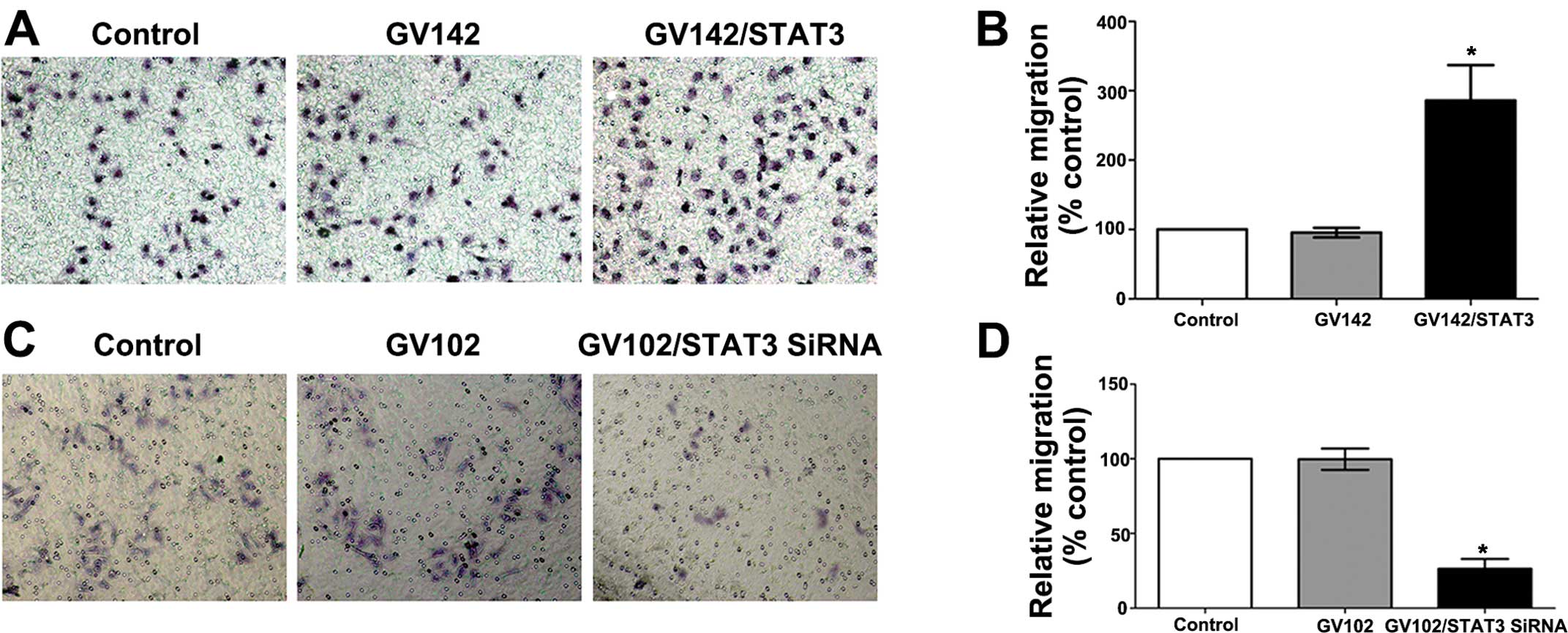
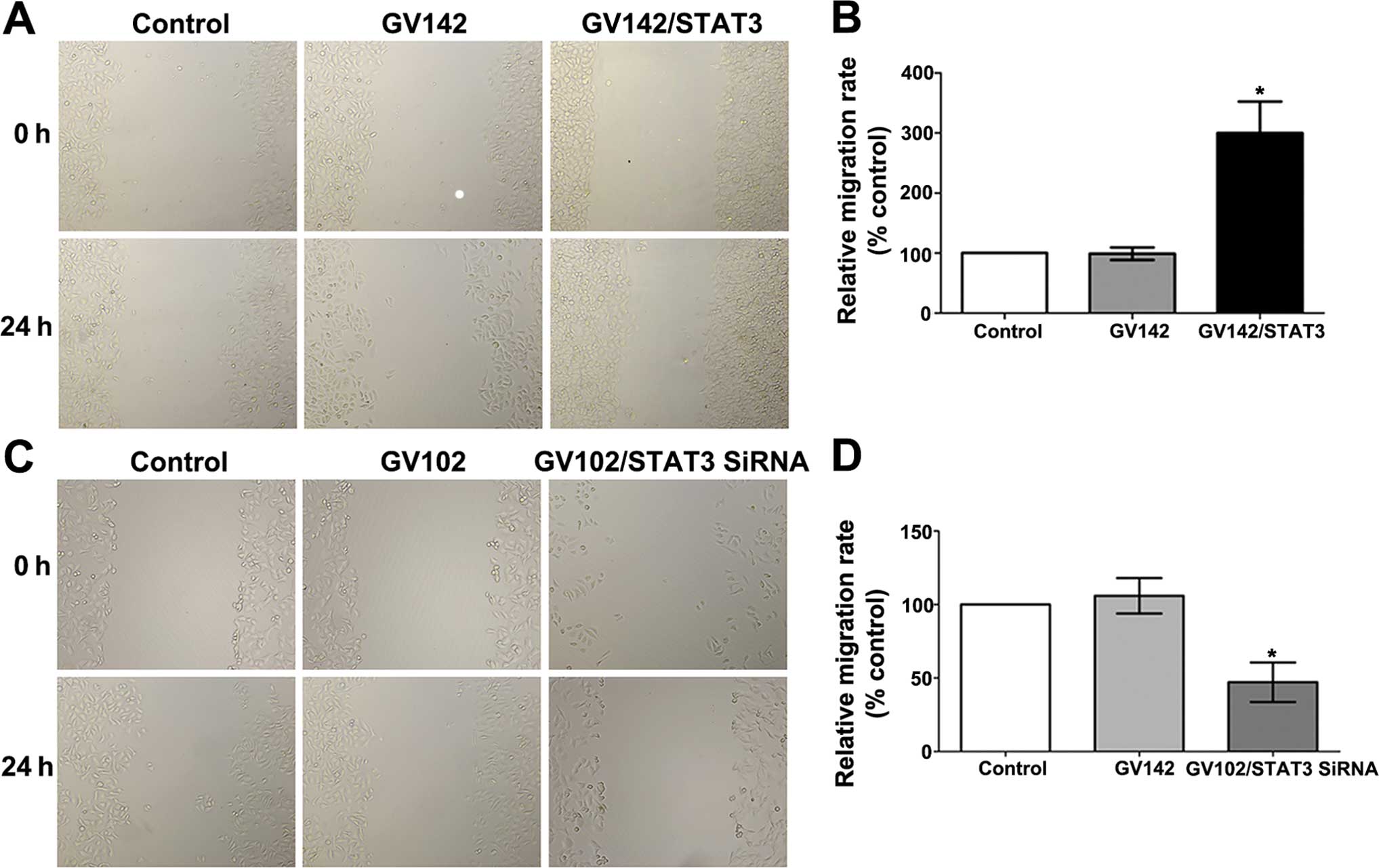
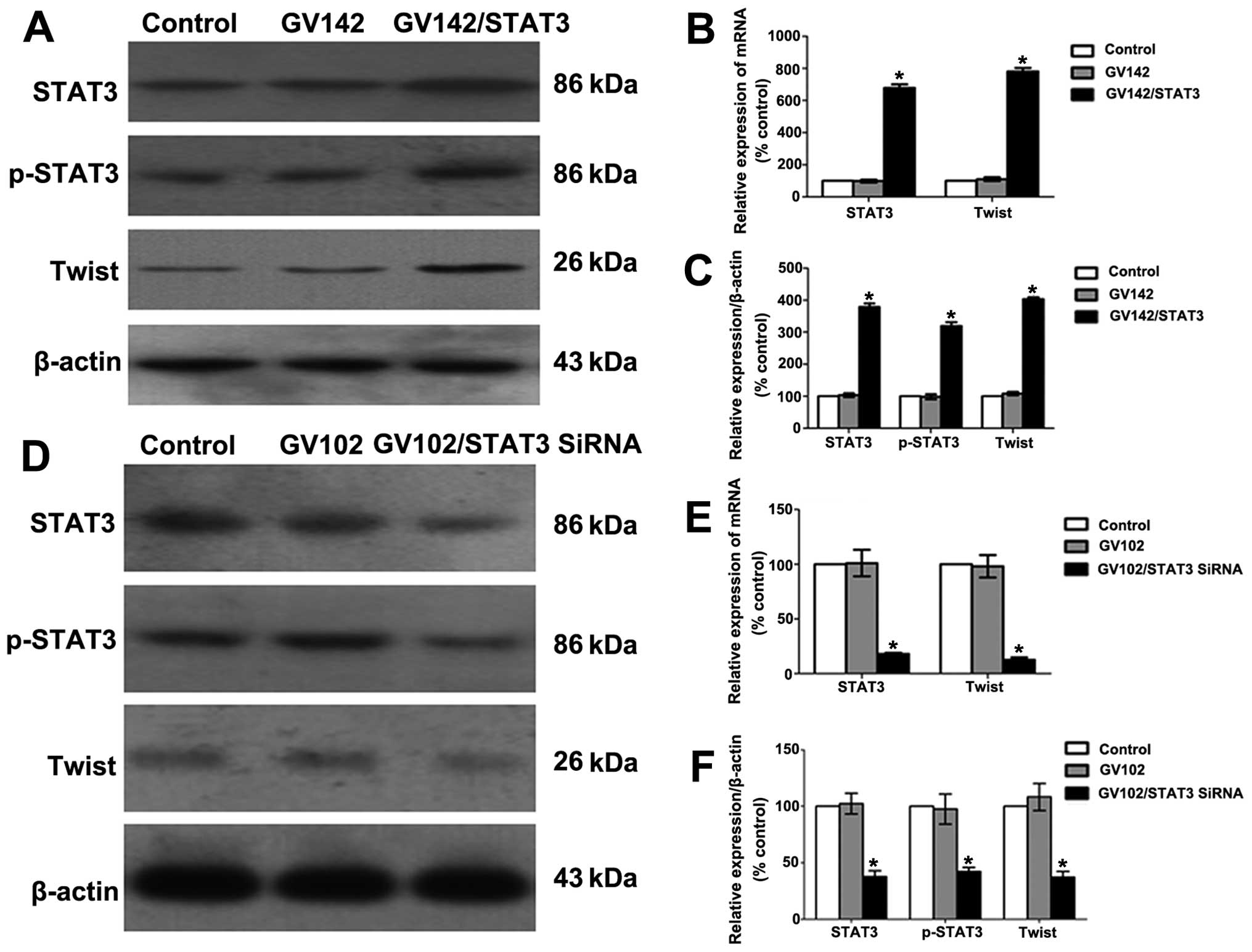
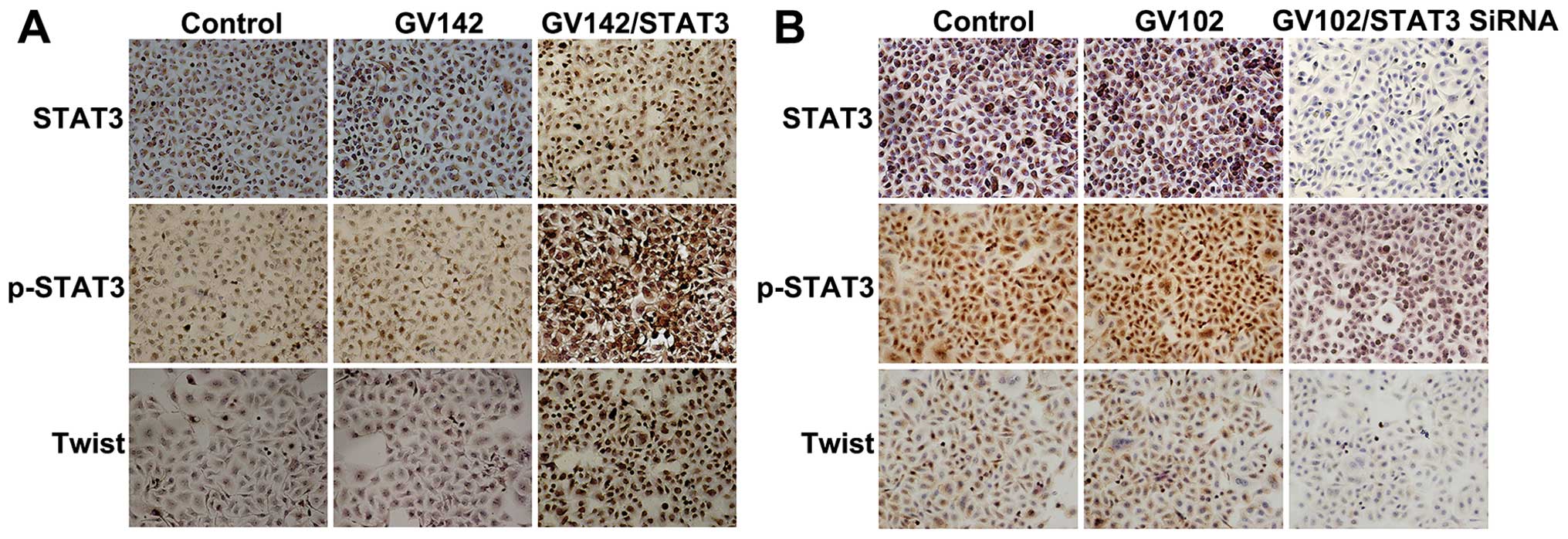
|
1
|
Kensler TW, Qian GS, Chen JG and Groopman
JD: Translational strategies for cancer prevention in liver. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:321–329. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tung-Ping Poon R, Fan ST and Wong J: Risk
factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence
after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 232:10–24.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grünert S, Jechlinger M and Beug H:
Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial
plasticity and metastasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:657–665. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee TK, Man K, Poon RT, Lo CM, Yuen AP, Ng
IO, Ng KT, Leonard W and Fan ST: Signal transducers and activators
of transcription 5b activation enhances hepatocellular carcinoma
aggressiveness through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cancer Res. 66:9948–9956. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang C, Cao J, Huang KJ, Zhang F, Jiang
T, Zhu L and Qiu ZJ: Inhibition of STAT3 activity with AG490
decreases the invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro.
Cancer Sci. 97:1417–1423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata
Y, Yoshizaki A, Nagayasu T and Sekine I: Expression of p-STAT3 in
human colorectal adenocarcinoma and adenoma; correlation with
clinicopathological factors. J Clin Pathol. 58:833–838. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suiqing C, Min Z and Lirong C:
Overexpression of phosphorylated-STAT3 correlated with the invasion
and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Dermatol.
32:354–360. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang C, Yang G, Jiang T, Zhu G, Li H and
Qiu Z: The effects and mechanisms of blockage of STAT3 signaling
pathway on IL-6 inducing EMT in human pancreatic cancer cells in
vitro. Neoplasma. 58:396–405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Xia W, Cao X, Shih JY, Wei
Y, Abbruzzese JL, Hortobagyi GN and Hung MC: Epidermal growth
factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer
Res. 67:9066–9076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng GZ, Zhang WZ, Sun M, Wang Q, Coppola
D, Mansour M, Xu LM, Costanzo C, Cheng JQ and Wang LH: Twist is
transcriptionally induced by activation of STAT3 and mediates STAT3
oncogenic function. J Biol Chem. 283:14665–14673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiong H, Hong J, Du W, et al: Roles of
STAT3 and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human
colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
287:5819–5832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Zhang CH, Xu GL, Jia WD, Li JS, Ma JL, Ren
WH, Ge YS, Yu JH, Liu WB and Wang W: Activation of STAT3 signal
pathway correlates with twist and E-cadherin expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significance. J Surg
Res. 174:120–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang W, Zhu XD, Sun HC, Xiong YQ, Zhuang
PY, Xu HX, Kong LQ, Wang L, Wu WZ and Tang ZY: Depletion of
tumor-associated macrophages enhances the effect of sorafenib in
metastatic liver cancer models by antimetastatic and antiangiogenic
effects. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3420–3430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Tian B, Yang J, Zhao L, Wu X, Ye SL,
Liu YK and Tang ZY: Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials
established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on
metastatic characteristics. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 130:460–468.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Levy DE and Darnell JE Jr: Stats:
Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 3:651–662. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu Q, Briggs J, Park S, et al: Targeting
Stat3 blocks both HIF-1 and VEGF expression induced by multiple
oncogenic growth signaling pathways. Oncogene. 24:5552–5560. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S,
Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and
Weinberg RA: Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an
essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 117:927–939. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen L, Chan TH, Yuan YF, et al: CHD1L
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis in
mice and is associated with these processes in human patients. J
Clin Invest. 120:1178–1191. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, Xie D, Chen L, Fu
L, Lau SH, Li Y, Li Y and Guan XY: Overexpression of eukaryotic
initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor
metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51:1255–1263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho KH, Jeong KJ, Shin SC, Kang J, Park CG
and Lee HY: STAT3 mediates TGF-β1-induced TWIST1 expression and
prostate cancer invasion. Cancer Lett. 336:167–173. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taylor KM, Hiscox S and Nicholson RI: Zinc
transporter LIV-1: a link between cellular development and cancer
progression. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 15:461–463. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, Eberle G,
Voss B, Warda A, Löchner D and Birchmeier W: E-cadherin-mediated
cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells.
J Cell Biol. 113:173–185. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Birchmeier W and Behrens J: Cadherin
expression in carcinomas: role in the formation of cell junctions
and the prevention of invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1198:11–26. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Troyanovsky S: Cadherin dimers in
cell-cell adhesion. Eur J Cell Biol. 84:225–233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bukholm IK, Nesland JM, Kåresen R,
Jacobsen U and Børresen-Dale AL: E-cadherin and α-, β-, and
γ-catenin protein expression in relation to metastasis in human
breast carcinoma. J Pathol. 185:262–266. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomita K, van Bokhoven A, van Leenders GJ,
Ruijter ET, Jansen CF, Bussemakers MJ and Schalken JA: Cadherin
switching in human prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res.
60:3650–3654. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Islam S, Carey TE, Wolf GT, Wheelock MJ
and Johnson KR: Expression of N-cadherin by human squamous
carcinoma cells induces a scattered fibroblastic phenotype with
disrupted cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 135:1643–1654. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Iwatsuki H, Sasaki K, Suda M and Itano C:
Vimentin intermediate filament protein as differentiation marker of
optic vesicle epithelium in the chick embryo. Acta Histochem.
101:369–382. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu L, Lau SH, Tzang CH, et al: Association
of Vimentin overexpression and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.
Oncogene. 23:298–302. 2004.
|
|
32
|
Grimstad IA: Direct evidence that cancer
cell locomotion contributes importantly to invasion. Exp Cell Res.
173:515–523. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peinado H, Portillo F and Cano A:
Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and
carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 48:365–375. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tania M, Khan MA and Fu J: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition inducing transcription factors and
metastatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:7335–7342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP, et al: Twist
overexpression correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis
through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:5369–5376. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang Y and Massagué J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Twist in development and
metastasis. Cell. 118:277–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|