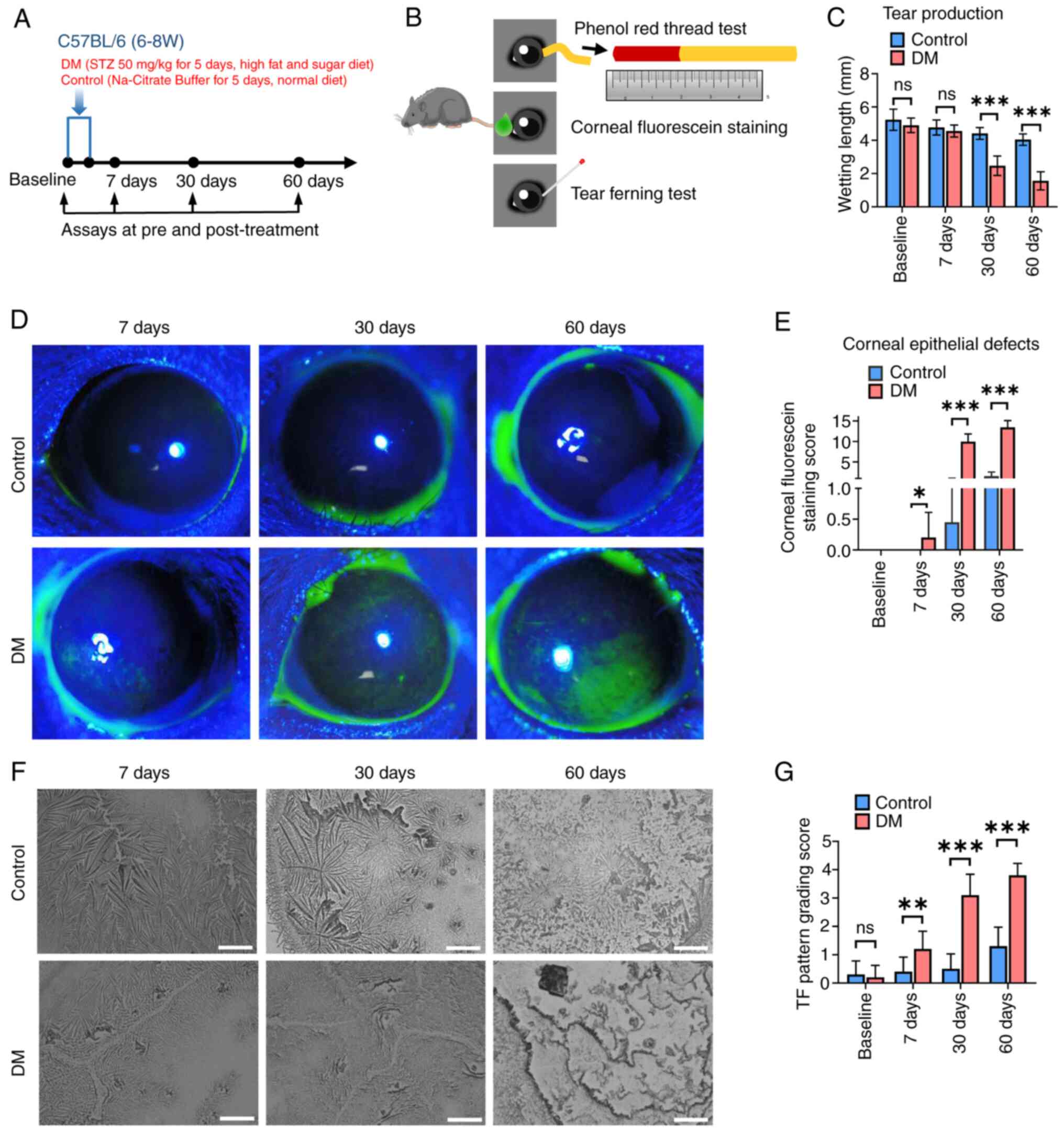
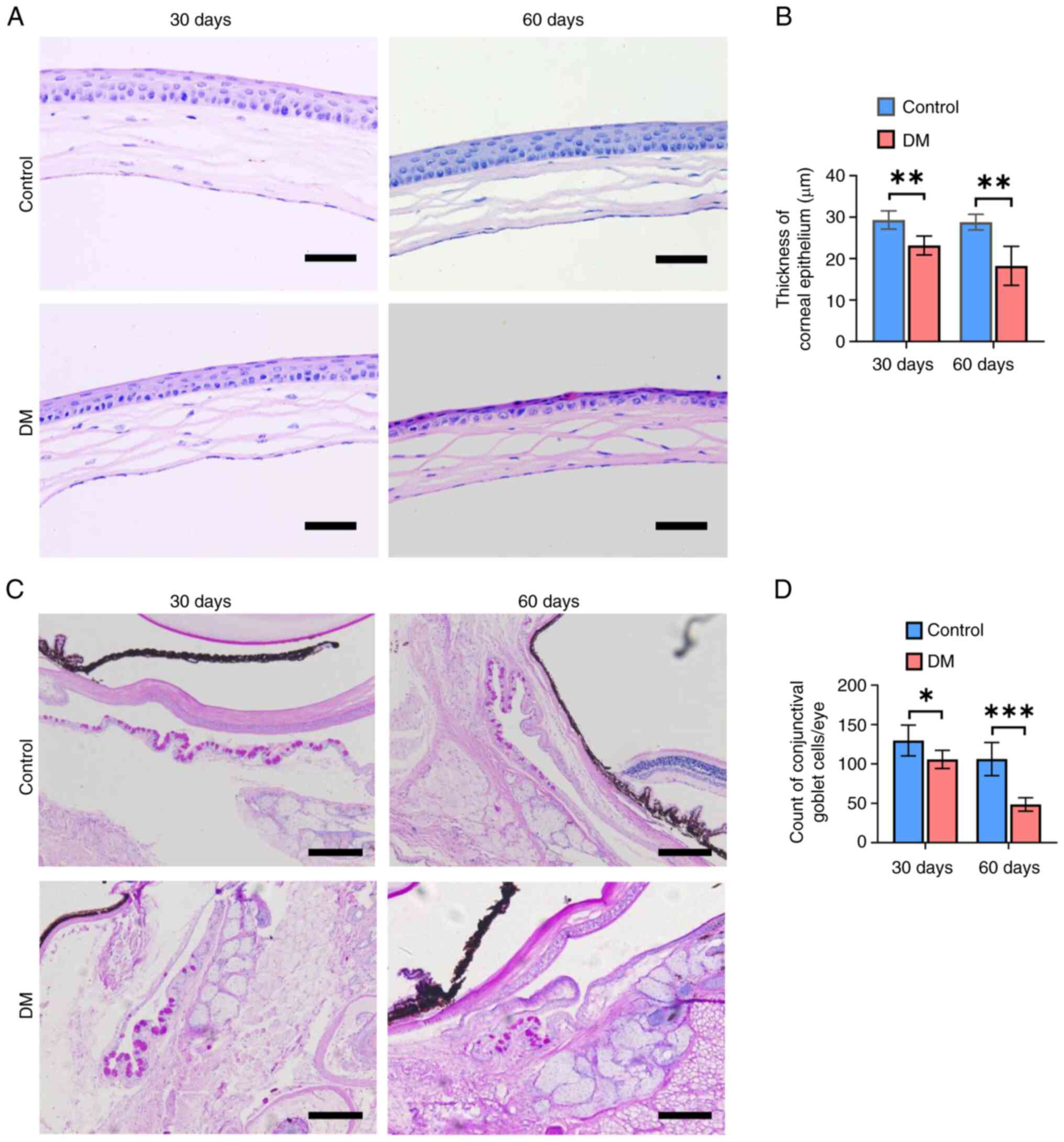
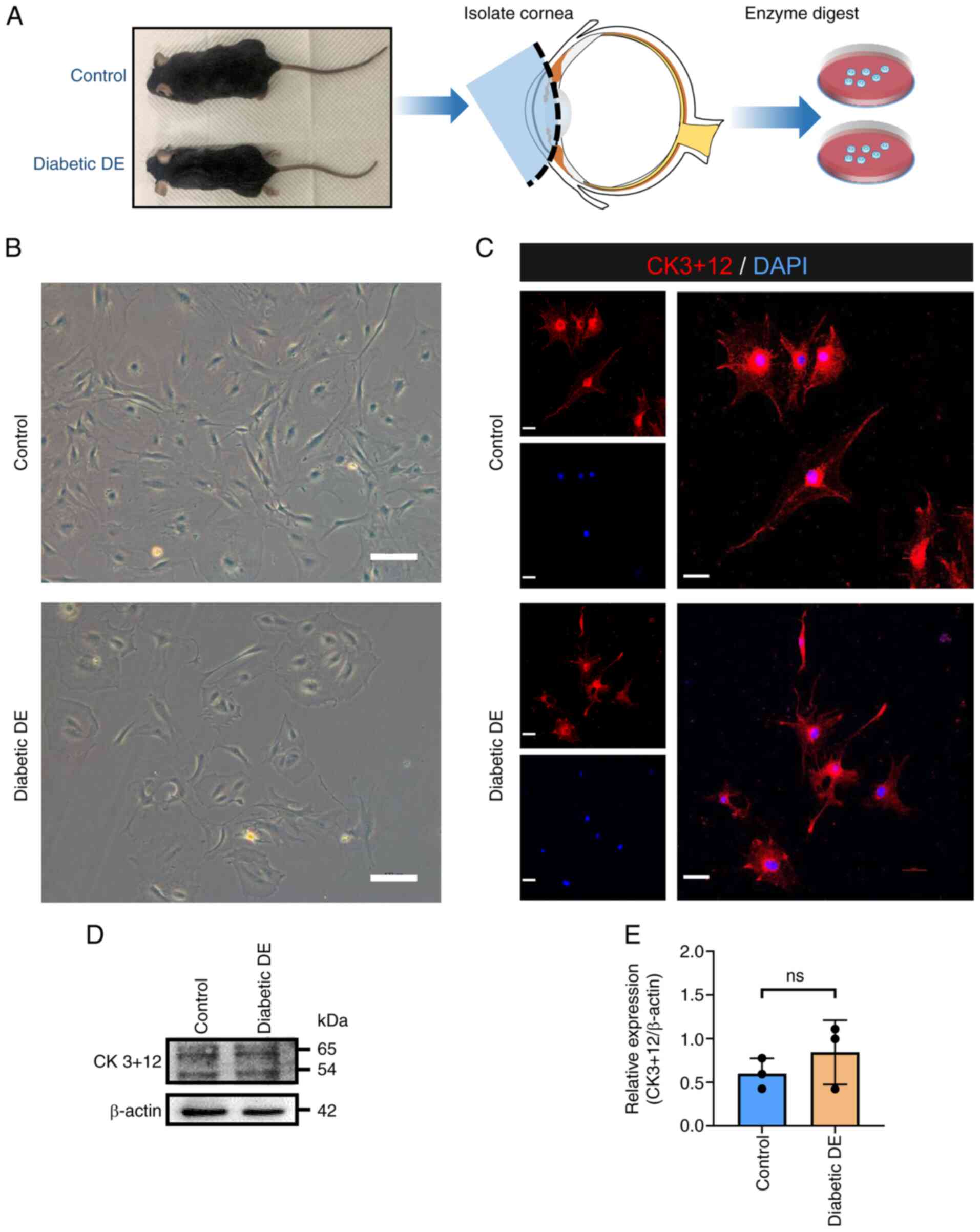
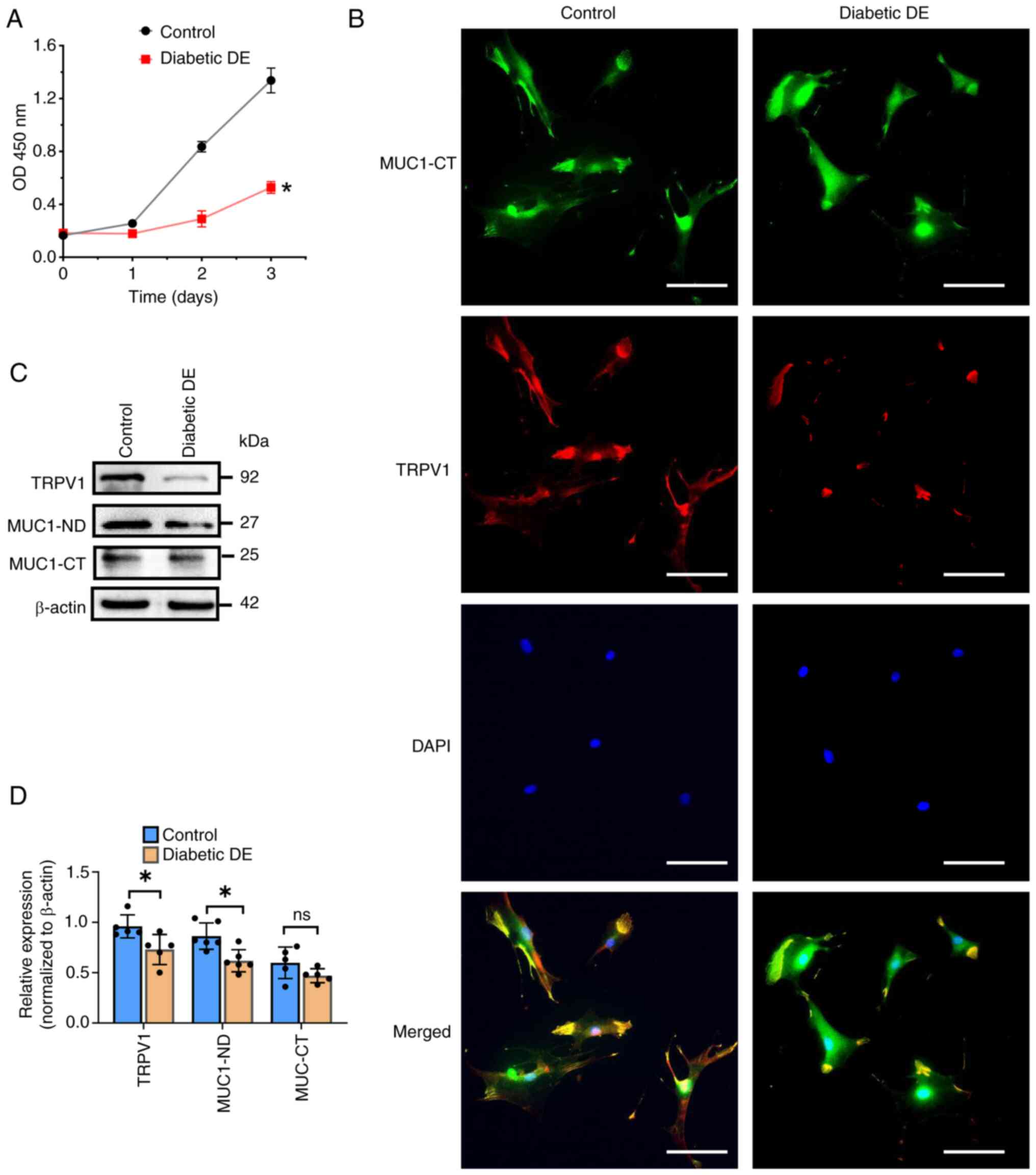
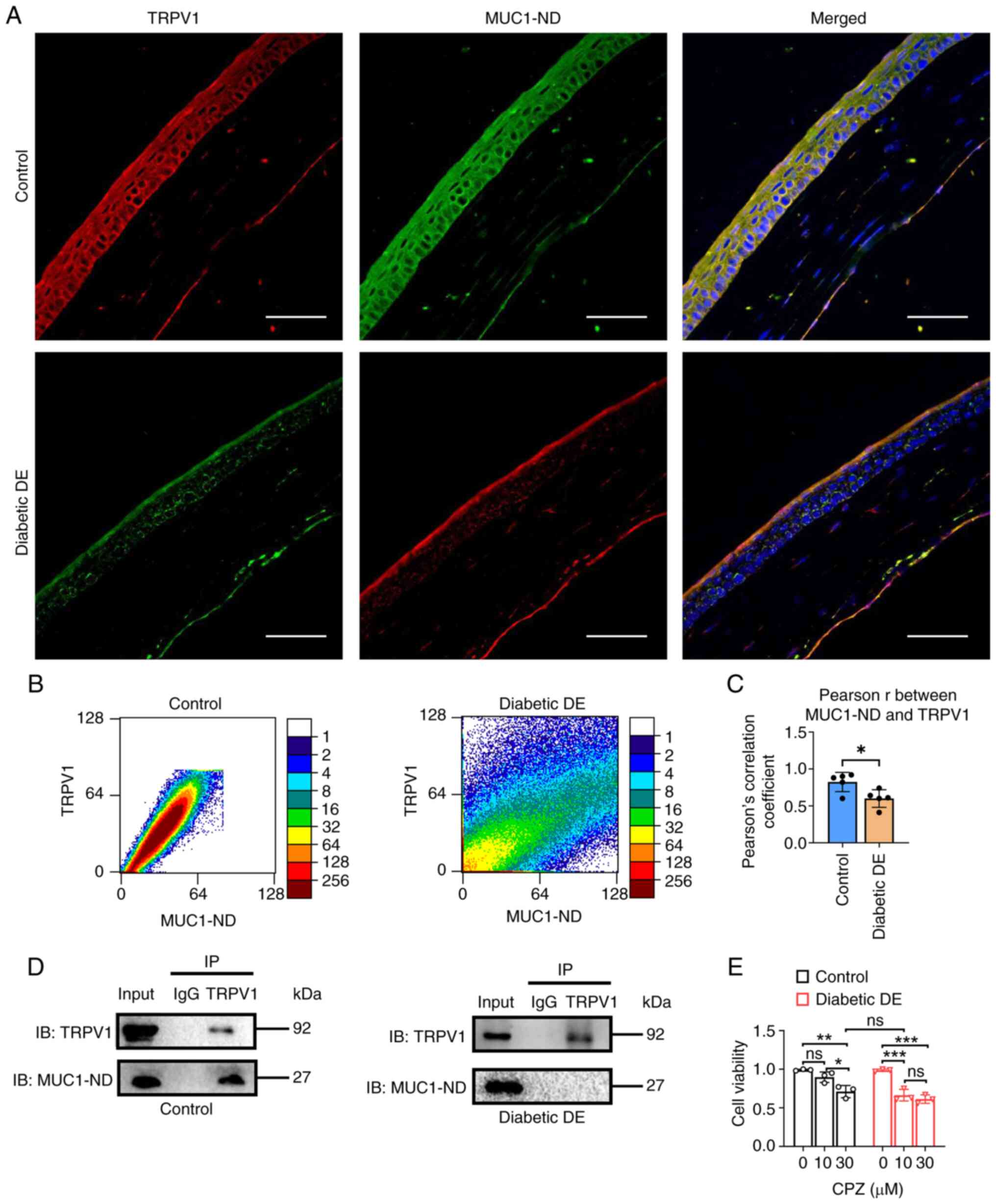
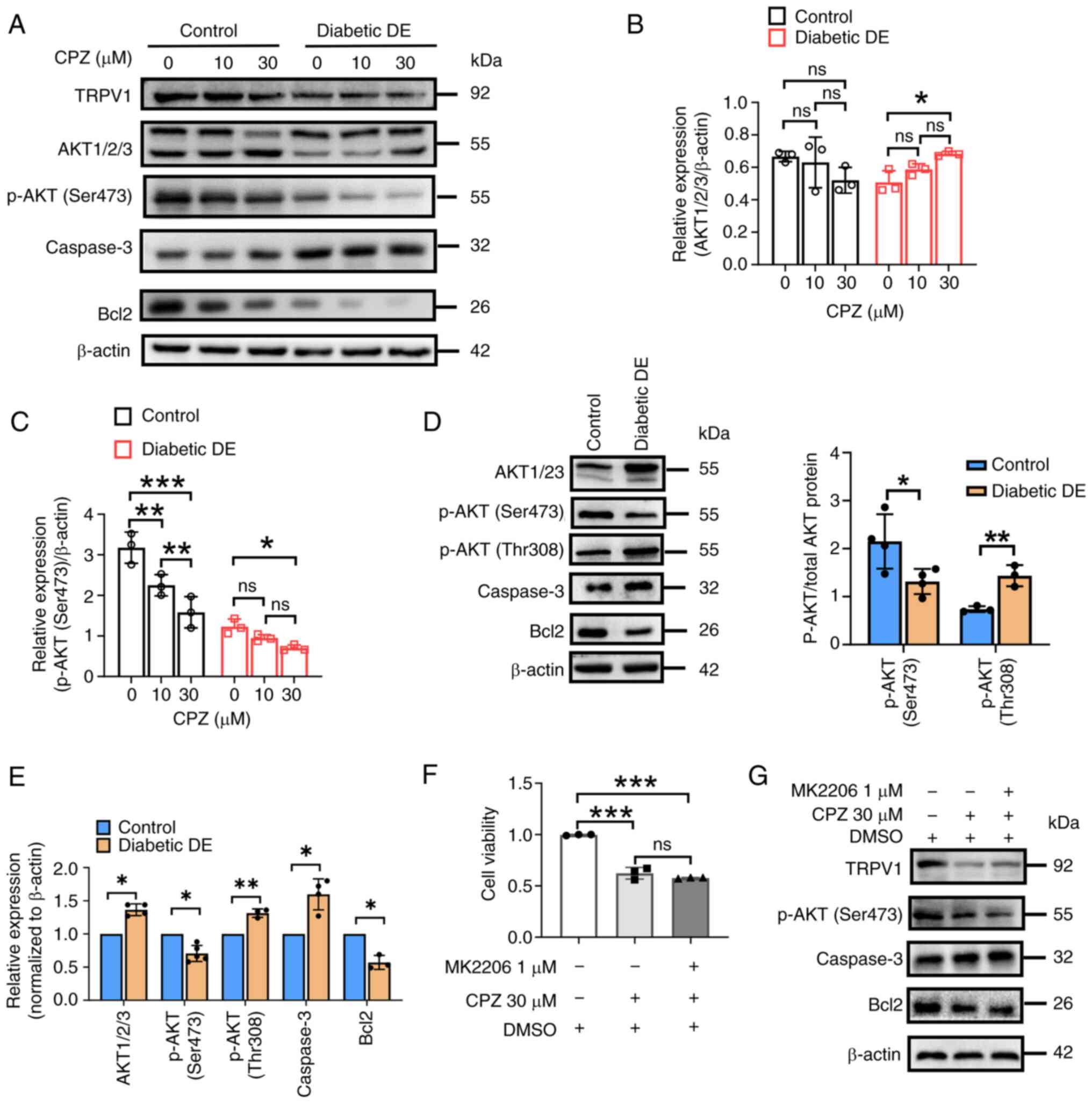
|
1
|
Ogurtsova K, Guariguata L, Barengo NC,
Ruiz PL, Sacre JW, Karuranga S, Sun H, Boyko EJ and Magliano DJ:
IDF diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in
adults for 2021. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 183:1091182022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Craig JP, Nichols KK, Akpek EK, Caffery B,
Dua HS, Joo CK, Liu Z, Nelson JD, Nichols JJ, Tsubota K and
Stapleton F: TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report.
Ocul Surf. 15:276–283. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stapleton F, Alves M, Bunya VY, Jalbert I,
Lekhanont K, Malet F, Na KS, Schaumberg D, Uchino M, Vehof J, et
al: TFOS DEWS II epidemiology report. Ocul Surf. 15:334–365. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Manaviat MR, Rashidi M, Afkhami-Ardekani M
and Shoja MR: Prevalence of dry eye syndrome and diabetic
retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. BMC Ophthalmol. 8:102008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Zhao L, Deng S, Sun X and Wang N:
Dry eye syndrome in patients with diabetes mellitus: Prevalence,
etiology, and clinical characteristics. J Ophthalmol.
2016:82010532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Belmonte C, Nichols JJ, Cox SM, Brock JA,
Begley CG, Bereiter DA, Dartt DA, Galor A, Hamrah P, Ivanusic JJ,
et al: TFOS DEWS II pain and sensation report. Ocul Surf.
15:404–437. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shih KC, Lam KS and Tong L: A systematic
review on the impact of diabetes mellitus on the ocular surface.
Nutr Diabetes. 7:e2512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han SB, Yang HK and Hyon JY: Influence of
diabetes mellitus on anterior segment of the eye. Clin Interv
Aging. 14:53–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaiserman I, Kaiserman N, Nakar S and
Vinker S: Dry eye in diabetic patients. Am J Ophthalmol.
139:498–503. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu L, Titone R and Robertson DM: The
impact of hyperglycemia on the corneal epithelium: Molecular
mechanisms and insight. Ocul Surf. 17:644–654. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Georgiev GA, Eftimov P and Yokoi N:
Contribution of mucins towards the physical properties of the tear
film: A modern update. Int J Mol Sci. 20:61322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ablamowicz AF and Nichols JJ: Ocular
surface membrane-associated mucins. Ocul Surf. 14:331–341. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shirai K and Saika S: Ocular surface
mucins and local inflammation-studies in genetically modified mouse
lines. BMC Ophthalmol. 15 (Suppl 1):S1542015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Martinez-Carrasco R, Argüeso P and Fini
ME: Membrane-associated mucins of the human ocular surface in
health and disease. Ocul Surf. 21:313–330. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fini ME, Jeong S, Gong H,
Martinez-Carrasco R, Laver NMV, Hijikata M, Keicho N and Argüeso P:
Membrane-associated mucins of the ocular surface: New genes, new
protein functions and new biological roles in human and mouse. Prog
Retin Eye Res. 75:1007772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schroeder JA, Thompson MC, Gardner MM and
Gendler SJ: Transgenic MUC1 interacts with epidermal growth factor
receptor and correlates with mitogen-activated protein kinase
activation in the mouse mammary gland. J Biol Chem.
276:13057–13064. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Ren J, Yu W, Li Q, Kuwahara H, Yin
L, Carraway KL III and Kufe D: The epidermal growth factor receptor
regulates interaction of the human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma antigen with
c-Src and beta-catenin. J Biol Chem. 276:35239–35242. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morimoto Y, Yamashita N, Daimon T, Hirose
H, Yamano S, Haratake N, Ishikawa S, Bhattacharya A, Fushimi A,
Ahmad R, et al: MUC1-C is a master regulator of MICA/B NKG2D ligand
and exosome secretion in human cancer cells. J Immunother Cancer.
11:e0062382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thathiah A, Blobel CP and Carson DD: Tumor
Necrosis Factor-alpha Converting Enzyme/ADAM 17 Mediates MUC1
Shedding. J Biol Chem. 278:3386–3394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thathiah A and Carson DD: MT1-MMP mediates
MUC1 shedding independent of TACE/ADAM17. Biochem J. 382((Pt 1)):
363–373. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyazaki K, Kishimoto H, Kobayashi H,
Suzuki A, Higuchi K, Shirasaka Y and Inoue K: The glycosylated
N-terminal domain of MUC1 is involved in chemoresistance by
modulating drug permeation across the plasma membrane. Mol
Pharmacol. 103:166–175. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu R, Chen L, Zhao X, Bao L, Wei R and Wu
X: MUC1 promotes RIF by regulating macrophage ROS-SHP2 signaling
pathway to up-regulate inflammatory response and inhibit
angiogenesis. Aging (Albany NY). 16:3790–3802. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu L, Zhou L, Wang L, Mao Z, Zheng P,
Zhang F, Zhang H and Liu H: MUC1 attenuates neutrophilic airway
inflammation in asthma by reducing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated
pyroptosis through the inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.
Respir Res. 24:2552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Comes N, Gasull X and Callejo G: Proton
sensing on the ocular surface: Implications in eye pain. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7738712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang Y, Yang H, Wang Z, Okada Y, Saika S
and Reinach PS: Wakayama symposium: Dependence of corneal
epithelial homeostasis on transient receptor potential function.
Ocul Surf. 11:8–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang XL, Wang X, Shao L, Jiang GT, Min JW,
Mei XY, He XH, Liu WH, Huang WX and Peng BW: TRPV1 mediates
astrocyte activation and interleukin-1β release induced by hypoxic
ischemia (HI). J Neuroinflammation. 16:1142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Yang XL, Kong WL, Zeng ML, Shao L,
Jiang GT, Cheng JJ, Kong S, He XH, Liu WH, et al: TRPV1
translocated to astrocytic membrane to promote migration and
inflammatory infiltration thus promotes epilepsy after hypoxic
ischemia in immature brain. J Neuroinflammation. 16:2142019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu MJ, Chen YS, Huang HS and Ma MC:
Hypoxic preconditioning protects rat hearts against
ischemia-reperfusion injury via the
arachidonate12-lipoxygenase/transient receptor potential vanilloid
1 pathway. Basic Res Cardiol. 109:4142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang H, Wang Z, Capó-Aponte JE, Zhang F,
Pan Z and Reinach PS: Epidermal growth factor receptor
transactivation by the cannabinoid receptor (CB1) and transient
receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) induces differential
responses in corneal epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 91:462–471.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nie M, Bal MS, Yang Z, Liu J, Rivera C,
Wenzel A, Beck BB, Sakhaee K, Marciano DK and Wolf MT: Mucin-1
Increases Renal TRPV5 activity in vitro, and urinary level
associates with calcium nephrolithiasis in patients. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 27:3447–3458. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Al-Bataineh MM, Kinlough CL, Marciszyn A,
Lam T, Ye L, Kidd K, Maggiore JC, Poland PA, Kmoch S, Bleyer A, et
al: Influence of glycoprotein MUC1 on trafficking of the
Ca2+-selective ion channels, TRPV5 and TRPV6, and on in vivo
calcium homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 299:1029252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
The Association for Research in Vision and
Ophthalmology:ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic
and Vision Research. The Association for Research in Vision and
Ophthalmology; Rockville, MD: 2021
|
|
33
|
Masmali AM, Murphy PJ and Purslow C:
Development of a new grading scale for tear ferning. Cont Lens
Anterior Eye. 37:178–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rahman MM, Kim DH, Park CK and Kim YH:
Experimental models, induction protocols, and measured parameters
in dry eye disease: Focusing on practical implications for
experimental research. Int J Mol Sci. 22:121022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu J, Inomata T, Shih KC, Okumura Y,
Fujio K, Huang T, Nagino K, Akasaki Y, Fujimoto K, Yanagawa A, et
al: Application of animal models in interpreting dry eye disease.
Front Med (Lausanne). 9:8305922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qu M, Wan L, Dong M, Wang Y, Xie L and
Zhou Q: Hyperglycemia-induced severe mitochondrial bioenergetic
deficit of lacrimal gland contributes to the early onset of dry eye
in diabetic mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 166:313–323. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bai J, Fu H, Bazinet L, Birsner AE and
D'Amato RJ: A method for developing novel 3D Cornea-on-a-Chip using
primary murine corneal epithelial and endothelial cells. Front
Pharmacol. 11:4532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Corrales RM, Narayanan S, Fernández I,
Mayo A, Galarreta DJ, Fuentes-Páez G, Chaves FJ, Herreras JM and
Calonge M: Ocular mucin gene expression levels as biomarkers for
the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
52:8363–8369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Spurr-Michaud S, Argüeso P and Gipson I:
Assay of mucins in human tear fluid. Exp Eye Res. 84:939–950. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhai K, Liskova A, Kubatka P and
Büsselberg D: Calcium Entry through TRPV1: A potential target for
the regulation of proliferation and apoptosis in cancerous and
healthy cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:41772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sumioka T, Okada Y, Reinach PS, Shirai K,
Miyajima M, Yamanaka O and Saika S: Impairment of corneal
epithelial wound healing in a TRPV1-deficient mouse. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:3295–3302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Okada Y, Reinach PS, Shirai K, Kitano A,
Kao WW, Flanders KC, Miyajima M, Liu H, Zhang J and Saika S: TRPV1
involvement in inflammatory tissue fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol.
178:2654–2664. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nidegawa-Saitoh Y, Sumioka T, Okada Y,
Reinach PS, Flanders KC, Liu CY, Yamanaka O, Kao WW and Saika S:
Impaired healing of cornea incision injury in a TRPV1-deficient
mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 374:329–338. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pan Z, Wang Z, Yang H, Zhang F and Reinach
PS: TRPV1 activation is required for hypertonicity-stimulated
inflammatory cytokine release in human corneal epithelial cells.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:485–493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Reinach PS, Mergler S, Okada Y and Saika
S: Ocular transient receptor potential channel function in health
and disease. BMC Ophthalmol. 15 (Suppl 1):S1532015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jeon BH, Yoo YM, Jung EM and Jeung EB:
Dexamethasone treatment increases the intracellular calcium level
through TRPV6 in A549 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:10502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Manning BD and Toker A: AKT/PKB Signaling:
Navigating the network. Cell. 169:381–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Y, Li J, Zhao C, Yang L, Qi X, Wang X,
Zhou Q and Shi W: Hyperglycemia-reduced NAD+ biosynthesis impairs
corneal epithelial wound healing in diabetic mice. Metabolism.
114:1544022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pham TH, Jin SW, Lee GH, Park JS, Kim JY,
Thai TN, Han EH and Jeong HG: Sesamin induces endothelial nitric
oxide synthase activation via transient receptor potential
vanilloid type 1. J Agric Food Chem. 68:3474–3484. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|