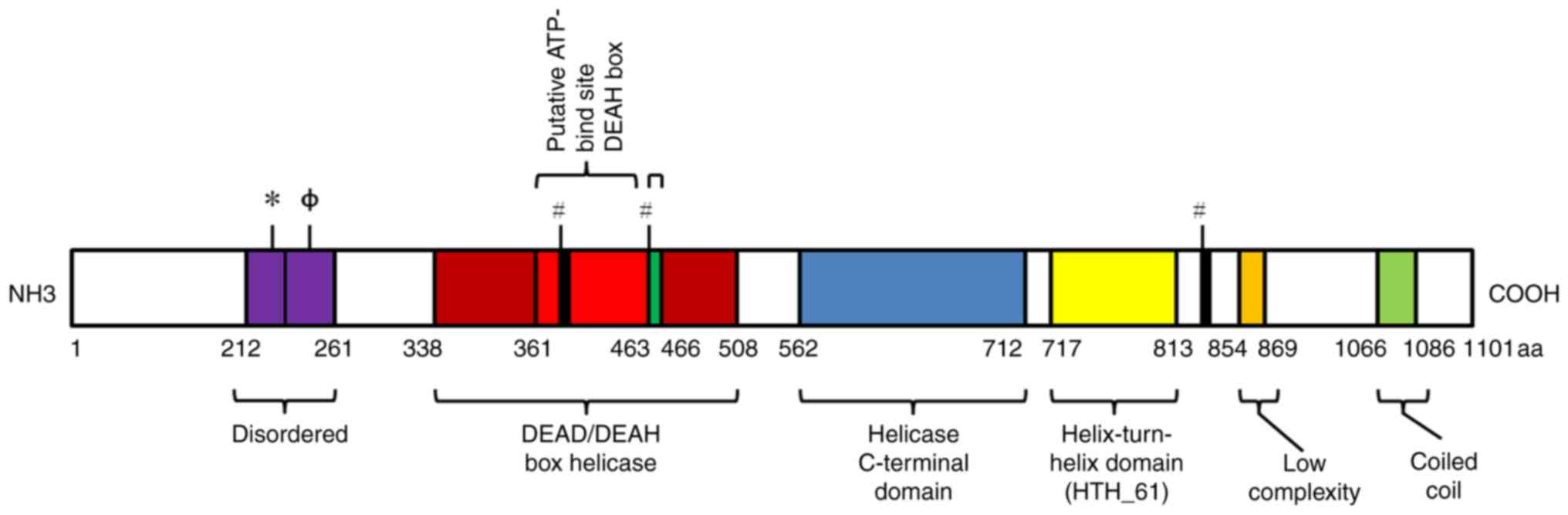
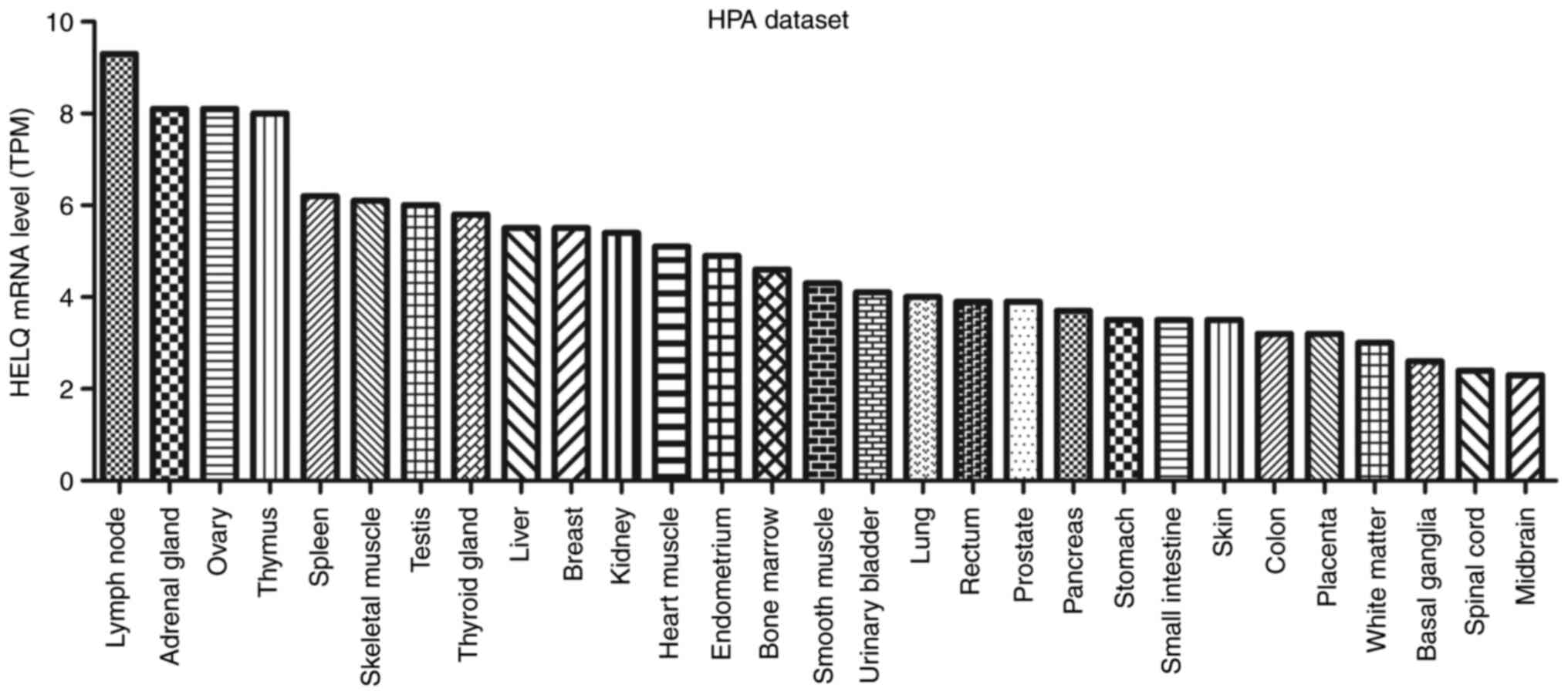
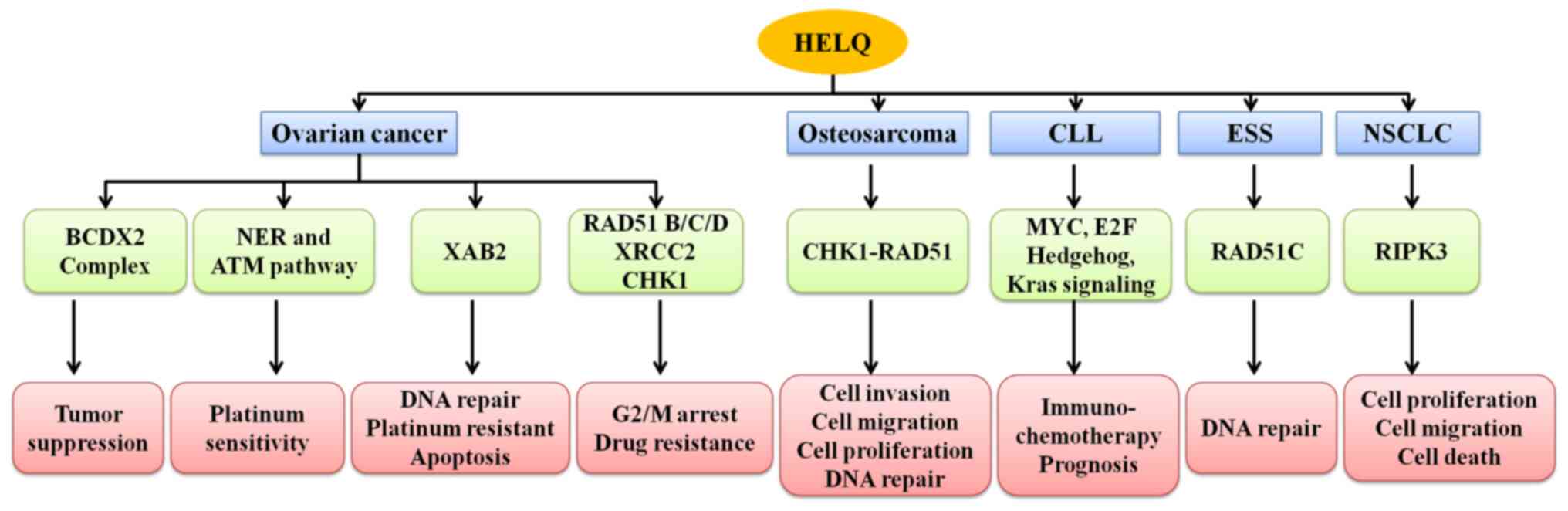
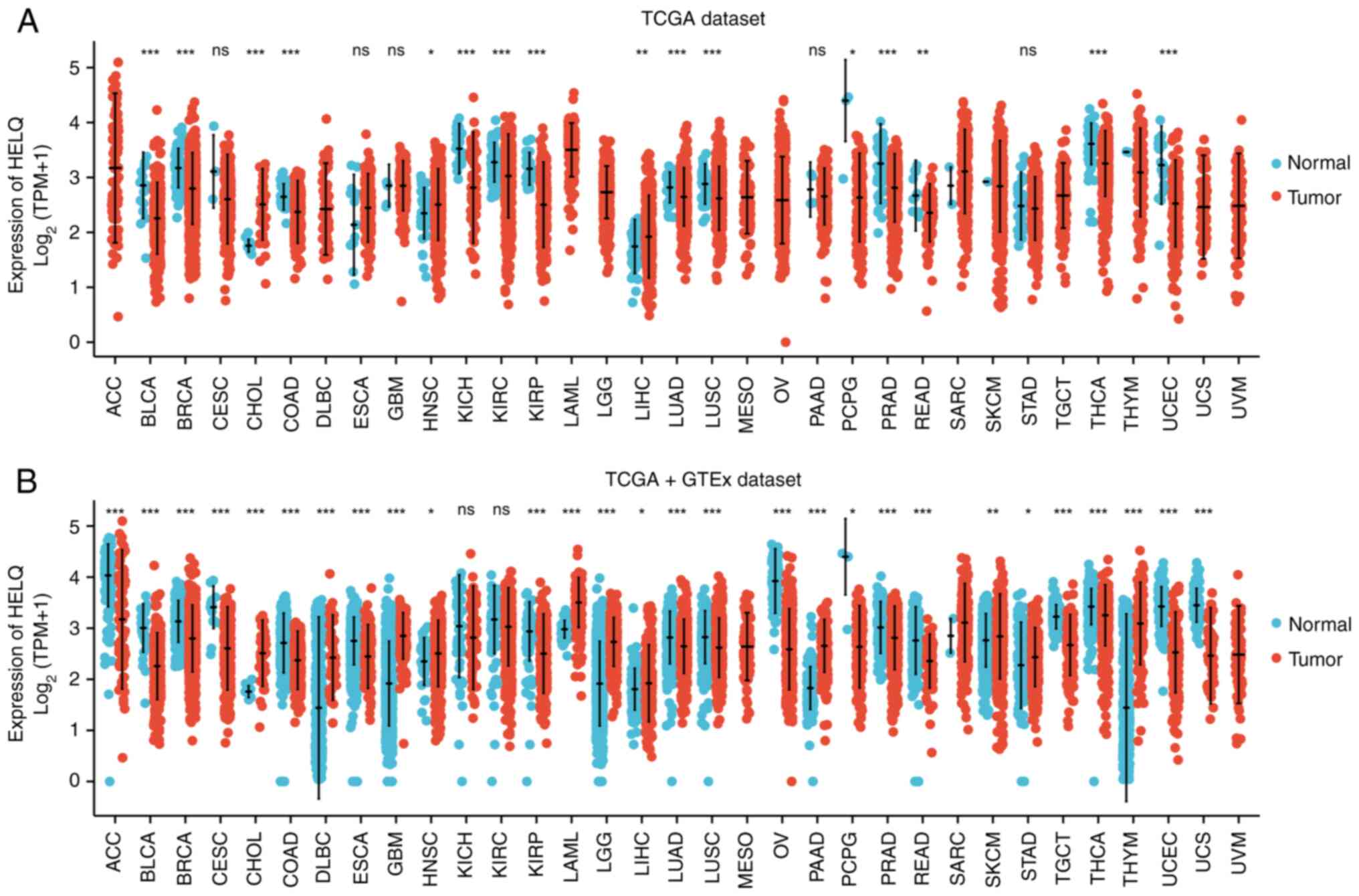
|
1
|
Marini F and Wood RD: A human DNA helicase
homologous to the DNA cross-link sensitivity protein Mus308. J Biol
Chem. 277:8716–8723. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Richards JD, Johnson KA, Liu H, McRobbie
AM, McMahon S, Oke M, Carter L, Naismith JH and White MF: Structure
of the DNA repair helicase hel308 reveals DNA binding and
autoinhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 283:5118–5126. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tafel AA, Wu L and McHugh PJ: Human HEL308
localizes to damaged replication forks and unwinds lagging strand
structures. J Biol Chem. 286:15832–15840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Woodman IL and Bolt EL: Winged helix
domains with unknown function in Hel308 and related helicases.
Biochem Soc Trans. 39:140–144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singleton MR, Dillingham MS and Wigley DB:
Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases.
Ann Rev Biochem. 76:23–50. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fairman-Williams ME, Guenther UP and
Jankowsky E: SF1 and SF2 helicases: Family matters. Curr Opin
Struct Biol. 20:313–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bleichert F and Baserga SJ: The long
unwinding road of RNA helicases. Mol Cell. 27:339–352. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Woodman IL, Briggs GS and Bolt EL:
Archaeal Hel308 domain V couples DNA binding to ATP hydrolysis and
positions DNA for unwinding over the helicase ratchet. J Mol Biol.
374:1139–1144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anand R, Buechelmaier E, Belan O, Newton
M, Vancevska A, Kaczmarczyk A, Takaki T, Rueda DS, Powell SN and
Boulton SJ: HELQ is a dual-function DSB repair enzyme modulated by
RPA and RAD51. Nature. 601:268–273. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guy CP and Bolt EL: Archaeal Hel308
helicase targets replication forks in vivo and in vitro and unwinds
lagging strands. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:3678–3690. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adelman CA, Lolo RL, Birkbak NJ, Murina O,
Matsuzaki K, Horejsi Z, Parmar K, Borel V, Skehel JM, Stamp G, et
al: HELQ promotes RAD51 paralogue-dependent repair to avert germ
cell loss and tumorigenesis. Nature. 502:381–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takata K, Reh S, Tomida J, Person MD and
Wood RD: Human DNA helicase HELQ participates in DNA interstrand
crosslink tolerance with ATR and RAD51 paralogs. Nat Commun.
4:23382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Long J, Zhu JY, Liu YB, Fu K, Tian Y, Li
PY, Yang WQ, Yang SY, Yin JY, Yin G and Zhang Y: Helicase POLQ-like
(HELQ) as a novel indicator of platinum-based chemoresistance for
epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 149:341–349. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song X, Ni J and Shen Y: Structure-based
genetic analysis of Hel308a in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon
Sulfolobus islandicus. J Genet Genomics. 43:405–413. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gorbalenya AE, Koonin EV, Donchenko AP and
Blinov VM: Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved
in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA
genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 17:4713–4730. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caruthers JM and McKay DB: Helicase
structure and mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 12:123–133. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pyle AM: Translocation and unwinding
mechanisms of RNA and DNA helicases. Ann Rev Biophys. 37:317–336.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jankowsky E: RNA helicases at work:
Binding and rearranging. Trends Biochem Sci. 36:19–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Johnson SJ and Jackson RN: Ski2-like RNA
helicase structures: Common themes and complex assemblies. RNA
Biol. 10:33–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bennett RJ and Keck JL: Structure and
function of RecQ DNA helicases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol.
39:79–97. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fuller-Pace FV: DExD/H box RNA helicases:
Multifunctional proteins with important roles in transcriptional
regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:4206–4215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lusser A and Kadonaga JT: Chromatin
remodeling by ATP-dependent molecular machines. Bioessays.
25:1192–1200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jankowsky E and Fairman ME: RNA
helicases-one fold for many functions. Curr Opin Struct Biol.
17:316–324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jankowsky E and Bowers H: Remodeling of
ribonucleoprotein complexes with DExH/D RNA helicases. Nucleic
Acids Res. 34:4181–4188. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Byrd AK and Raney KD: Superfamily 2
helicases. Front Bioscience. 17:2070–2088. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han X, Zhao L and Li X: HELQ in cancer and
reproduction. Neoplasma. 63:825–835. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cordin O, Banroques J, Tanner NK and
Linder P: The DEAD-box protein family of RNA helicases. Gene.
367:17–37. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heung LJ and Del Poeta M: Unlocking the
DEAD-box: A key to cryptococcal virulence? J Clin Invest.
115:593–595. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de la Cruz J, Kressler D and Linder P:
Unwinding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DEAD-box proteins and
related families. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:192–198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aubourg S, Kreis M and Lecharny A: The
DEAD box RNA helicase family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids
Res. 27:628–636. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tanner NK and Linder P: DExD/H box RNA
helicases: From generic motors to specific dissociation functions.
Mol Cell. 8:251–262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huffman JL and Brennan RG: Prokaryotic
transcription regulators: More than just the helix-turn-helix
motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 12:98–106. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kitano K, Kim SY and Hakoshima T:
Structural basis for DNA strand separation by the unconventional
winged-helix domain of RecQ helicase WRN. Structure. 18:177–187.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li YP, Yang JJ, Xu H, Guo EY and Yu Y:
Structure-function analysis of DNA helicase HELQ: A new diagnostic
marker in ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:4439–4444. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jenkins T, Northall SJ, Ptchelkine D,
Lever R, Cubbon A, Betts H, Taresco V, Cooper CDO, McHugh PJ,
Soultanas P and Bolt EL: The HelQ human DNA repair helicase
utilizes a PWI-like domain for DNA loading through interaction with
RPA, triggering DNA unwinding by the HelQ helicase core. NAR
Cancer. 3:zcaa0432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gaudet P, Livstone MS, Lewis SE and Thomas
PD: Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within
the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 12:449–462. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moldovan GL, Madhavan MV, Mirchandani KD,
McCaffrey RM, Vinciguerra P and D'Andrea AD: DNA polymerase POLN
participates in cross-link repair and homologous recombination. Mol
Cell Biol. 30:1088–1096. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu L and Hickson ID: DNA helicases
required for homologous recombination and repair of damaged
replication forks. Ann Rev Genet. 40:279–306. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Ann Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li X and Heyer WD: Homologous
recombination in DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance. Cell Res.
18:99–113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Roy S: Maintenance of genome stability in
plants: Repairing DNA double strand breaks and chromatin structure
stability. Front Plant Sci. 5:4872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Martin LP, Hamilton TC and Schilder RJ:
Platinum resistance: The role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:1291–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kamp JA, Lemmens B, Romeijn RJ, Changoer
SC, van Schendel R and Tijsterman M: Helicase Q promotes
homology-driven DNA double-strand break repair and prevents tandem
duplications. Nat Commun. 12:71262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hoeijmakers JH: Genome maintenance
mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature. 411:366–374. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Scully R, Panday A, Elango R and Willis
NA: DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic
mammalian cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:698–714. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gartner A and Engebrecht J: DNA repair,
recombination, and damage signaling. Genetics. 220:iyab1782022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ward JD, Muzzini DM, Petalcorin MI,
Martinez-Perez E, Martin JS, Plevani P, Cassata G, Marini F and
Boulton SJ: Overlapping mechanisms promote postsynaptic RAD-51
filament disassembly during meiotic double-strand break repair. Mol
Cell. 37:259–272. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
San Filippo J, Sung P and Klein H:
Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Ann Rev Biochem.
77:229–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hustedt N, Saito Y, Zimmermann M,
Alvarez-Quilon A, Setiaputra D, Adam S, McEwan A, Yuan JY, Olivieri
M, Zhao Y, et al: Control of homologous recombination by the
HROB-MCM8-MCM9 pathway. Genes Dev. 33:1397–1415. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Niedernhofer LJ, Daniels JS, Rouzer CA,
Greene RE and Marnett LJ: Malondialdehyde, a product of lipid
peroxidation, is mutagenic in human cells. J Biol Chem.
278:31426–31433. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McHugh PJ, Spanswick VJ and Hartley JA:
Repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks: Molecular mechanisms and
clinical relevance. Lancet Oncol. 2:483–490. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Adelman CA and Boulton SJ: Metabolism of
postsynaptic recombination intermediates. FEBS Lett. 584:3709–3716.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Luebben SW, Kawabata T, Akre MK, Lee WL,
Johnson CS, O'Sullivan MG and Shima N: Helq acts in parallel to
Fancc to suppress replication-associated genome instability.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:10283–10297. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Garcia-Higuera I, Taniguchi T, Ganesan S,
Meyn MS, Timmers C, Hejna J, Grompe M and D'Andrea AD: Interaction
of the Fanconi anemia proteins and BRCA1 in a common pathway. Mol
Cell. 7:249–262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Northall SJ, Buckley R, Jones N, Penedo
JC, Soultanas P and Bolt EL: DNA binding and unwinding by Hel308
helicase requires dual functions of a winged helix domain. DNA
Repair. 57:125–132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fujikane R, Shinagawa H and Ishino Y: The
archaeal Hjm helicase has recQ-like functions, and may be involved
in repair of stalled replication fork. Genes Cells. 11:99–110.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Smith J, Tho LM, Xu N and Gillespie DA:
The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 108:73–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Montano R, Thompson R, Chung I, Hou H,
Khan N and Eastman A: Sensitization of human cancer cells to
gemcitabine by the Chk1 inhibitor MK-8776: Cell cycle perturbation
and impact of administration schedule in vitro and in vivo. BMC
Cancer. 13:6042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Krajewska M, Fehrmann RS, Schoonen PM,
Labib S, de Vries EG, Franke L and van Vugt MA: ATR inhibition
preferentially targets homologous recombination-deficient tumor
cells. Oncogene. 34:3474–3481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bagby GC Jr: Genetic basis of Fanconi
anemia. Curr Opin Hematol. 10:68–76. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Seki S, Ohzeki M, Uchida A, Hirano S,
Matsushita N, Kitao H, Oda T, Yamashita T, Kashihara N, Tsubahara
A, et al: A requirement of FancL and FancD2 monoubiquitination in
DNA repair. Genes Cells. 12:299–310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Nepal M, Che R, Ma C, Zhang J and Fei P:
FANCD2 and DNA Damage. Int J Mol Sci. 18:18042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Muzzini DM, Plevani P, Boulton SJ, Cassata
G and Marini F: Caenorhabditis elegans POLQ-1 and HEL-308 function
in two distinct DNA interstrand cross-link repair pathways. DNA
Repair. 7:941–950. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Richardson CD, Kazane KR, Feng SJ, Zelin
E, Bray NL, Schäfer AJ, Floor SN and Corn JE: CRISPR-Cas9 genome
editing in human cells occurs via the Fanconi anemia pathway. Nat
Genet. 50:1132–1139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zellweger R, Dalcher D, Mutreja K, Berti
M, Schmid JA, Herrador R, Vindigni A and Lopes M: Rad51-mediated
replication fork reversal is a global response to genotoxic
treatments in human cells. J Cell Biol. 208:563–579. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bhat KP and Cortez D: RPA and RAD51: Fork
reversal, fork protection, and genome stability. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 25:446–453. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bonilla B, Hengel SR, Grundy MK and
Bernstein KA: RAD51 gene family structure and function. Ann Rev
Genet. 54:25–46. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Somyajit K, Subramanya S and Nagaraju G:
RAD51C: A novel cancer susceptibility gene is linked to Fanconi
anemia and breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:2031–2038. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Suwaki N, Klare K and Tarsounas M: RAD51
paralogs: Roles in DNA damage signalling, recombinational repair
and tumorigenesis. Seminars Cell Dev Biol. 22:898–905. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Somyajit K, Saxena S, Babu S, Mishra A and
Nagaraju G: Mammalian RAD51 paralogs protect nascent DNA at stalled
forks and mediate replication restart. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:9835–9855. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Masson JY, Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, Benson
FE and West SC: Complex formation by the human RAD51C and XRCC3
recombination repair proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:8440–8446. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Rein HL, Bernstein KA and Baldock RA:
RAD51 paralog function in replicative DNA Damage and tolerance.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 71:86–91. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chen R and Wold MS: Replication protein A:
Single-stranded DNA's first responder: Dynamic DNA-interactions
allow replication protein A to direct single-strand DNA
intermediates into different pathways for synthesis or repair.
Bioessays. 36:1156–1161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Oakley GG and Patrick SM: Replication
protein A: Directing traffic at the intersection of replication and
repair. Front Bioscience. 15:883–900. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Marini F, Kim N, Schuffert A and Wood RD:
POLN, a nuclear PolA family DNA polymerase homologous to the DNA
cross-link sensitivity protein Mus308. J Biol Chem.
278:32014–32019. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Murtaza G, Yang L, Khan I, Unar A, Khan M,
Huan Z, Khan R and Shi Q: Identification and functional
investigation of novel heterozygous HELQ mutations in patients with
Sertoli Cell-only Syndrome. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 25:654–659.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang W, Zhao S, Zhuang L, Li W, Qin Y and
Chen ZJ: The screening of HELQ gene in Chinese patients with
premature ovarian failure. Reprod Biomed Online. 31:573–576. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
McKay JD, Truong T, Gaborieau V, Chabrier
A, Chuang SC, Byrnes G, Zaridze D, Shangina O, Szeszenia-Dabrowska
N, Lissowska J, et al: A genome-wide association study of upper
aerodigestive tract cancers conducted within the INHANCE
consortium. PLoS Genet. 7:e10013332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Babron MC, Kazma R, Gaborieau V, McKay J,
Brennan P, Sarasin A and Benhamou S: Genetic variants in DNA repair
pathways and risk of upper aerodigestive tract cancers: Combined
analysis of data from two genome-wide association studies in
European populations. Carcinogenesis. 35:1523–1527. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gao Y, He Y, Xu J, Xu L, Du J, Zhu C, Gu
H, Ma H, Hu Z, Jin G, et al: Genetic variants at 4q21, 4q23 and
12q24 are associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk
in a Chinese population. Hum Genet. 132:649–656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li WQ, Hu N, Hyland PL, Gao Y, Wang ZM, Yu
K, Su H, Wang CY, Wang LM, Chanock SJ, et al: Genetic variants in
DNA repair pathway genes and risk of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma and gastric adenocarcinoma in a Chinese population.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1536–1542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liang C, Marsit CJ, Houseman EA, Butler R,
Nelson HH, McClean MD and Kelsey KT: Gene-environment interactions
of novel variants associated with head and neck cancer. Head Neck.
34:1111–1118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Pelttari LM, Kinnunen L, Kiiski JI, Khan
S, Blomqvist C, Aittomaki K and Nevanlinna H: Screening of HELQ in
breast and ovarian cancer families. Fam Cancer. 15:19–23. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Hamdi Y, Soucy P, Adoue V, Michailidou K,
Canisius S, Lemacon A, Droit A, Andrulis IL, Anton-Culver H, Arndt
V, et al: Association of breast cancer risk with genetic variants
showing differential allelic expression: Identification of a novel
breast cancer susceptibility locus at 4q21. Oncotarget.
7:80140–80163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Homer MV, Charo LM, Natarajan L,
Haunschild C, Chung K, Mao JJ, DeMichele AM and Su HI: Genetic
variants of age at menopause are not related to timing of ovarian
failure in breast cancer survivors. Menopause. 24:663–668. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu DN, Zhou YF, Peng AF, Long XH, Chen
XY, Liu ZL and Xia H: HELQ reverses the malignant phenotype of
osteosarcoma cells via CHK1-RAD51 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
37:1107–1113. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhu F, Yang S, Lei M, He Q, Wu L and Zhang
Y: DNA repair protein HELQ and XAB2 as chemoresponse and prognosis
biomarkers in ascites tumor cells of high-grade serous ovarian
cancer. J Oncol. 2022:75219342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Guo C, Gao YY, Ju QQ, Zhang CX, Gong M and
Li ZL: HELQ and EGR3 expression correlate with IGHV mutation status
and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Transl Med.
19:422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhong NS, Tong WL, Zhang Y, Xiao SN, Liu
JM, Li AA, Yao GL, Lin Q and Liu ZL: HELQ suppresses migration and
proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells by repairing DNA
damage and inducing necrosis. Cell Biol Int. 47:188–200. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y and Tian Y: Expressions of
HELQ and RAD51C in endometrial stromal sarcoma and their clinical
significance. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 40:936–941. 2020.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gimenez N, Martinez-Trillos A, Montraveta
A, Lopez-Guerra M, Rosich L, Nadeu F, Valero JG, Aymerich M,
Magnano L, Rozman M, et al: Mutations in the RAS-BRAF-MAPK-ERK
pathway define a specific subgroup of patients with adverse
clinical features and provide new therapeutic options in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 104:576–586. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Thomas A, Cox J, Wolfe KB, Mingalone CH,
Yaspan HR and McVey M: Division of Labor by the HELQ, BLM, and
FANCM Helicases during Homologous Recombination Repair in
Drosophila melanogaster. Genes (Basel). 13:4742022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Scott DE, Francis-Newton NJ, Marsh ME,
Coyne AG, Fischer G, Moschetti T, Bayly AR, Sharpe TD, Haas KT,
Barber L, et al: A small-molecule inhibitor of the BRCA2-RAD51
interaction modulates RAD51 assembly and potentiates DNA
damage-induced cell death. Cell Chem Biol. 28:835–847.e5. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|