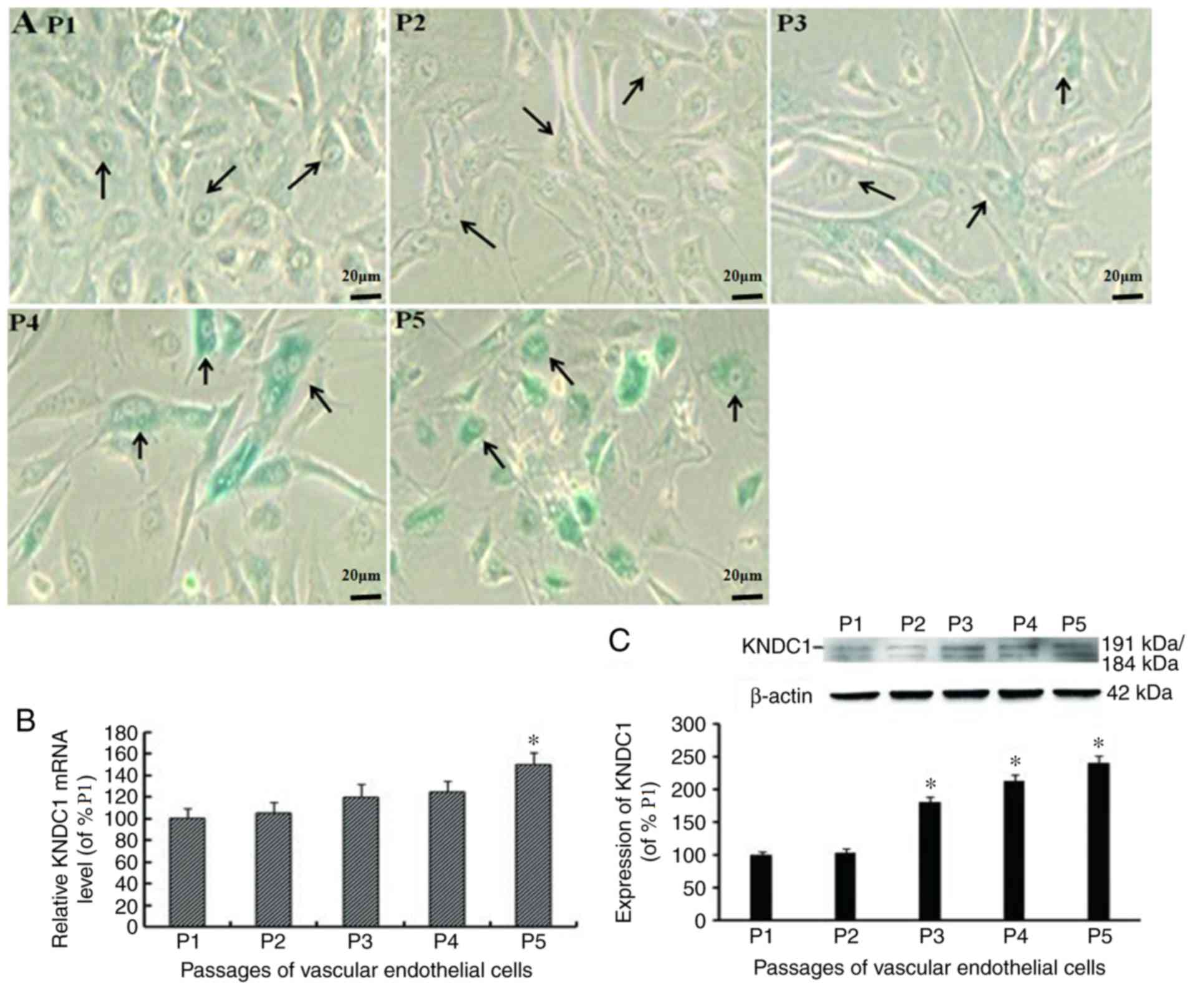
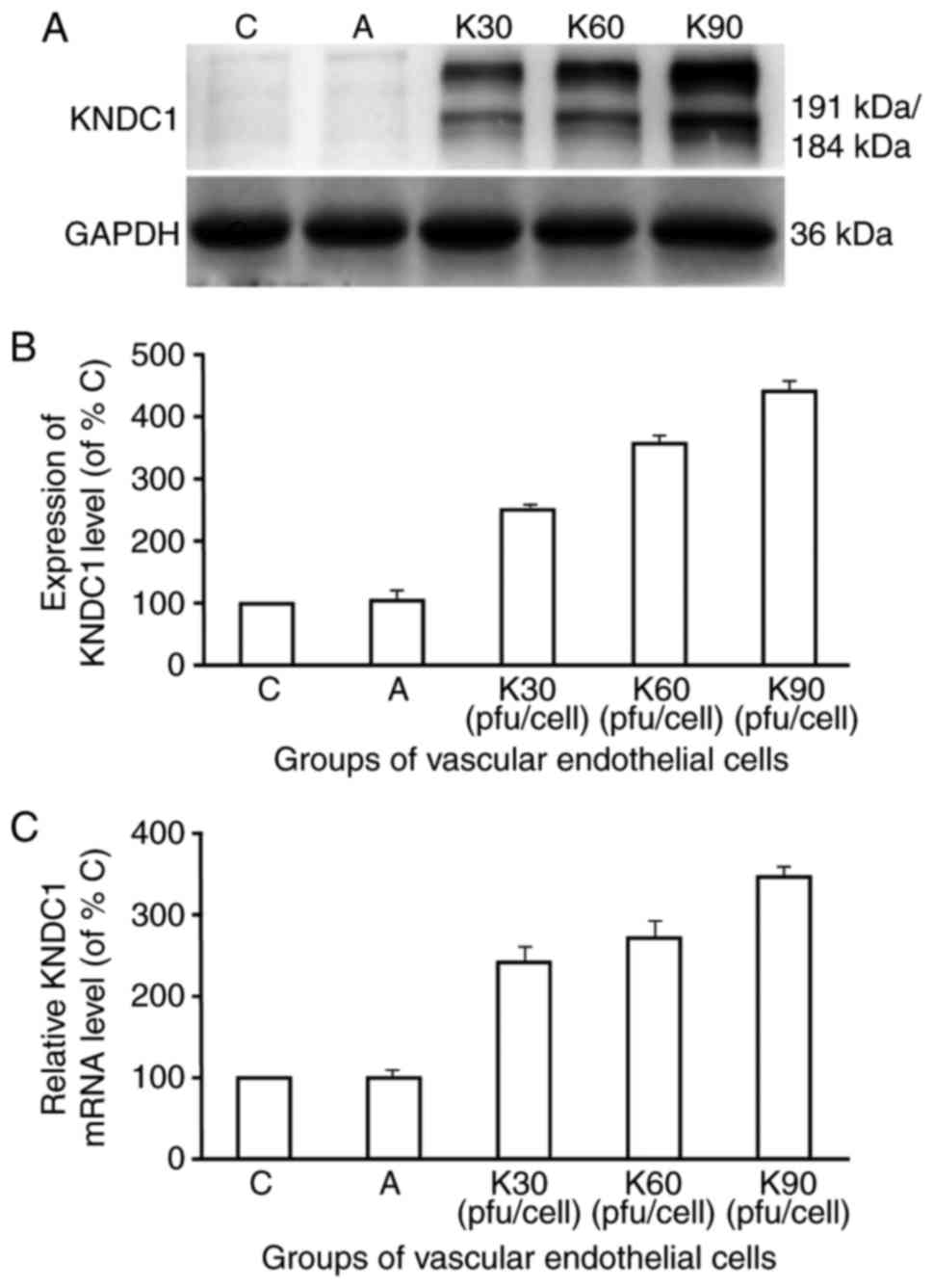
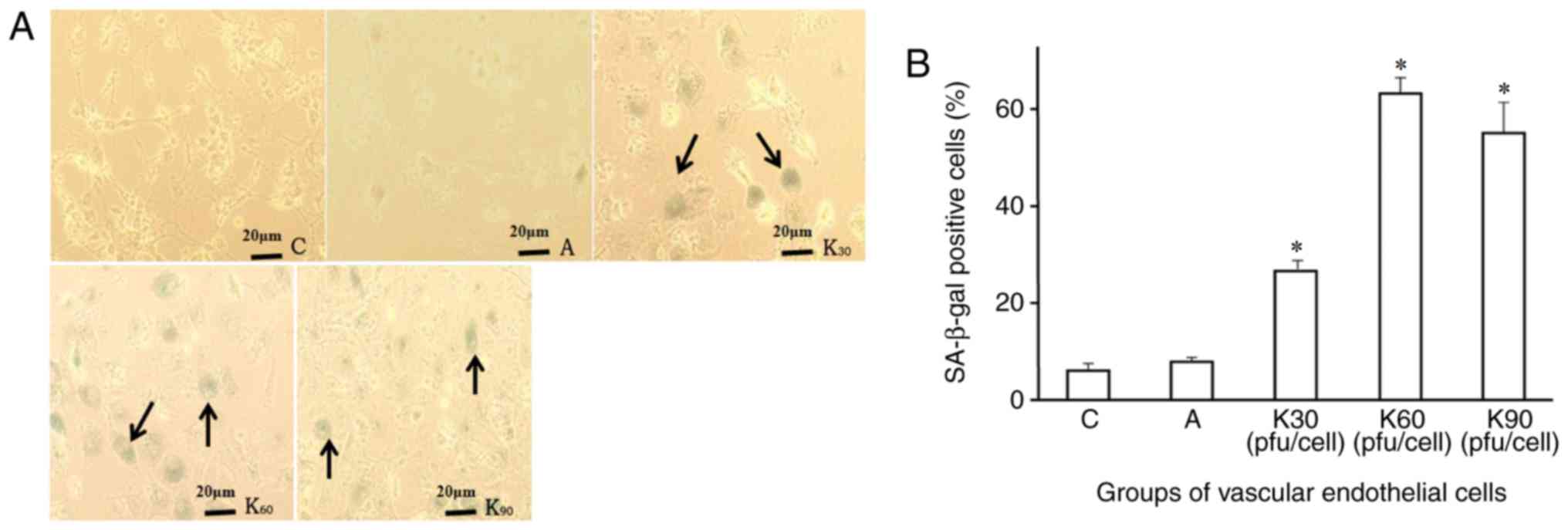
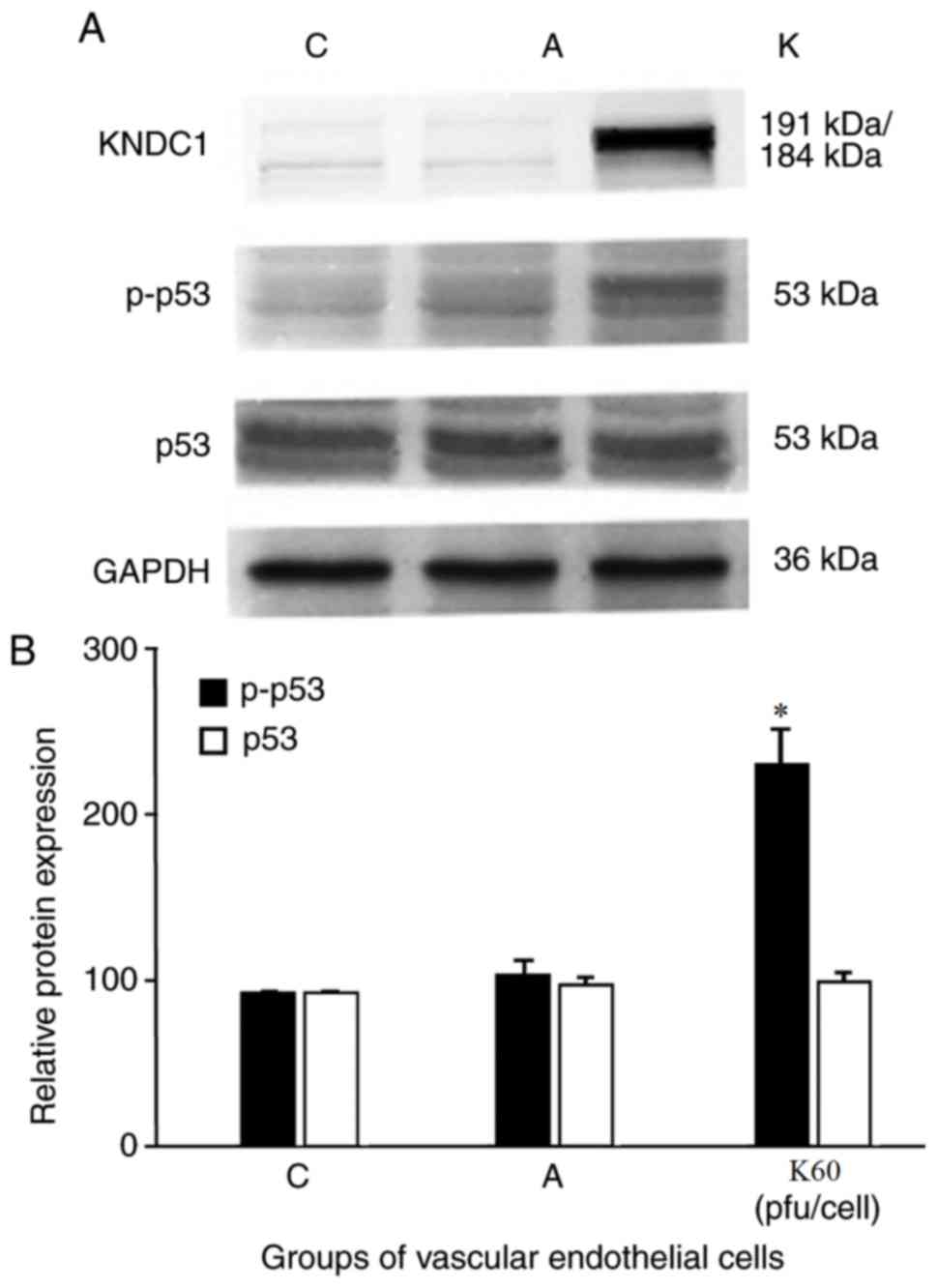
|
1
|
Seals DR: Edward F: Adolph distinguished
lecture: The remarkable anti-aging effects of aerobic exercise on
systemic arteries. J Appl Physiol (1985). 117:425–439. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hafner F, Kieninger A, Meinitzer A, Gary
T, Froehlich H, Haas E, Hackl G, Eller P, Brodmann M and Seinost G:
Endothelial dysfunction and brachial intima-media thickness: Long
term cardiovascular risk with claudication related to peripheral
arterial disease: A prospective analysis. PLoS One. 9:e933572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sikora E, Bielak-Zmijewska A and Mosieniak
G: Cellular senescence in ageing, age-related disease and
longevity. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 12:698–706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Shaer MH, Choueiri NE, Correia ML,
Sinkey CA, Barenz TA and Haynes WG: Effects of aging and
atherosclerosis on endothelial and vascular smooth muscle function
in humans. Int J Cardiol. 109:201–206. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Erusalimsky JD: Vascular endothelial
senescence: From mechanisms to pathophysiology. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 106:326–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cardus A, Uryga AK, Walters G and
Erusalimsky JD: SIRT6 protects human endothelial cells from DNA
damage, telomere dysfunction, and senescence. Cardiovasc Res.
97:571–579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang C, Zhen YZ, Lin YJ, Liu J, Wei J, Xu
R and Hu G: KNDC1 knockdown protects human umbilical vein
endothelial cells from senescence. Mol Med Rep. 10:82–88. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dickinson RJ, Delavaine L, Cejudo-Marín R,
Stewart G, Staples CJ, Didmon MP, Trinidad AG, Alonso A, Pulido R
and Keyse SM: Phosphorylation of the kinase interaction motif in
mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinasephosphatase-4 mediates
cross-talk between protein kinase A and MAP kinase signaling
pathways. J Biol Chem. 286:38018–38026. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Basu K, Mukhopadhyay A, Ghosh I and Datta
K: Nuclear morphology and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 expression
differentiate serum-starved oxidative stress signalling from
hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in retinal neuronal cell line.
Cell Biol Int. 36:1021–1027. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang SK, Xiao L, Li J, Liu F, Sun L and
Kanwar YS: Role of guanin-nucleotide exchange factor Epac in renal
physiology and pathopysiology. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
304:F831–F839. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang J, Furuya A, Hayashi K and Furuichi
T: Interaction between very-KIND Ras guanine exchange factor and
microtubule-associated protein 2, and its role in dendrite
growth-structure and function of the second kinase noncatalytic
C-lobe domain. FEBS J. 278:1651–1661. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rezk N, Elkotb SM and Naguib YM: Swimming
Exercise Ameliorates Elevated Blood Pressure and Vascular
Endothelial Dysfunction in Old Rats. Am J Med Med Sci. 4:192–202.
2014.
|
|
14
|
Zhao X, Zhao Q, Luo Z, Yu Y, Xiao N, Sun X
and Cheng L: Spontaneous immortalization of mouse liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 35:617–624. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sosińska P, Mikuła-Pietrasik J, Ryżek M,
Naumowicz E and Książek K: Specificity of cytochemical and
fluorescence methods of senescence-associated β-galactosidase
detection for ageing driven by replication and time.
Biogerontology. 15:407–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vo NT, Mikhaeil MS, Lee LE, Pham PH and
Bols NC: Senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining in fish
cell lines and primary cultures from several tissues and species,
including rainbow trout coelomic fluid and milt. In Vitro Cell Dev
Biol Anim. 51:361–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mees A, Rock R, Ciccarelli FD, Leberfinger
CB, Borawski JM, Bork P, Wiese S, Gessler M and Kerkhoff E:
Very-KIND is a novel nervous system specific guanine nucleotide
exchange factor for Ras GTPases. Gene Expr Patterns. 6:79–85. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang J, Furuya A and Furuichi T:
Very-KIND, a KIND domain containing RasGEF, controls dendrite
growth by linking Ras small GTPases and MAP2. J Cell Biol.
179:539–552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hayashi K, Furuya A, Sakamaki Y, Akagi T,
Shinoda Y, Sadakata T, Hashikawa T, Shimizu K, Minami H, Sano Y, et
al: The brain-specific RasGEF very-KIND is required for normal
dendritic growth in cerebellar granule cells and proper motor
coordination. PLoS One. 12:e01731752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Levine EM and Mueller SN: Cultured
vascular endothelial cells as a model system for the study of
cellular senescence. Int Rev Cytol. Suppl:67–76. 1979.
|
|
21
|
Muck C, Micutkova L, Zwerschke W and
Jansen-Durr P: Role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3
in human umbilical vein endothelial cell senescence. Rejuvenation
Res. 11:449–453. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Madden SL, Galella EA, Riley D, Bertelsen
AH and Beaudry GA: Induction of cell growth regulatory genes by
p53. Cancer Res. 56:5384–5390. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Speidel D: The role of DNA damage
responses in p53 biology. Arch Toxicol. 89:501–517. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyauchi H, Minamino T, Tateno K, Kunieda
T, Toko H and Komuro I: Akt negatively regulates human endothelial
cell lifespan via the p53/p21 dependent pathway. EMBO J.
23:212–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim KS, Kang KW, Seu YB, Baek SH and Kim
JR: Interferon-gamma induces cellular senescence through
p53-dependent DNA damage signaling in human endothelial cells. Mech
Ageing Dev. 130:179–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carstens MJ, Krempler A, Triplett AA, Van
Lohuizen M and Wagner KU: Cell cycle arrest and cell death are
controlled by p53-dependent and p53-independent mechanisms in
Tsg101-deficient cells. J Biol Chem. 279:35984–35994. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Z, Wang CZ, Du GJ, Qi LW, Calway T,
He TC, Du W and Yuan CS: Genistein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent pathway in human colon cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 43:289–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakamura S, Roth JA and Mukhopadhyay T:
Multiple lysine mutations in the C-terminal domain of p53 interfere
with MDM2-dependent protein degradation and ubiquitination. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:9391–9398. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu W and Roeder RG: Activation of p53
sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal
domain. Cell. 90:595–606. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hernández-Reséndiz I, Román-Rosales A,
García-Villa E, López-Macay A, Pineda E, Saavedra E, Gallardo-Pérez
JC, Alvarez-Ríos E, Gariglio P, Moreno-Sánchez R and
Rodríguez-Enríquez S: Dual regulation of energy metabolism by p53
in human cervix and breast cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1853:3266–3278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jeong SG and Cho GW: Endogenous ROS levels
are increased in replicativesenescence in human bone marrow
mesenchymal stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 460:971–976.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Valent L and Strasser A: Distinct target
genes and effector processes appear to be critical for
p53-activated responses to acute DNA damage versus p53-mediated
tumour suppression. Biodiscovery. 8:1–16. 2013.
|
|
33
|
Chatoo W, Abdouh M and Bernier G: p53
pro-oxidant activity in the centralnervous system: Implication in
aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:1729–1737. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sinha VC, Qin L and Li Y: A
p53/ARF-dependent anticancer barrier activates senescence and
blocks tumorigenesis without impacting apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res.
13:231–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu J, Song T, Liu S, Li X, Li G and Xu J:
Icariside II inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle
arrest through the ROS-p38-p53 signaling pathway in A375 human
melanoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:410–416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|