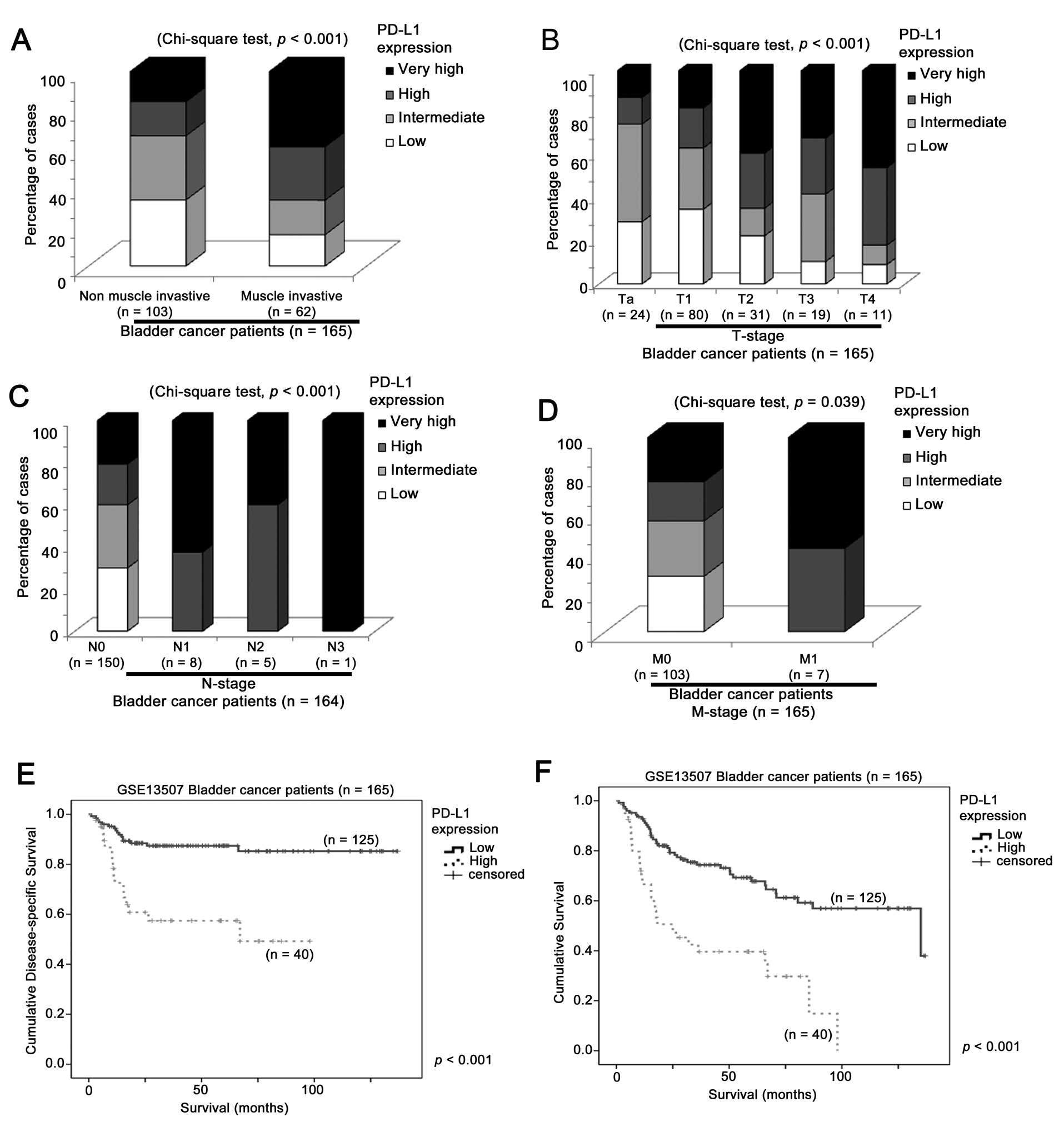
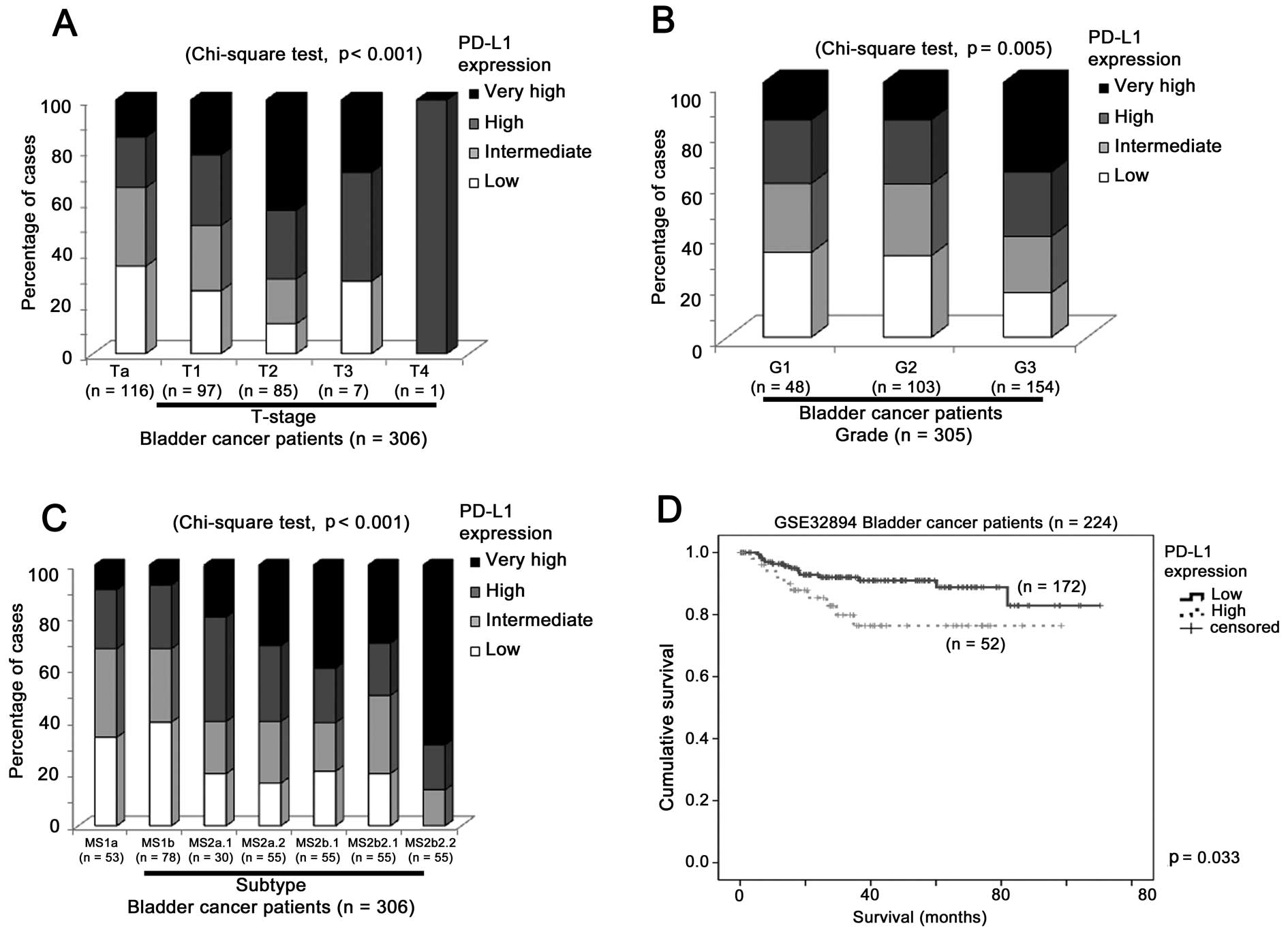
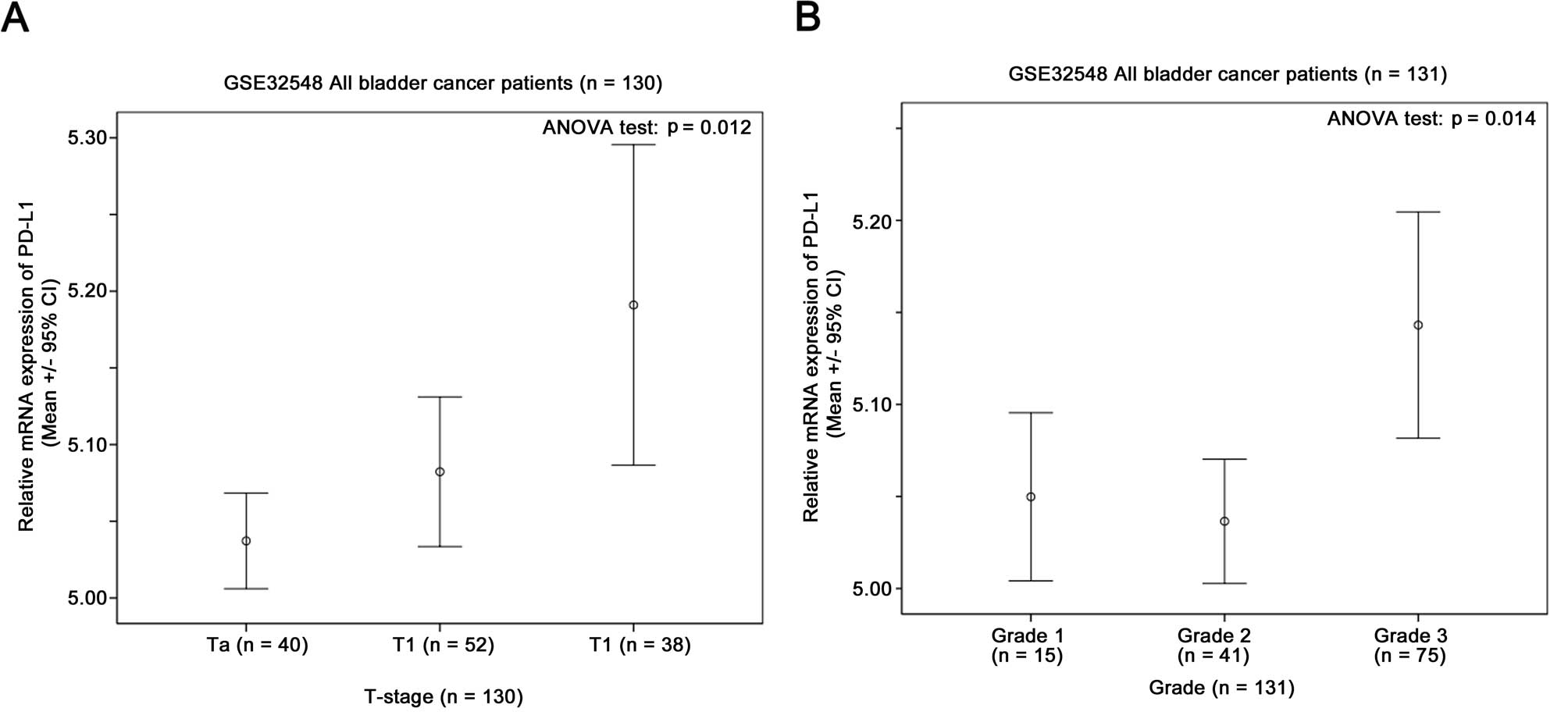
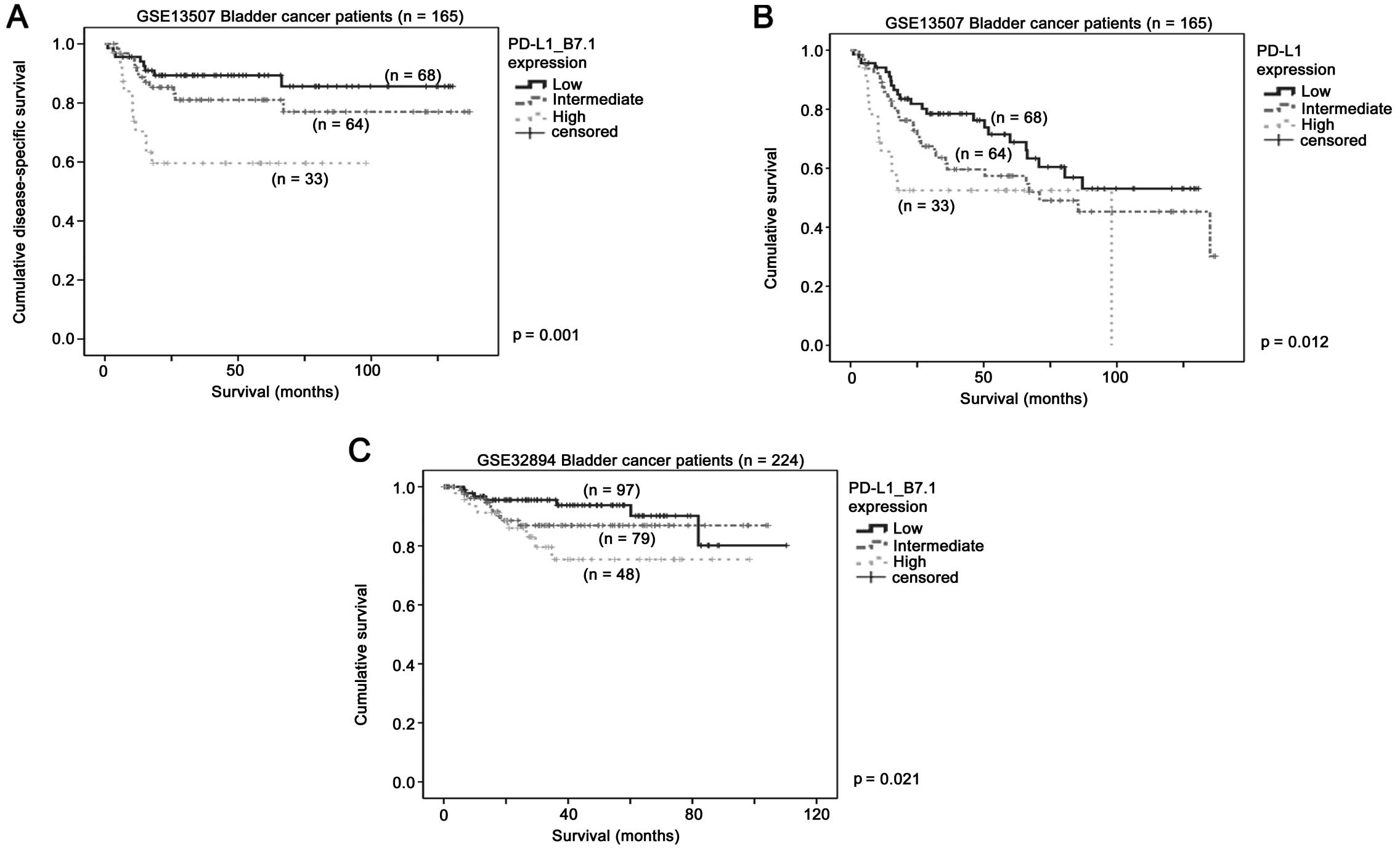
|
1
|
Liakou CI, Narayanan S, Ng Tang D,
Logothetis CJ and Sharma P: Focus on TILs: Prognostic significance
of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human bladder cancer. Cancer
Immun. 7:102007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Redelman-Sidi G, Glickman MS and Bochner
BH: The mechanism of action of BCG therapy for bladder cancer - a
current perspective. Nat Rev Urol. 11:153–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alexandroff AB, Jackson AM, O’Donnell MA
and James K: BCG immunotherapy of bladder cancer: 20 years on.
Lancet. 353:1689–1694. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen DS, Irving BA and Hodi FS: Molecular
pathways: Next-generation immunotherapy - inhibiting programmed
death-ligand 1 and programmed death-1. Clin Cancer Res.
18:6580–6587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakanishi J, Wada Y, Matsumoto K, Azuma M,
Kikuchi K and Ueda S: Overexpression of B7-H1 (PD-L1) significantly
associates with tumor grade and postoperative prognosis in human
urothelial cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 56:1173–1182. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Inman BA, Sebo TJ, Frigola X, Dong H,
Bergstralh EJ, Frank I, Fradet Y, Lacombe L and Kwon ED: PD-L1
(B7-H1) expression by urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and
BCG-induced granulomata: Associations with localized stage
progression. Cancer. 109:1499–1505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boorjian SA, Sheinin Y, Crispen PL, Farmer
SA, Lohse CM, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Kwon ED and Frank I: T-cell
coregulatory molecule expression in urothelial cell carcinoma:
Clinicopathologic correlations and association with survival. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:4800–4808. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xylinas E, Robinson BD, Kluth LA, Volkmer
BG, Hautmann R, Küfer R, Zerbib M, Kwon E, Thompson RH, Boorjian
SA, et al: Association of T-cell co-regulatory protein expression
with clinical outcomes following radical cystectomy for urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. Eur J Surg Oncol. 40:121–127. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Powles T, Vogelzang NJ, Fine GD, Eder JP,
Braiteh FS, Loriot Y, Zambrano CC, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Teng SM,
et al: Inhibition of PD-L1 by MPDL3280A and clinical activity in
pts with metastatic urothelial bladder cancer (UBC). J Clin Oncol
(ASCO Meeting Abstracts). 32:50112014.
|
|
10
|
Lee JS, Leem SH, Lee SY, Kim SC, Park ES,
Kim SB, Kim SK, Kim YJ, Kim WJ and Chu IS: Expression signature of
E2F1 and its associated genes predict superficial to invasive
progression of bladder tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:2660–2667. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sjödahl G, Lauss M, Lövgren K, Chebil G,
Gudjonsson S, Veerla S, Patschan O, Aine M, Fernö M, Ringnér M, et
al: A molecular taxonomy for urothelial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3377–3386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lindgren D, Sjödahl G, Lauss M, Staaf J,
Chebil G, Lövgren K, Gudjonsson S, Liedberg F, Patschan O, Månsson
W, et al: Integrated genomic and gene expression profiling
identifies two major genomic circuits in urothelial carcinoma. PLoS
One. 7:e388632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kulbe H, Levinson NR, Balkwill F and
Wilson JL: The chemokine network in cancer - much more than
directing cell movement. Int J Dev Biol. 48:489–496. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Corthay A: Does the immune system
naturally protect against cancer? Front Immunol. 5:1972014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kyi C and Postow MA: Checkpoint blocking
antibodies in cancer immunotherapy. FEBS Lett. 588:368–376. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Langer CJ: Emerging immunotherapies in the
treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): The role of immune
checkpoint inhibitors. Am J Clin Oncol. Mar 28–2014.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eruslanov E, Neuberger M, Daurkin I,
Perrin GQ, Algood C, Dahm P, Rosser C, Vieweg J, Gilbert SM and
Kusmartsev S: Circulating and tumor-infiltrating myeloid cell
subsets in patients with bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
130:1109–1119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Urquidi V, Kim J, Chang M, Dai Y, Rosser
CJ and Goodison S: CCL18 in a multiplex urine-based assay for the
detection of bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e377972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goodison S, Chang M, Dai Y, Urquidi V and
Rosser CJ: A multianalyte assay for the non-invasive detection of
bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e474692012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Miyake M, Ross S, Lawton A, Chang M, Dai
Y, Mengual L, Alcaraz A, Giacoia EG, Goodison S and Rosser CJ:
Investigation of CCL18 and A1AT as potential urinary biomarkers for
bladder cancer detection. BMC Urol. 13:422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D,
Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, Makrigiannakis A, Gray H,
Schlienger K, Liebman MN, et al: Intratumoral T cells, recurrence,
and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med.
348:203–213. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Oncology meets
immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity. 39:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gandhi C, Khan MM, Lentz SR and Chauhan
AK: ADAMTS13 reduces vascular inflammation and the development of
early atherosclerosis in mice. Blood. 119:2385–2391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Chauhan AK, Kisucka J, Brill A, Walsh MT,
Scheiflinger F and Wagner DD: ADAMTS13: A new link between
thrombosis and inflammation. J Exp Med. 205:2065–2074. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Atsumi T, Singh R, Sabharwal L, Bando H,
Meng J, Arima Y, Yamada M, Harada M, Jiang JJ, Kamimura D, et al:
Inflammation amplifier, a new paradigm in cancer biology. Cancer
Res. 74:8–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|