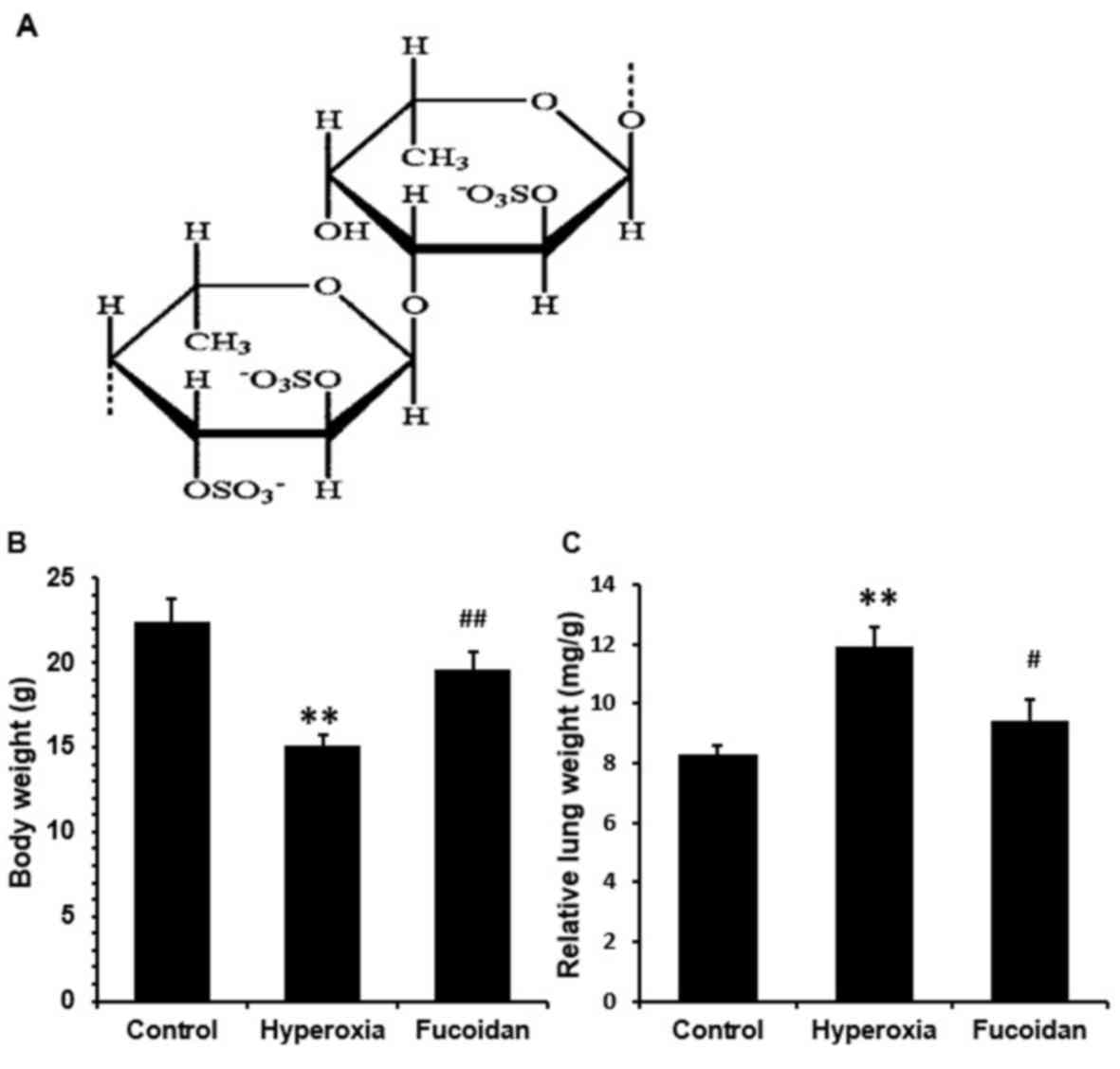
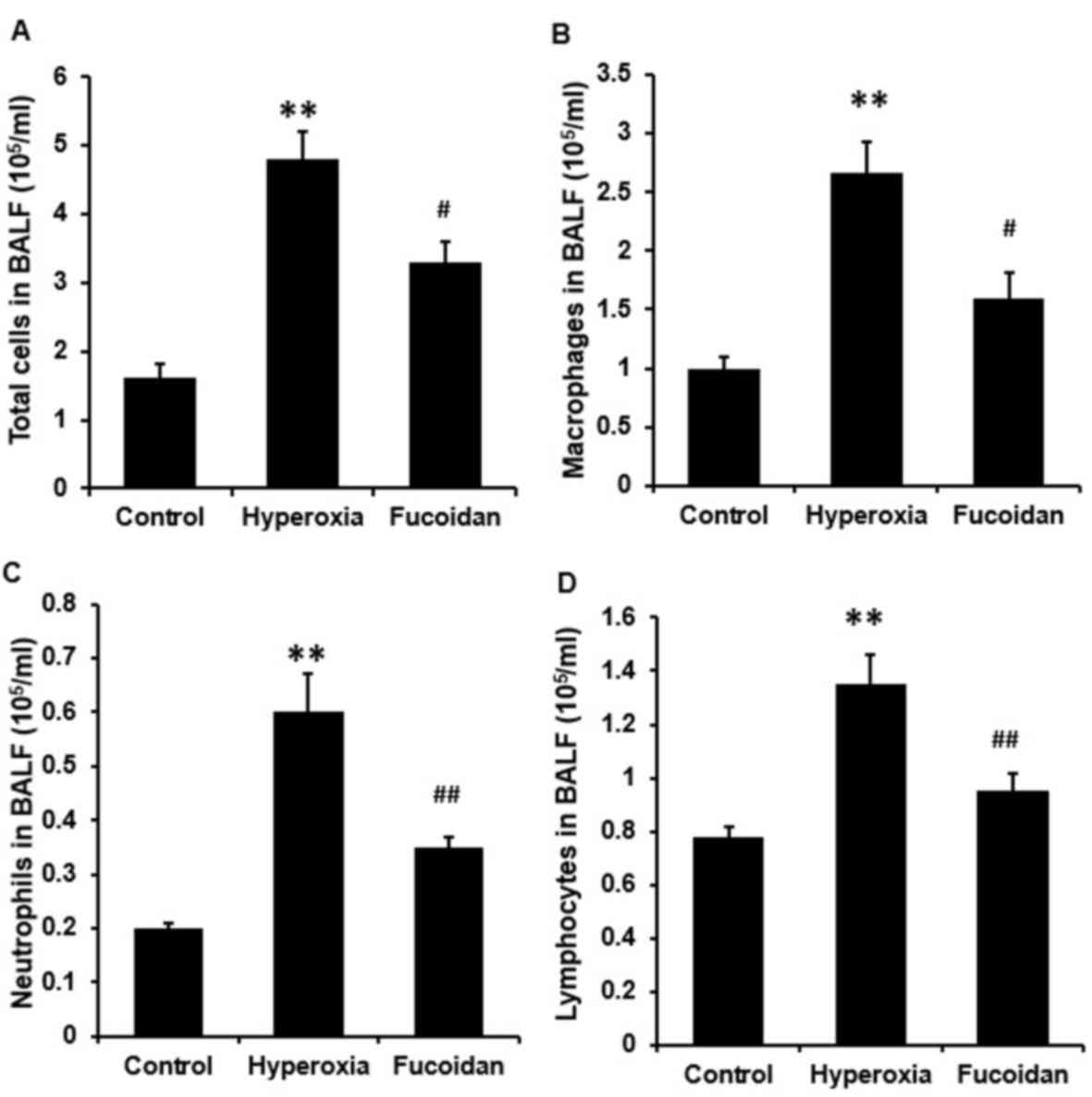
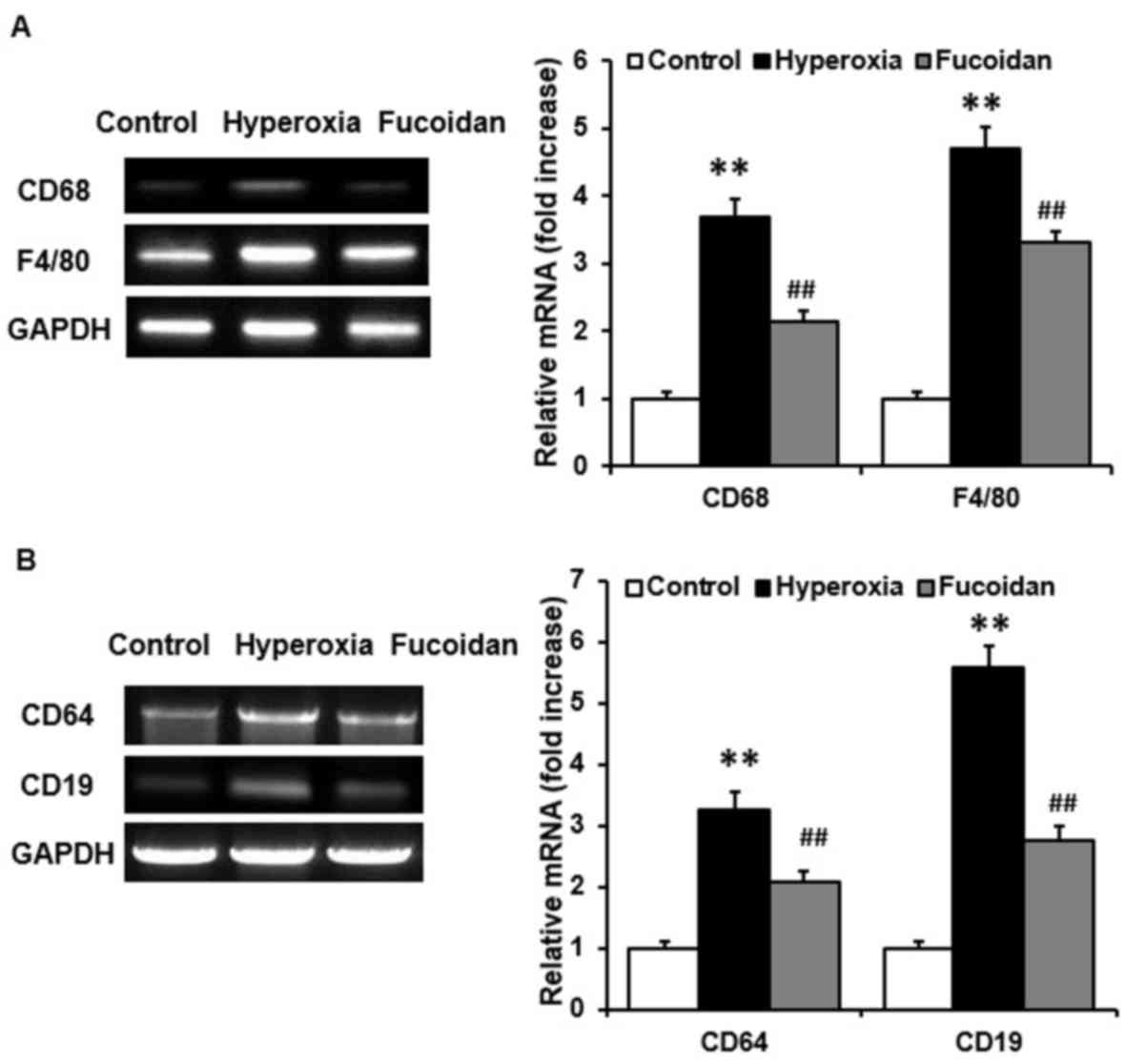
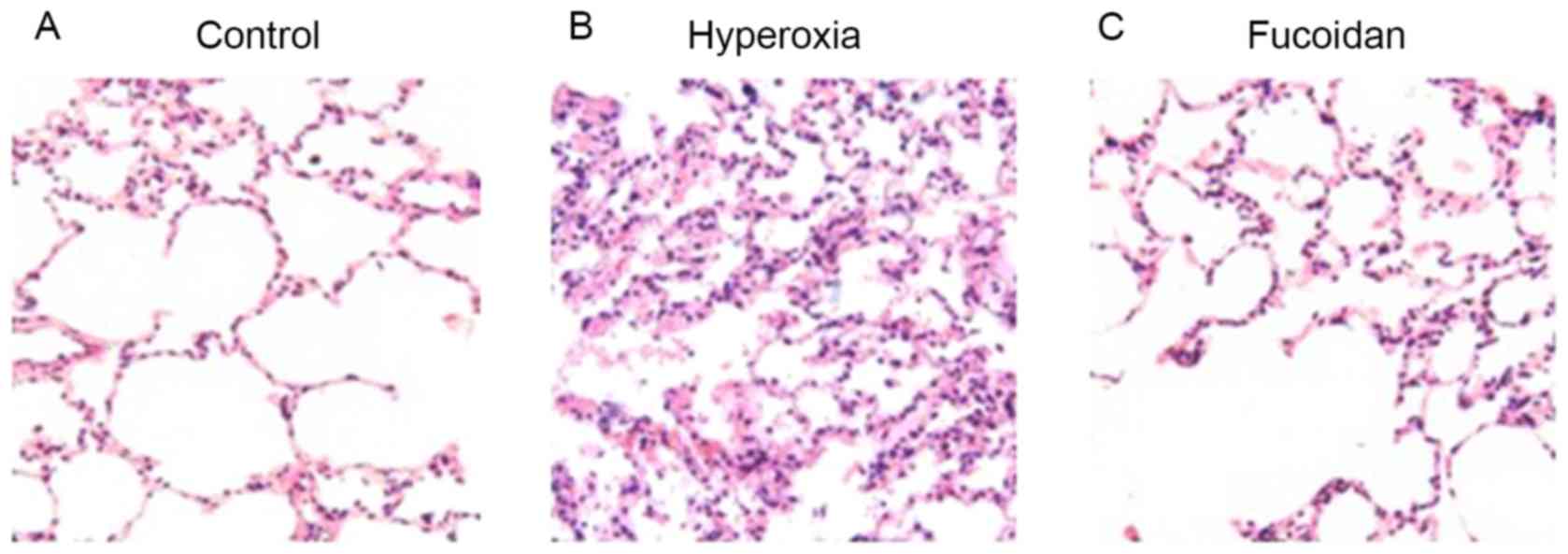
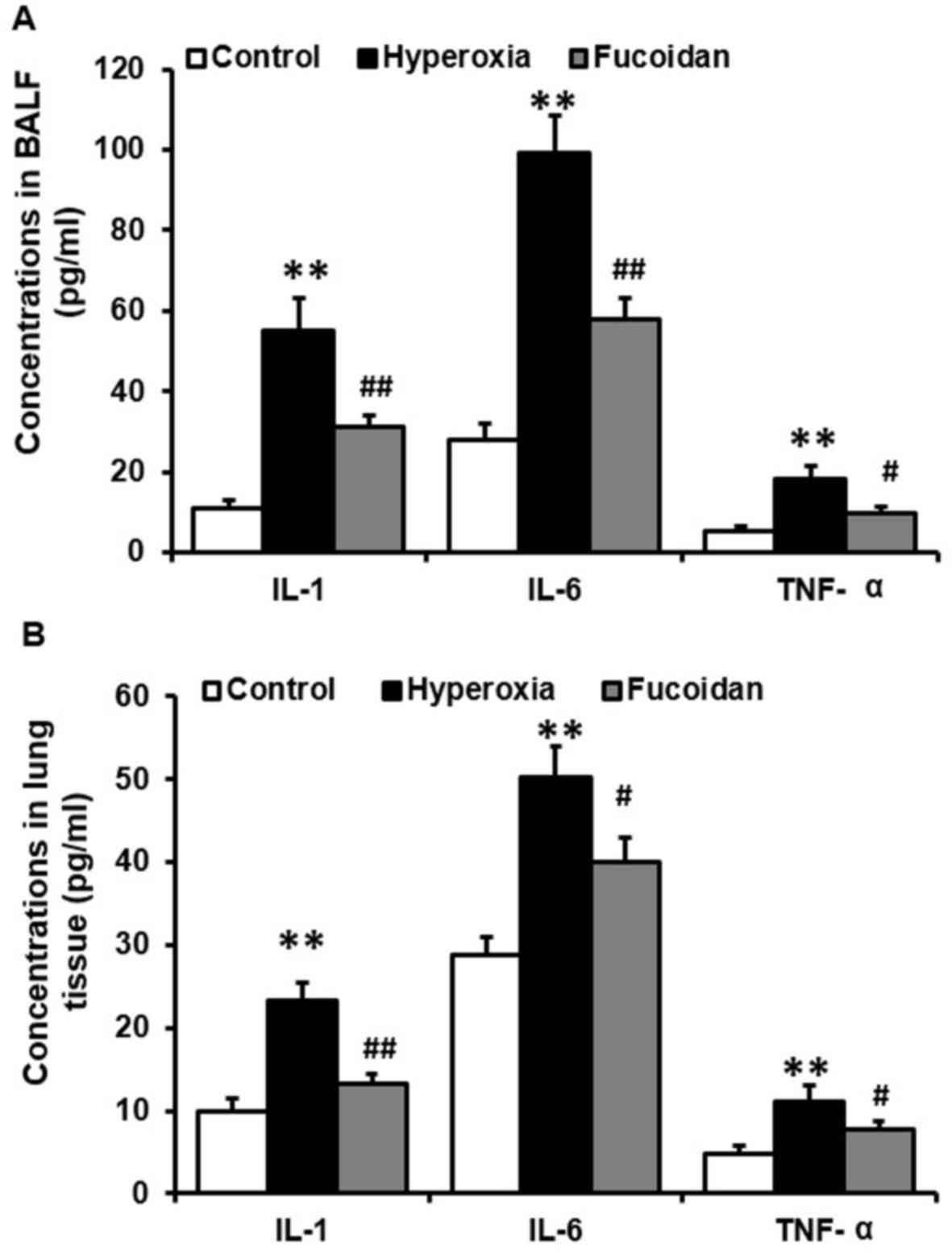
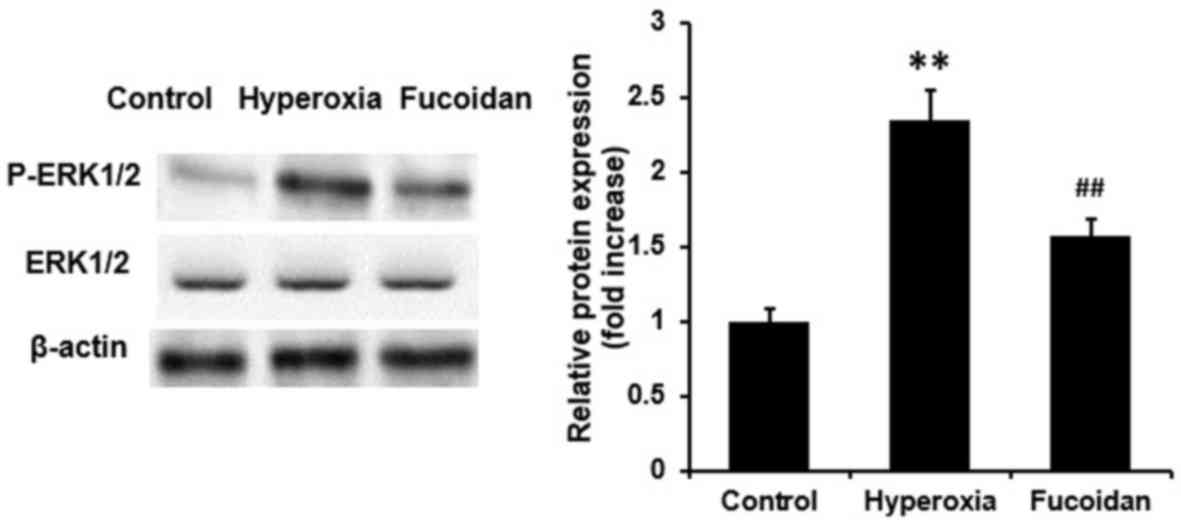
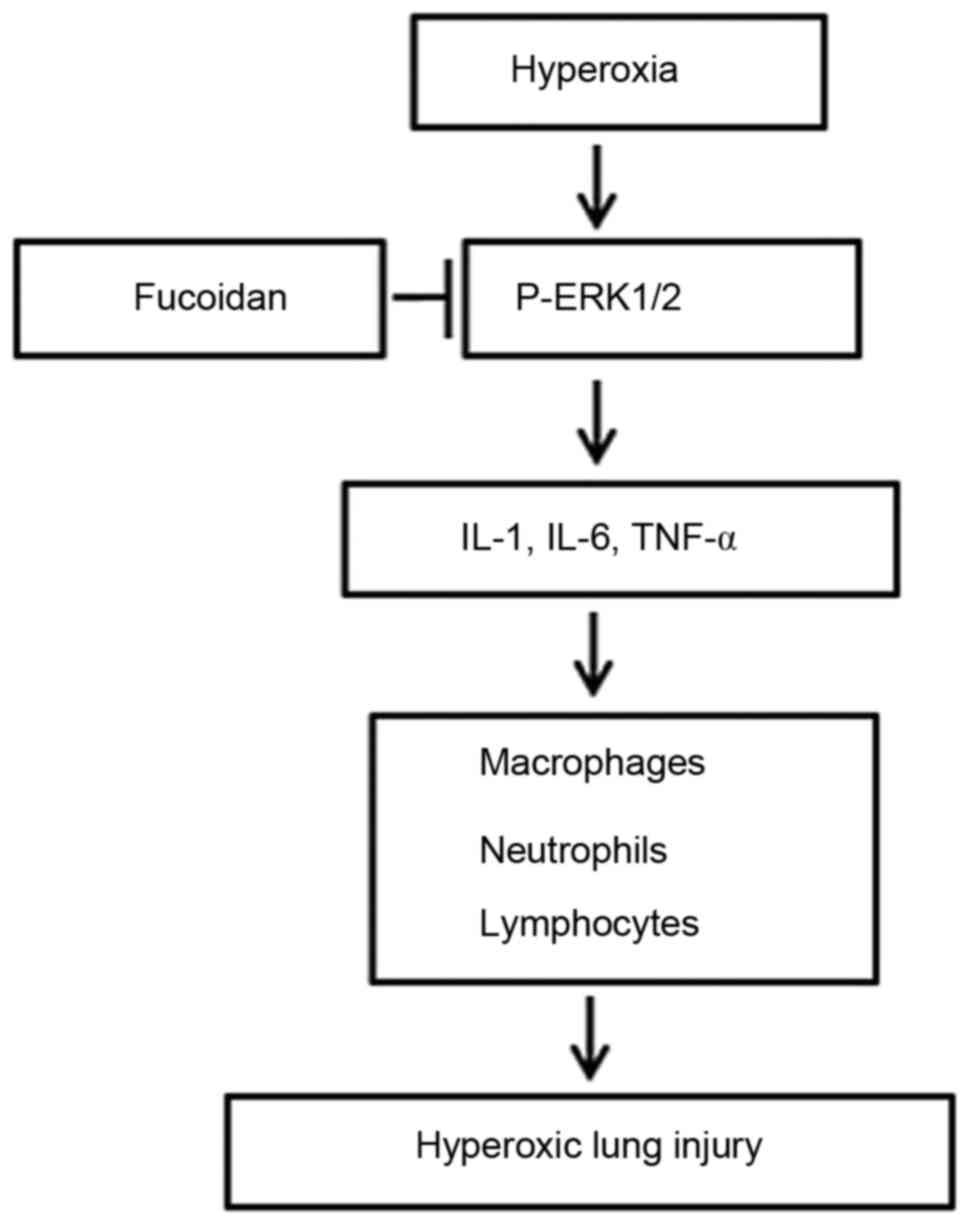
|
1
|
Xu Y, Tian Z and Xie P: Targeting
complement anaphylatoxin C5a receptor in hyperoxic lung injury in
mice. Mol Med Rep. 10:1786–1792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Vitacca M, Bianchi L, Bazza A and Clini
EM: Advanced COPD patients under home mechanical ventilation and/or
long term oxygen therapy: Italian healthcare costs. Monaldi Arch
Chest Dis. 75:207–214. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Panikkanvalappil SR, James M, Hira SM,
Mobley J, Jilling T, Ambalavanan N and El-Sayed MA: Hyperoxia
induces intracellular acidification in neonatal mouse lung
fibroblasts: Real-time investigation using plasmonically enhanced
Raman spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 138:3779–3788. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vosdoganes P, Lim R, Koulaeva E, Chan ST,
Acharya R, Moss TJ and Wallace EM: Human amnion epithelial cells
modulate hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury in mice.
Cytotherapy. 15:1021–1029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
George CL, Fantuzzi G, Bursten S, Leer L
and Abraham E: Effects of lisofylline on hyperoxia-induced lung
injury. Am J Physiol. 276:L776–L785. 1999.
|
|
6
|
Kallet RH and Matthay MA: Hyperoxic acute
lung injury. Respir Care. 58:123–141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Johnson-Varghese L, Brodsky N and Bhandari
V: Effect of antioxidants on apoptosis and cytokine release in
fetal rat Type II pneumocytes exposed to hyperoxia and nitric
oxide. Cytokine. 28:10–16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fukuhara K, Nakashima T, Abe M, Masuda T,
Hamada H, Iwamoto H, Fujitaka K, Kohno N and Hattori N: Suplatast
tosilate protects the lung against hyperoxic lung injury by
scavenging hydroxyl radicals. Free Radic Biol Med. 106:1–9. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xie P, Fujii I, Zhao J, Shinohara M and
Matsukura M: A novel polysaccharide compound derived from algae
extracts protects retinal pigment epithelial cells from high
glucose-induced oxidative damage in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull.
35:1447–1453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kasai A, Arafuka S, Koshiba N, Takahashi D
and Toshima K: Systematic synthesis of low-molecular weight
fucoidan derivatives and their effect on cancer cells. Org Biomol
Chem. 13:10556–10568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fukahori S, Yano H, Akiba J, Ogasawara S,
Momosaki S, Sanada S, Kuratomi K, Ishizaki Y, Moriya F, Yagi M and
Kojiro M: Fucoidan, a major component of brown seaweed, prohibits
the growth of human cancer cell lines in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
1:537–542. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Li X, Zhao H, Wang Q, Liang H and Jiang X:
Fucoidan protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress via
normalization of reactive oxygen species generation through the
Ca2+-dependent ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
11:3746–3752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Nie M, Lu Y, Wang R, Li J, Yang B,
Xia M, Zhang H and Li X: Fucoidan exerts protective effects against
diabetic nephropathy related to spontaneous diabetes through the
NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Int J Mol Med.
35:1067–1073. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Glotin AL, Calipel A, Brossas JY, Faussat
AM, Tréton J and Mascarelli F: Sustained versus transient ERK1/2
signaling underlies the anti- and proapoptotic effects of oxidative
stress in human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:4614–4623.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, Wang CC, Hong W and
Melendez AJ: VAMP8 is essential in anaphylatoxin-induced
degranulation, TNF-alpha secretion, peritonitis, and systemic
inflammation. J Immunol. 183:1413–1418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Davies J, Karmouty-Quintana H, Le TT, Chen
NY, Weng T, Luo F, Molina J, Moorthy B and Blackburn MR: Adenosine
promotes vascular barrier function in hyperoxic lung injury.
Physiol Rep. 2:pii: e12155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Mikawa K, Nishina K, Maekawa N and Obara
H: Attenuation of hyperoxic lung injury in rabbits with superoxide
dismutase: Effects on inflammatory mediators. Acta Anaesthesiol
Scand. 39:317–322. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Takao Y, Mikawa K, Nishina K, Maekawa N
and Obara H: Lidocaine attenuates hyperoxic lung injury in rabbits.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 40:318–325. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Dolinay T, Wu W, Kaminski N, Ifedigbo E,
Kaynar AM, Szilasi M, Watkins SC, Ryter SW, Hoetzel A and Choi AM:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate susceptibility to
ventilator-induced lung injury. PLoS One. 3:e16012008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Camacho Villarreal JL, Torres Mendoza E,
Cadena C, Prieto J, Varela Prieto LL and DA Torregroza Villanueva:
The use of factorial design, image analysis, and an efficiency
calculation for multiplex PCR optimization. J Clin Lab Anal.
27:249–252. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jiang X, Ma Y, Yu J, Li H and Xie F:
Protective effect of C4a against hyperoxic lung injury via a
macrophage-dependent but not a neutrophil/lymphocyte-dependent
signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:1250–1256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Runzi M, Raptopoulos V, Saluja AK, Kaiser
AM, Nishino H, Gerdes D and Steer ML: Evaluation of necrotizing
pancreatitis in the opossum by dynamic contrast-enhanced computed
tomography: Correlation between radiographic and morphologic
changes. J Am Coll Surg. 180:673–682. 1995.
|
|
24
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tsuruta T, Yamamoto T, Matsubara S,
Nagasawa S, Tanase S, Tanaka J, Takagi K and Kambara T: Novel
function of C4a anaphylatoxin. Release from monocytes of protein
which inhibits monocyte chemotaxis. Am J Pathol. 142:1848–1857.
1993.
|
|
26
|
Matsubara S, Yamamoto T, Tsuruta T, Takagi
K and Kambara T: Complement C4-derived monocyte-directed chemotaxis
inhibitory factor. A molecular mechanism to cause polymorphonuclear
leukocyte-predominant infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis synovial
cavities. Am J Pathol. 138:1279–1291. 1991.
|
|
27
|
Janssen WJ, Barthel L, Muldrow A,
Oberley-Deegan RE, Kearns MT, Jakubzick C and Henson PM: Fas
determines differential fates of resident and recruited macrophages
during resolution of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
184:547–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Zhao Y, Xu H, Yu W and Xie BD: Complement
anaphylatoxin C4a inhibits C5a-induced neointima formation
following arterial injury. Mol Med Rep. 10:45–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Jones SA: Directing transition from innate
to acquired immunity: Defining a role for IL-6. J Immunol.
175:3463–3468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bao JP, Jiang LF, Li J, Chen WP, Hu PF and
Wu LD: Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor
inhibits interleukin-1β-induced catabolic and inflammatory
responses in murine chondrocytes. Mol Med Rep. 10:2191–2197. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wolters PJ, Wray C, Sutherland RE, Kim SS,
Koff J, Mao Y and Frank JA: Neutrophil-derived IL-6 limits alveolar
barrier disruption in experimental ventilator-induced lung injury.
J Immunol. 182:8056–8062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Frank JA, Parsons PE and Matthay MA:
Pathogenetic significance of biological markers of
ventilator-associated lung injury in experimental and clinical
studies. Chest. 130:1906–1914. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Sappino AP
and Vassalli P: Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for
development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature.
344:245–247. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Guillonneau X, Régnier-Ricard F, Dupuis C,
Courtois Y and Mascarelli F: Paracrine effects of phosphorylated
and excreted FGF1 by retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Growth
Factors. 15:95–112. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|