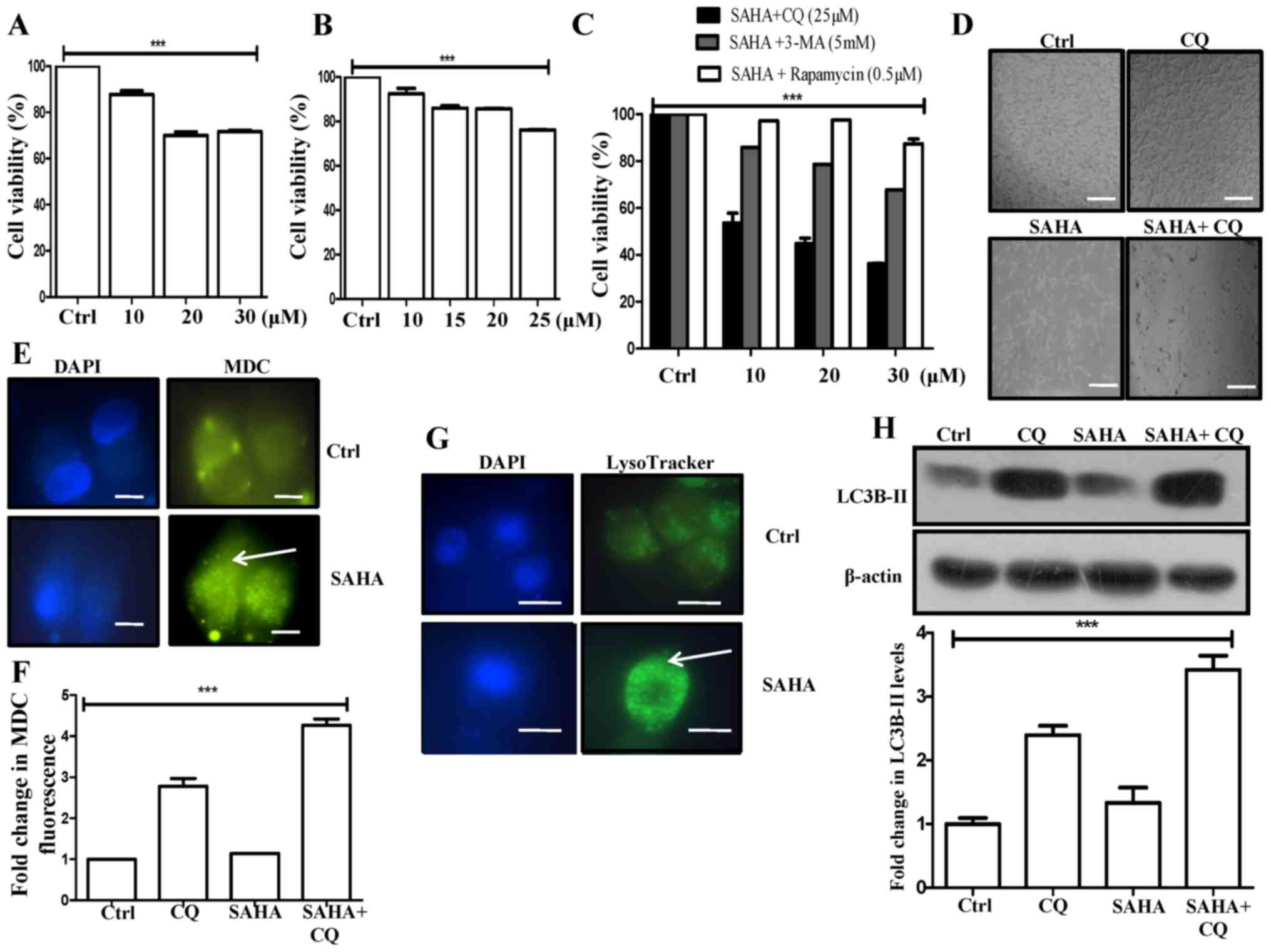
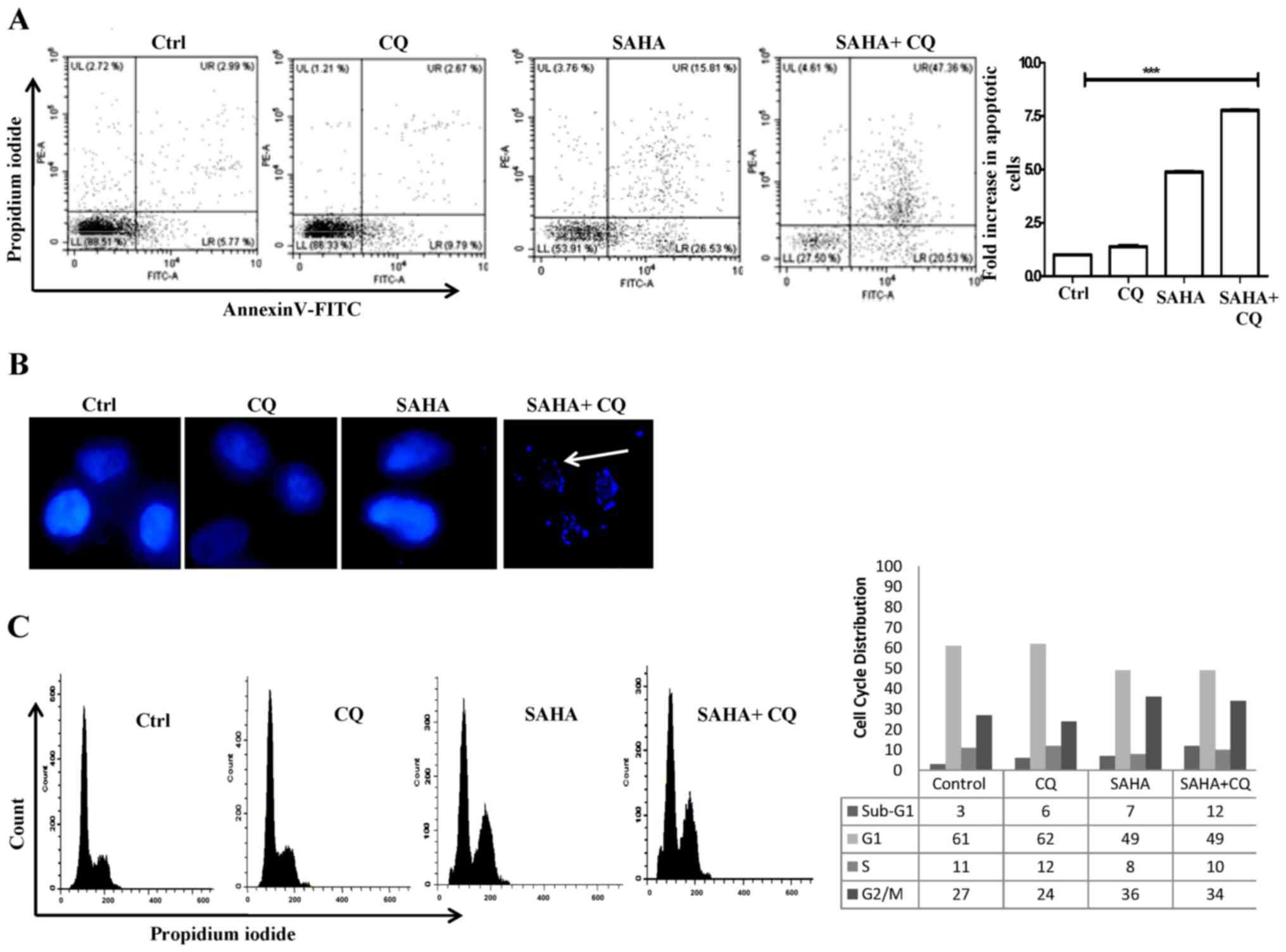
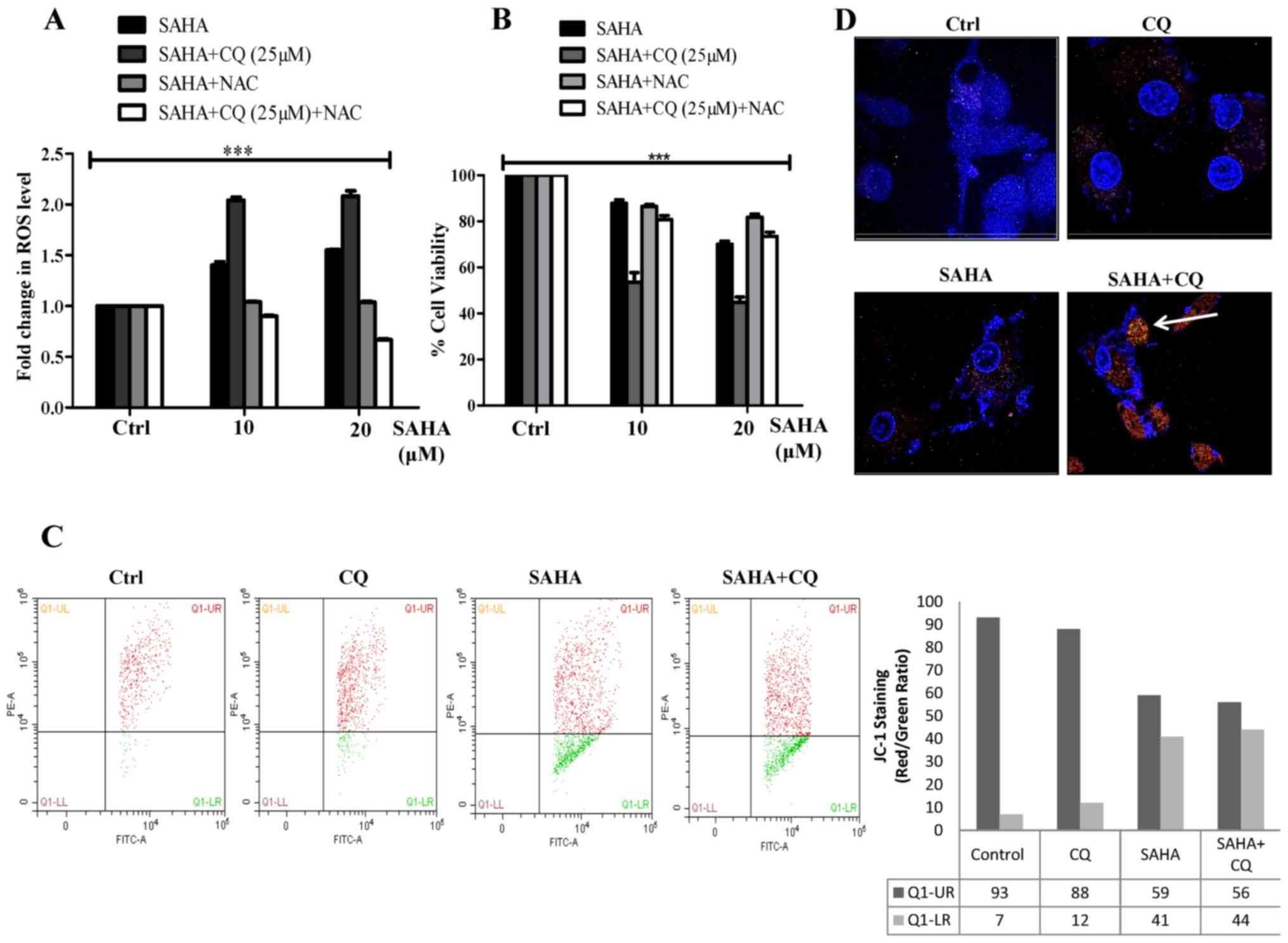
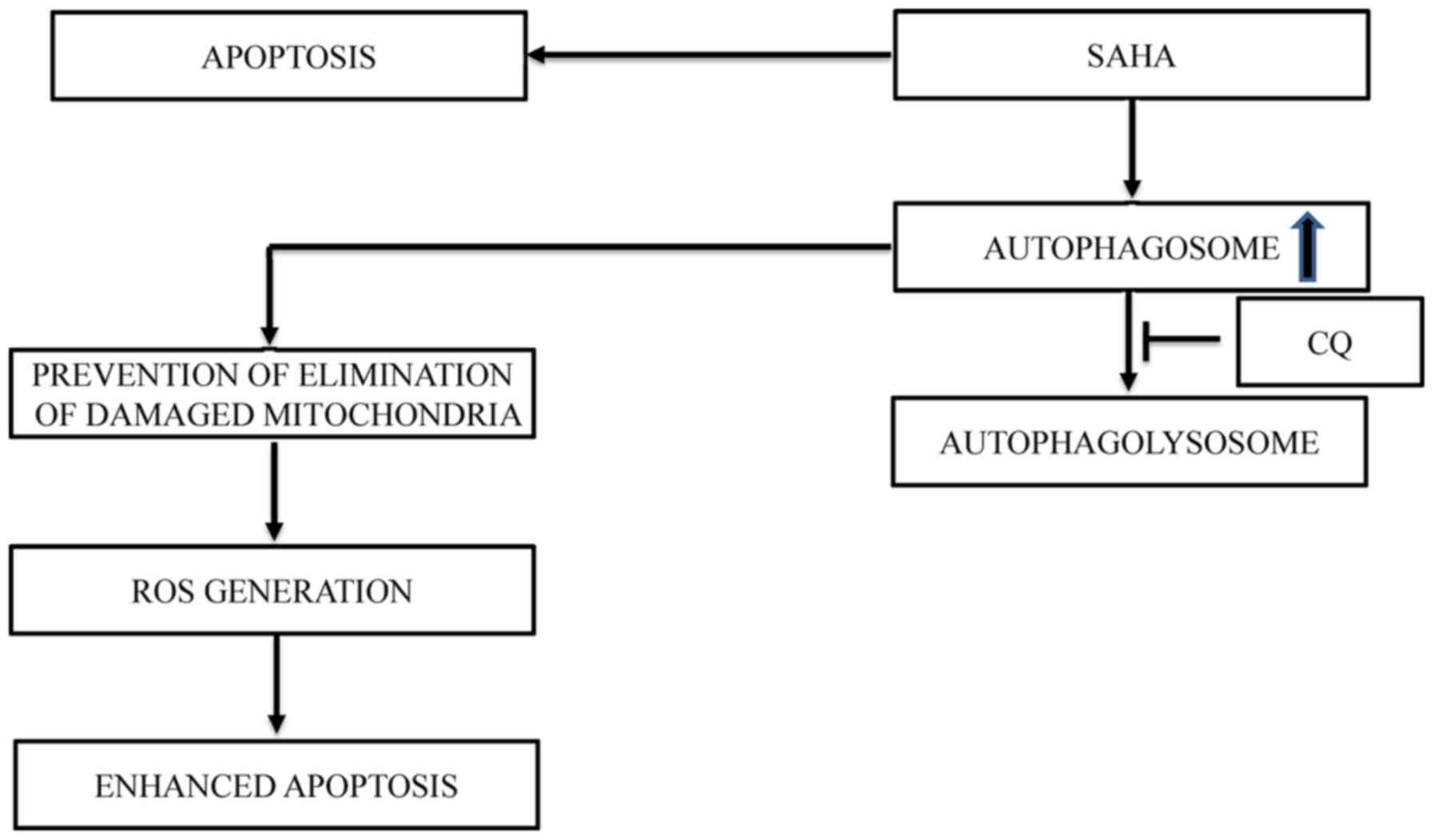
|
1
|
Iacob G and Dinca EB: Current data and
strategy in glioblastoma multiforme. J Med Life. 2:386–293.
2009.
|
|
2
|
Jung WH, Choi S, Oh KK and Chi JG:
Congenital glioblastoma multiforme-report of an autopsy case. J
Korean Med Sci. 5:225–231. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, Kowalik
U, Hovinga KE, Geber A, Fligelman B, Leversha M, Brennan C and
Tabar V: Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour
endothelium. Nature. 468:829–833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Linkous AG and Yazlovitskaya EM:
Angiogenesis in glioblastoma multiforme: Navigating the maze.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:712–718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Van Tellingen O, Yetkin-Arik B, de Gooijer
MC, Wesseling P, Wurdinger T and de Vries HE: Overcoming the
blood-brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment.
Drug Resist Updat. 19:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang WJ, Chen WW and Zhang X:
Glioblastoma multiforme: Effect of hypoxia and hypoxia inducible
factors on therapeutic approaches. Oncol Lett. 12:2283–2288. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Thomas AA, Ernstoff MS and Fadul CE:
Immunotherapy for the treatment of glioblastoma. Cancer J.
18:59–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jovčevska I, Kočevar N and Komel R: Glioma
and glioblastoma-how much do we (not) know? Mol Clin Oncol.
1:935–941. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N,
Zhang M, Han W, Lou F, Yang J, Zhang Q, et al: Autophagy and
chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer
treatment. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8382013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang J, Stevens MF and Bradshaw TD:
Temozolomide: Mechanisms of action, repair and resistance. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 5:102–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Beier D, Schulz JB and Beier CP:
Chemoresistance of glioblastoma cancer stem cells-much more complex
than expected. Mol Cancer. 10:1282011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wilson TA, Karajannis MA and Harter DH:
Glioblastoma multiforme: State of the art and future therapeutics.
Surg Neurol Int. 5:642014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Haar CP, Hebbar P, Wallace GC IV, Das A,
Vandergrift WA III, Smith JA, Giglio P, Patel SJ, Ray SK and Banik
NL: Drug resistance in glioblastoma: A mini review. Neurochem Res.
37:1192–1200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al: Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and
adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in
glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of
the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kaza N, Kohli L and Roth KA: Autophagy in
brain tumors: A new target for therapeutic intervention. Brain
Pathol. 22:89–98. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cheng CK, Fan QW and Weiss WA: PI3K
signaling in glioma-animal models and therapeutic challenges. Brain
Pathol. 19:112–120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Carrasco-García E, Saceda M, Grasso S,
Rocamora-Reverte L, Conde M, Gómez-Martínez A, García-Morales P,
Ferragut JA and Martínez-Lacaci I: Small tyrosine kinase inhibitors
interrupt EGFR signaling by interacting with erbB3 and erbB4 in
glioblastoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 317:1476–1489. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rich JN, Reardon DA, Peery T, Dowell JM,
Quinn JA, Penne KL, Wikstrand CJ, Van Duyn LB, Dancey JE, McLendon
RE, et al: Phase II trial of gefitinib in recurrent glioblastoma. J
Clin Oncol. 22:133–142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fan QW, Knight ZA, Goldenberg DD, Yu W,
Mostov KE, Stokoe D, Shokat KM and Weiss WA: A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR
inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma. Cancer Cell.
9:341–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fan QW, Cheng C, Hackett C, Feldman M,
Houseman BT, Nicolaides T, Haas-Kogan D, James CD, Oakes SA,
Debnath J, et al: Akt and autophagy cooperate to promote survival
of drug-resistant glioma. Sci Signal. 3:ra812010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika
P, Kelly C, Chiao JH, Reilly JF, Ricker JL, Richon VM and Frankel
SR: Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic
acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood.
109:31–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Munster PN, Thurn KT, Thomas S, Raha P,
Lacevic M, Miller A, Melisko M, Ismail-Khan R, Rugo H, Moasser M
and Minton SE: A phase II study of the histone deacetylase
inhibitor vorinostat combined with tamoxifen for the treatment of
patients with hormone therapy-resistant breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
104:1828–1835. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shao Y, Gao Z, Marks PA and Jiang X:
Apoptotic and autophagic cell death induced by histone deacetylase
inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:18030–18035. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hrzenjak A, Kremser ML, Strohmeier B,
Moinfar F, Zatloukal K and Denk H: SAHA induces
caspase-independent, autophagic cell death of endometrial stromal
sarcoma cells by influencing the mTOR pathway. J Pathol.
216:495–504. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yonekawa T and Thorburn A: Autophagy and
cell death. Essays Biochem. 55:105–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim EL, Wüstenberg R, Rübsam A,
Schmitz-Salue C, Warnecke G, Bücker EM, Pettkus N, Speidel D, Rohde
V, Schulz-Schaeffer W, et al: Chloroquine activates the p53 pathway
and induces apoptosis in human glioma cells. Neuro Oncol.
12:389–400. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chowdhury R, Chowdhury S, Roychoudhury P,
Mandal C and Chaudhuri K: Arsenic induced apoptosis in malignant
melanoma cells is enhanced by menadione through ROS generation, p38
signaling and p53 activation. Apoptosis. 14:108–123. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pajaniradje S, Mohankumar K, Pamidimukkala
R, Subramanian S and Rajagopalan R: Antiproliferative and apoptotic
effects of Sesbania grandiflora leaves in human cancer cells.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:4749532014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Laporte AN, Barrott JJ, Yao RJ, Poulin NM,
Brodin BA, Jones KB, Underhill TM and Nielsen TO: HDAC and
proteasome inhibitors synergize to activate pro-apoptotic factors
in synovial sarcoma. PLoS One. 12:e01694072017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mizushima N: Methods for monitoring
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2491–2502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Munafó DB and Colombo MI: A novel assay to
study autophagy: Regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino
acid deprivation. J Cell Sci. 114:3619–3629. 2001.
|
|
32
|
Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Kim I, Currin RT and
Lemasters JJ: Tracker dyes to probe mitochondrial autophagy
(mitophagy) in rat hepatocytes. Autophagy. 2:39–46. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Adamson C, Kanu OO, Mehta AI, Di C, Lin N,
Mattox AK and Bigner DD: Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of where
we have been and where we are going. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
18:1061–1083. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kanzawa T, Bedwell J, Kondo Y, Kondo S and
Germano IM: Inhibition of DNA repair for sensitizing resistant
glioma cells to temozolomide. J Neurosurg. 99:1047–1052. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fu J, Liu ZG, Liu XM, Chen FR, Shi HL,
Pangjesse CS, Ng HK and Chen ZP: Glioblastoma stem cells resistant
to temozolomide-induced autophagy. Chin Med J (Engl).
122:1255–1259. 2009.
|
|
36
|
Wojton J, Elder J and Kaur B: How
efficient are autophagy inhibitors as treatment for glioblastoma?
CNS Oncol. 3:5–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hegi ME, Liu L, Herman JG, Stupp R, Wick
W, Weller M, Mehta MP and Gilbert MR: Correlation of
O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation with
clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical strategies to
modulate MGMT activity. J Clin Oncol. 26:4189–4199. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu YL, Yang PM, Shun CT, Wu MS, Weng JR
and Chen CC: Autophagy potentiates the anti-cancer effects of the
histone deacetylase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Autophagy. 6:1057–1065. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gammoh N, Lam D, Puente C, Ganley I, Marks
PA and Jiang X: Role of autophagy in histone deacetylase
inhibitor-induced apoptotic and nonapoptotic cell death. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:6561–6565. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Guha S, Coffey EE, Lu W, Lim JC, Beckel
JM, Laties AM, Boesze-Battaglia K and Mitchell CH: Approaches for
detecting lysosomal alkalinization and impaired degradation in
fresh and cultured RPE cells: Evidence for a role in retinal
degenerations. Exp Eye Res. 126:68–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Perry CN, Kyoi S, Hariharan N, Takagi H,
Sadoshima J and Gottlieb RA: Novel methods for measuring cardiac
autophagy in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 453:325–342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Iwai-Kanai E, Yuan H, Huang C, Sayen MR,
Perry-Garza CN, Kim L and Gottlieb RA: A method to measure cardiac
autophagic flux in vivo. Autophagy. 4:322–329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kim HJ and Bae SC: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action and clinical trials as
anti-cancer drugs. Am J Transl Res. 3:166–179. 2011.
|
|
44
|
Gomes LR, Vessoni AT and Menck CFM:
Microenvironment and autophagy cross-talk: Implications in cancer
therapy. Pharmacol Res. 107:300–307. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Poillet-Perez L, Despouy G,
Delage-Mourroux R and Boyer-Guittaut M: Interplay between ROS and
autophagy in cancer cells, from tumor initiation to cancer therapy.
Redox Biol. 4:184–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ruefli AA, Ausserlechner MJ, Bernhard D,
Sutton VR, Tainton KM, Kofler R, Smyth MJ and Johnstone RW: The
histone deacetylase inhibitor and chemotherapeutic agent
suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) induces a cell-death pathway
characterized by cleavage of Bid and production of reactive oxygen
species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:10833–10838. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ray S, Bonafede MM and Mohile NA:
Treatment patterns, survival, and healthcare costs of patients with
malignant gliomas in a large US commercially insured population. Am
Health Drug Benefits. 7:140–149. 2014.
|
|
48
|
Zhang J, Stevens MF, Laughton CA,
Madhusudan S and Bradshaw TD: Acquired resistance to temozolomide
in glioma cell lines: Molecular mechanisms and potential
translational applications. Oncology. 78:103–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Fulda S and Kögel D: Cell death by
autophagy: Emerging molecular mechanisms and implications for
cancer therapy. Oncogene. 34:5105–5113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Katayama M, Kawaguchi T, Berger M and
Pieper R: DNA damaging agent-induced autophagy produces a
cytoprotective adenosine triphosphate surge in malignant glioma
cells. Cell Death Differ. 14:548–558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Voss V, Senft C, Lang V, Ronellenfitsch
MW, Steinbach JP, Seifert V and Kögel D: The pan-Bcl-2 inhibitor
(−)-gossypol triggers autophagic cell death in malignant glioma.
Mol Cancer Res. 8:1002–1016. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Falkenberg KJ and Johnstone RW: Histone
deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases
and immune disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:673–691. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lee YJ, Won AJ, Lee J, Jung JH, Yoon S,
Lee BM and Kim HS: Molecular mechanism of SAHA on regulation of
autophagic cell death in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Int J Med Sci. 9:881–993. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Carew JS, Nawrocki ST, Kahue CN, Zhang H,
Yang C, Chung L, Houghton JA, Huang P, Giles FJ and Cleveland JL:
Targeting autophagy augments the anticancer activity of the histone
deacetylase inhibitor SAHA to overcome Bcr-Abl-mediated drug
resistance. Blood. 110:313–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Rosenfeld MR, Ye X, Supko JG, Desideri S,
Grossman SA, Brem S, Mikkelson T, Wang D, Chang YC, Hu J, et al: A
phase I/II trial of hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with
radiation therapy and concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in
patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Autophagy.
10:1359–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Das G, Shravage BV and Baehrecke EH:
Regulation and function of autophagy during cell survival and cell
death. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:pii: 008813. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Navarro-Yepes J, Burns M, Anandhan A,
Khalimonchuk O, del Razo LM, Quintanilla-Vega B, Pappa A,
Panayiotidis MI and Franco R: Oxidative stress, redox signaling,
and autophagy: Cell death versus survival. Antioxid Redox Signal.
21:66–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Gong C, Song E, Codogno P and Mehrpour M:
The roles of BECN1 and autophagy in cancer are context dependent.
Autophagy. 8:1853–1855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
White E: The role for autophagy in cancer.
J Clin Invest. 125:42–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|