|
1
|
Sampson UK, Norman PE, Fowkes FG, Aboyans
V, Song Y, Harrell FE Jr, Forouzanfar MH, Naghavi M, Denenberg JO,
McDermott MM, et al: Estimation of global and regional incidence
and prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms 1990 to 2010. Global
heart. 9:159–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomas M, Gavrila D, McCormick ML, Miller
FJ Jr, Daugherty A, Cassis LA, Dellsperger KC and Weintraub NL:
Deletion of p47phox attenuates angiotensin II-induced abdominal
aortic aneurysm formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Circulation. 114:404–413. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma AK, Lu G, Jester A, Johnston WF,
Zhao Y, Hajzus VA, Saadatzadeh MR, Su G, Bhamidipati CM, Mehta GS,
et al: Experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm formation is mediated
by IL-17 and attenuated by mesenchymal stem cell treatment.
Circulation. 126 11 Suppl 1:S38–S45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harrison SC, Smith AJ, Jones GT, Swerdlow
DI, Rampuri R, Bown MJ; Aneurysm Consortium, ; Folkersen L, Baas
AF, de Borst GJ, et al: Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in
abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur Heart J. 34:3707–3716. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li MW, Mian MO, Barhoumi T, Rehman A, Mann
K, Paradis P and Schiffrin EL: Endothelin-1 overexpression
exacerbates atherosclerosis and induces aortic aneurysms in
apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
33:2306–2315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hannawa KK, Cho BS, Sinha I, Roelofs KJ,
Myers DD, Wakefield TJ, Stanley JC, Henke PK and Upchurch GR Jr:
Attenuation of experimental aortic aneurysm formation in P-selectin
knockout mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1085:353–359. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piqueras L, Kubes P, Alvarez A, O'Connor
E, Issekutz AC, Esplugues JV and Sanz MJ: Angiotensin II induces
leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions in vivo via AT(1) and AT(2)
receptor-mediated P-selectin upregulation. Circulation.
102:2118–2123. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu Y, Zhang Q, Luo D, Wang J and Duan D:
Low molecular weight fucoidan modulates P-selectin and alleviates
diabetic nephropathy. Int J Biol Macromol. 91:233–240. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin W, Wang J, Jiang H, Song N, Zhang W
and Zhang Q: The neuroprotective activities of
heteropolysaccharides extracted from Saccharina Japonica.
Carbohydr Polym. 97:116–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13S. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Daugherty A and Cassis LA: Mouse models of
abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
24:429–434. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Biros E, Moran CS, Rush CM, Gäbel G,
Schreurs C, Lindeman JH, Walker PJ, Nataatmadja M, West M, Holdt
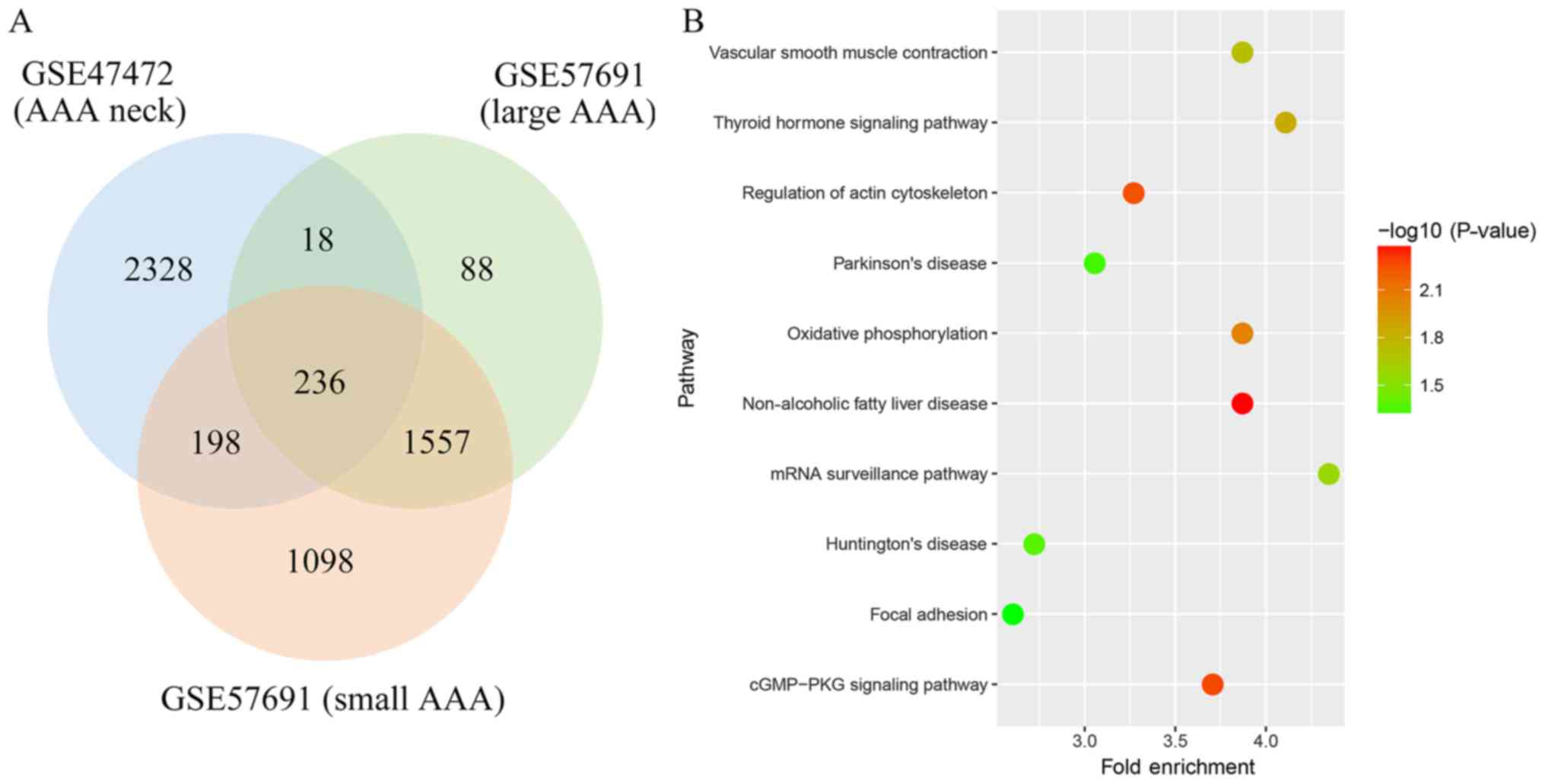
LM, et al: Differential gene expression in the proximal neck of
human abdominal aortic aneurysm. Atherosclerosis. 233:211–218.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Biros E, Gäbel G, Moran CS, Schreurs C,
Lindeman JH, Walker PJ, Nataatmadja M, West M, Holdt LM,
Hinterseher I, et al: Differential gene expression in human
abdominal aortic aneurysm and aortic occlusive disease. Oncotarget.
6:12984–12996. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshida S, Fuster JJ and Walsh K:
Adiponectin attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in
hyperlipidemic mice. Atherosclerosis. 235:339–346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu HY, Huang CY, Shih CM, Chang WH, Tsai
CS, Lin FY and Shih CC: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor decreases
abdominal aortic aneurysm formation through GLP-1-dependent
monocytic activity in mice. PLoS One. 10:e01210772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hlawaty H, Suffee N, Sutton A, Oudar O,
Haddad O, Ollivier V, Laguillier-Morizot C, Gattegno L, Letourneur
D and Charnaux N: Low molecular weight fucoidan prevents intimal
hyperplasia in rat injured thoracic aorta through the modulation of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression. Biochem Pharmacol.
81:233–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alsac JM, Delbosc S, Rouer M, Journé C,
Louedec L, Meilhac O and Michel JB: Fucoidan interferes with
Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced aneurysm enlargement by decreasing
neutrophil activation. J Vasc Surg. 57:796–805. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
da Cunha V, Tham DM, Martin-McNulty B,
Deng G, Ho JJ, Wilson DW, Rutledge JC, Vergona R, Sullivan ME and
Wang YX: Enalapril attenuates angiotensin II-induced
atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation. Atherosclerosis.
178:9–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cui W, Zheng Y, Zhang Q, Wang J, Wang L,
Yang W, Guo C, Gao W, Wang X and Luo D: Low-molecular-weight
fucoidan protects endothelial function and ameliorates basal
hypertension in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Lab Invest.
94:382–393. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iida Y, Xu B, Schultz GM, Chow V, White
JJ, Sulaimon S, Hezi-Yamit A, Peterson SR and Dalman RL: Efficacy
and mechanism of angiotensin II receptor blocker treatment in
experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms. PLoS One. 7:e496422012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mieth A, Revermann M, Babelova A, Weigert
A, Schermuly RT and Brandes RP: L-type calcium channel inhibitor
diltiazem prevents aneurysm formation by blood pressure-independent
anti-inflammatory effects. Hypertension. 62:1098–1104. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mateo T, Abu Nabah YN, Abu Taha M, Mata M,
Cerdá-Nicolás M, Proudfoot AE, Stahl RA, Issekutz AC, Cortijo J,
Morcillo EJ, et al: Angiotensin II-induced mononuclear leukocyte
interactions with arteriolar and venular endothelium are mediated
by the release of different CC chemokines. J Immunol.
176:5577–5586. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Iida Y, Xu B, Xuan H, Glover KJ, Tanaka H,
Hu X, Fujimura N, Wang W, Schultz JR, Turner CR and Dalman RL:
Peptide inhibitor of CXCL4-CCL5 heterodimer formation, MKEY,
inhibits experimental aortic aneurysm initiation and progression.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:718–726. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li B, Juenet M, Aid-Launais R, Maire M,
Ollivier V, Letourneur D and Chauvierre C: Development of polymer
microcapsules functionalized with fucoidan to target P-selectin
overexpressed in cardiovascular diseases. Adv Healthc Mater.
6:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bonnard T, Serfaty JM, Journé C, Ho Tin
Noe B, Arnaud D, Louedec L, Derkaoui SM, Letourneur D, Chauvierre C
and Le Visage C: Leukocyte mimetic polysaccharide microparticles
tracked in vivo on activated endothelium and in abdominal aortic
aneurysm. Acta Biomater. 10:3535–3545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rouzet F, Bachelet-Violette L, Alsac JM,
Suzuki M, Meulemans A, Louedec L, Petiet A, Jandrot-Perrus M,
Chaubet F and Michel JB: Radiolabeled fucoidan as a p-selectin
targeting agent for in vivo imaging of platelet-rich thrombus and
endothelial activation. J Nucl Med. 52:1433–1440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen A, Lan Y, Liu J, Zhang F, Zhang L, Li
B and Zhao X: The structure property and endothelial protective
activity of fucoidan from Laminaria japonica. Int J Biol
Macromol. 105:1421–1429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bouvard C, Galy-Fauroux I, Grelac F,
Carpentier W, Lokajczyk A, Gandrille S, Colliec-Jouault S, Fischer
AM and Helley D: Low-molecular-weight fucoidan induces endothelial
cell migration via the PI3K/AKT pathway and modulates the
transcription of genes involved in angiogenesis. Mar Drugs.
13:7446–7462. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu Z, Zhang Q, Chen L, Ren S, Xu P, Tang
Y and Luo D: Higher specificity of the activity of low molecular
weight fucoidan for thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb
Res. 125:419–426. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bachelet L, Bertholon I, Lavigne D, Vassy
R, Jandrot-Perrus M, Chaubet F and Letourneur D: Affinity of low
molecular weight fucoidan for P-selectin triggers its binding to
activated human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1790:141–146.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao X, Guo F, Hu J, Zhang L, Xue C, Zhang
Z and Li B: Antithrombotic activity of oral administered low
molecular weight fucoidan from Laminaria Japonica. Thromb Res.
144:46–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deux JF, Meddahi-Pellé A, Le Blanche AF,
Feldman LJ, Colliec-Jouault S, Brée F, Boudghène F, Michel JB and
Letourneur D: Low molecular weight fucoidan prevents neointimal
hyperplasia in rabbit iliac artery in-stent restenosis model.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:1604–1609. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsai HL, Tai CJ, Huang CW, Chang FR and
Wang JY: Efficacy of low-molecular-weight fucoidan as a
supplemental therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: A
double-blind randomized controlled trial. Mar Drugs. 15:pii: E122.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hwang PA, Yan MD, Lin HT, Li KL and Lin
YC: Toxicological evaluation of low molecular weight fucoidan in
vitro and in vivo. Mar Drugs. 14:pii: E121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|