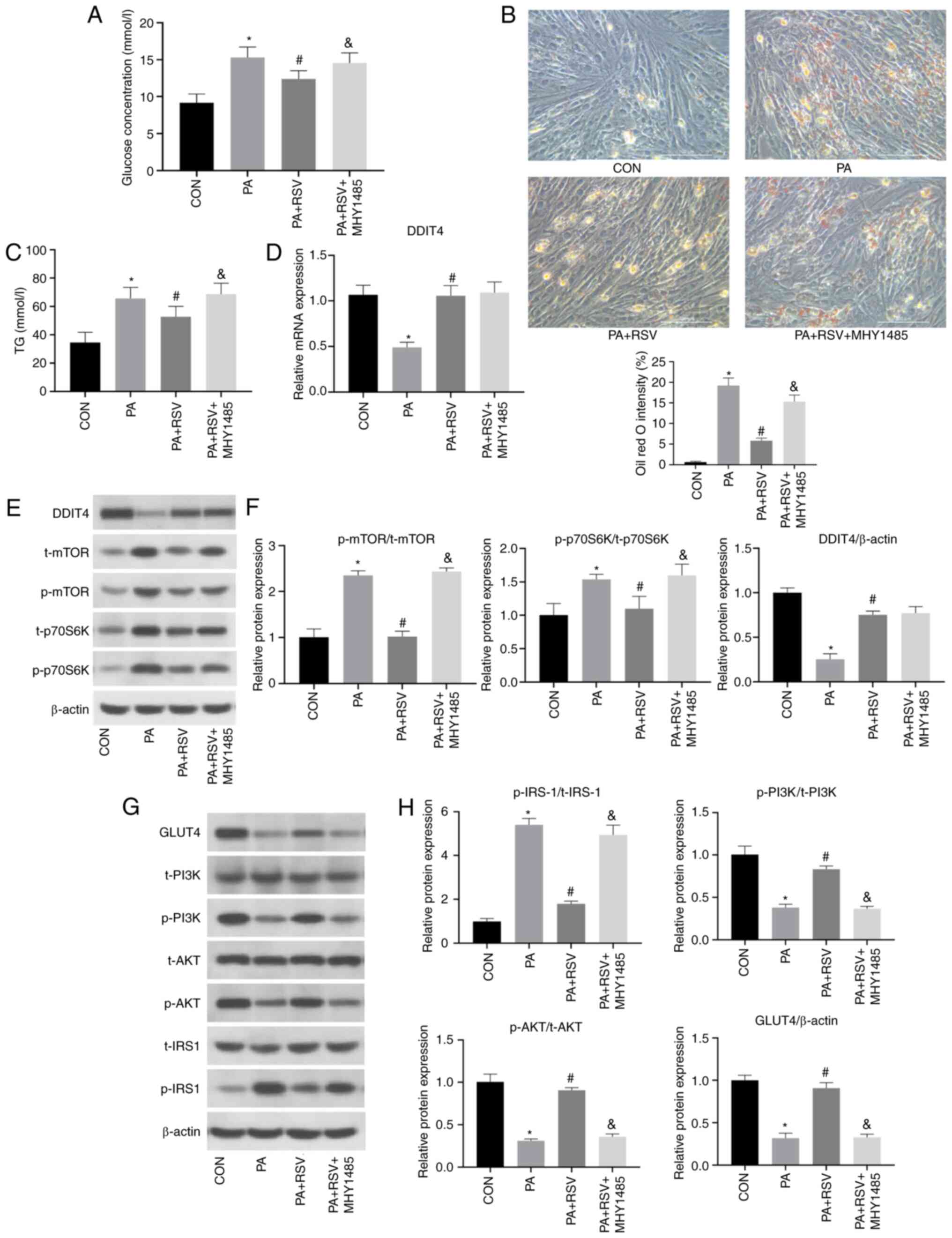
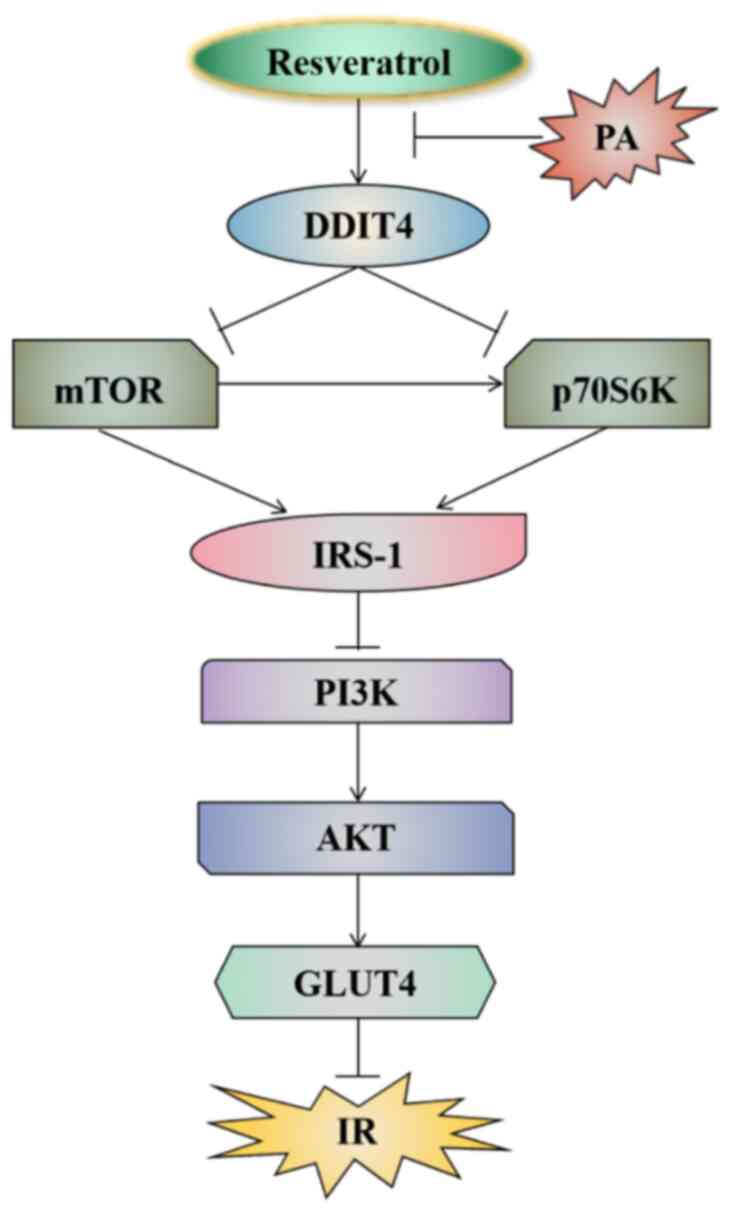
|
1
|
Wang Y, Yang LZ, Yang DG, Zhang QY, Deng
ZN, Wang K and Mao XJ: MiR-21 antagomir improves insulin resistance
and lipid metabolism disorder in streptozotocin-induced type 2
diabetes mellitus rats. Ann Palliat Med. 9:394–404. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fernandes GW and Bocco BMLC: Hepatic
mediators of lipid metabolism and ketogenesis: Focus on fatty liver
and diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 17:e1103201875392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petersen MC and Shulman GI: Mechanisms of
insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol Rev. 98:2133–2223.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Merz KE and Thurmond DC: Role of skeletal
muscle in insulin resistance and glucose uptake. Compr Physiol.
10:785–809. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Houzelle A, Jörgensen JA, Schaart G,
Daemen S, van Polanen N, Fealy CE, Hesselink MKC, Schrauwen P and
Hoeks J: Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial dynamics in relation
to oxidative capacity and insulin sensitivity. Diabetologia.
64:424–436. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Robertson I, Wai Hau T, Sami F, Sajid Al
M, Badgujar V, Murtuja S, Saquib Hasnain M, Khan A, Majeed S and
Tahir Ansari M: The science of resveratrol, formulation,
pharmacokinetic barriers and its chemotherapeutic potential. Int J
Pharm. 618:1216052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su M, Zhao W, Xu S and Weng J: Resveratrol
in treating diabetes and its cardiovascular complications: A review
of its mechanisms of action. Antioxidants (Basel). 11:10852022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mongioì LM, La Vignera S, Cannarella R,
Cimino L, Compagnone M, Condorell RA and Calogero AE: The role of
resveratrol administration in human obesity. Int J Mol Sci.
22:43622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barber TM, Kabisch S, Randeva HS, Pfeiffer
AFH and Weickert MO: Implications of resveratrol in obesity and
insulin resistance: A state-of-the-art review. Nutrients.
14:28702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang BB and Chiang BH: Amelioration of
insulin resistance using the additive effect of ferulic acid and
resveratrol on vesicle trafficking for skeletal muscle glucose
metabolism. Phytother Res. 34:808–816. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abo Alrob O, Al-Horani RA, Altaany Z and
Nusair MB: Synergistic beneficial effects of resveratrol and diet
on high-fat diet-induced obesity. Medicina (Kaunas). 58:13012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meng Q, Li J, Wang C and Shan A:
Biological function of resveratrol and its application in animal
production: A review. J Anim Sci Biotechno. 14:252023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shahwan M, Alhumaydhi F, Ashraf GM, Hasan
PMZ and Shamsi A: Role of polyphenols in combating type 2 diabetes
and insulin resistance. Int J Biol Macromol. 206:567–579. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koundouros N and Blenis J: Targeting mTOR
in the context of diet and whole-body metabolism. Endocrinology.
163:bqac0412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan H, Wu Y, Yu S, Li X, Wang A, Wang S,
Chen W and Lu Y: Critical role of mTOR in regulating aerobic
glycolysis in carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 58:9–19. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rapaka D, Bitra VR, Challa SR and Adiukwu
PC: mTOR signaling as a molecular target for the alleviation of
Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Neurochem Int. 155:1053112022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ong PS, Wang LZ, Dai X, Tseng SH, Loo SJ
and Sethi G: Judicious toggling of mTOR activity to combat insulin
resistance and cancer: Current evidence and perspectives. Front
Pharmacol. 7:3952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pan S, Lin H, Luo H, Gao F, Meng L, Zhou
C, Jiang C, Guo Y, Ji Z, Chi J and Guo H: Folic acid inhibits
dedifferentiation of PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cells
by suppressing mTOR/P70S6K signaling. Am J Transl Res. 9:1307–1316.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Faheem Sivasubrmanian S: Fathoming the
role of mTOR in diabetes mellitus and its complications. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 16:520–529. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hayasaka M, Tsunekawa H, Yoshinaga M and
Murakami T: Endurance exercise induces REDD1 expression and
transiently decreases mTORC1 signaling in rat skeletal muscle.
Physiol Rep. 2:e122542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gordon BS, Williamson DL, Lang CH,
Jefferson LS and Kimball SR: Nutrient-induced stimulation of
protein synthesis in mouse skeletal muscle is limited by the mTORC1
repressor REDD1. J Nutr. 145:708–713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lipina C and Hundal HS: Is REDD1 a
metabolic éminence grise? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 27:868–880.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
DeYoung MP, Horak P, Sofer A, Sgroi D and
Ellisen LW: Hypoxia regulates TSC1/2-mTOR signaling and tumor
suppression through REDD1-mediated 14-3-3 shuttling. Genes Dev.
22:239–251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Regazzetti C, Dumas K, Le Marchand-Brustel
Y, Peraldi P, Tanti JF and Giorgetti-Peraldi S: Regulated in
development and DNA damage responses-1 (REDD1) protein contributes
to insulin signaling pathway in adipocytes. PLoS One. 7:e521542012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shengchen W, Jing L, Yujie Y, Yue W and
Shiwen X: Polystyrene microplastics-induced ROS overproduction
disrupts the skeletal muscle regeneration by converting myoblasts
into adipocytes. J Hazard Mater. 417:1259622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Babacanoglu C, Yildirim N, Sadi G, Pektas
MB and Akar F: Resveratrol prevents high-fructose corn
syrup-induced vascular insulin resistance and dysfunction in rats.
Food Chem Toxicol. 60:160–167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sung MM, Kim TT, Denou E, Soltys CM, Hamza
SM, Byrne NJ, Masson G, Park H, Wishart DS, Madsen KL, et al:
Improved glucose homeostasis in obese mice treated with resveratrol
is associated with alterations in the gut microbiome. Diabetes.
66:418–425. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu C, Xing H, Yang L, Chen K, Shu L, Zhao
X and Song G: Resveratrol ameliorates high-fat-diet-induced
abnormalities in hepatic glucose metabolism in mice via the
AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2021:66169062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shu L, Zhao H, Huang W, Hou G, Song G and
Ma H: Resveratrol upregulates mmu-miR-363-3p via the PI3K-Akt
pathway to improve insulin resistance induced by a high-fat diet in
mice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 13:391–403. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Z, Zhang Z, Song G, Wang X, Xing H and
Wang C: Resveratrol alleviates skeletal muscle insulin resistance
by downregulating long noncoding RNA. Int J Endocrinol.
2022:25395192020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang YJ, Zhao H, Dong L, Zhen YF, Xing
HY, Ma HJ and Song GY: Resveratrol ameliorates high-fat
diet-induced insulin resistance and fatty acid oxidation via
ATM-AMPK axis in skeletal muscle. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:9117–9125. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dennis MD, Coleman CS, Berg A, Jefferson
LS and Kimball SR: REDD1 enhances protein phosphatase 2A-mediated
dephosphorylation of Akt to repress mTORC1 signaling. Sci Signal.
7:ra682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ellisen LW, Ramsayer KD, Johannessen CM,
Yang A, Beppu H, Minda K, Oliner JD, McKeon F and Haber DA: REDD1,
a developmentally regulated transcriptional target of p63 and p53,
links p63 to regulation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
10:995–1005. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shoshani T, Faerman A, Mett I, Zelin E,
Tenne T, Gorodin S, Moshel Y, Elbaz S, Budanov A, Chajut A, et al:
Identification of a novel hypoxia-inducible factor 1-responsive
gene, RTP801, involved in apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 22:2283–2293.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Z, Malone MH, Thomenius MJ, Zhong F,
Xu F and Distelhorst CW: Dexamethasone-induced gene 2 (dig2) is a
novel pro-survival stress gene induced rapidly by diverse apoptotic
signals. J Biol Chem. 278:27053–27058. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dungan CM, Wright DC and Williamson DL:
Lack of REDD1 reduces whole body glucose and insulin tolerance, and
impairs skeletal muscle insulin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 453:778–783. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jin HO, Hong SE, Kim JH, Choi HN, Kim K,
An S, Choe TB, Hwang CS, Lee JH, Kim JI, et al: Sustained
overexpression of Redd1 leads to Akt activation involved in cell
survival. Cancer Lett. 336:319–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Z, Liu F, Qu H, Wang H, Xiao X and
Deng H: 1, 25(OH)2D3 protects β cell against high
glucose-induced apoptosis through mTOR suppressing. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 414:111–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen DP, Ma YP, Zhuo L, Zhang Z, Zou GM,
Yang Y, Gao HM and Li WG: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3
inhibits the proliferation of rat mesangial cells induced by high
glucose via DDIT4. Oncotarget. 9:418–427. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang H, Wang J, Qu H, Wei H, Ji B, Yang Z,
Wu J, He Q, Luo Y, Liu D, et al: In vitro and in vivo inhibition of
mTOR by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 to improve early
diabetic nephropathy via the DDIT4/TSC2/mTOR pathway. Endocrine.
54:348–359. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vlavcheski F and Tsiani E: Attenuation of
free fatty acid-induced muscle insulin resistance by rosemary
extract. Nutrients. 10:16232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Den Hartogh DJ, Vlavcheski F, Giacca A and
Tsiani E: Attenuation of free fatty acid (FFA)-induced skeletal
muscle cell insulin resistance by resveratrol is linked to
activation of AMPK and inhibition of mTOR and p70S6K. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:49002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|