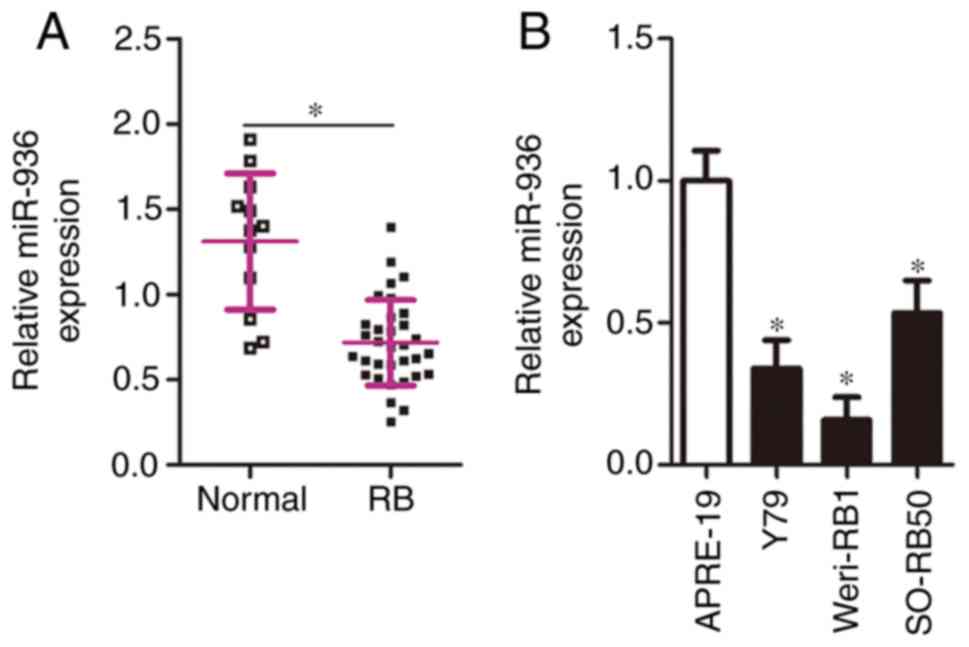
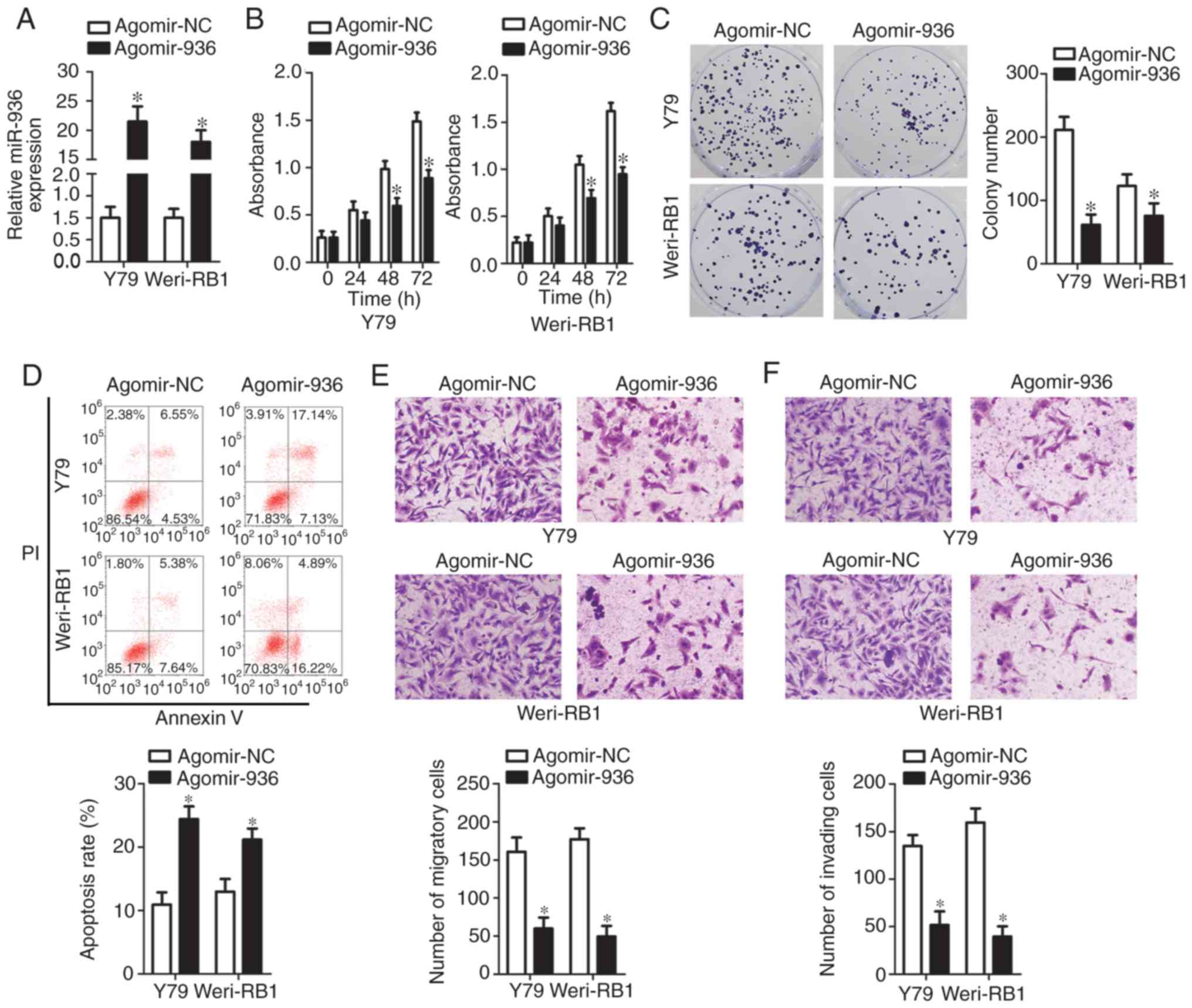
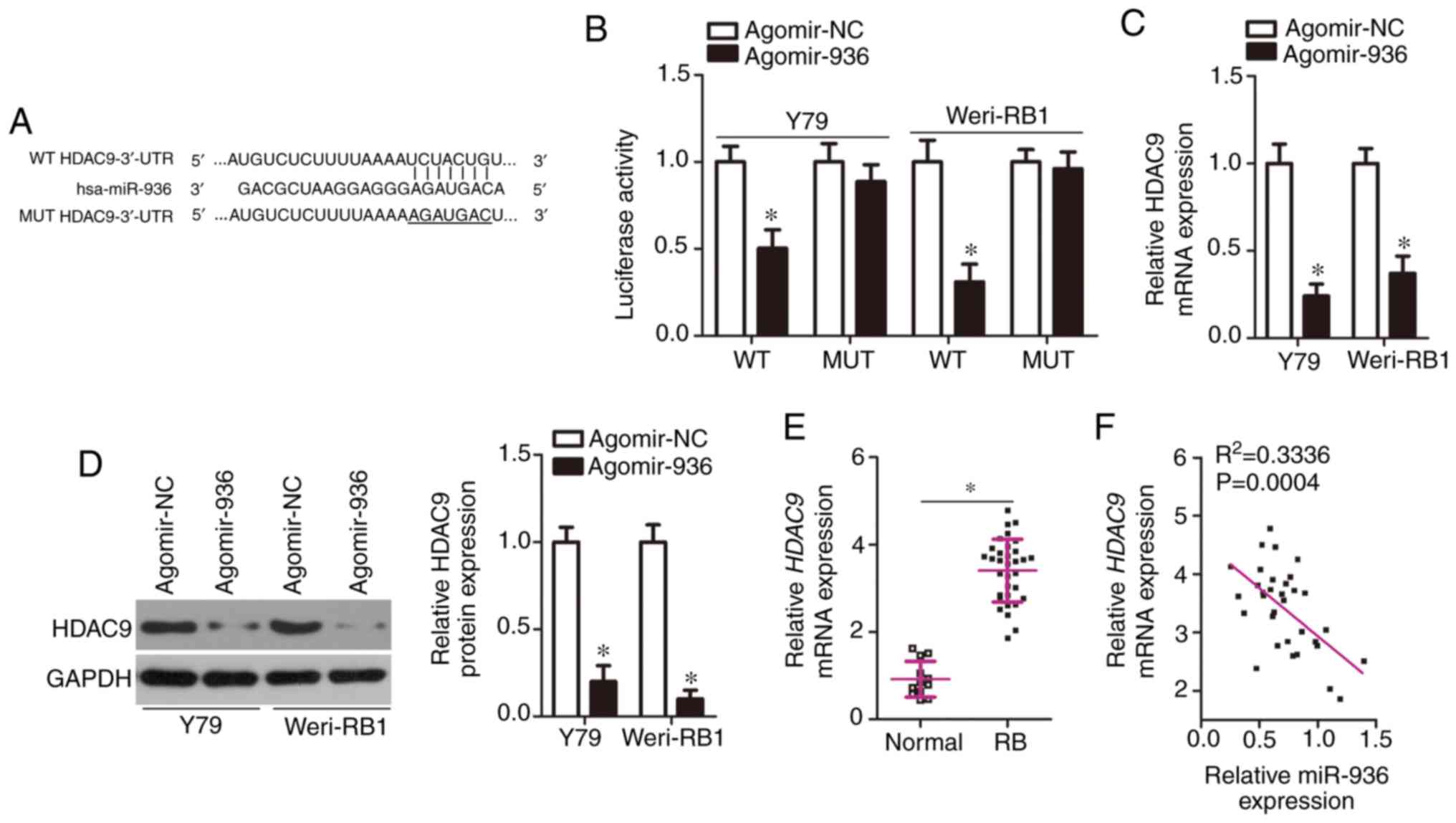
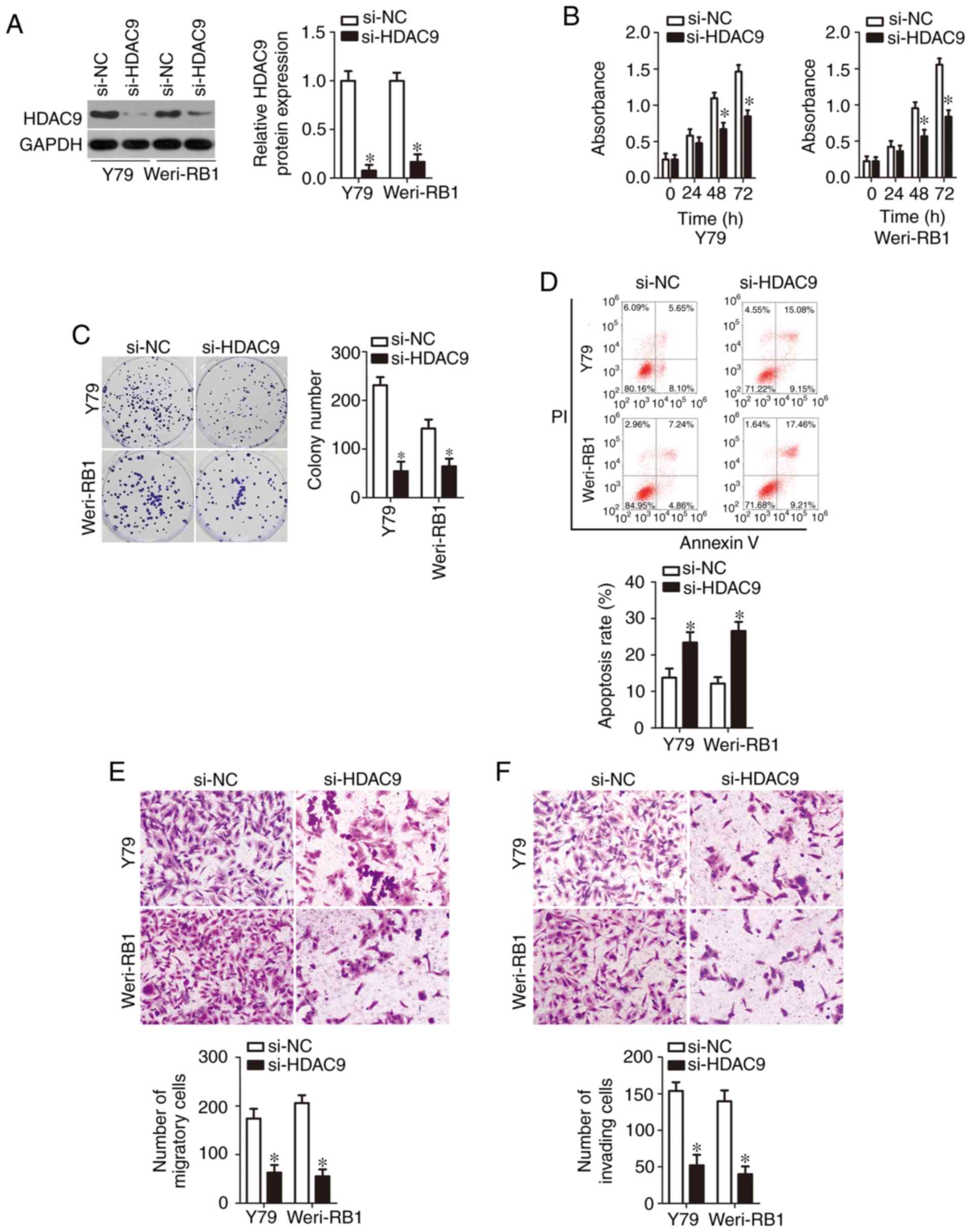
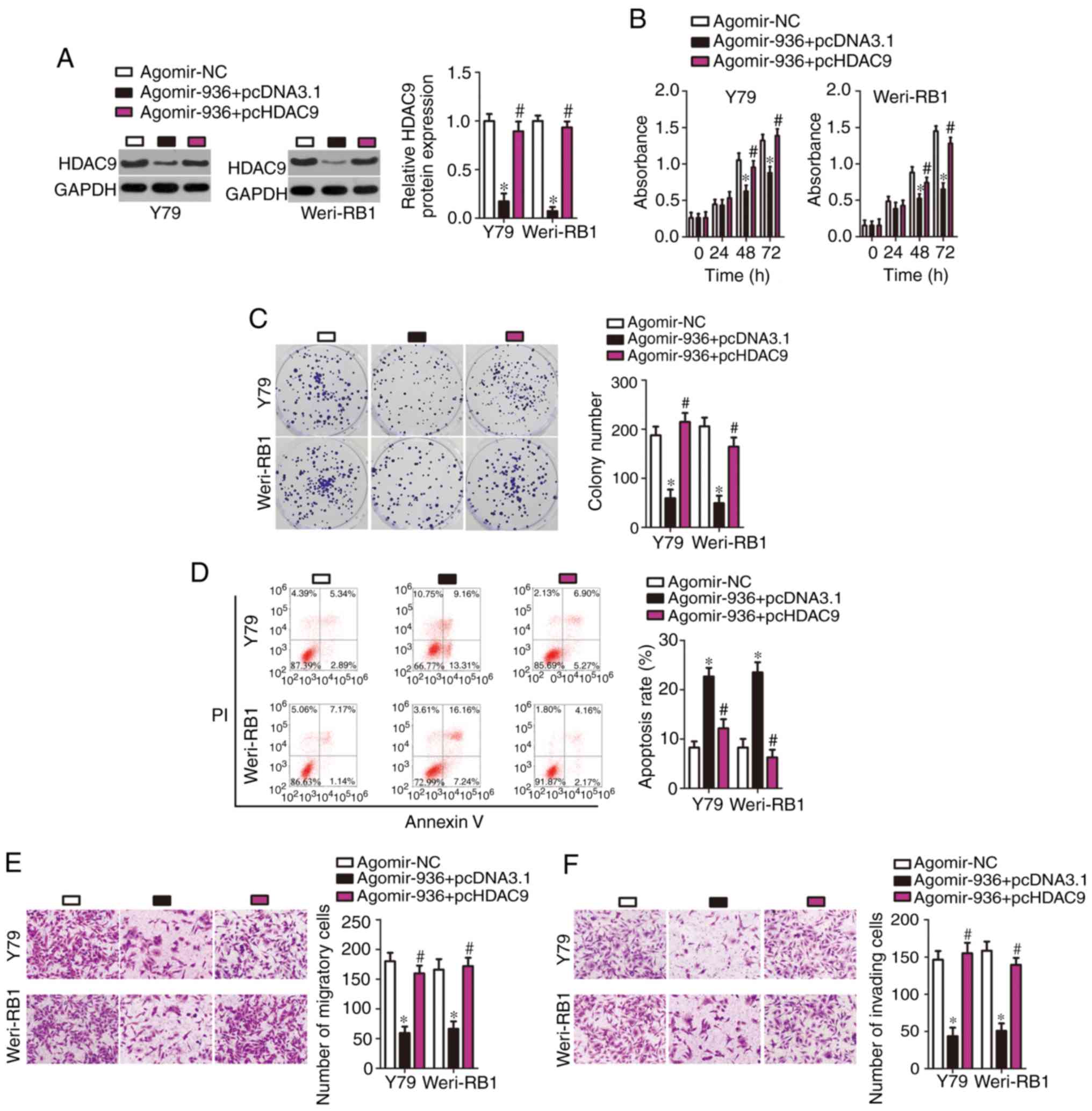
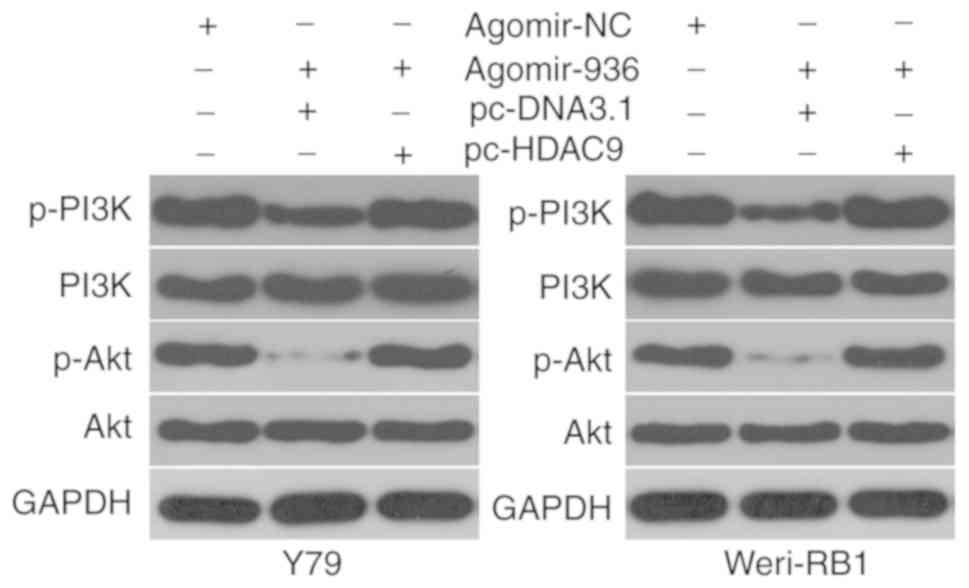
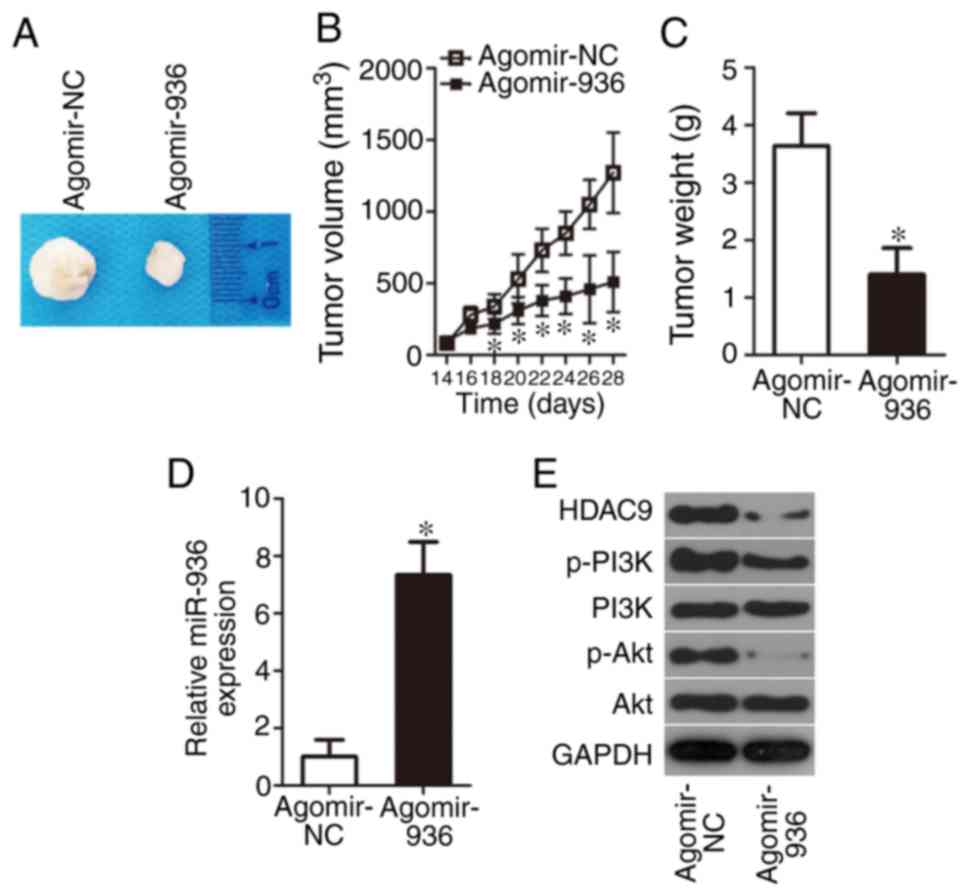
|
1
|
Dimaras H, Kimani K, Dimba EA, Gronsdahl
P, White A, Chan HS and Gallie BL: Retinoblastoma. Lancet.
379:1436–1446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kivelä T: The epidemiological challenge of
the most frequent eye cancer: Retinoblastoma, an issue of birth and
death. Br J Ophthalmol. 93:1129–1131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He MY, An Y, Gao YJ, Qian XW, Li G and
Qian J: Screening of RB1 gene mutations in Chinese patients with
retinoblastoma and preliminary exploration of genotype-phenotype
correlations. Mol Vis. 20:545–552. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Balmer A, Zografos L and Munier F:
Diagnosis and current management of retinoblastoma. Oncogene.
25:5341–5349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tian T, Ji XD, Zhang Q, Peng J and Zhao
PQ: A delayed diagnosis of unsuspected retinoblastoma in an in
vitro fertilisation infant with retinopathy of prematurity. Int J
Ophthalmol. 9:1361–1363. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abramson DH, Shields CL, Munier FL and
Chantada GL: Treatment of retinoblastoma in 2015: Agreement and
disagreement. JAMA Ophthalmol. 133:1341–1347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Correa-Acosta A, González-Alviar ME and
Gaviria-Bravo ML: Retinoblastoma and optic nerve enhancement in a
brain magnetic resonance scan: Is it always a metastasis? Arch Soc
Esp Oftalmol. 93:251–254. 2018.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lytle JR, Yario TA and Steitz JA: Target
mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the
5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9667–9672.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guarnieri DJ and DiLeone RJ: MicroRNAs: A
new class of gene regulators. Ann Med. 40:197–208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Delsin LEA, Salomao KB, Pezuk JA and
Brassesco MS: Expression profiles and prognostic value of miRNAs in
retinoblastoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 145:1–10. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li W, Wang J, Zhang D, Zhang X, Xu J and
Zhao L: MicroRNA-98 targets HMGA2 to inhibit the development of
retinoblastoma through mediating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer
Biomark. 25:79–88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu S, Han M and Zhang C: Overexpression of
microRNA-186 inhibits angiogenesis in retinoblastoma via the
Hedgehog signaling pathway by targeting ATAD2. J Cell Physiol.
234:19059–19072. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Du S, Lv Y, Zhang F and Wang W:
MicroRNA-665 inhibits the oncogenicity of retinoblastoma by
directly targeting high-mobility group box 1 and inactivating the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 11:3111–3123. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cao Y, Xia F, Wang P and Gao M:
MicroRNA-93-5p promotes the progression of human retinoblastoma by
regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
18:5807–5814. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bu W, Wang Y and Min X: MicroRNA-106b
promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of
retinoblastoma cells by inhibiting the expression of ZBTB4 protein.
Exp Ther Med. 16:4537–4545. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou X and Tao H: Overexpression of
microRNA-936 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell
proliferation and invasion via targeting E2F2. Exp Ther Med.
16:2696–2702. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang D, Zhi T, Xu X, Bao Z, Fan L, Li Z,
Ji J and Liu N: MicroRNA-936 induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits
glioma cell proliferation by targeting CKS1. Am J Cancer Res.
7:2131–2143. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang R, Wu Y, Wang M, Sun Z, Zou J, Zhang
Y and Cui H: HDAC9 promotes glioblastoma growth via TAZ-mediated
EGFR pathway activation. Oncotarget. 6:7644–7656. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Wang X and Zhao R:
microRNA-497 overexpression decreases proliferation, migration and
invasion of human retinoblastoma cells via targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor A. Oncol Lett. 13:5021–5027. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang Y, Chen X and Liang Z: MicroRNA-320
regulates autophagy in retinoblastoma by targeting hypoxia
inducible factor-1α. Exp Ther Med. 14:2367–2372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J and You X: MicroRNA-758 inhibits
malignant progression of retinoblastoma by directly targeting PAX6.
Oncol Rep. 40:1777–1786. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Golabchi K, Soleimani-Jelodar R, Aghadoost
N, Momeni F, Moridikia A, Nahand JS, Masoudifar A, Razmjoo H and
Mirzaei H: MicroRNAs in retinoblastoma: Potential diagnostic and
therapeutic biomarkers. J Cell Physiol. 233:3016–3023. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Singh A, Patel P, Patel VK, Jain DK,
Veerasamy R, Sharma PC and Rajak H: Histone deacetylase inhibitors
for the treatment of colorectal cancer: Recent progress and future
prospects. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 17:456–466. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dokmanovic M and Marks PA: Prospects:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Cell Biochem. 96:293–304. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marks PA, Richon VM, Kelly WK, Chiao JH
and Miller T: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Development as cancer
therapy. Novartis Found Symp. 259:269–281; discussion 281–288.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Wu D, Xia F, Xian H, Zhu X, Cui H
and Huang Z: Downregulation of HDAC9 inhibits cell proliferation
and tumor formation by inducing cell cycle arrest in
retinoblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:600–606. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin Q, He W, Chen L, Yang Y, Shi K and You
Z: MicroRNA-101-3p inhibits proliferation in retinoblastoma cells
by targeting EZH2 and HDAC9. Exp Ther Med. 16:1663–1670.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li M, Tang Y, Wu L, Mo F, Wang X, Li H, Qi
R, Zhang H, Srivastava A and Ling C: The hepatocyte-specific
HNF4α/miR-122 pathway contributes to iron overload-mediated hepatic
inflammation. Blood. 130:1041–1051. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|