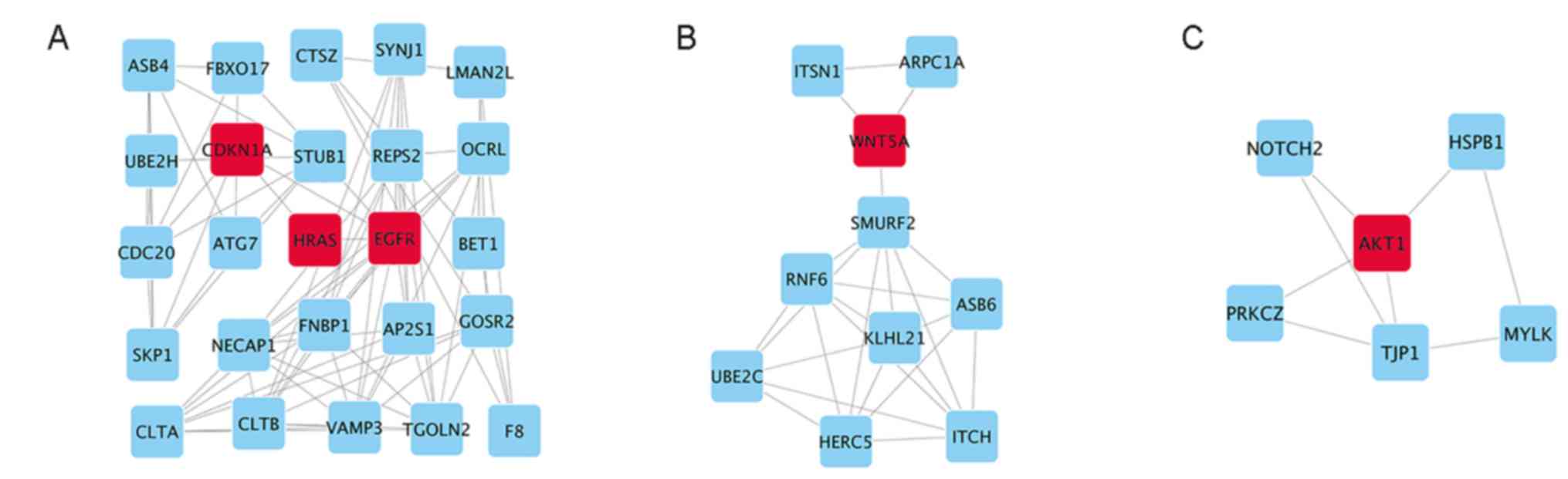
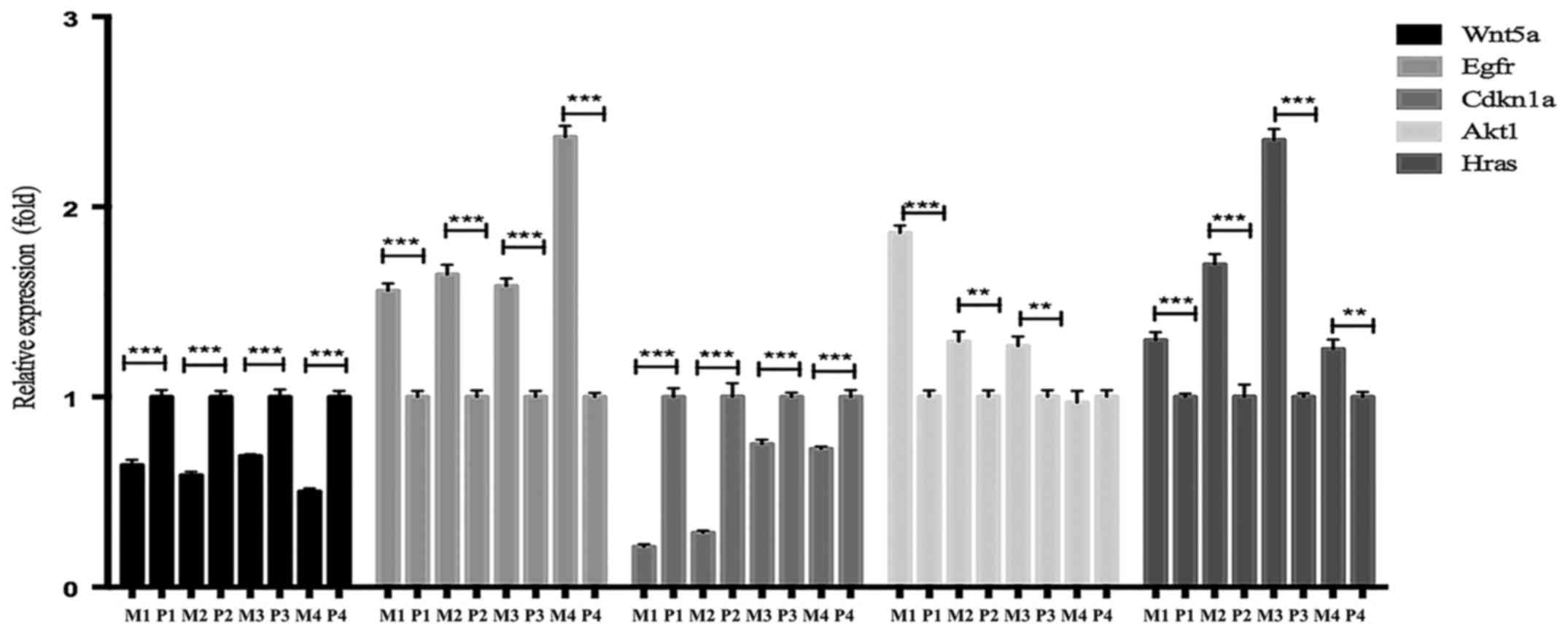
|
1
|
Choi Y, Sateia HF, Peairs KS and Stewart
RW: Screening for colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol. 44:34–44. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Manku G, Hueso A, Brimo F, Chan P,
Gonzalez-Peramato P, Jabado N, Gayden T, Bourgey M, Riazalhosseini
Y and Culty M: Changes in the expression profiles of claudins
during gonocyte differentiation and in seminomas. Andrology.
4:95–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Basu A, Seth S, Arora K and Verma M:
Evaluating estradiol levels in male patients with colorectal
carcinoma. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:BC08–BC10. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ciombor KK, Wu C and Goldberg RM: Recent
therapeutic advances in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Annu
Rev Med. 66:83–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu H, Gao G, Jiang L, Guo L, Lin M, Jiao
X, Jia W and Huang J: Decreased expression of miR-218 is associated
with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 6:2904–2911. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou C, Cui F, Li J, Wang D, Wei Y, Wu Y,
Wang J, Zhu H and Wang S: miR-650 represses high-risk
non-metastatic colorectal cancer progression via inhibition of
AKT2/GSK3β/E-cadherin pathway. Oncotarget. 8:49534–49547.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Rosa M, Pace U, Rega D, Costabile V,
Duraturo F, Izzo P and Delrio P: Genetics, diagnosis and management
of colorectal cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 34:1087–1096. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamasaki M, Takemasa I, Komori T, Watanabe
S, Sekimoto M, Doki Y, Matsubara K and Monden M: The gene
expression profile represents the molecular nature of liver
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 30:129–138.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hagland HR, Berg M, Jolma IW, Carlsen A
and Søreide K: Molecular pathways and cellular metabolism in
colorectal cancer. Dig Surg. 30:12–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao M, Zhong A, Patel N, Alur C and Vyas
D: High throughput RNA sequencing utility for diagnosis and
prognosis in colon diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 23:2819–2825.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Serratì S, De Summa S, Pilato B, Petriella
D, Lacalamita R, Tommasi S and Pinto R: Next-generation sequencing:
Advances and applications in cancer diagnosis. Onco Targets Ther.
9:7355–7365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Provenzani A, Fronza R, Loreni F, Pascale
A, Amadio M and Quattrone A: Global alterations in mRNA polysomal
recruitment in a cell model of colorectal cancer progression to
metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 27:1323–1333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . The Gene
Ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D322–D326.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . Gene Ontology
Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(D1): D1049–D1056.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1): 27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Köhler S, Bauer S, Horn D and Robinson PN:
Walking the interactome for prioritization of candidate disease
genes. Am J Hum Genet. 82:949–958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aran V, Victorino AP, Thuler LC and
Ferreira CG: Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, disease mechanisms
and interventions to reduce onset and mortality. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 15:195–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taylor-Weiner A, Zack T, O'Donnell E,
Guerriero JL, Bernard B, Reddy A, Han GC, AlDubayan S, Amin-Mansour
A, Schumacher SE, et al: Genomic evolution and chemoresistance in
germ-cell tumours. Nature. 540:114–118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang YT, Tseng HC, Huang CC, Chen YP,
Chiang HC and Chou FP: Relative down-regulation of apoptosis and
autophagy genes in colorectal cancer. Eur J Clin Invest. 41:84–92.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perez R, Wu N, Klipfel AA and Beart RW Jr:
A better cell cycle target for gene therapy of colorectal cancer:
Cyclin G. J Gastrointest Surg. 7:884–889. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fini MA, Elias A, Johnson RJ and Wright
RM: Contribution of uric acid to cancer risk, recurrence, and
mortality. Clin Transl Med. 1:162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ikegami T, Natsumeda Y and Weber G:
Decreased concentration of xanthine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.204) in
rat hepatomas. Cancer Res. 46:3838–3841. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun AS and Cederbaum AI: Oxidoreductase
activities in normal rat liver, tumor-bearing rat liver, and
hepatoma HC-252. Cancer Res. 40:4677–4681. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tanriverdi O, Cokmert S, Oktay E, Pilanci
KN, Menekse S, Kocar M, Sen CA, Avci N, Akman T, Ordu C, et al:
Prognostic significance of the baseline serum uric acid level in
non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line
chemotherapy: A study of the Turkish Descriptive Oncological
Researches Group. Med Oncol. 31:2172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cetin AO, Omar M, Calp S, Tunca H, Yimaz
N, Ozseker B and Tanriverdi O: Hyperuricemia at the time of
diagnosis is a factor for poor prognosis in patients with stage II
and III colorectal cancer (uric acid and colorectal cancer). Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:485–490. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao B, Li L, Lei Q and Guan KL: The
Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: An
updated version. Genes Dev. 24:862–874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu H, Jiang D, Chi F and Zhao B: The
Hippo pathway regulates stem cell proliferation, self-renewal, and
differentiation. Protein Cell. 3:291–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wierzbicki PM and Rybarczyk A: The Hippo
pathway in colorectal cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 53:105–119.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Serra R, Easter SL, Jiang W and Baxley SE:
Wnt5a as an effector of TGFβ in mammary development and cancer. J
Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 16:157–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Endo M, Nishita M, Fujii M and Minami Y:
Insight into the role of Wnt5a-induced signaling in normal and
cancer cells. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 314:117–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu B, Wang Q, Wang YA, Hua S, Sauvé CG,
Ong D, Lan ZD, Chang Q, Ho YW, Monasterio MM, et al: Epigenetic
activation of WNT5A drives glioblastoma stem cell differentiation
and invasive growth. Cell. 167:1281–1295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kurayoshi M, Oue N, Yamamoto H, Kishida M,
Inoue A, Asahara T, Yasui W and Kikuchi A: Expression of Wnt-5a is
correlated with aggressiveness of gastric cancer by stimulating
cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 66:10439–10448. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yong BC, Lu JC, Xie XB, Su Q, Tan PX, Tang
QL, Wang J, Huang G, Han J, Xu HW, et al: LDOC1 regulates Wnt5a
expression and osteosarcoma cell metastasis and is correlated with
the survival of osteosarcoma patients. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176911882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mikels AJ and Nusse R: Purified Wnt5a
protein activates or inhibits beta-catenin-TCF signaling depending
on receptor context. PLoS Biol. 4:e1152006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prasad CP, Chaurasiya SK, Axelsson L and
Andersson T: WNT-5A triggers Cdc42 activation leading to an ERK1/2
dependent decrease in MMP9 activity and invasive migration of
breast cancer cells. Mol Oncol. 7:870–883. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Säfholm A, Tuomela J, Rosenkvist J, Dejmek
J, Härkönen P and Andersson T: The Wnt-5a-derived hexapeptide
Foxy-5 inhibits breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting cell
motility. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6556–6563. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jönsson M, Dejmek J, Bendahl PO and
Andersson T: Loss of Wnt-5a protein is associated with early
relapse in invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Cancer Res.
62:409–416. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ying J, Li H, Yu J, Ng KM, Poon FF, Wong
SC, Chan AT, Sung JJ and Tao Q: WNT5A exhibits tumor-suppressive
activity through antagonizing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and is
frequently methylated in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:55–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Elbjeirami WM and Sughayer MA: KRAS
mutations and subtyping in colorectal cancer in Jordanian patients.
Oncol Lett. 4:705–710. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nakano H, Yamamoto F, Neville C, Evans D,
Mizuno T and Perucho M: Isolation of transforming sequences of two
human lung carcinomas: Structural and functional analysis of the
activated c-K-ras oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:71–75.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Santos E, Martin-Zanca D, Reddy EP,
Pierotti MA, Della Porta G and Barbacid M: Malignant activation of
a K-ras oncogene in lung carcinoma but not in normal tissue of the
same patient. Science. 223:661–664. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Espada J, Pérez-Moreno M, Braga VM,
Rodriguez-Viciana P and Cano A: H-Ras activation promotes
cytoplasmic accumulation and phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase
association of beta-catenin in epidermal keratinocytes. J Cell
Biol. 146:967–980. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mendoza MC, Er EE and Blenis J: The
Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends
Biochem Sci. 36:320–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH,
Vanhaesebroeck B, Waterfield MD and Downward J: Activation of
phosphoinositide 3-kinase by interaction with Ras and by point
mutation. EMBO J. 15:2442–2451. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Michael JV, Wurtzel JG and Goldfinger LE:
Inhibition of galectin-1 sensitizes HRAS-driven tumor growth to
rapamycin treatment. Anticancer Res. 36:5053–5061. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chang YY, Lin PC, Lin HH, Lin JK, Chen WS,
Jiang JK, Yang SH, Liang WY and Chang SC: Mutation spectra of RAS
gene family in colorectal cancer. Am J Surg. 212:537–544. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Feng J, Hua F, Shuo R, Chongfeng G,
Huimian X, Nakajima T, Subao W and Tsuchida N: Upregulation of
non-mutated H-ras and its upstream and downstream signaling
proteins in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 8:1409–1413.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Riggio M, Perrone MC, Polo ML, Rodriguez
MJ, May M, Abba M, Lanari C and Novaro V: AKT1 and AKT2 isoforms
play distinct roles during breast cancer progression through the
regulation of specific downstream proteins. Sci Rep. 7:442442017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hofbauer SW, Krenn PW, Hofbauer Piñόn J,
Pucher S, Asslaber D, Egle A, Hartmann TN and Greil R: The AKT1
isoform plays a dominant role in the survival and chemoresistance
of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol. 172:815–819.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sahlberg Häggblad S, Mortensen AC, Haglöf
J, Engskog MK, Arvidsson T, Pettersson C, Glimelius B, Stenerlöw B
and Nestor M: Different functions of AKT1 and AKT2 in molecular
pathways, cell migration and metabolism in colon cancer cells. Int
J Oncol. 50:5–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Irie HY, Pearline RV, Grueneberg D, Hsia
M, Ravichandran P, Kothari N, Natesan S and Brugge JS: Distinct
roles of Akt1 and Akt2 in regulating cell migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 171:1023–1034.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang S and Basson MD: Akt directly
regulates focal adhesion kinase through association and serine
phosphorylation: Implication for pressure-induced colon cancer
metastasis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 300:C657–C670. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Papadimitriou K, Rolfo C, Dewaele E, VanDe
Wiel M, Van den Brande J, Altintas S, Huizing M, Specenier P and
Peeters M: Incorporating anti-VEGF pathway therapy as a continuum
of care in metastatic colorectal cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol.
16:182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xu WW, Li B, Lam AK, Tsao SW, Law SY, Chan
KW, Yuan QJ and Cheung AL: Targeting VEGFR1- and VEGFR2-expressing
non-tumor cells is essential for esophageal cancer therapy.
Oncotarget. 6:1790–1805. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang H, Zhang C, Ning Z, Xu L, Zhu X and
Meng Z: Bufalin enhances anti-angiogenic effect of sorafenib via
AKT/VEGF signaling. Int J Oncol. 48:1229–1241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F and
Normanno N: Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their
receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
19:183–232. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mayer A, Takimoto M, Fritz E, Schellander
G, Kofler K and Ludwig H: The prognostic significance of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen, epidermal growth factor
receptor, and mdr gene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer.
71:2454–2460. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Srivatsa S, Paul MC, Cardone C, Holcmann
M, Amberg N, Pathria P, Diamanti MA, Linder M, Timelthaler G,
Dienes HP, et al: EGFR in tumor-associated myeloid cells promotes
development of colorectal cancer in mice and associates with
outcomes of patients. Gastroenterology. 153:178–190. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bardelli A and Siena S: Molecular
mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:1254–1261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Georgakilas AG, Martin OA and Bonner WM:
p21: A two-faced genome guardian. Trends Mol Med. 23:310–319. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
el-Deiry WS, Harper JW, O'Connor PM,
Velculescu VE, Canman CE, Jackman J, Pietenpol JA, Burrell M, Hill
DE and Wang Y: WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 54:1169–1174. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy
DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression.
Cell. 75:817–825. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K
and Elledge SJ: The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 75:805–816. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yasui W, Akama Y, Yokozaki H, Semba S,
Kudo Y, Shimamoto F and Tahara E: Expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 in
colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas and its correlation with
p53 protein expression. Pathol Int. 47:470–477. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Matsushita K, Kobayashi S, Kato M, Itoh Y,
Okuyama K, Sakiyama S and Isono K: Reduced messenger RNA expression
level of p21 CIP1 in human colorectal carcinoma tissues and its
association with p53 gene mutation. Int J Cancer. 69:259–264. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Schwandner O, Bruch HP and Broll R:
Prognostic significance of p21 and p27 protein, apoptosis, clinical
and histologic factors in rectal cancer without lymph node
metastases. Eur Surg Res. 34:389–396. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|