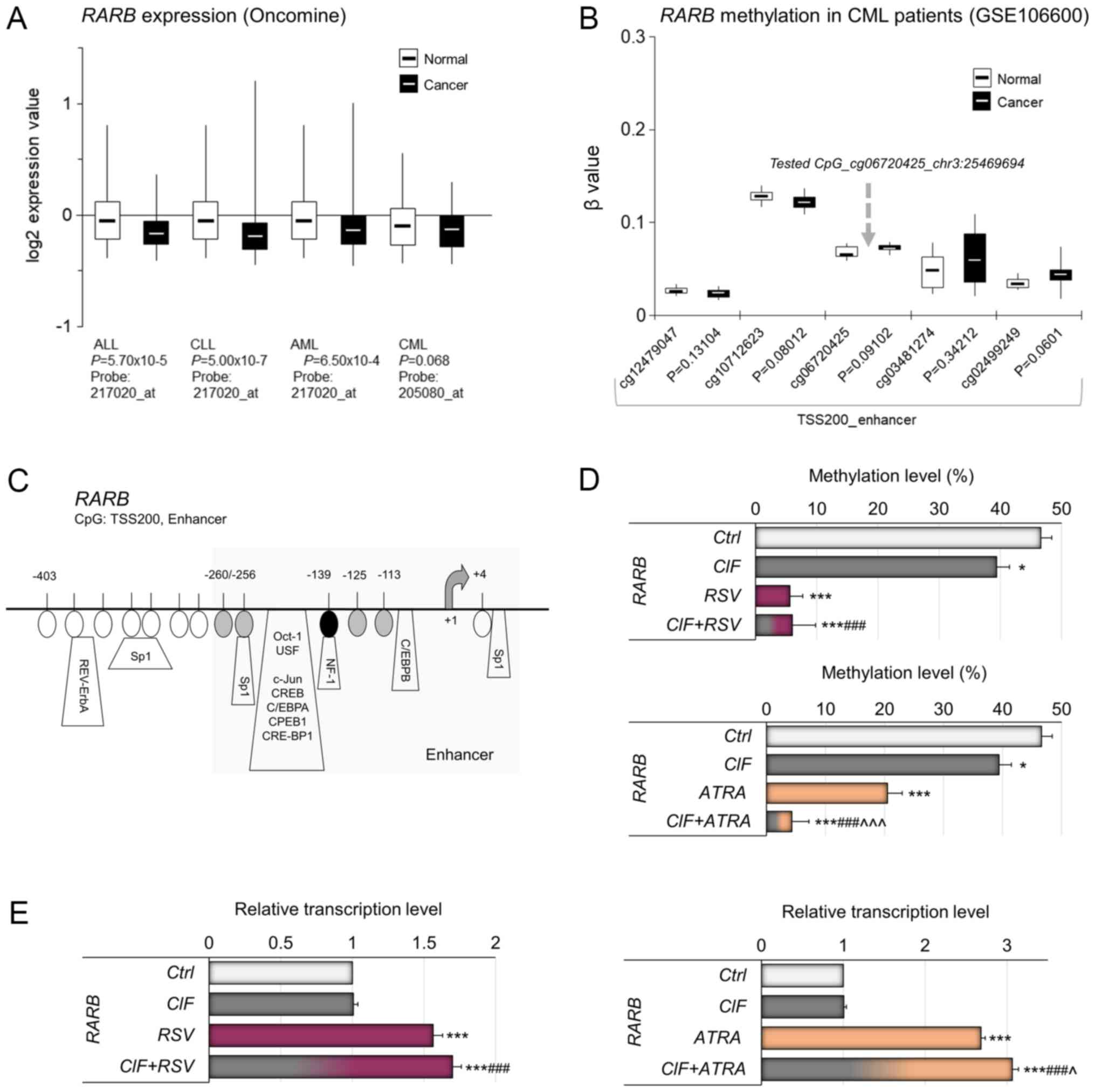
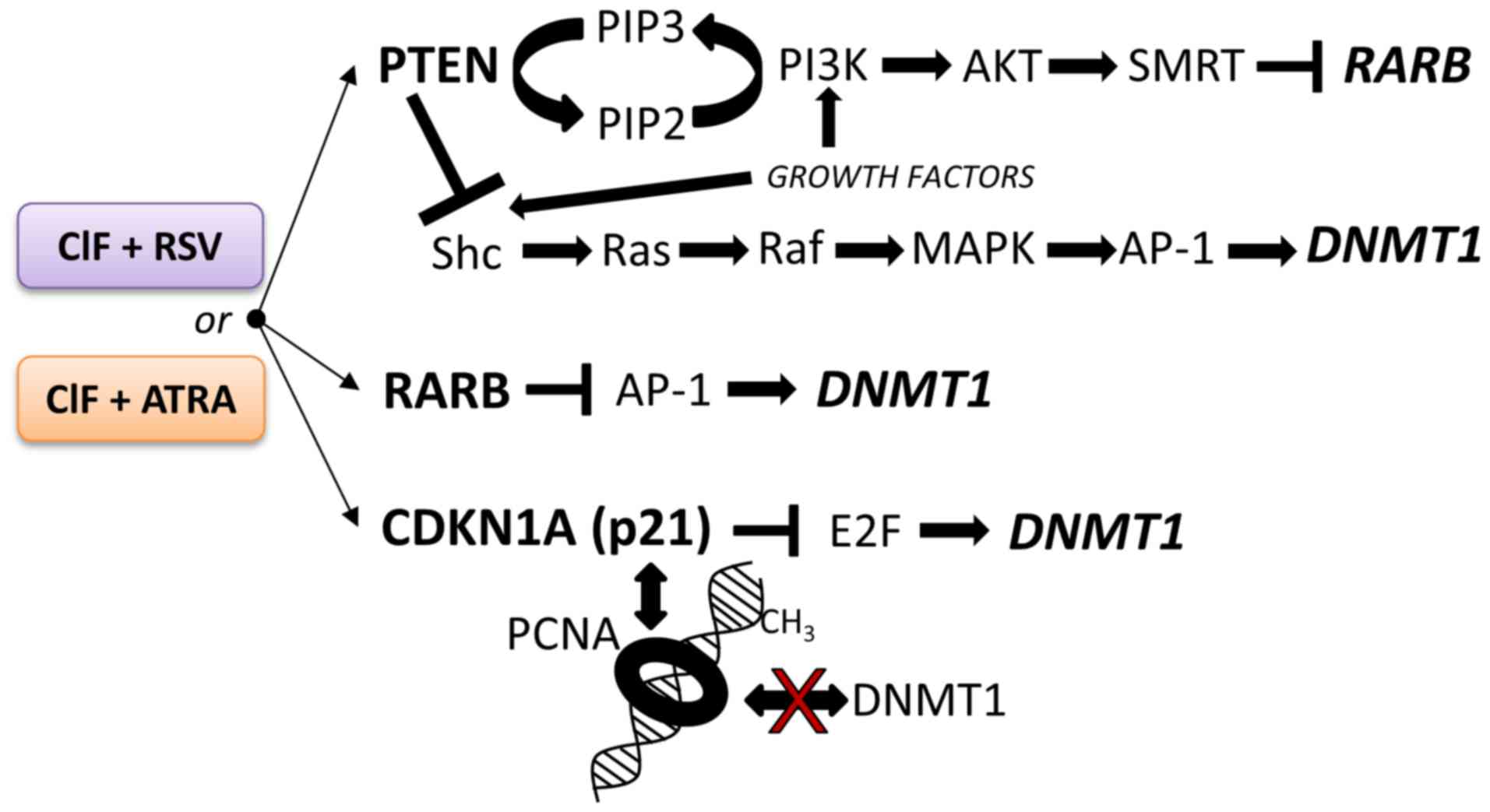
|
1
|
Chen Y, Peng C, Li D and Li S: Molecular
and cellular bases of chronic myeloid leukemia. Protein Cell.
1:124–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soverini S, de Benedittis C, Mancini M and
Martinelli G: Mutations in the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain and elsewhere
in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 15
(Suppl):S120–S128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B,
Buchdunger E, Ford JM, Lydon NB, Kantarjian H, Capdeville R,
Ohno-Jones S and Sawyers CL: Efficacy and safety of a specific
inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 344:1031–1037. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bhatia R, Holtz M, Niu N, Gray R, Snyder
DS, Sawyers CL, Arber DA, Slovak ML and Forman SJ: Persistence of
malignant hematopoietic progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia
patients in complete cytogenetic remission following imatinib
mesylate treatment. Blood. 101:4701–4707. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chomel JC, Bonnet ML, Sorel N, Bertrand A,
Meunier MC, Fichelson S, Melkus M, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Guilhot F
and Turhan AG: Leukemic stem cell persistence in chronic myeloid
leukemia patients with sustained undetectable molecular residual
disease. Blood. 118:3657–3660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leo E and Martinelli G: DNA methylation in
chronic myeloid leukemia. J Mol Genet Med. 8:1182014.
|
|
7
|
Koschmieder S and Vetrie D: Epigenetic
dysregulation in chronic myeloid leukaemia: A myriad of mechanisms
and therapeutic options. Semin Cancer Biol. 51:180–197. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Robertson KD: Epigenetic mechanisms of
gene regulationDNA Methylation and Cancer Therapy. Medical
Intelligence Unit. Springer; Boston, MA: pp. 13–30. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jaenisch R and Bird A: Epigenetic
regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic
and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 33 (Suppl):S245–S254. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The epigenomics of
cancer. Cell. 128:683–692. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chik F, Szyf M and Rabbani SA: Role of
epigenetics in cancer initiation and progression. Adv Exp Med Biol.
720:91–104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen T and Li E: Structure and function of
eukaryotic DNA methyltransferases. Curr Top Dev Biol. 60:55–89.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Majda K, Kaufman-Szymczyk A,
Lubecka-Pietruszewska K, Bednarek A and Fabianowska-Majewska K:
Influence of clofarabine on transcriptional activity of PTEN, APC,
RARB2, ZAP70 genes in K562 cells. Anticancer Res. 30:4601–4606.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lubecka-Pietruszewska K, Kaufman-Szymczyk
A, Stefanska B, Cebula-Obrzut B, Smolewski P and
Fabianowska-Majewska K: Clofarabine, a novel adenosine analogue,
reactivates DNA methylation-silenced tumour suppressor genes and
inhibits cell growth in breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
723:276–287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ghanem H Jabbour E, Faderl S, Ghandhi V,
Plunkett W and Kantarjian H: Clofarabine in leukemia. Expert Rev
Hematol. 3:15–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ghanem H, Kantarjian H, Ohanian M and
Jabbour E: The role of clofarabine in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 54:688–698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stefanska B, Karlic H, Varga F,
Fabianowska-Majewska K and Haslberger A: Epigenetic mechanisms in
anti-cancer actions of bioactive food components-the implications
in cancer prevention. Br J Pharmacol. 167:279–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stefanska B, Salamé P, Bednarek A and
Fabianowska-Majewska K: Comparative effects of retinoic acid,
vitamin D and resveratrol alone and in combination with adenosine
analogues on methylation and expression of phosphatase and tensin
homologue tumour suppressor gene in breast cancer cells. Br J Nutr.
107:781–790. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lubecka K, Kurzava L, Flower K, Buvala H,
Zhang H, Teegarden D, Camarillo I, Suderman M, Kuang S, Andrisani
O, et al: Stilbenoids remodel the DNA methylation patterns in
breast cancer cells and inhibit oncogenic NOTCH signaling through
epigenetic regulation of MAML2 transcriptional activity.
Carcinogenesis. 37:656–668. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee YJ, Lee YJ, Im JH, Won SY, Kim YB, Cho
MK, Nam HS, Choi YJ and Lee SH: Synergistic anti-cancer effects of
resveratrol and chemotherapeutic agent clofarabine against human
malignant mesothelioma MSTO-211H cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
52:61–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee YJ, Hwang IS, Lee YJ, Lee CH, Kim SH,
Nam HS, Choi YJ and Lee SH: Knockdown of Bcl-xL enhances
growth-inhibiting and apoptosis-inducing effects of resveratrol and
clofarabine in malignant mesothelioma H-2452 cells. J Korean Med
Sci. 29:1464–1472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee YJ, Lee YJ and Lee SH: Resveratrol and
clofarabine induces a preferential apoptosis-activating effect on
malignant mesothelioma cells by Mcl-1 down-regulation and caspase-3
activation. BMB Rep. 48:166–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kulkarni SS and Cantó C: The molecular
targets of resveratrol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1114–1123. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Theodosiou M, Laudet V and Schubert M:
From carrot to clinic: An overview of the retinoic acid signaling
pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1423–1445. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang XH and Gudas LJ: Retinoids, retinoic
acid receptors, and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:345–364. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Connolly R, Nguyen NK and Sukumar S:
Molecular pathways: Current role and future directions of the
retinoic acid pathway in cancer prevention and treatment. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1651–1659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schenk T, Stengel S and Zelent A:
Unlocking the potential of retinoic acid in anticancer therapy. Br
J Cancer. 111:2039–2045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang W and Xu J: DNA methyltransferases
and their roles in tumorigenesis. Biomark Res. 5:12017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu Q, Chen ZM and Su WJ: Anticancer effect
of retinoic acid via AP-1 activity repression is mediated by
retinoic acid receptor alpha and beta in gastric cancer cells. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 34:1102–1114. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stefanska B, Rudnicka K, Bednarek A and
Fabianowska-Majewska K: Hypomethylation and induction of retinoic
acid receptor beta 2 by concurrent action of adenosine analogues
and natural compounds in breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
638:47–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McCabe MT, Davis JN and Day ML: Regulation
of DNA methyltransferase 1 by the pRb/E2F1 pathway. Cancer Res.
65:3624–3632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Delavaine L and La Thangue NB: Control of
E2F activity by p21Waf1/Cip1. Oncogene. 18:5381–5392. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chuang LS, Ian HI, Koh TW, Ng HH, Xu G and
Li BF: Human DNA-(cytosine-5) methyltransferase-PCNA complex as a
target for p21WAF1. Science. 277:1996–2000. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iida T, Suetake I, Tajima S, Morioka H,
Ohta S, Obuse C and Tsurimoto T: PCNA clamp facilitates action of
DNA cytosine methyltransferase 1 on hemimethylated DNA. Genes
Cells. 7:997–1007. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamada KM and Araki M: Tumor suppressor
PTEN: Modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis.
J Cell Sci. 114:2375–2382. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Iwase H, Omoto Y, Iwata H, Toyama T, Hara
Y, Ando Y, Ito Y, Fujii Y and Kobayashi S: DNA methylation analysis
at distal and proximal promoter regions of the oestrogen receptor
gene in breast cancers. Br J Cancer. 80:1982–1986. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sui T, Ma L, Bai X, Li Q and Xu X:
Resveratrol inhibits the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/protein
kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in the
human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cell line. Oncol Lett.
7:2093–2098. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang B, Liu J and Gong Z: Resveratrol
induces apoptosis in K562 cells via the regulation of mitochondrial
signaling pathways. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:16926–16933.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mizuno S, Chijiwa T, Okamura T, Akashi K,
Fukumaki Y, Niho Y and Sasaki H: Expression of DNA
methyltransferases DNMT1, 3A, and 3B in normal hematopoiesis and in
acute and chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 97:1172–1179. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tan HH and Porter AG: p21(WAF1) negatively
regulates DNMT1 expression in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 382:171–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu M, Iavarone A and Freedman LP:
Transcriptional activation of the human p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene by
retinoic acid receptor. Correlation with retinoid induction of U937
cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 271:31723–31728. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu Z, Li W, Lu Q, Wang L, Zhang X, Han P,
Chen P and Pei Y: p21 is required for atRA-mediated growth
inhibition of MEPM cells, which involves RAR. J Cell Biochem.
104:2185–2192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bowers JL, Tyulmenkov VV, Jernigan SC and
Klinge CM: Resveratrol acts as a mixed agonist/antagonist for
estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Endocrinology. 141:3657–3667.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Parveen A, Akash MS, Rehman K and Kyunn
WW: Dual role of p21 in the progression of cancer and its
treatment. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 26:49–62. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Montiel-Duarte C, Cordeu L, Agirre X,
Román-Gómez J, Jiménez-Velasco A, José-Eneriz ES, Gárate L, Andreu
EJ, Calasanz MJ, Heiniger A, et al: Resistance to Imatinib
mesylate-induced apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia is
associated with PTEN down-regulation due to promoter
hypermethylation. Leuk Res. 32:709–716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
García JM, Silva J, Peña C, Garcia V,
Rodríguez R, Cruz MA, Cantos B, Provencio M, España P and Bonilla
F: Promoter methylation of the PTEN gene is a common molecular
change in breast cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 41:117–124.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Goel A, Arnold CN, Niedzwiecki D,
Carethers JM, Dowell JM, Wasserman L, Compton C, Mayer RJ,
Bertagnolli MM and Boland CR: Frequent inactivation of PTEN by
promoter hypermethylation in microsatellite instability-high
sporadic colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 64:3014–3021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wyczechowska D and Fabianowska-Majewska K:
The effects of cladribine and fludarabine on DNA methylation in
K562 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 65:219–225. 2003.
|
|
50
|
Lefebvre B, Brand C, Flajollet S and
Lefebvre P: Down-regulation of the tumour suppressor gene retinoic
acid receptor beta2 through the phosphoinositide 3-knase/Akt
signaling pathway. Mol Endocrinol. 20:2109–2121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lussana F, Intermesoli T, Stefanoni P and
Rambaldi A: Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapies in
chronic myeloid leukemia. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 249:231–250. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J and Yokoyama
A: Long-term exposure of leukemia cells to multi-targeted tyrosine
kinase inhibitor induces activations of AKT, ERK and STAT5
signaling via epigenetic silencing of the PTEN gene. Leukemia.
24:1631–1640. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Udaka K and
Yokoyama A: Imatinib causes epigenetic alterations of PTEN gene via
upregulation of DNA methyltransferases and polycomb group proteins.
Blood Cancer J. 1:e482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Can G, Cakir Z, Kartal M, Gunduz U and
Baran Y: Apoptotic effects of resveratrol, a grape polyphenol, on
imatinib-sensitive and resistant K562 chronic myeloid leukemia
cells. Anticancer Res. 32:2673–2678. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|