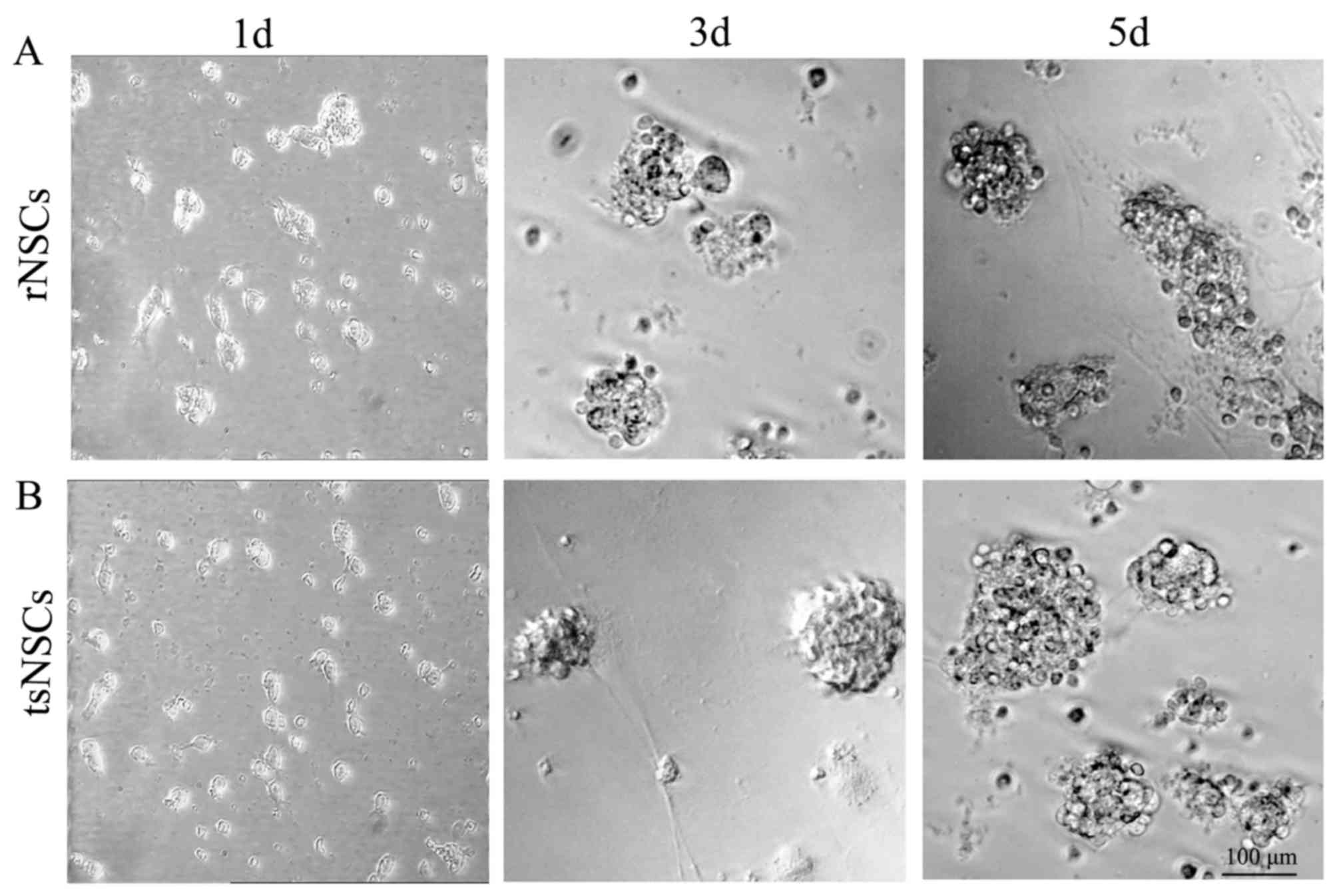
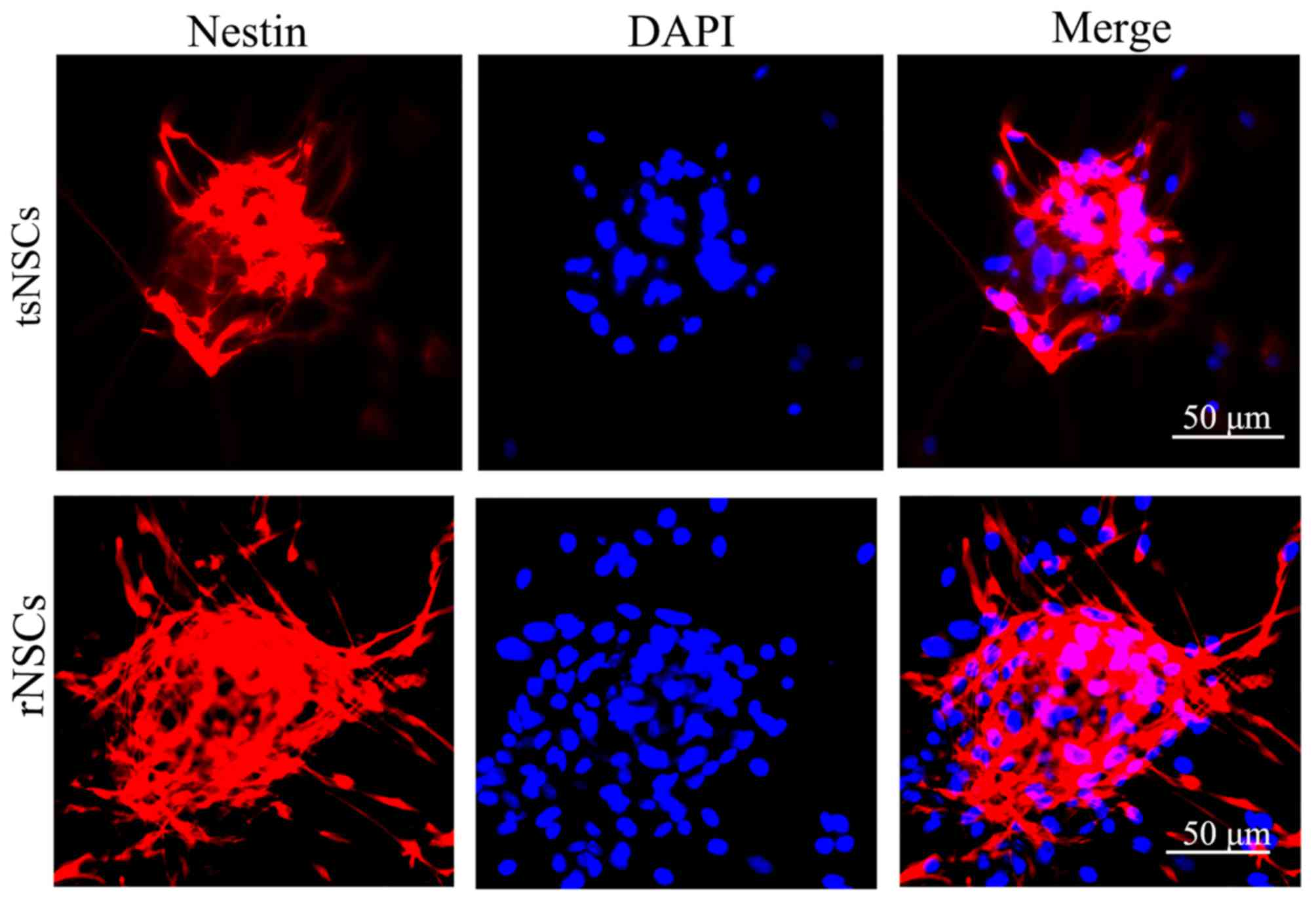
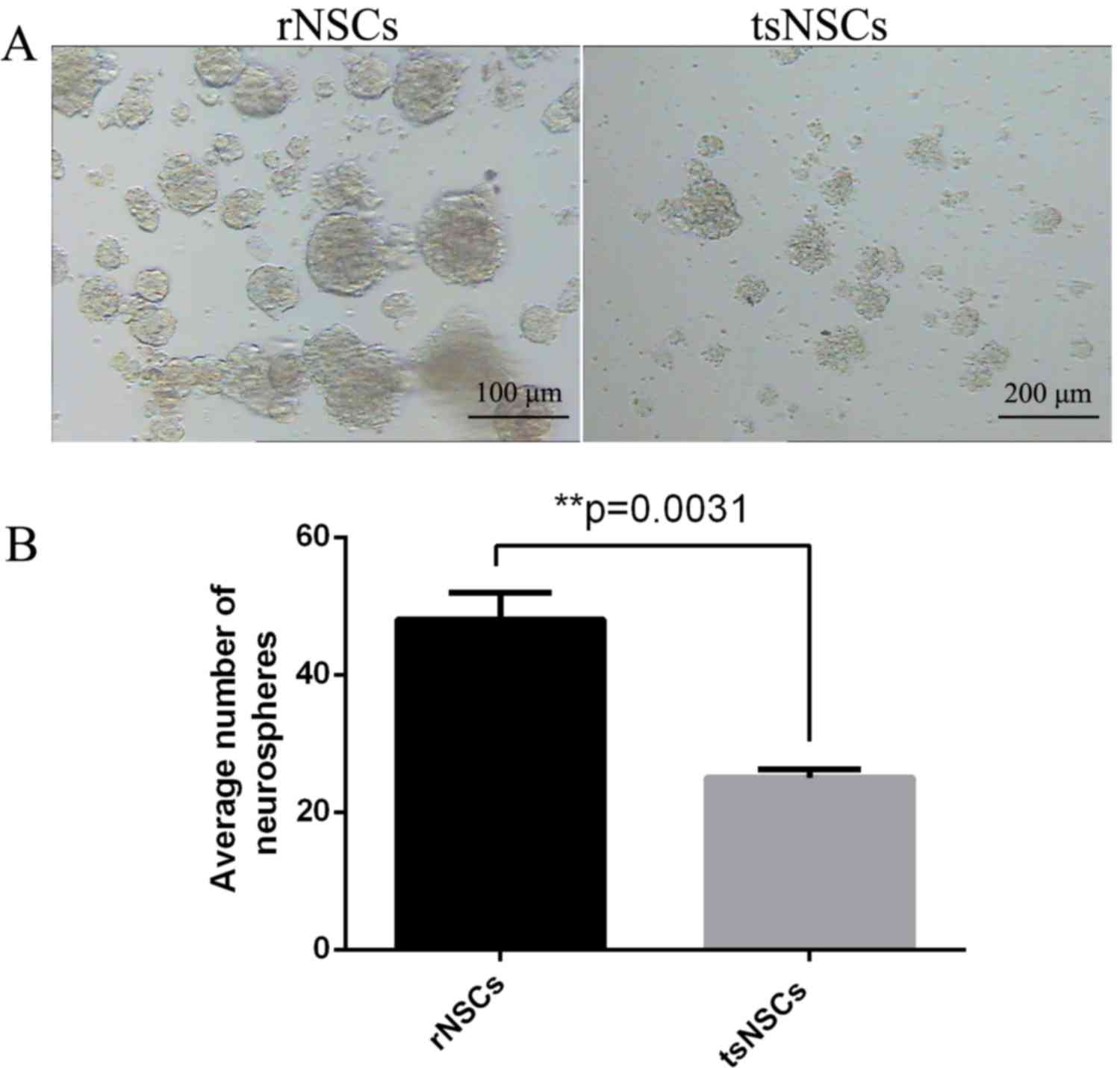
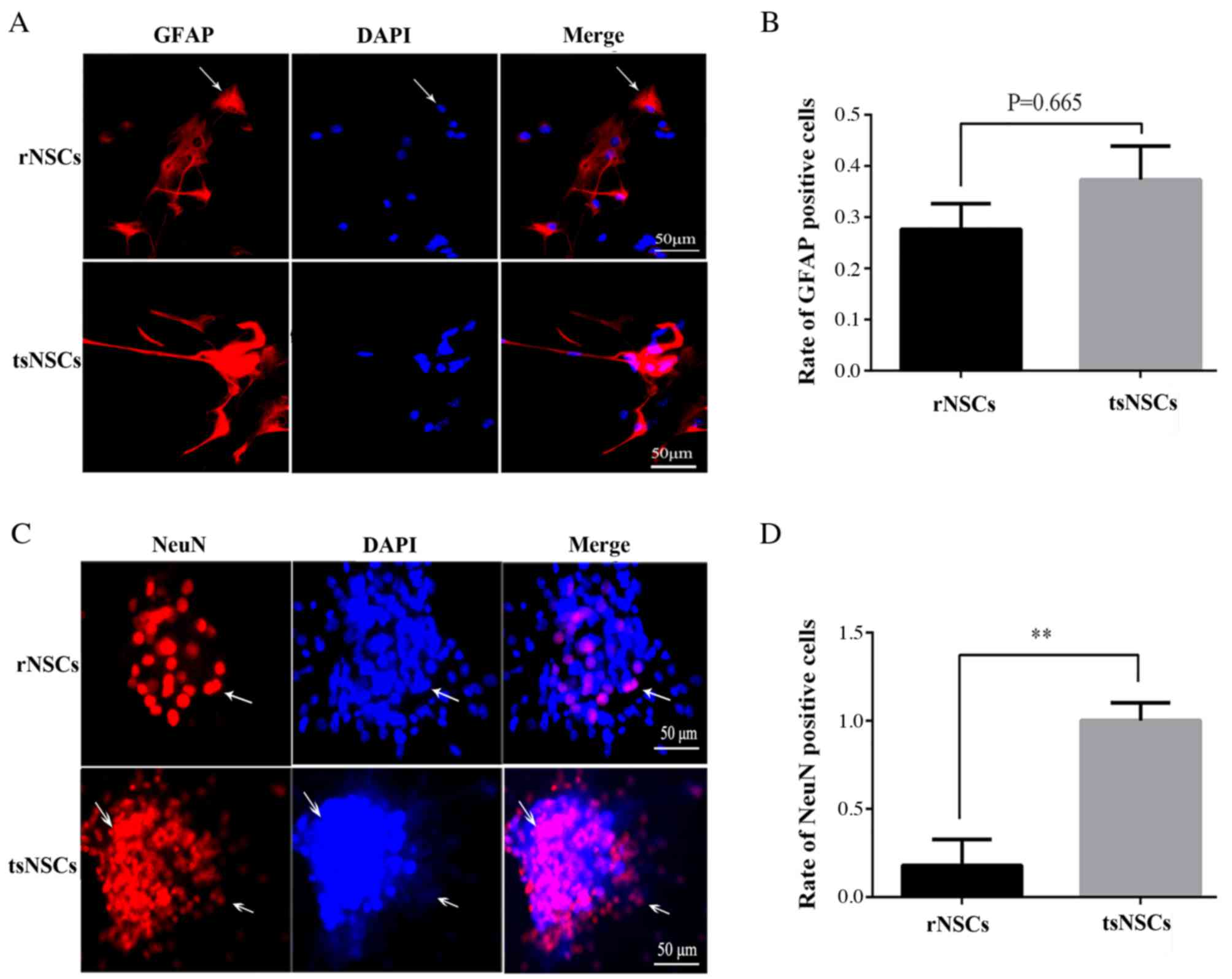
|
1
|
Gage FH and Temple S: Neural stem cells:
Generating and regenerating the brain. Neuron. 80:588–601. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blurton JM, Kitazawa M, Martinez CH,
Castello NA, Müller FJ, Loring JF, Yamasaki TR, Poon WW, Green KN
and LaFerla FM: Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a
transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:pp. 13594–13599. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suksuphew S and Noisa P: Neural stem cells
could serve as a therapeutic material for age-related
neurodegenerative diseases. World J Stem Cells. 7:502–511. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dooley D, Vidal P and Hendrix S:
Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell
therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair. Pharmacol
Ther. 141:21–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu P, Jones LL, Snyder EY and Tuszynski
MH: Neural stem cells constitutively secrete neurotrophic factors
and promote extensive host axonal growth after spinal cord injury.
Exp Neurol. 181:115–129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bergström T and Forsbery NK: Neural stem
cells: Brain building blocks and beyond. Ups J Med Sci.
117:132–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stenudd M, Sabelström H and Frisén J: Role
of endogenous neural stem cells in spinal cord injury and repair.
JAMA Neurol. 72:235–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Engel U and Wolswijk G:
Oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte (O-2A) progenitor cells derived
from adult rat spinal cord: In vitro characteristics and response
to PDGF, bFGF and NT-3. Glia. 16:16–26. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y: Survial and migration of neural
stem cells in rat spinal cord (unpublished PhD thesis). Ji Lin
University. 2007.
|
|
10
|
Seaberg RM and van der Kooy D: Adult
rodent neurogenic regions: The ventricular subependymacontains
neural stem cells, but the dentate gyrus contains restricted
progenitors. J Neurosci. 22:1784–1793. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu Y: Proliferation and differentiation of
neural stem cells from newborn mouse hippocampi in vitro. Chin J
Tissue Eng Res 79–85. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Hu YR: In vitro culture, induction and
differentiation of neural stem cells from rat embryo. J Clin
Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 1–3655. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Sun YX: Culture and differentiation of
cynomolgus monkey neural stem cells. J Clin Rehabili Tissue Eng
Res. 8821–8824. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Zhao CL: Establishment of in vitro culture
method of neural stem cells from human embryonic hippocampus. J
Capital Univ Med Sci. 1–146. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Fan Y, Huang ZY, Cao CC, Chen CS, Chen YX,
Fan DD, He J, Hou HL, Hu L, Hu XT, et al: Genome of the Chinese
tree shrew. Nat Commun. 4:14262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fan Y, Yu D and Yao YG: Tree shrew
database (TreeshrewDB): A genomic knowledge base for the Chinese
tree shrew. Sci Rep. 4:71452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1278. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reynolds BA, Tetzlaff W and Weiss S: A
multipotent EGF-responsive striatal embryonic progenitor cell
produces neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci. 12:4565–4574.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fuchs E: Social stress in tree shrews as
an animal model of depression: An example of a behavioral model of
a CNS disorder. CNS Spectr. 10:182–190. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang D, Gao L, Zhang YX, Sun L, Feng Y,
He YW, Xia XS and Zhang HT: Crucial factors for de novo
establishment of long-term primary culture of tree shrew
hepatocytes. Zoological Res. 01:24–30. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang JJ, Su JJ and Yang G: Two isolating
and culturemethods of primary tupaia hepatocytes in vitro. Sichuan
J Zoology. 02:168–171. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Gong M, Li SQ and Li F: Primary culture
and purification of cerebral astrocyte of tree shrew. Sheng Li Xue
Bao. 63:89–92. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu YZ: Culture in vitro and identification
of neural stem cells from hippocampus of neonataltree shrew
(unpublished PhD thesis). Guang Xi Medical University. 2013.
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research, . Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US);
1996
|
|
25
|
Yang WQ: The sino-burmese tree colts
guangxi said Burma in the monkey brain stereotaxic atlas. Guangxi
Science and Technology Press; Nanning: pp. 47–69. 1990
|
|
26
|
Pan LC, Yin ZS, Wang W, Hu Y, Gao RB, Wang
ML and Ren YG: Comparative study on the characteristics of culture
and differentiation of neural stem cells from fetal and neonatal
rat. Chinese J Clin Rehabi. 05:25–27+195. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Tian HB: Studies of establishment of mouse
and goat embryonic stem cell lines and differentiation of them into
neuron (unpublished PhD thesis). Shan Dong University. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Cao C: The in vitro culture of rat neural
stem cells and its directed differentiation into neuron (D)
(unpublished PhD thesis). Hei Bei Medical University. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Xu P: Cultivation in vitro of rat neural
stem cells and its conditioned medium effectson the differentiation
of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells into neural stem
cells (unpublished PhD thesis). An Hui Medical University.
2014.
|
|
30
|
Wang SQ: Effects of Hypoxia on
proliferation and differentiation of rats neural stem cells and
analysis of signaling pathway (unpublished PhD thesis). Shang Hai
University of Sport. 2013.
|
|
31
|
Wang LQ: Study on culture and
differentiation of neural stem cells from neonatal rats in vitro
(unpublished PhD thesis). Su Zhou University. 2004.
|
|
32
|
Gulino R, Lombardo SA, Casabona A, Leanza
G and Perciavalle V: Levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
and neurotrophin-4 in lumbar motoneurons after low-thoracic spinal
cord hemisection. Brain Res. 1013:174–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He BL, Liu RW, Chen LL, et al: BDNF
Expression in the Central Nervous System of Tree Shrews. J Kunming
Med Univ. 09:21–23. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Xiao Q, Luo H and Zhao KX:
Effects of angiotensin-(1–7) on hippocampal expressions of GFAP and
GDNF and cognitive function in rats with diabetes mellitus. Nan
Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 35:646–651. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiao JL, Hao L, Zheng H, et al: The
relation of BDNF Expression in the Central Nervous System and
function of study of Tree Shrews. J Kunming Med Univ.
05:1382010.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Jiao JL, He BL, Zheng H, LI B and Shen PQ:
The comparative study of brain development among tree shrews
(Tupaia blangeri chinensis), rhesus monkeys and rats. J Kunming
Medical University. 05:39–41. 2010.
|
|
37
|
Yan RQ, Su JJ, Huang DR, Gan YC, Yang C
and Huang GH: Human hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma.
I. Experimental infection of tree shrews with hepatitis B virus. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 122:283–288. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fuchs E, Czéh B and Flügge G: Examining
novel concepts of the pathophysiology of depression in the chronic
psychosocial stress paradigm in tree shrews. Behav Pharmacol.
15:315–325. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang J, Chai A, Zhou Q, Lv L, Wang L, Yang
Y and Xu L: Chronic clomipramine treatment reverses core symptom of
depression in subordinate tree shrews. PLoS One. 8:e809802013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|