Introduction
Ectodomain (ECD) shedding is an important regulatory
mechanism, which controls spectrum and abundance of cell surface
proteins mediating cellular responses to molecular and
physiological signals (1).
Concurrently, it generates soluble protein variants executing
autocrine and/or paracrine signaling. Proper ECD shedding is
essential for diverse biological processes, including cell fate
decisions, proliferation, migration, metabolism, tissue and organ
development, and its dysregulation contributes to various
pathologies including cancer (2).
ECD shedding occurs via proteolytic cleavage of the
extracellular portions of type I or II transmembrane proteins, or
GPI-anchored proteins. It can be accomplished by various
proteinases, among which a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM)
family members have a prominent position (3,4). Out
of 22 ADAM family members, ADAM17 and ADAM10 attract a lot of
attention due to their functional implications in key signaling
pathways. ADAM17, originally identified as TNFα-converting enzyme
(TACE), is primarily related to EGFR signaling and represents a
major sheddase for proinflammatory cytokines, whereas ADAM10 has
been implicated mainly in Notch1 signaling and cleaves mostly cell
adhesion molecules (5). However,
ADAM17 and ADAM10 can also share several substrates (such as CD44,
APP, DLL1, Notch, HB-EGF and TNFβ) suggesting that their
complementary and/or compensatory activities are needed in certain
cell or tissue contexts (6,7).
It was previously demonstrated by the authors that
ADAM17 cleaves the ECD of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) (8–11).
CA IX is a cancer-associated, hypoxia-induced type I transmembrane
protein participating in pH regulation, metabolic adaptation to
hypoxia/acidosis and in cell migration-invasion-metastasis
(12–17). CA IX ECD consists of two structural
components: a highly active enzyme domain (CA) catalyzing the
reversible conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and proton,
and an N-terminal proteoglycan-like region (PG). While the CA
domain catalytic activity participates in the control of tumor pH
(14,15,18,19),
the PG region mediates non-catalytic proton extrusion across the
plasma membrane and is implicated in cell adhesion (20–24).
A short stalk connecting the CA IX ECD to a single-pass
transmembrane region contains the ADAM17 cleavage site. Deletion of
10 amino acids from the stalk completely prevents CA IX ECD
shedding and reinforces the tumorigenic phenotype of CA
IX-expressing cells (11).
However, neither silencing nor inhibition of ADAM17
are sufficient to fully block CA IX ECD release suggesting that an
additional protease can participate in this process (8,11).
As ADAM10 is structurally and functionally related to ADAM17, its
possible involvement in CA IX ECD shedding was investigated. In the
present study, the first experimental evidence was provided using
biochemical and molecular/cell biology approaches that ADAM10 can
cleave the CA IX ECD via an overlapping cleavage site with ADAM17
and it was showed that both proteinases contribute to CA IX ECD
shedding in a non-redundant manner.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Wild-type hamster ovary CHOwt cells and human
cervical carcinoma C33a cells were transfected with the full-length
(FL) human CA9 cDNA and its non-shed (NS) deletion mutant
(del393-402 aa) using TurboFect™ transfection reagent (Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) as previously described (11). The cells were routinely cultured in
DMEM medium with 10% FCS (BioWhittaker; Lonza Group, Ltd.) in a
humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37°C. Cell lines have
been authenticated using STR profiling within the past 3 years. All
experiments were performed with mycoplasma-free cells.
rhADAM10 cleavage activity assays
Catalytic activity of recombinant rhADAM10
encompassing the catalytic domain (100 ng/ml, R&D Systems,
Inc.) was verified by hydrolytic processing of Fluorogenic Peptide
Substrate IX Mca-K-P-L-G-L-Dpa-A-R-NH2 (10 µM; R&D
Systems, Inc.) followed by monitoring of increasing fluorescence
intensity at excitation and emission wavelengths of 320 and 405 nm
(top read), respectively, in kinetic mode for 30, 40, 50 and 120
min at 37°C using a Synergy H4 plate reader (BioTek Instruments,
Inc.). All reactions were performed in a fluorogenic buffer
containing 25 mM Tris pH 9, 150 mM NaCl, 2.5 µM ZnCl2
and 0.005% Brij-35.
For the evaluation of ADAM10 cleavage of the cell
membrane-bound CA IX, CHOwt cells transiently transfected with the
FL human CA9 cDNA (CHOwt-FL-CA IX) and its deletion mutant NS CA IX
(del393-402) (CHOwt-NS-CA IX), respectively, were treated with
rhADAM10 (500 ng/ml) added to culture medium for 24 h. Thereafter,
cell culture medium was harvested and CA IX ECD level was
determined by ELISA.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
(ELISA)
For the CA IX ECD quantification, 1×105
cells per well were seeded and cultured in a 24-well plate for 24
h. After medium exchange, the cells were incubated with either
inhibitors or activators of shedding (as described below) and all
supernatants were subsequently analyzed using in-house developed
sandwich ELISA as previously described (8). The capture monoclonal antibody (Mab)
V/10 specific for the catalytic domain of CA IX [10 µg/ml,
generated in-house, (25)] was
immobilized on the surface of microplate wells overnight at room
temperature. After blocking and washing, diluted samples were added
to the coated wells at room temperature for 2 h. The attached CA IX
ECD was then allowed to react with the mixture of the PG
domain-specific biotinylated Mabs [M75 and IV/18, generated and
biotinylated in-house, (25)]
diluted 1:7,500 (200 ng/ml) in the blocking buffer. The amount of
bound detector antibodies was determined with peroxidase-conjugated
streptavidin (Pierce; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) using the
peroxidase substrate orthophenylene diamine (MilliporeSigma) after
incubation for 1 h.
Indirect immunofluorescence
For detection of ADAM10, cells cultured on glass
coverslips were incubated with anti-human ADAM10 ECD mouse Mab
IgG2B Clone 163003 (R&D Systems, Inc.; cat. no. MAB1427, 1:100
in cultivation medium) for 1 h at 37°C, gently washed with PBS and
fixed with methanol for 5 min at −20°C. Non-specific binding was
blocked by incubation with PBS containing 1% BSA (MilliporeSigma)
for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were then incubated with secondary donkey
anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor®488-conjugated antibody
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; cat. no. A-21202)
diluted 1:1,000 in the blocking buffer for 1 h at 37°C. Finally,
the coverslips were mounted onto slides in the Mounting Media with
DAPI (cat. no. ab104139; Abcam), and analyzed by the confocal laser
scanning microscope Zeiss LSM 510 Meta.
Proximity ligation assay (PLA)
PLA was performed in a humid chamber at 37°C
according to the manufacturer's instructions (Olink) (26). Cells were seeded on glass
coverslips and allowed to attach for 24 h. Then they were fixed
with methanol, blocked with blocking buffer for 30 min and
incubated with a mixture of antibodies against the ECDs of human CA
IX (Abcam; rabbit, cat. no. ab15086) and ADAM10 (R&D Systems,
Inc.; mouse MAB1427) each in 10 µg/ml concentration for 1 h.
Following the incubation with plus and minus PLA probes for 1 h, a
ligation mixture containing connector oligonucleotides and an
amplification mixture containing fluorescently labeled DNA probe
was added for 40 and 100 min, respectively. Samples were analyzed
using a Zeiss LSM 510 Meta confocal microscope.
Internalization analyses
C33a-FL-CA IX (300,000 cells/dish) were plated on
glass coverslips placed in Petri dishes of 3.5 cm diameter 24 h
before the experiment. To analyze ADAM10 internalization induced by
its inhibition, live cells were pre-incubated with anti-ADAM10
mouse MAB1427 from R&D Systems, Inc. (diluted 1:100 in culture
medium) at 4°C for 30 min. Then the culture medium was removed,
replenished by the medium containing preferential ADAM10 inhibitor
GI254023X (GI; 10 µM; MilliporeSigma) in DMSO at 0.1 % (v/v) final
concentration and the cells were incubated for additional 2, 4, 8
or 24 h at 37°C. Control samples were incubated without GI in
medium containing DMSO at 0.1% (v/v) final concentration. After
each incubation time point, parallel GI-treated and control samples
were fixed for 5 min in ice-cold methanol at −20°C and stored for
subsequent immunofluorescence. All samples were then subjected to
indirect immunofluorescence using secondary donkey anti-mouse Alexa
Fluor®488-conjugated antibody (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.; cat. no. A-21202) diluted 1:1,000 in blocking
buffer containing 1% BSA for 1 h at 37°C. Finally, the coverslips
were mounted onto slides in the Mounting Media with DAPI, and
analyzed by a confocal laser scanning microscope Zeiss LSM 510
Meta.
To analyze the ADAM10 subcellular localization in
response to internalization of CA IX, live cells were pre-incubated
with anti-ADAM10 mouse MAB1427 from R&D Systems, Inc. (diluted
1:100 in culture medium) simultaneously with anti-CA IX humanized
CA9hu-1 Mab capable of stimulating CA IX internalization [50 µg/ml;
provided by Professor J. Pastorek, MABPRO, a.s. (27)] at 4°C for 30 min. Control samples
were pre-incubated with anti-ADAM10 mouse MAB1427 only. Immediately
after removal from 4°C, samples were transferred to 37°C to allow
for internalization and then incubated for additional 2, 4, 8 and
24 h. After each incubation time point, parallel samples were fixed
with methanol and stored as aforementioned. Fixed and blocked
control samples that were not pre-treated with the CA9hu-1 antibody
at the beginning of the experiment were post-incubated with that
antibody, for 1 h at 37°C. All samples were then incubated with the
mixture of secondary donkey anti-mouse Alexa
Fluor®488-conjugated antibodies and goat anti-human
Alexa Fluor®555-conjugated antibodies (Invitrogen;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; cat. no. A-21433) diluted 1:1,000
in the blocking buffer containing 1% BSA for 1 h at 37°C. Finally,
the coverslips were mounted onto slides in Mounting Media with
DAPI, and analyzed by the confocal laser scanning microscope Zeiss
LSM 510 Meta.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was isolated using RNeasy Plus Mini Kit
(Qiagen) and reverse transcription of 1 µg RNA for each sample was
performed with the High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit
(Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to
the manufacturer's instructions. qPCR was carried out using Maxima
SYBR Green PCR Master mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) with the
following gene-specific primers: ADAM10 sense,
5′-GACCACAGACTTCTCCGGAAT-3′ and antisense
5′-TGAAGGTGCTCCAACCCAAG-3′; ADAM17 sense,
5′-TGGATGAAGGAGAAGAGTGTGA-3′ and antisense,
5′-AAGATCCAAGCAAACAGTGTCAT-3′; and β-actin sense,
5′-TCCTCCCTGGAGAAGAGCTA-3′ and antisense,
5′-ACATCTGCTGGAAGGTGGAC-3′. qPCR was performed for 10 min at 95°C
for initial denaturation followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec
and 60°C for 1 min. Sample CT values were normalized to β-actin.
Relative expression was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCq
method (28). All amplifications
were performed in triplicates.
RNA interference
For siRNA-mediated silencing of de novo
ADAM10 synthesis, C33a-FL-CA IX cells were seeded at
8×104 cells/cm2. One day later, cells were
transfected with 1 µg of either MISSION®
enzymatically-prepared small interfering RNA (esiRNA) human ADAM10
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA; cat. no. EHU129311) or control esiRNA
targeting RLUC (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA; cat. no. EHURLUC) using
Attractene transfection reagent (Qiagen) according to the
manufacturer's recommendations. Briefly, esiRNA was diluted in
serum-free DMEM medium and Attractane Transfection Reagent in a
total volume of 100 µl, and incubated for 15 min at room
temperature. Following the medium exchange, the transfection
reagent/esiRNA mixture was added drop-wise onto C33a-FL-CA IX
cells. The day after transfection, cells were incubated with fresh
cultivation medium either with or without 10 µM GI inhibitor for 24
h [as previously described (29)]
and subsequently processed for ELISA analysis. Effect of ADAM10
silencing was evaluated by RT-qPCR in transfected versus control
cells.
Expression of dominant-negative mutant
of ADAM10 (ΔMP)
C33a-FL-CA IX cells were plated into 35-mm Petri
dishes to reach ~70% monolayer density on the next day. Transient
transfection was performed with 6 µg of pcDNA3-Delta (Pro-MP)
ADAM10-HA plasmid encoding a ΔMP mutant lacking prodomain and
metalloprotease domain, a gift from Axel Ullrich (Addgene, Inc;
plasmid cat. no. 65107; http://n2t.net/addgene:65107; RRID: Addgene_65107)
using TurboFect™ reagent according to the manufacturer's
recommendation. Briefly, plasmid DNA (6 µg) was diluted in
serum-free DMEM medium and TurboFect Transfection Reagent in a
total volume of 200 µl, and incubated for 15 min at room
temperature. The transfection reagent/plasmid DNA mixture was added
drop-wise to each dish without medium exchange. Cells transfected
with empty vector served as negative control. One day later,
transfected cells were trypsinized and plated in six-well plates.
Half of the transfected cells were incubated in the presence of GI
inhibitor diluted in DMEM to working concentration of 10 µM. As a
negative control, DMSO was added in a volume corresponding to the
concentration of the inhibitor. After 24 h, proteins from
transfected cells were extracted and cell culture medium was
collected for ELISA.
Western blotting
Western blotting was performed as previously
described (8). In brief,
C33a-FL-CA IX and C33a-NS-CA IX cells were lysed in ice-cold RIPA
buffer (150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 0.05% NaDOC, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1%
SDS, 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4) containing inhibitors of proteases
(Roche Applied Science). Cell lysates were collected and cleared by
centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C. Total protein
concentration was determined using the BCA protein assay reagent
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 50 µg/ml of total proteins
mixed with Laemmli buffer were loaded per lane, separated in 10%
SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membrane (Macherey-Nagel GmbH;
cat. no. 741260). The membranes were treated with blocking buffer
containing 5% (w/v) non-fat milk with 0.2% Nonidet P40 for 1 h and
probed with the following primary antibodies: in-house generated
anti-CA IX M75 Mab (hybridoma medium 1:3 in 5% non-fat dry milk
with 0.2% Nonidet P40 in PBS, 1 h, room temperature); anti-ADAM17
(cat. no. 3976; 1:1,000 in 3% BSA in TBS-T buffer, overnight, 4°C),
anti-ADAM10 (cat. no. 14194; 1:1,000 in 3 % BSA in TBS-T buffer,
overnight, 4°C); anti-β-actin (cat. no. 3700) 1:5,000 in 3% BSA in
TBS-T buffer (0,1% Tween-20), 1 h, room temperature; all from Cell
Signaling Technology, Inc). After washing with 0.1% Tween-20 in
PBS, the membranes were incubated for 1 h at room temperature, with
the secondary antibodies: HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA; cat. no. A0168) or HRP-conjugated goat
anti-rabbit IgG (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; cat. no. 1721019)
diluted 1:5,000 in blocking buffer for 1 h at room temperature.
Protein bands were detected using enhanced chemiluminescence kit
(GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences).
Activation and inhibition of CA IX ECD
shedding
For the activation of shedding, treatment of cells
with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA; MilliporeSigma) at 20 µM
final concentrations, and/or ionomycin (IONO; MilliporeSigma) at
final concentration of 1 µg/ml was performed for 3 h. For the
inhibition of shedding, cells were treated with serum-free medium
containing preferential ADAM10 inhibitor GI (1 µM), and/or
ADAM17-inhbiting antibody D1(A12) (200 nM; Abcam; cat. no.
ab215268) for 3 h at 37°C.
Bioinformatics
In silico analysis of the ADAM10 and ADAM17
promoters was performed using MatInspector (https://www.genomatix.de) (30,31).
The promoter sequences with the overall length of 1,418 and 1,643
bp were extracted directly from the ElDorado genome database for
the ADAM10 and ADAM17 genes, respectively. Transcription factors
(TFs) were selected according to the core (0.75) and matrix
(optimized) similarity. The accurate position of predicted binding
elements was calculated according to the transcription start site.
Phenotype heatmaps containing comparisons of relative
transcriptional patterns of CA9, ADAM10, and ADAM17 in tumor tissue
specimens from glioblastoma and colorectal carcinoma patients were
generated through IST (in silico transcriptomics) online
Medisapiens database (https://ist.medisapiens.com, accessed on March 10,
2021, currently available at http://tracxn.com/d/companies/medisapiens.com).
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using unpaired two-tailed
Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple
comparison test using GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software, Inc.).
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
CA IX cleavage by recombinant human
ADAM10
It was first aimed to gain biochemical evidence that
CA IX is an ADAM10 substrate. Therefore, a recombinant human ADAM10
catalytic domain (rhADAM10) was used, the activity of which was
proven by the cleavage of a commercial fluorogenic peptide
(Fig. 1A). RhADAM10 was then shown
to cleave a transiently expressed full-length (FL) CA IX from the
surface of transfected wild-type CHOwt cells, that express a
functional ADAM17 proteinase, but lack an endogenous ADAM10
proteinase (Fig. 1B). In line with
this finding, incubation of CHOwt-FL-CA IX cells with ADAM17
activator PMA resulted in shedding of CA IX ECD, while ADAM10
activator IONO had no effect (Fig.
1C). However, CA IX ECD was shed to culture medium upon
external addition of rhADAM10 (Fig.
1C).
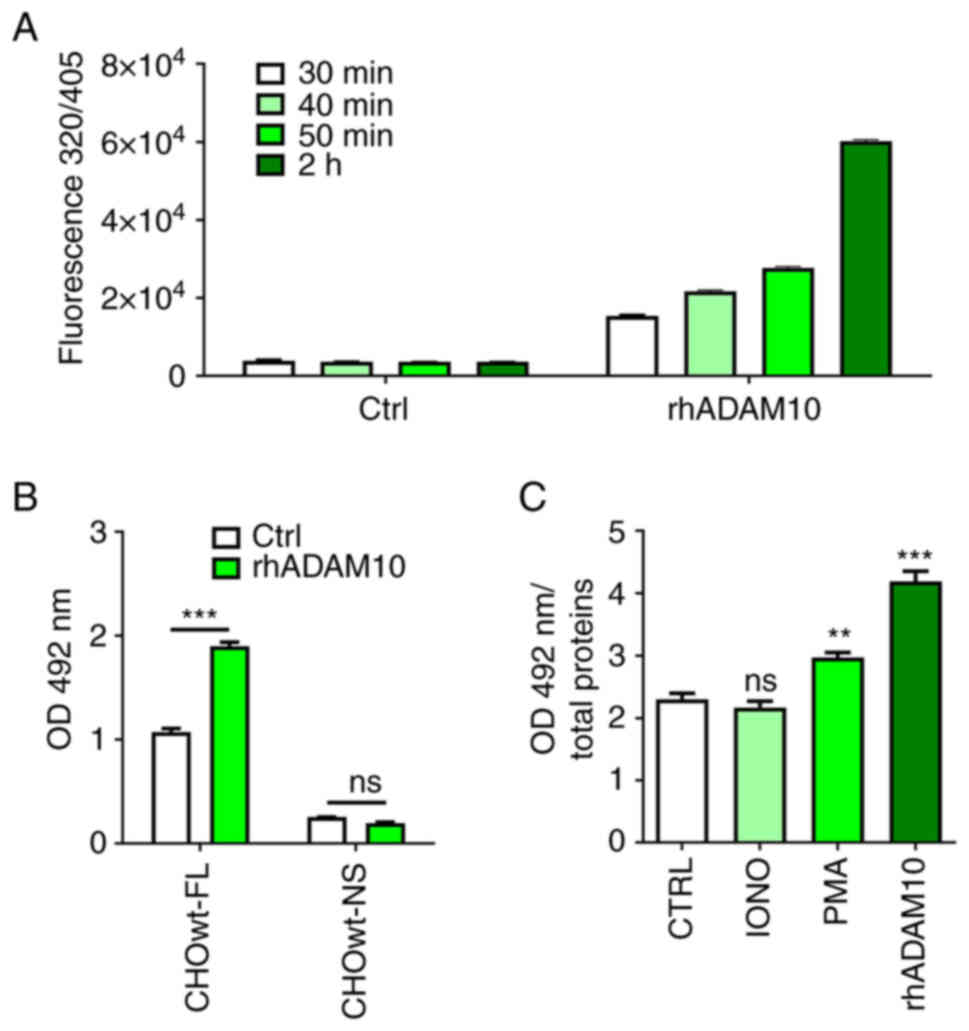 | Figure 1.Biochemical evidence for
ADAM10-mediated CA IX ECD cleavage. (A) Verification of the
cleavage activity of rhADAM10 catalytic domain towards the
fluorogenic peptide Mca-K-P-L-G-L-Dpa-A-R-NH2. The
peptide was used at the final concentration of 10 µM in a total of
100 µl reaction mixture with 10 ng of the rhADAM10. The cleavage
was allowed to proceed for 30, 40, 50 and 120 min. Time-related
increase of the fluorescence emitted from the peptide proves that
rhADAM10 was active in comparison to negative control without
rhADAM10. (B) ELISA analysis of CA IX ECD in culture medium
obtained from CHOwt-FL-CA IX and CHOwt-NS-CA IX cells transiently
expressing FL-CA IX and NS-CA IX, respectively. Transfected cells
were treated with rhADAM10 (500 ng/ml) for 24 h (Data were analyzed
by Student's t-test). (C) Incubation of CHOwt-FL-CA IX cells with
ADAM17 activator PMA (20 µM, 3 h), ADAM10 activator IONO (1 µg/ml,
3 h) or rhADAM10 (500 ng/ml, 24 h). Data were analyzed using
one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test. Experiments were
performed in triplicates and repeated twice. The results were
expressed as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. ADAM, a
disintegrin and metalloproteinase; CA IX, carbonic anhydrase IX;
rhADAM10, recombinant human ADAM10; ECD, ectodomain; FL,
full-length; NS, non-shed; IONO, ionomycin; PMA, phorbol
12-myristate 13-acetate; ns, non-significant. |
Moreover, rhADAM10 was used to treat transiently
transfected CHOwt-NS-CA IX cells expressing the NS CA IX variant
generated by the deletion of 10 amino acids from the stalk region
(11). As recently demonstrated,
the NS CA IX variant exhibits cell surface expression similar to FL
CA IX (11). Even though rhADAM10
was able to significantly increase the level of ECD shed from FL CA
IX, it could not cleave the NS CA IX variant (Fig. 1B). These findings demonstrated that
CA IX is a direct ADAM10 substrate and that the ADAM10 cleavage
site is localized in the fragment deleted from the NS variant,
which also contains the cleavage site for ADAM17 (11).
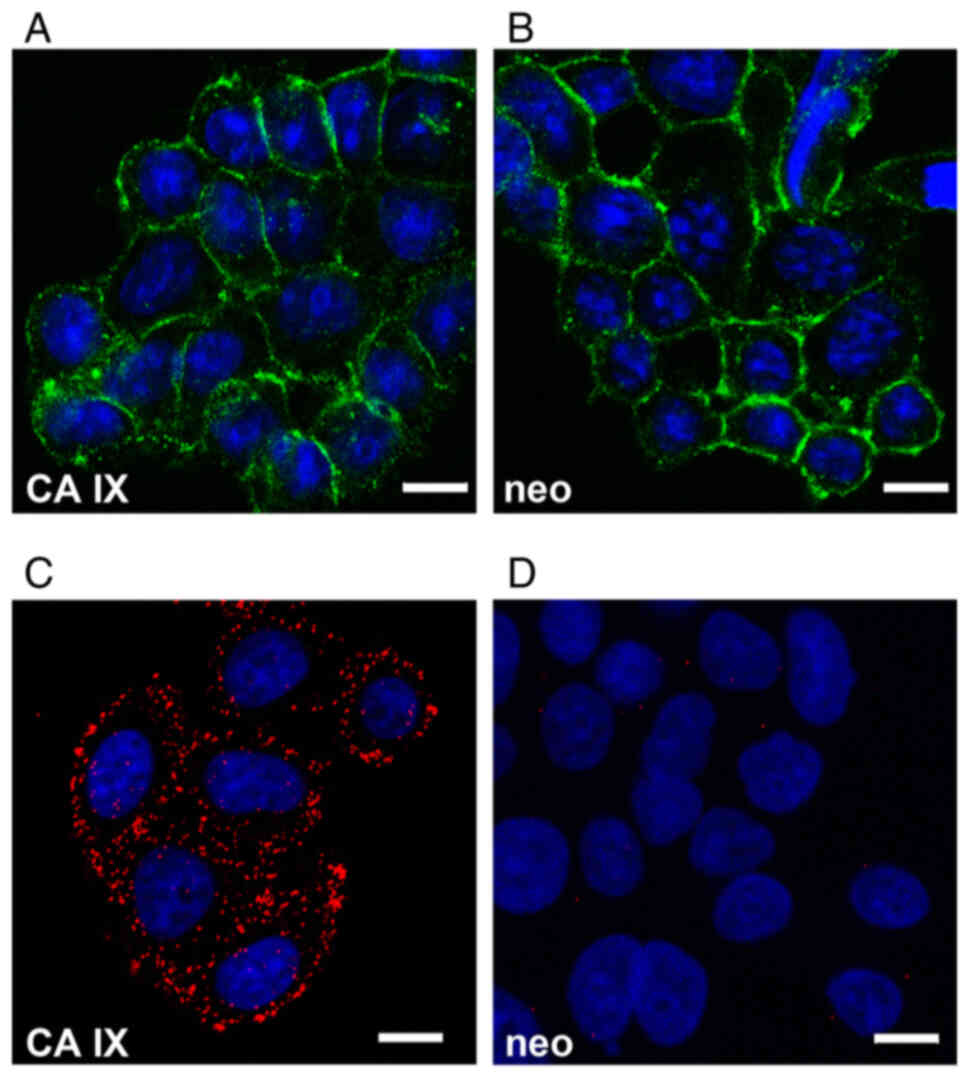
Colocalization and proximity of ADAM10
and CA IX
The role of endogenous ADAM10 in ECD shedding from
the CA IX protein expressed on the surface of human cancer cells
was next examined. For this purpose, stably transfected C33a
cervical carcinoma cells constitutively expressing FL CA IX were
employed. C33a-FL-CA IX cells express ADAM10 at the mRNA and
protein levels and subcellular localization similar to control
C33a-neo cells, as demonstrated by indirect immunofluorescence
using the MAB1427 antibody specific for human ADAM10 (Fig. 2A and B). To further explore the
spatial relationship between ADAM10 and CA IX, PLA was performed,
which visualizes protein-protein interactions in situ. This
in-cell co-immunoprecipitation represents an alternative to
conventional co-immunoprecipitation of extracted proteins while
preserving the natural context of the analyzed interactors
(26). PLA was executed with the
primary antibodies binding to the N-terminal regions of ADAM10 and
CA IX. Results revealed a clear fluorescent signal suggesting that
ADAM10 is in close proximity and can interact with CA IX (Fig. 2C). No PLA signal was observed in
the control C33a-neo cells (Fig.
2D).
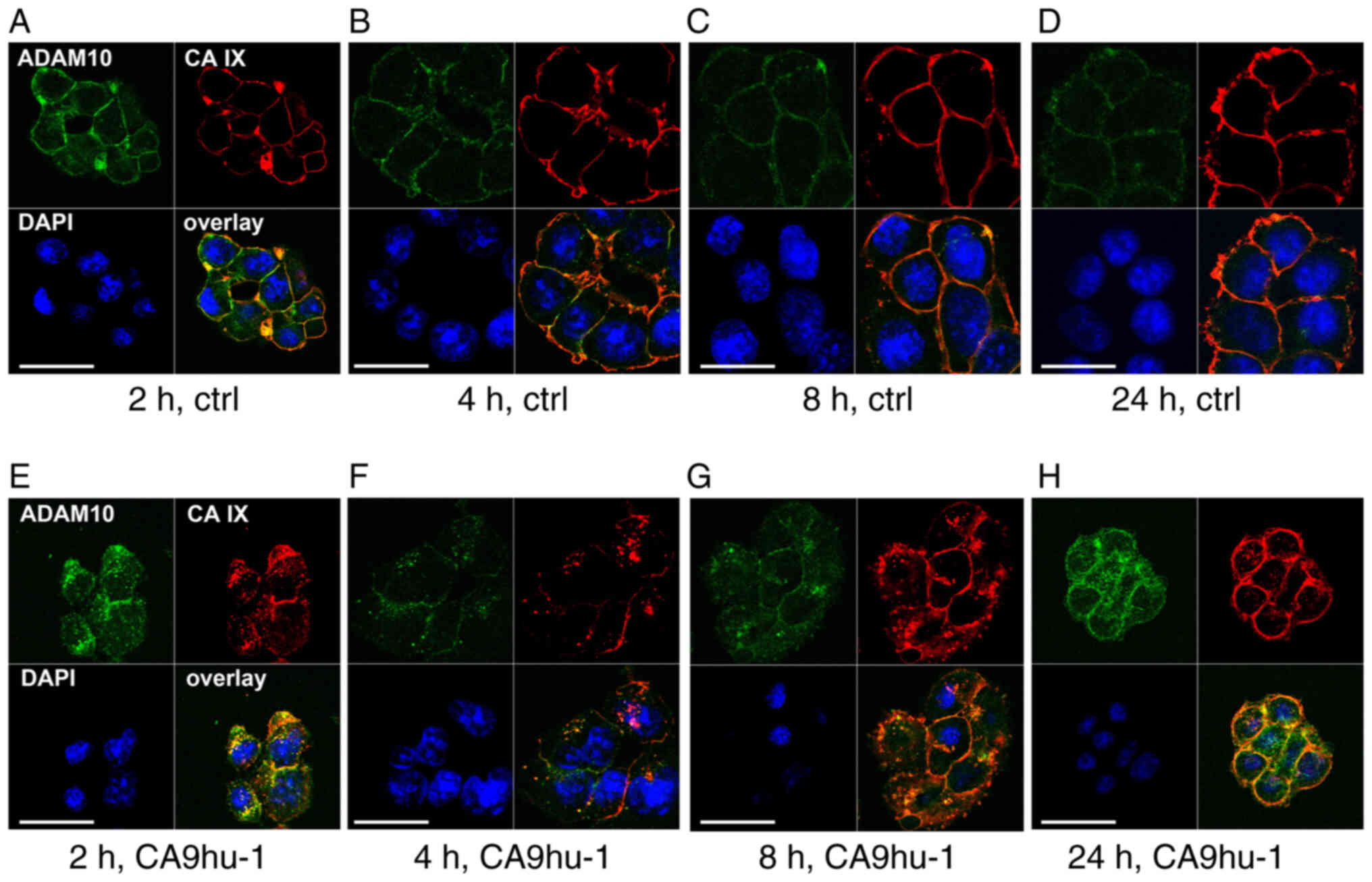
Co-internalization of ADAM10 and CA
IX
It was next aimed to determine whether ADAM10
remains co-distributed with CA IX during internalization induced by
the specific CA9hu-1 Mab directed to the CA IX catalytic domain
(27). For that purpose,
C33a-FL-CA IX cells were first incubated at 4°C with both
anti-ADAM10 and anti-CA IX antibodies to enable their binding only
to the subpopulation of ADAM10 and CA IX molecules present on the
cell surface. Control samples were pre-treated only with ADAM10
antibody, which is unable to trigger internalization. The pre-bound
antibodies could enter the cells together with their antigens only
via active endocytosis (i.e. internalization), which was
facilitated by transferring the cells to 37°C. This approach
allowed us to observe the endocytosis and recycling of the
complexes of the primary antibodies bound to their antigens
throughout the experimental period and detect them with the
corresponding secondary antibodies at different time points. In the
absence of internalization-inducing CA9hu-1 antibody, both CA IX
and ADAM10 displayed plasma membrane localization (Fig. 3A-D). By contrast, CA9hu-1
antibody-induced internalization of CA IX was clearly visible
already after 2 h and was accompanied by internalization of ADAM10
as indicated by their overlapping fluorescence signals (Fig. 3E-G). Later on, both molecules
recycled back to the plasma membrane (Fig. 3G and H).
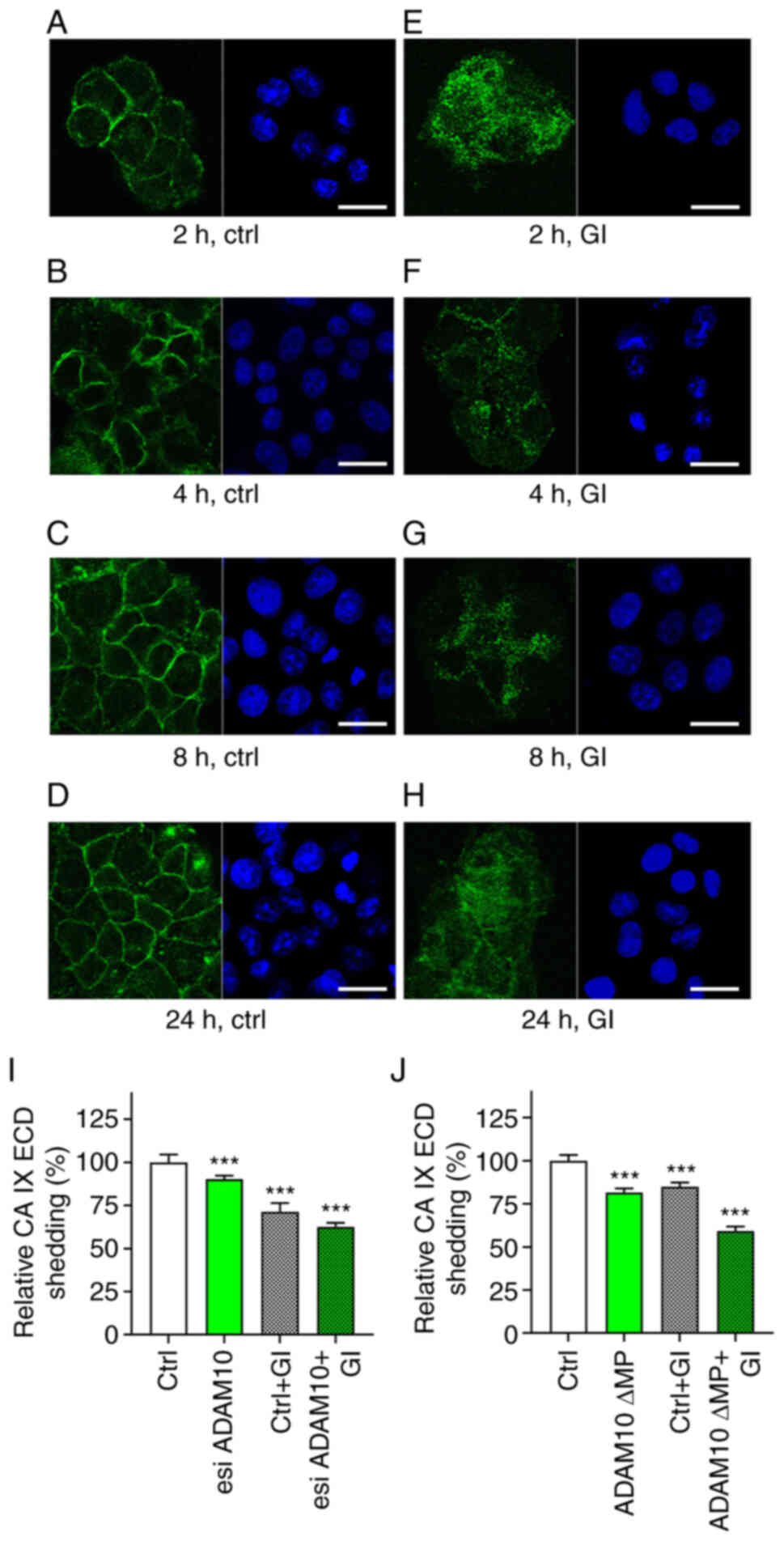
Effect of molecular targeting of
ADAM10 on CA IX ECD shedding
Based on the aforementioned observations, it was
aimed to directly target ADAM10 expression in C33a-FL-CA IX cells
by RNA interference and follow its impact on CA IX ECD shedding.
The initial attempts to suppress ADAM10 were not fully satisfactory
despite the clear downregulation of ADAM10 transcription (Fig. S1A), possibly due to the fact that
the reduced de novo synthesis of ADAM10 protein remained
unrecognized within the large pool of existing ADAM10 molecules. To
solve this problem, an approach inspired by the study of Seifert
et al (29) was chosen,
where it was revealed that exposing cells to GI, a preferential
ADAM10 inhibitor that binds to the protease active-site, leads to
its internalization followed by lysosomal degradation of mature
ADAM10 molecules. Therefore, it was assumed that inactivation
linked to a reduction in the pool of existing mature ADAM10
molecules would enhance the effect of ADAM10 suppression. We first
verified that GI causes the ADAM10 internalization also in
C33a-FL-CA IX cells (Fig. 4). This
was performed by pre-incubation of live cells with anti-ADAM10
antibody to allow for its binding only to the molecules exposed on
the cell surface. Then the cells were incubated with or without GI
at 37°C to enable endocytosis. Afterwards, the cells were fixed and
stained with the secondary antibody. The cells without added GI
inhibitor displayed ADAM10 on the plasma membrane (Fig. 4A-D). By contrast, exposure of cells
to 10 µM GI at 37°C led to a reduced membrane localization of
ADAM10 apparently due to its internalization (Fig. 4E-H).
Then, transient esiRNA-mediated ADAM10 silencing was
performed, followed by 24 h incubation of the transfected cells
with and without GI inhibitor at 10 µM concentration (Fig. 4I). Rather than using a single
chemically-synthesized siRNA, it was decided to employ an esiRNA
made up of a diverse pool of siRNA that all target the same mRNA
sequence. Each individual siRNA has a lower concentration in the
pool, leading to lower off-target effects while producing an
efficient knockdown. Alternatively, transient expression of a ∆MP
lacking the pro- and metalloprotease domains was accomplished
(Figs. 4J and S1B) (32) again followed by the 24 h treatment
with or without 10 µM GI. As recently demonstrated, the long-term
effect (24 h) of 10 µM GI is limited to ADAM10 and not observed for
ADAM17, which is not a primary target of this inhibitor (29). Culture media from cells subjected
to esiRNA or ∆MP transfections incubated with and without GI were
then analyzed for CA IX ECD by ELISA (Fig. 4I and J).
Both approaches led to similar effects on CA IX ECD
shedding (Fig. 4I and J).
Targeting of ADAM10 alone reduced CA IX ECD release to medium by 9%
for esiRNA and 18% for ∆MP. Silencing of de novo synthesis
was inferior compared with the ∆MP expression as ∆MP protein could
potentially dimerize with existing ADAM10 molecules and perturb
their function. Inhibition of mature ADAM10 by GI in
non-transfected cells decreased CA IX ECD shedding by 15% for
esiRNA and 28% for ∆MP. However, simultaneous targeting and
inhibition of ADAM10 resulted in 37% (esiRNA) and 41% (∆MP)
reduction of CA IX ECD release to the culture medium. These data
are in line with the aforementioned biochemical and co-localization
experiments and further support the view that ADAM10 is involved in
the CA IX ECD shedding.
Additive effects of ADAM10 and ADAM17
activators and inhibitors on CA IX ECD shedding
Since C33a cells express both ADAM10 (Fig. 2A) and ADAM17 (11), they represent a suitable cell model
to investigate possible relationship between these two ADAMs in CA
IX ECD shedding. qPCR analysis of C33a cells revealed that the
level of ADAM10 transcript is significantly higher (~2.5-times)
than the level of ADAM17 in these cells irrespectively of whether
they express FL CA IX or NS CA IX (Fig. 5A). Expression of both
metalloproteinases in C33a cells was also revealed by Western
blotting (Fig. 5B). Although the
intensity of protein bands appeared to be similar, these two
results cannot be directly compared due to the fact that the
antibodies specific for ADAM10 and ADAM17, respectively, may differ
in the binding properties. As revealed in the present study for
ADAM10 (Figs. 2 and 3) and recently for ADAM17 (11) by indirect immunofluorescence of
live cells, both metalloproteinases are localized on the cell
surface in CA IX proximity where they can accomplish CA IX ECD
cleavage.
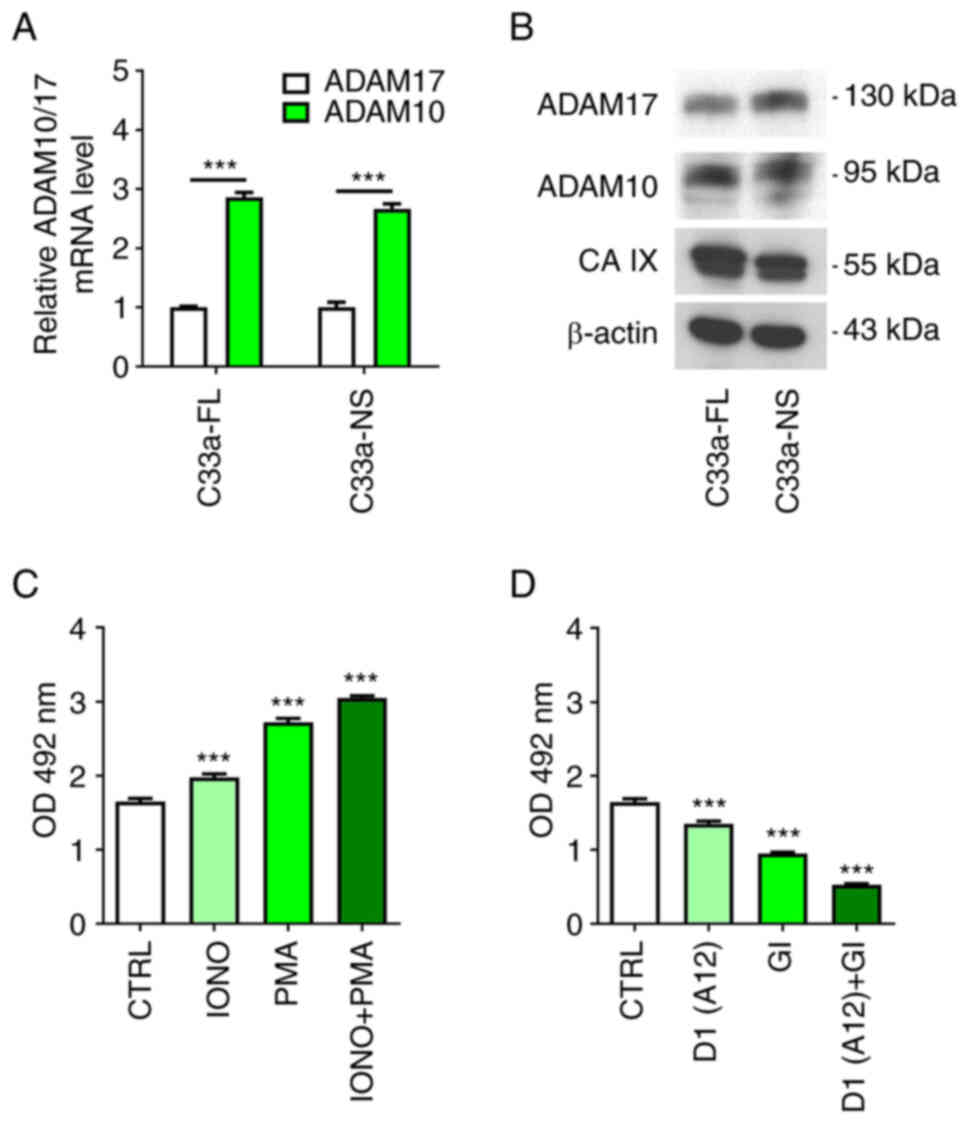 | Figure 5.Additive effect of ADAM10 and ADAM17
activation/inhibition. (A) Quantitative PCR analysis of ADAM10 and
ADAM17 mRNA levels in C33a-FL-CA IX and C33a-NS-CA IX cells
normalized to the level of β-actin mRNA. (B) Western blot analysis
of ADAM10, ADAM17 and CA IX protein in C33a-FL-CA IX and C33a-NS-CA
IX cells. The anti-actin antibody was used as a loading control. (C
and D) ELISA analysis of CA IX ECD in culture medium collected from
C33-FL-CA IX cells after the treatment with IONO (1 µg/ml), PMA (20
µM), IONO + PMA (1 µg/ml; 20 µM), D1(A12) antibody (200 nM), GI
inhibitor (1 µM) or D1(A12) + GI (200 nM; 1 µM) for 3 h in
comparison to non-treated cells (CTRL). Experiment was performed in
triplicates and repeated two times. Data were analyzed by (A)
Student's t-test and (C and D) one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's
test. Results were expressed as the mean relative levels of mRNA or
CA IX ECD ± SD. ***P<0.001. ADAM, a disintegrin and
metalloproteinase; FL, full-length; CA IX, carbonic anhydrase IX;
NS, non-shed; ECT, ectodomain; IONO, ionomycin; PMA, phorbol
12-myristate 13-acetate; GI, GI254023X. |
C33a-FL-CA IX cells were treated either with IONO
that is known to activate primarily ADAM10 or with PMA
predominantly activates ADAM17 (33), or simultaneously with both
activators to find out their individual and combined effect on
activated CA IX ECD shedding. Medium was harvested from the cells
treated with activators for 3 h and analyzed for CA IX ECD by
ELISA. As revealed in Fig. 5C,
each activator was able to significantly increase the level of CA
IX ECD from C33a-FL-CA IX cells and moreover, they showed an
additive effect when used together. No basal ECD shedding and no
activation was observed in C33a-NS-CA IX cells (data not
shown).
C33a-FL-CA IX cells were then treated with
inhibitors (Fig. 5D), namely the
ADAM17-inhibiting antibody D1(A12) that binds to a
conformation-sensitive cross-domain epitope on ADAM17 molecule
(34) and GI at 1 µM concentration
that is fully specific for ADAM10 and not sufficient for inhibition
of ADAM17 in this experimental setting (35) (Fig.
S1D). D1(A12) Mab was used because it is specific only for
ADAM17, whereas other known ADAM10 inhibitor, a hydroxamate-based
TAPI-0, can inhibit not only ADAM17 but also MMP metalloproteinases
and potentially also carbonic anhydrases (36). GI was used at 1 µM concentration,
since at 10 µM concentration it could slightly reduce shedding of
CA IX from the surface of live CHO cells that express only ADAM17
but not ADAM10 (Fig. S1C and D).
In the internalization experiments, slight inhibition of ADAM17
alongside full inhibition of ADAM10 did not interfere with the
ADAM10 endocytosis. However, in the experiments aimed at CA IX ECD
shedding from C33a cells that express both sheddases, it was
required to be certain that GI specifically inhibits only ADAM10.
Importantly, a significant additive effect of inhibitors was
observed on constitutive CA IX shedding from C33a-FL-CA IX
(Fig. 5D), suggesting contribution
of both ADAM17 and ADAM10.
Collectively, these data suggested that CA IX ECD
shedding is mediated not only by ADAM17, as previously described
(8,11), but also by ADAM10, as demonstrated
in the present study.
Discussion
CA IX is a cancer-associated carbonic anhydrase
isoform expressed in a broad range of tumor types, where it is
primarily localized on the surface of cells exposed to chronic
hypoxia and/or cells with oncogenic mutation(s) leading to
activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway. The cell
surface position allows CA IX to use the exofacial catalytic domain
to regulate tumor pH via reversible conversion of CO2
generated by oncogenic metabolism to bicarbonate ions and protons.
Bicarbonate ions are imported into the cytoplasm by bicarbonate
transporters to maintain slightly alkaline intracellular pH, which
is crucial for cell survival and proliferation, whereas protons
remain in pericellular space and contribute to extracellular
acidosis, which supports invasiveness and metastasis. The
N-terminal proteoglycan-like region of the extracellular domain of
CA IX mediates cell adhesion and participates in a non-catalytic
export of protons in co-operation with lactate transporters
[reviewed in (13,37)].
It was previously demonstrated by the authors that
CA IX is a highly stable protein with a half-life close to 40 h
(38). However, ~10% of the CA IX
molecules undergo constitutive shedding of their ECD, which is
sensitive to metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (8). Even though hypoxia increases the
level of the shed ECD, the fraction of the soluble CA IX ECD is
proportional to the hypoxia-induced expression of the
cell-associated protein. Nevertheless, it was identified that CA IX
ECD shedding can be increased by PMA, which activates ADAM17
through the PKC pathway, and both biochemical and molecular
evidences were provided for the ADAM17-mediated CA IX shedding via
the cleavage site localized in the stalk region proximal to the
transmembrane region of the CA IX molecule (8,11).
In the present study, it was shown for the first
time that CA IX ECD can be also cleaved by ADAM10. In addition, it
was demonstrated that CA IX and ADAM10 are localized in close
proximity. This is further supported by the finding that the
antibody-triggered internalization of CA IX is associated with the
internalization of ADAM10. Both molecules exhibit overlapping
subcellular distribution not only during endocytosis, but also
during recycling to the plasma membrane indicating that they remain
associated throughout the intracellular path. Thus, the
co-localization of ADAM10 with CA IX fulfils the spatial
prerequisite for their interaction and CA IX ECD cleavage.
The data obtained with the NS CA IX variant
suggested that ADAM10 can mediate CA IX ECD shedding via the
cleavage site overlapping with that of ADAM17. Based on comparison
of the sequence of amino acids deleted from the NS mutant with the
predicted cleavage sites for dual ADAM10&17 substrates
(39), it can be deduced that the
cleavage site may be localized on the CA IX molecule between the
positions 402*403 corresponding to PRAAE*PVQ sequence. Moreover,
data obtained in the present study supported the view that ADAM10
and ADAM17 proteinases are involved in both constitutive shedding
(as demonstrated by inhibitors) and activated shedding (as
demonstrated by activators) of CA IX.
ADAM10 is regulated by different pathways and can
cleave a spectrum of molecular targets only partially overlapping
with targets of ADAM17 (5,33). Thus, ADAM10 appears to facilitate
CA IX ECD shedding in additional signaling and physiological
contexts, and thereby can affect responses mediated by soluble CA
IX also in the absence of ADAM17. Based on previous data by the
authors, soluble CA IX appears to interfere with the local
functions of the cell-tethered CA IX protein that are required for
tumorigenic and metastatic phenotype, including proper execution of
the pH-regulatory and adhesion functions, presumably via
competitive interactions with CA IX partner proteins in the plasma
membrane or in the extracellular space (11).
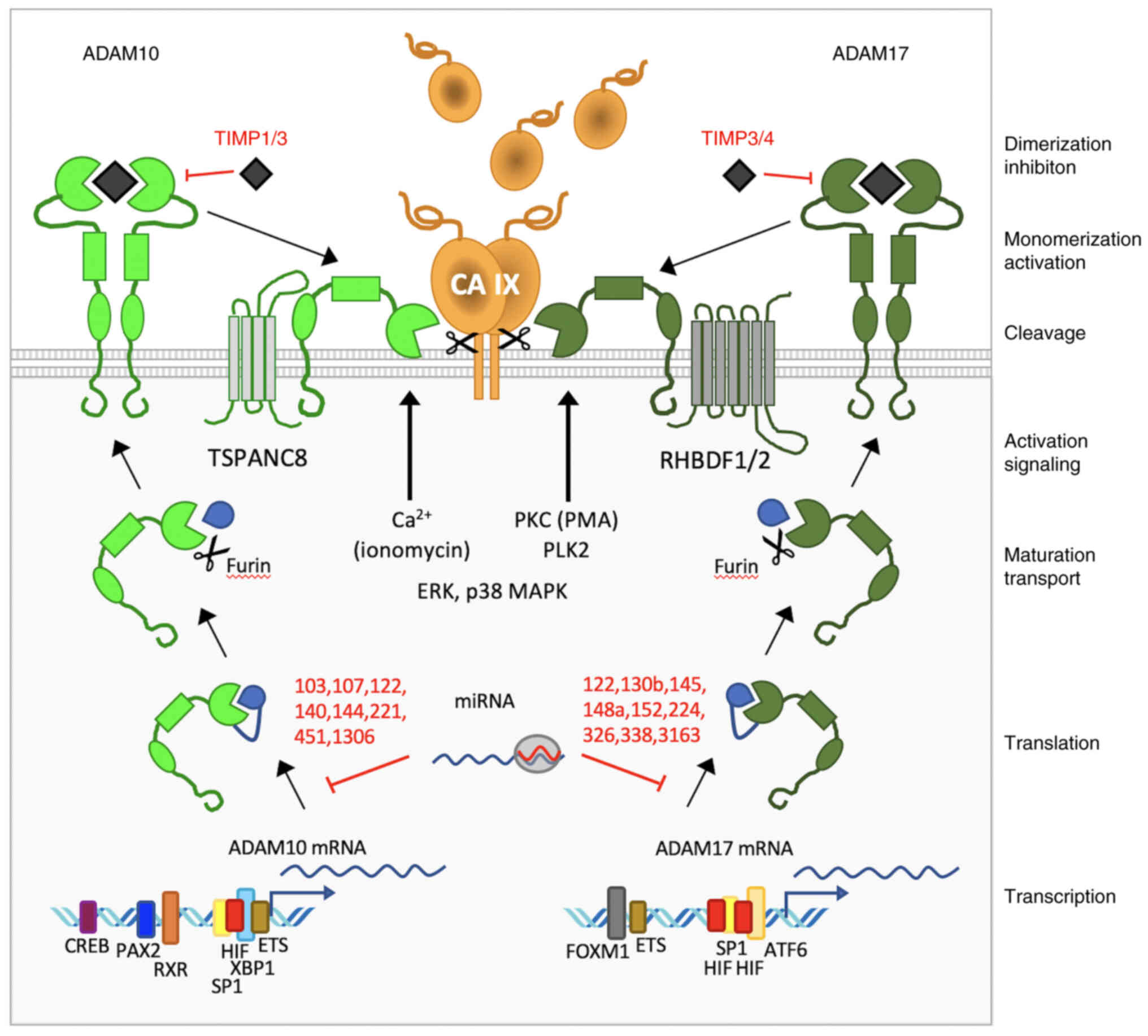
When looking more closely at the regulation and
effector functions of ADAM10 versus ADAM17, a large diversity of
molecular events can be observed, that play a role in distinct
expression patterns as well as activities of these two related
proteinases, which execute CA IX ECD shedding (Fig. 6).
Data from the literature and from in silico
analysis of ADAM10 and ADAM17 promoters using the MatInspector tool
(Fig. S2) suggested involvement
of the general TF SP1 through multiple binding sites in
transcription of both ADAM10 and ADAM17 genes (40,41).
Both genes were also shown to be transcriptionally activated by
hypoxia (42,43). Typical hypoxia-response element
sequences recognized by the HIF TF were found and functionally
proven in ADAM17 promoter, while ADAM10 promoter appears to contain
just a HIF-ancillary sequence and two ARNT (i.e. HIF-β) binding
sequences. In addition, both ADAM10 and ADAM17 promoters include
several binding sites for ETS1 factor, which can cooperate with
other TFs, including CREB, SP1 and HIF. Notably, while ADAM10 seems
to respond also to moderate hypoxia (0.5–5% of oxygen), ADAM17 is
transcriptionally induced by severe hypoxia (below 0.1%
O2) (42,43). Moreover, transcription of ADAM10
was shown to be induced by retinoic acid (RA) through its binding
to RA receptor and retinoid receptors to RXR motifs in the ADAM10
promoter (40). ADAM10 (but not
ADAM17) is also regulated by paired box 2 TF, particularly in
WT1-mutated kidney cancers through multiple promoter binding sites
and by XBP1 factor involved in response to DNA damage (44–46).
On the other hand, ADAM17 transcription is regulated by forkhead
box M1 (47). Both ADAM10 and
ADAM17 can be also regulated post-transcriptionally by distinct
sets of miRNAs (48).
Another level of expression diversity is given by
the post-translational regulation. Maturation of ADAM10 depends on
tetraspanins (TSPANC8), whereas maturation of ADAM17 is driven by
rhomboid chaperones iRhom1 and iRhom2 encoded by RHBDF1 and 2 genes
(49,50). Moreover, ADAM10 can be inhibited by
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) 1 and TIMP3, whereas
ADAM17 can be inhibited by the TIMP3 and TIMP4 molecules, which are
expressed in various tumor types at various levels and can locally
impair the cleavage of ADAMs' substrates including CA IX (51). Finally, activation of shedding can
be mediated either by release of Ca2+ ions through
ADAM10 or by pathways involving PKC, EGFR/PI3K, ERK, TNFα or NF-κB
signaling through ADAM17 (33).
All these circumstances create specific tumor tissue
contexts, where the shedding of CA IX ECD may depend on multiple
factors such as those driving the expression of CA IX, expression
of ADAM10 and ADAM17, or on their inhibitors and activators
(Fig. 6). This complex picture is
evident from the phenotype heatmap generated by IST Medisapiens
(https://ist.medisapiens.com) analysis of
the RNA-seq metadata for glioblastoma and colorectal carcinoma,
illustrating expression of selected genes in tumor tissues of
individual patients (Fig. S3A and
B). The analysis showed distinct transcription patterns of CA
IX, ADAM17 and ADAM10, suggesting that in certain CA IX-expressing
tumors lacking ADAM17, CA IX ECD shedding can be potentially
executed by ADAM10. This renders CA IX shedding possible in a
broader range of tumor tissues. Similarly, distinct expression
patterns can be observed also in other tumor types.
Accumulating experimental and clinical studies
demonstrate correlations of CA IX expression in cancer or stromal
cells to aggressive tumor phenotype, poor patient prognosis and
resistance to therapy. However, potential clinical value of CA IX
ECD shedding remains unclear despite numerous efforts to exploit
soluble CA IX as non-invasive tumor biomarker. While certain
studies support its prognostic and/or predictive value, others do
not show any significant relationship between the CA IX ECD levels
and clinical parameters. This can be at least in part due to
complex regulation of the CA IX ECD shedding. Uncovering the
involvement of ADAM10 in the CA IX ECD cleavage sheds a new light
on this intricate phenomenon and represents an important step
towards its improved understanding in terms of both tumor biology
and clinical applications.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank professor Jaromír
Pastorek (MABPRO, a. s.) for generous gift of the CA9hu-1 Mab and
Dr Tereza Golias (Biomedical Research Center SAS) for language
editing.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Slovak Scientific Grant
Agency (grant nos. VEGA 2/0074/20 and VEGA 2/0076/20), the Research
& Developmental Support Agency (grant nos. APVV-15-0697 and
APVV-19-0098) and the George Schwab and Leona Lauder
Foundation.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
MZ, IK and MT designed and performed the
experiments, analyzed/interpreted the data and contributed to the
manuscript writing. LJ contributed to immunofluorescence and ELISA
assays. OS performed the qPCR experiments. ML contributed to
confocal microscopy. MT performed bioinformatic analyses. SP
designed the study, supervised the experiments, interpreted the
data, wrote and edited the manuscript. MZ, IK and MT confirm the
authenticity of all raw data. All authors have read and approved
the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
SP, MZ and MT are co-inventors of patents related to
CA IX. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
ADAM
|
a disintegrin and
metalloproteinase
|
|
CA IX
|
carbonic anhydrase IX
|
|
CHO
|
Chinese hamster ovary cells
|
|
ECD
|
ectodomain
|
|
FL
|
full-length
|
|
GI
|
GI254023X
|
|
HIF
|
hypoxia-inducible factor
|
|
Mab
|
monoclonal antibody
|
|
∆MP
|
dominant-negative mutant of ADAM10
|
|
NS
|
non-shed
|
|
PLA
|
proximity ligation assay
|
|
PMA
|
phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
|
|
TF
|
transcription factor
|
|
TIMP
|
tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases
|
References
|
1
|
Lichtenthaler SF, Lemberg MK and Fluhrer
R: Proteolytic ectodomain shedding of membrane proteins in
mammals-hardware, concepts, and recent developments. EMBO J.
37:e994562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hayashida K, Bartlett AH, Chen Y and Park
PW: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of ectodomain shedding. Anat
Rec (Hoboken). 293:925–937. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murphy G: The ADAMs: Signalling scissors
in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:929–941. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mullooly M, McGowan PM, Crown J and Duffy
MJ: The ADAMs family of proteases as targets for the treatment of
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 17:870–880. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saftig P and Reiss K: The ‘A Disintegrin
And Metalloproteases’ ADAM10 and ADAM17: Novel drug targets with
therapeutic potential? Eur J Cell Biol. 90:527–535. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pruessmeyer J and Ludwig A: The good, the
bad and the ugly substrates for ADAM10 and ADAM17 in brain
pathology, inflammation and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
20:164–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vincent B and Checler F: α-Secretase in
Alzheimer's disease and beyond: Mechanistic, regulation and
function in the shedding of membrane proteins. Curr Alzheimer Res.
9:140–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zaťovičová M, Sedláková O, Švastová E,
Ohradanova A, Ciampor F, Arribas J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S:
Ectodomain shedding of the hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX is
a metalloprotease-dependent process regulated by TACE/ADAM17. Br J
Cancer. 93:1267–1276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zaťovičová M and Pastoreková S: Modulation
of cell surface density of carbonic anhydrase IX by shedding of the
ectodomain and endocytosis. Acta Virol. 57:257–264. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vidlickova I, Dequiedt F, Jelenska L,
Sedlakova O, Pastorek M, Stuchlik S, Pastorek J, Zatovicova M and
Pastorekova S: Apoptosis-induced ectodomain shedding of
hypoxia-regulated carbonic anhydrase IX from tumor cells: A
double-edged response to chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 16:2392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kajanova I, Zatovicova M, Jelenska L,
Sedlakova O, Barathova M, Csaderova L, Debreova M, Lukacikova L,
Grossmannova K, Labudova M, et al: Impairment of carbonic anhydrase
IX ectodomain cleavage reinforces tumorigenic and metastatic
phenotype of cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 122:1590–1603. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Russell S, Xu L, Kam Y, Abrahams D, Ordway
B, Lopez AS, Bui MM, Johnson J, Epstein T, Ruiz E, et al: Proton
export upregulates aerobic glycolysis. BMC Biol. 20:1632022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pastorek J and Pastoreková S:
Hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for cancer
therapy: From biology to clinical use. Semin Cancer Biol. 31:52–64.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Švastová E, Hulíková A, Rafajová M,
Zat'ovicová M, Gibadulinová A, Casini A, Cecchi A, Scozzafava A,
Supuran CT, Pastorek J and Pastoreková S: Hypoxia activates the
capacity of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX to acidify
extracellular pH. FEBS Lett. 577:439–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Švastová E, Witarski W, Csaderová L, Kosik
I, Skvarkova L, Hulikova A, Zatovicova M, Barathova M, Kopacek J,
Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX interacts with
bicarbonate transporters in lamellipodia and increases cell
migration via its catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 287:3392–3402.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benej M, Svastova E, Banova R, Kopacek J,
Gibadulinova A, Kery M, Arena S, Scaloni A, Vitale M, Zambrano N,
et al: CA IX stabilizes intracellular pH to maintain metabolic
reprogramming and proliferation in hypoxia. Front Oncol.
10:14622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gibadulinova A, Bullova P, Strnad H,
Pohlodek K, Jurkovicova D, Takacova M, Pastorekova S and Svastova
E: CAIX-mediated control of LIN28/let-7 axis contributes to
metabolic adaptation of breast cancer cells to hypoxia. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:42992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Swietach P, Patiar S, Supuran CT, Harris
AL and Vaughan-Jones RD: The role of carbonic anhydrase 9 in
regulating extracellular and intracellular pH in three-dimensional
tumor cell growths. J Biol Chem. 284:20299–20310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chiche J, Ilc K, Laferriere J, Trottier E,
Dayan F, Mazure NM, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur J:
Hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase IX and XII promote tumor cell
growth by counteracting acidosis through the regulation of the
intracellular pH. Cancer Res. 69:358–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Závada J, Závadová Z, Pastorek J, Biesová
Z, Jezek J and Velek J: Human tumour-associated cell adhesion
protein MN/CA IX: Identification of M75 epitope and of the region
mediating cell adhesion. Br J Cancer. 82:1808–1813. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jamali S, Klier M, Ames S, Barros LF,
McKenna R, Deitmer JW and Becker HM: Hypoxia-induced carbonic
anhydrase IX facilitates lactate flux in human breast cancer cells
by non-catalytic function. Sci Rep. 5:136052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ames S, Pastorekova S and Becker HM: The
proteoglycan-like domain of carbonic anhydrase IX mediates
non-catalytic facilitation of lactate transport in cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 9:27940–27957. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Csaderová L, Debreová M, Radvák P, Stano
M, Vrestiakova M, Kopacek J, Pastorekova S and Svastova E: The
effect of carbonic anhydrase IX on focal contacts during cell
spreading and migration. Front Physiol. 4:1–12. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Radvák P, Repic M, Švastová E, Takacova M,
Csaderova L, Strnad H, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S and Kopacek J:
Suppression of carbonic anhydrase IX leads to aberrant focal
adhesion and decreased invasion of tumor cells. Oncol Rep.
29:1147–1153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zaťovičová M, Tarábková K, Švastová E,
Gibadulinová A, Mucha V, Jakubícková L, Biesová Z, Rafajová M, Gut
MO, Parkkila S, et al: Monoclonal antibodies generated in carbonic
anhydrase IX-deficient mice recognize different domains of
tumour-associated hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX. J Immunol
Methods. 282:117–134. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Söderberg O, Gullberg M, Jarvius M,
Ridderstråle K, Leuchowius KH, Jarvius J, Wester K, Hydbring P,
Bahram F, Larsson LG and Landegren U: Direct observation of
individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity
ligation. Nat Methods. 3:995–1000. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zatovicova M, Kajanova I, Barathova M,
Takacova M, Labudova M, Csaderova L, Jelenska L, Svastova E,
Pastorekova S, Harris AL and Pastorek J: Novel humanized monoclonal
antibodies for targeting hypoxic human tumors via two distinct
extracellular domains of carbonic anhydrase IX. Cancer Metab.
10:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Seifert A, Düsterhöft S, Wozniak J, Koo
CZ, Tomlinson MG, Nuti E, Rossello A, Cuffaro D, Yildiz D and
Ludwig A: The metalloproteinase ADAM10 requires its activity to
sustain surface expression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:715–732. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cartharius K, Frech K, Grote K, Klocke B,
Haltmeier M, Klingenhoff A, Frisch M, Bayerlein M and Werner T:
MatInspector and beyond: Promoter analysis based on transcription
factor binding sites. Bioinformatics. 21:2933–2942. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E
and Werner T: Matlnd and matlnspector: New fast and versatile tools
for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 23:4878–4884. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gschwind A, Hart S, Fischer OM and Ullrich
A: TACE cleavage of proamphiregulin regulates GPCR-induced
proliferation and motility of cancer cells. EMBO J. 22:2411–2421.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Le Gall S, Bobé P, Reiss K, Horiuchi K,
Niu XD, Lundell D, Gibb DR, Conrad D, Saftig P and Blobel CP: ADAMs
10 and 17 represent differentially regulated components of a
general shedding machinery for membrane proteins such as
transforming growth factor α, L-selectin, and tumor necrosis factor
alpha. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1785–1794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tape CJ, Willems SH, Dombernowsky SL,
Stanley PL, Fogarasi M, Ouwehand W, McCafferty J and Murphy G:
Cross-domain inhibition of TACE ectodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S
A. 108:5578–5583. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ludwig A, Hundhausen C, Lambert M,
Broadway N, Andrews RC, Bickett DM, Leesnitzer MA and Becherer JD:
Metalloproteinase inhibitors for the disintegrin-like
metalloproteinases ADAM10 and ADAM17 that differentially block
constitutive and phorbol ester-inducible shedding of cell surface
molecules. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 8:161–171. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Supuran CT: How many carbonic anhydrase
inhibition mechanisms exist? J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 31:345–360.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Becker HM: Carbonic anhydrase IX and acid
transport in cancer. Br J Cancer. 122:157–167. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rafajová M, Zatovicová M, Kettmann R,
Pastorek J and Pastoreková S: Induction by hypoxia combined with
low glucose or low bicarbonate and high posttranslational stability
upon reoxygenation contribute to carbonic anhydrase IX expression
in cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 24:995–1004. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tucher J, Linke D, Koudelka T, Cassidy L,
Tredup C, Wichert R, Pietrzik C, Becker-Pauly C and Tholey A: LC-MS
based cleavage site profiling of the proteases ADAM10 and ADAM17
using proteome-derived peptide libraries. J Proteome Res.
13:2205–2214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Prinzen C, Müller U, Enders K, Fahrenholz
F and Postina R: Genomic structure and functional characterization
of the human ADAM10 promoter. FASEB J. 11:1522–1524. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Szalad A, Katakowski M, Zheng X, Jiang F
and Chopp M: Transcription factor Sp1 induces ADAM17 and
contributes to tumor cell invasiveness under hypoxia. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 28:1292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barsoum IB, Hamilton TK, Li X, Cotechini
T, Miles EA, Siemens DR and Graham CH: Hypoxia induces escape from
innate immunity in cancer cells via increased expression of ADAM10:
Role of nitric oxide. Cancer Res. 71:7433–7441. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rzymski T, Petry A, Kračun D, Rieß F, Pike
L, Harris AL and Görlach A: The unfolded protein response controls
induction and activation of ADAM17/TACE by severe hypoxia and ER
stress. Oncogene. 31:3621–3634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee SB, Doberstein K, Baumgarten P,
Wieland A, Ungerer C, Bürger C, Hardt K, Boehncke WH, Pfeilschifter
J, Mihic-Probst D, et al: PAX2 regulates ADAM10 expression and
mediates anchorage-independent cell growth of melanoma cells. PLoS
One. 6:e223122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Doberstein K, Pfeilschifter J and Gutwein
P: The transcription factor PAX2 regulates ADAM10 expression in
renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 32:1713–1723. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Reinhardt S, Schuck F, Grösgen S,
Riemenschneider M, Hartmann T, Postina R, Grimm M and Endres K:
Unfolded protein response signaling by transcription factor XBP-1
regulates ADAM10 and is affected in Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J.
28:978–997. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim IM, Ramakrishna S, Gusarova GA, Yoder
HM, Costa RH and Kalinichenko VV: The Forkhead Box m1 transcription
factor is essential for embryonic development of pulmonary
vasculature. J Biol Chem. 280:22278–22286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vincent B: Regulation of the α-secretase
ADAM10 at transcriptional, translational and post-translational
levels. Brain Res Bull. 126:154–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Matthews AL, Noy PJ, Reyat JS and
Tomlinson MG: Regulation of A disintegrin and metalloproteinase
(ADAM) family sheddases ADAM10 and ADAM17: The emerging role of
tetraspanins and rhomboids. Platelets. 28:333–341. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Düsterhöft S, Babendreyer A, Giese AA,
Flasshove C and Ludwig A: Status update on iRhom and ADAM17: It's
still complicated. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1866:1567–1583. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jackson HW, Defamie V, Waterhouse P and
Khokha R: TIMPs: Versatile extracellular regulators in cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 17:38–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|