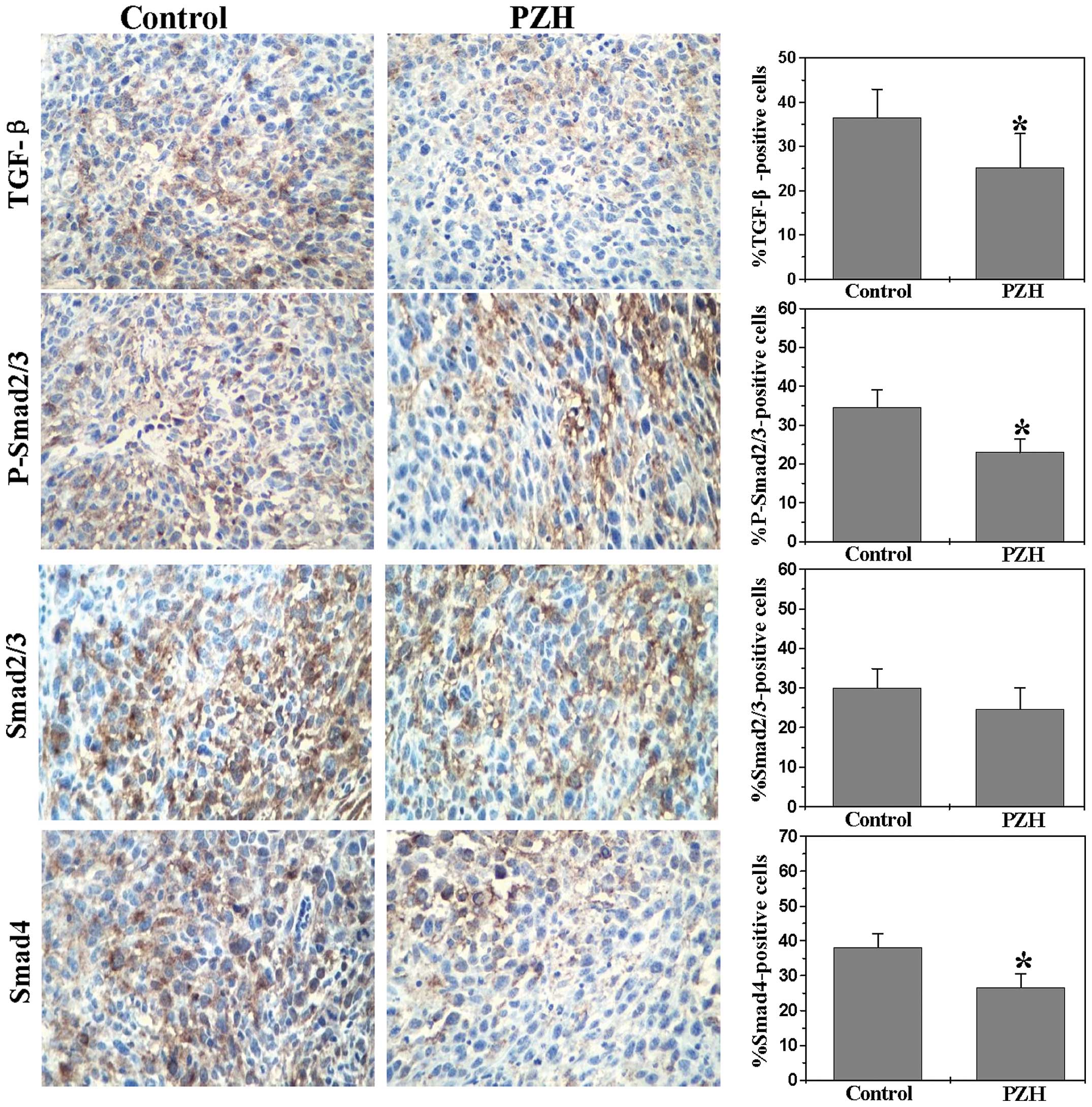
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gansler T, Ganz PA, Grant M, et al: Sixty
years of CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. CA Cancer J Clin.
60:345–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T and Thun M:
Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 52:23–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klymkowsky MW and Savagner P:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher’s conceptual
friend and foe. Am J Pathol. 174:1588–1593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Signaling
networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during
embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 98:1512–1520.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shinto O, Yashiro M, Kawajiri H, et al:
Inhibitory effect of a TGFbeta receptor type-I inhibitor, Ki26894,
on invasiveness of scirrhous gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
102:844–851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boose G and Stopper H: Genotoxicity of
several clinically used topoisomerase II inhibitors. Toxicol Lett.
116:7–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Newman D, Cragg G and Snader K: The
influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep.
17:215–234. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carmady B and Smith CA: Use of Chinese
medicine by cancer patients: a review of surveys. Chin Med.
9:222011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, .
Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. 1. Chinese Medical
Science and Technology Press; Beijing: pp. 573–575. 2010
|
|
13
|
Xu YY and Yu EX: Clinical analysis of the
effect of Pien Tze Huang in treatment of 42 patients with moderate
or advanced liver cancer. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med. 12:4–5.
1994.
|
|
14
|
Gu ZX: Therapeutical observation of
advanced colon cancer. Chin Tradit Patent Med. 15:231993.
|
|
15
|
Lin JM, Wei LH, Chen YQ, Liu XX, Hong ZF,
Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang induced apoptosis in human
colon cancer HT-29 cells is associated with regulation of the Bcl-2
family and activation of caspase 3. Chin J Integr Med. 17:685–690.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhuang QC, Hong F, Shen AL, et al: Pien
Tze Huang inhibits tumor cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis
via suppressing the STAT3 pathway in colorectal cancer mouse model.
Int J Oncol. 40:1569–1574. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen AL, Hong F, Liu LY, Lin JM, Zhuang
QC, Hong ZF and Peng J: Effects of Pien Tze Huang on angiogenesis
in vivo and in vitro. Chin J Integr Med. 18:431–436. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gumbiner BM: Regulation of
cadherin-mediated adhesion in morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
6:622–634. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Elliott RL and Blobe GC: Role of
transforming growth factor Beta in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
23:2078–2093. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Massagué J: TGFbeta signaling: receptors,
transducers, and Mad proteins. Cell. 85:947–950. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Caestecker MP, Piek E and Roberts AB:
Role of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1388–1402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Massagué J, Blain SW and Lo RS: TGFbeta
signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell.
103:295–309. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Sergina N, Ko TC, Gong J and
Brattain MG: Autocrine and exogenous transforming growth factor
beta control cell cycle inhibition through pathways with different
sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 279:40237–40244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oft M, Heider KH and Beug H: TGF-beta
signaling is necessary for carcinoma cell invasiveness and
metastasis. Curr Biol. 8:1243–1252. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Sun L, Myeroff L, et al:
Demonstration that mutation of the type II transforming growth
factor beta receptor inactivates its tumor suppressor activity in
replication error-positive colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
270:22044–22049. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Han W, Zborowska E, et al: Reduced
expression of transforming growth factor beta type I receptor
contributes to the malignancy of human colon carcinoma cells. J
Biol Chem. 271:17366–17371. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukushima T, Mashiko M, Takita K, et al:
Mutational analysis of TGF-beta type II receptor, Smad2, Smad3,
Smad4, Smad6 and Smad7 genes in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 22:315–320. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miyaki M, Iijima T, Konishi M, et al:
Higher frequency of Smad4 gene mutation in human colorectal cancer
with distant metastasis. Oncogene. 18:3098–3103. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van Roy F and Berx G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miyoshi J and Takai Y: Structural and
functional associations of apical junctions with cytoskeleton.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1778:670–691. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|