJ: Effects of habitual
coffee consumption on cardiometabolic disease, cardiovascular
health, and all-cause mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 62:1043–1051.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wilson DF: Effects of caffeine on
neuromuscular transmission in the rat. Am J Physiol. 225:862–865.
1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rousseau E, Ladine J, Liu QY and Meissner
G: Activation of the Ca2+ release channel of skeletal
muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum by caffeine and related compounds.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 267:75–86. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bessler H, Salman H, Bergman M and
Djaldetti M: Caffeine alters cytokine secretion by PBMC induced by
colon cancer cells. Cancer Invest. 30:87–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bode AM and Dong Z: The enigmatic effects
of caffeine in cell cycle and cancer. Cancer Lett. 247:26–39. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Conney AH, Zhou S, Lee MJ, Xie JG, Yang
CS, Lou YR and Lu Y: Stimulatory effect of oral administration of
tea, coffee or caffeine on UVB-induced apoptosis in the epidermis
of SKH-1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 224:209–213. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ku BM, Lee YK, Jeong JY, Ryu J, Choi J,
Kim JS, Cho YW, Roh GS, Kim HJ, Cho GJ, et al: Caffeine inhibits
cell proliferation and regulates PKA/GSK3beta pathways in U87MG
human glioma cells. Mol Cells. 31:275–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miwa S, Sugimoto N, Shirai T, Hayashi K,
Nishida H, Ohnari I, Takeuchi A, Yachie A and Tsuchiya H: Caffeine
activates tumor suppressor PTEN in sarcoma cells. Int J Oncol.
39:465–472. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hashimoto T, He Z, Ma WY, Schmid PC, Bode
AM, Yang CS and Dong Z: Caffeine inhibits cell proliferation by
G0/G1 phase arrest in JB6 cells. Cancer Res. 64:3344–3349. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Okano J, Nagahara T, Matsumoto K and
Murawaki Y: Caffeine inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer
cells and activates the MEK/ERK/EGFR signalling pathway. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 102:543–551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Al-Ansari MM and Aboussekhra A: Caffeine
mediates sustained inactivation of breast cancer-associated
myofibroblasts via up-regulation of tumor suppressor genes. PLoS
One. 9:e909072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rosendahl AH, Perks CM, Zeng L, Markkula
A, Simonsson M, Rose C, Ingvar C, Holly JM and Jernström H:
Caffeine and caffeic acid inhibit growth and modify estrogen
receptor and insulin-like growth factor I receptor levels in human
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1877–1887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu JD, Song LJ, Yan DJ, Feng YY, Zang YG
and Yang Y: Caffeine inhibits the growth of glioblastomas through
activating the caspase-3 signaling pathway in vitro. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 19:3080–3038. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsuoka S, Moriyama T, Ohara N, Tanimura
K and Maruo T: Caffeine induces apoptosis of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells through the caspase-9 pathway. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 22:48–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morgan ME and Vestal RE: Methylxanthine
effects on caudate dopamine release as measured by in vivo
electrochemistry. Life Sci. 45:2025–39. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Degubareff T and Sleator W Jr: Effects of
caffeine on mammalian atrial muscle, and its interaction with
adenosine and calcium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 148:202–214.
1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Solinas M, Ferré S, You ZB, Karcz-Kubicha
M, Popoli P and Goldberg SR: Caffeine induces dopamine and
glutamate release in the shell of the nucleus accumbens. J
Neurosci. 22:6321–6324. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Daly JW, Bruns RF and Snyder SH: Adenosine
receptors in the central nervous system: Relationship to the
central actions of methylxanthines. Life Sci. 28:2083–2097. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jarvis MJ: Does caffeine intake enhance
absolute levels of cognitive performance? Psychopharmacology
(Berl). 110:45–52. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Corley J, Jia X, Kyle JA, Gow AJ, Brett
CE, Starr JM, McNeill G and Deary IJ: Caffeine consumption and
cognitive function at age 70: The Lothian Birth Cohort 1936 study.
Psychosom Med. 72:206–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lindsay J, Laurin D, Verreault R, Hébert
R, Helliwell B, Hill GB and McDowell I: Risk factors for
Alzheimer's disease: A prospective analysis from the Canadian Study
of Health and Aging. Am J Epidemiol. 156:445–453. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen ZX: Brain cholinesterases: II. The
molecular and cellular basis of Alzheimer's disease. Med
Hypotheses. 63:308–321. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ross GW, Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, Morens
DM, Grandinetti A, Tung KH, Tanner CM, Masaki KH, Blanchette PL,
Curb JD, et al: Association of coffee and caffeine intake with the
risk of Parkinson disease. JAMA. 283:2674–2679. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Johnson-Kozlow M, Kritz-Silverstein D,
Barrett-Connor E and Morton D: Coffee consumption and cognitive
function among older adults. Am J Epidemiol. 156:842–850. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ferreira DD, Stutz B, de Mello FG, Reis RA
and Kubrusly RC: Caffeine potentiates the release of GABA mediated
by NMDA receptor activation: Involvement of A1 adenosine receptors.
Neuroscience. 281:208–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hursel R and Westerterp-Plantenga MS:
Catechin- and caffeine-rich teas for control of body weight in
humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 98:(6 Suppl). S1682–S1693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
van Dam RM and Feskens EJ: Coffee
consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet.
360:1477–1478. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tuomilehto J, Hu G, Bidel S, Lindström J
and Jousilahti P: Coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes
mellitus among middle-aged Finnish men and women. JAMA.
291:1213–1219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Salazar-Martinez E, Willett WC, Ascherio
A, Manson JE, Leitzmann MF, Stampfer MJ and Hu FB: Coffee
consumption and risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med.
140:1–8. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sartorelli DS, Fagherazzi G, Balkau B,
Touillaud MS, Boutron-Ruault MC, de Lauzon-Guillain B and
Clavel-Chapelon F: Differential effects of coffee on the risk of
type 2 diabetes according to meal consumption in a French cohort of
women: The E3N/EPIC cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 91:1002–1012.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carlsson S, Hammar N, Grill V and Kaprio
J: Coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in Finnish twins.
Int J Epidemiol. 33:616–617. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hamer M, Witte DR, Mosdøl A, Marmot MG and
Brunner EJ: Prospective study of coffee and tea consumption in
relation to risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus among men and women:
The Whitehall II study. Br J Nutr. 100:1046–1053. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Akash MS, Rehman K and Chen S: Effects of
coffee on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition. 30:755–763. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheng YC, Ding YM, Hueng DY, Chen JY and
Chen Y: Caffeine suppresses the progression of human glioblastoma
via cathepsin B and MAPK signaling pathway. J Nutr Biochem.
33:63–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hashibe M, Galeone C, Buys SS, Gren L,
Boffetta P, Zhang ZF and La Vecchia C: Coffee, tea, caffeine
intake, and the risk of cancer in the PLCO cohort. Br J Cancer.
113:809–816. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu S, Han J, Song F, Cho E, Gao X, Hunter
DJ and Qureshi AA: Caffeine intake, coffee consumption and risk of
cutaneous malignant melanoma. Epidemiology. 26:898–908. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dubrez L, Coll JL, Hurbin A, Solary E and
Favrot MC: Caffeine sensitizes human H358 cell line to p53-mediated
apoptosis by inducing mitochondrial translocation and
conformational change of BAX protein. J Biol Chem. 276:38980–38987.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jafari M and Rabbani A: Dose and time
dependent effects of caffeine on superoxide release, cell survival
and DNA fragmentation of alveolar macrophages from rat lung.
Toxicology. 149:101–108. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fernandez MJ, López A and Santa-Maria A:
Apoptosis induced by different doses of caffeine on Chinese hamster
ovary cells. J Appl Toxicol. 23:221–224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ito K, Nakazato T, Miyakawa Y, Yamato K,
Ikeda Y and Kizaki M: Caffeine induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis
via a novel p53-dependent pathway in NB4 promyelocytic leukemia
cells. J Cell Physiol. 196:276–283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Juliano LM, Huntley ED, Harrell PT and
Westerman AT: Development of the caffeine withdrawal symptom
questionnaire: Caffeine withdrawal symptoms cluster into 7 factors.
Drug Alcohol Depend. 124:229–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gong Y, Ren J, Liu K and Tang LM: Tumor
suppressor role of miR-133a in gastric cancer by repressing IGF1R.
World J Gastroenterol. 21:2949–2958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ren J, Huang HJ, Gong Y, Yue S, Tang LM
and Cheng SY: MicroRNA-206 suppresses gastric cancer cell growth
and metastasis. Cell Biosci. 4:262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rossi L, Bonmassar E and Faraoni I:
Modification of miR gene expression pattern in human colon cancer
cells following exposure to 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Pharmacol Res.
56:248–253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T,
Visentini M, Aqeilan R, Cimmino A, Wang H, Sun H, Volinia S, Alder
H, et al: MicroRNA gene expression during retinoic acid-induced
differentiation of human acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene.
26:4148–4157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yiannakopoulou E: Targeting epigenetic
mechanisms and microRNAs by aspirin and other non steroidal
anti-inflammatory agents-implications for cancer treatment and
chemoprevention. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 37:167–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Varma SD and Kovtun S: Protective effect
of caffeine against high sugar-induced transcription of microRNAs
and consequent gene silencing: A study using lenses of galactosemic
mice. Mol Vis. 19:493–500. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang W, Cheng B, Miao L, Mei Y and Wu M:
Mutant p53-R273H gains new function in sustained activation of EGFR
signaling via suppressing miR-27a expression. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Altman RD, Lang AE and Postuma RB:
Caffeine in Parkinson's disease: A pilot open-label,
dose-escalation study. Mov Disord. 26:2427–2431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lee IA, Low D, Kamba A, Llado V and
Mizoguchi E: Oral caffeine administration ameliorates acute colitis
by suppressing chitinase 3-like 1 expression in intestinal
epithelial cells. J Gastroenterol. 49:1206–1216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Guercio BJ, Sato K, Niedzwiecki D, Ye X,
Saltz LB, Mayer RJ, Mowat RB, Whittom R, Hantel A, Benson A, et al:
Coffee intake, recurrence and mortality in stage III colon cancer:
Results from CALGB 89803 (Alliance). J Clin Oncol. 33:3598–3607.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sanikini H, Dik VK, Siersema PD,
Bhoo-Pathy N, Uiterwaal CS, Peeters PH, González CA, Zamora-Ros R,
Overvad K, Tjønneland A, et al: Total, caffeinated and
decaffeinated coffee and tea intake and gastric cancer risk:
Results from the EPIC cohort study. Int J Cancer. 136:E720–E730.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hayashi M, Tsuchiya H, Yamamoto N, Karita
M, Shirai T, Nishida H, Takeuchi A and Tomita K:
Caffeine-potentiated chemotherapy for metastatic carcinoma and
lymphoma of bone and soft tissue. Anticancer Res. 25:2399–2405.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Miwa S, Kitamura S, Shirai T, Hayashi K,
Nishida H, Takeuchi A, Nojima T and Tsuchiya H: Desmoplastic small
round cell tumour successfully treated with caffeine-assisted
chemotherapy: A case report and review of the literature.
Anticancer Res. 30:3769–3774. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|