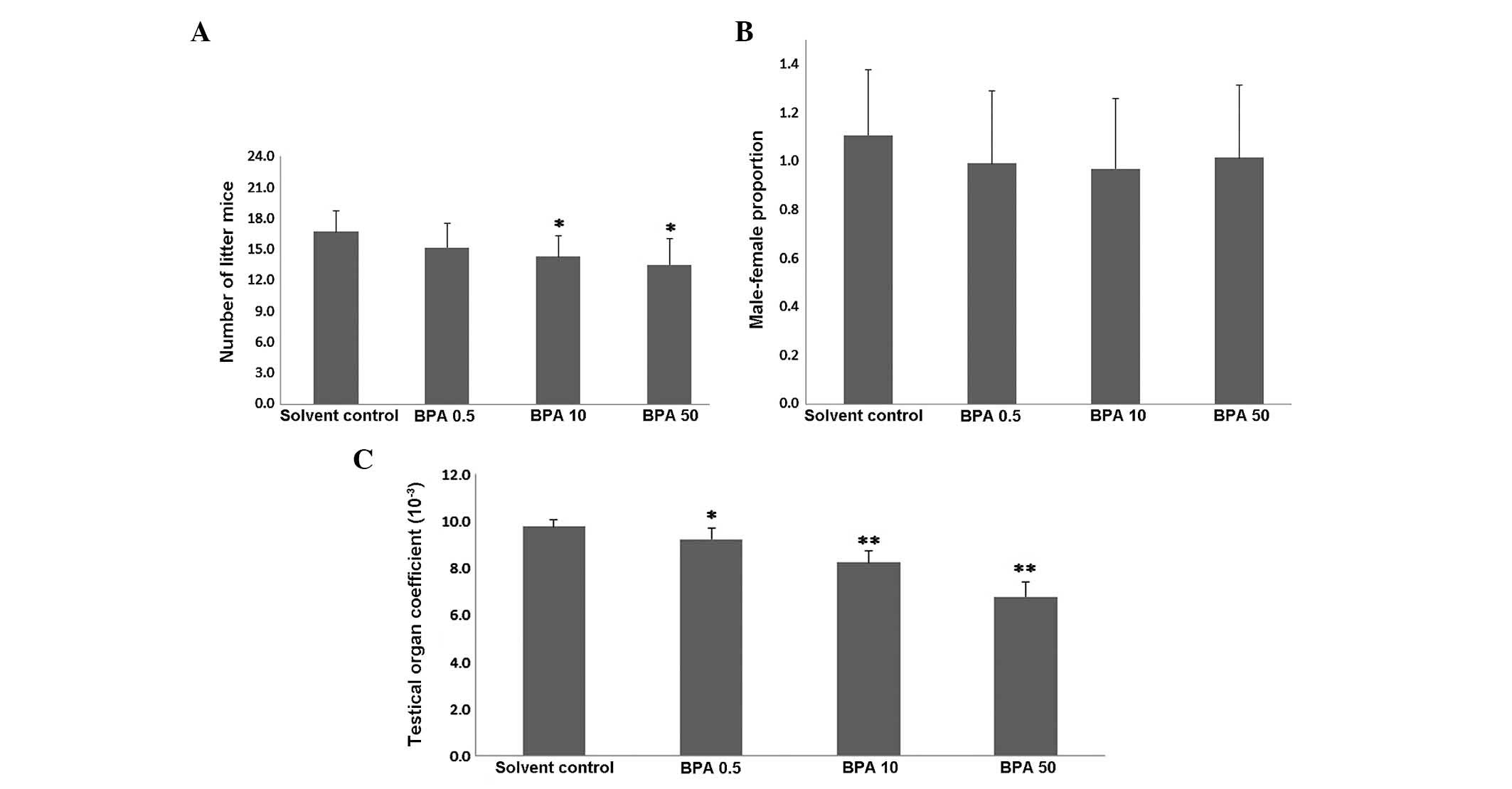
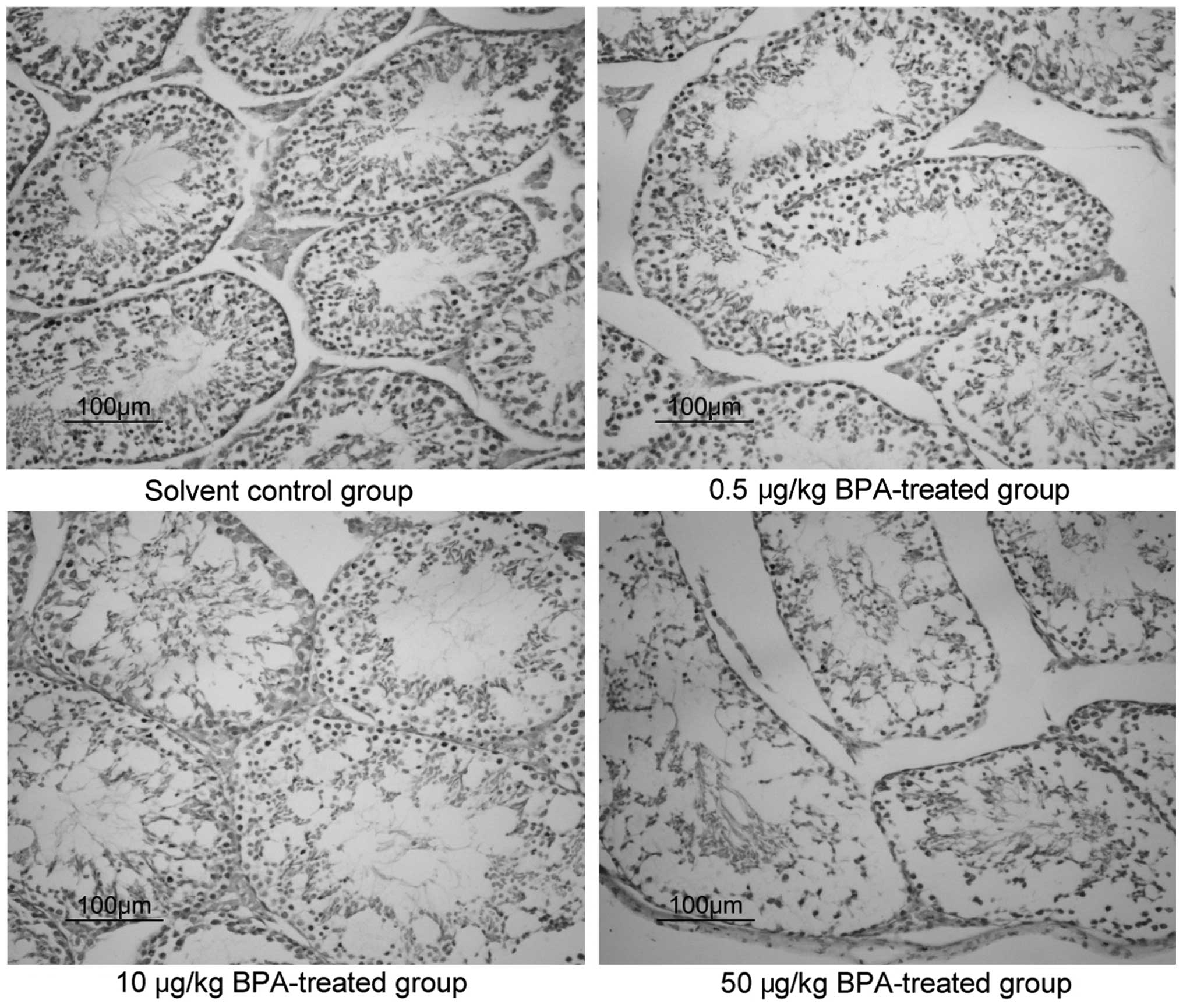
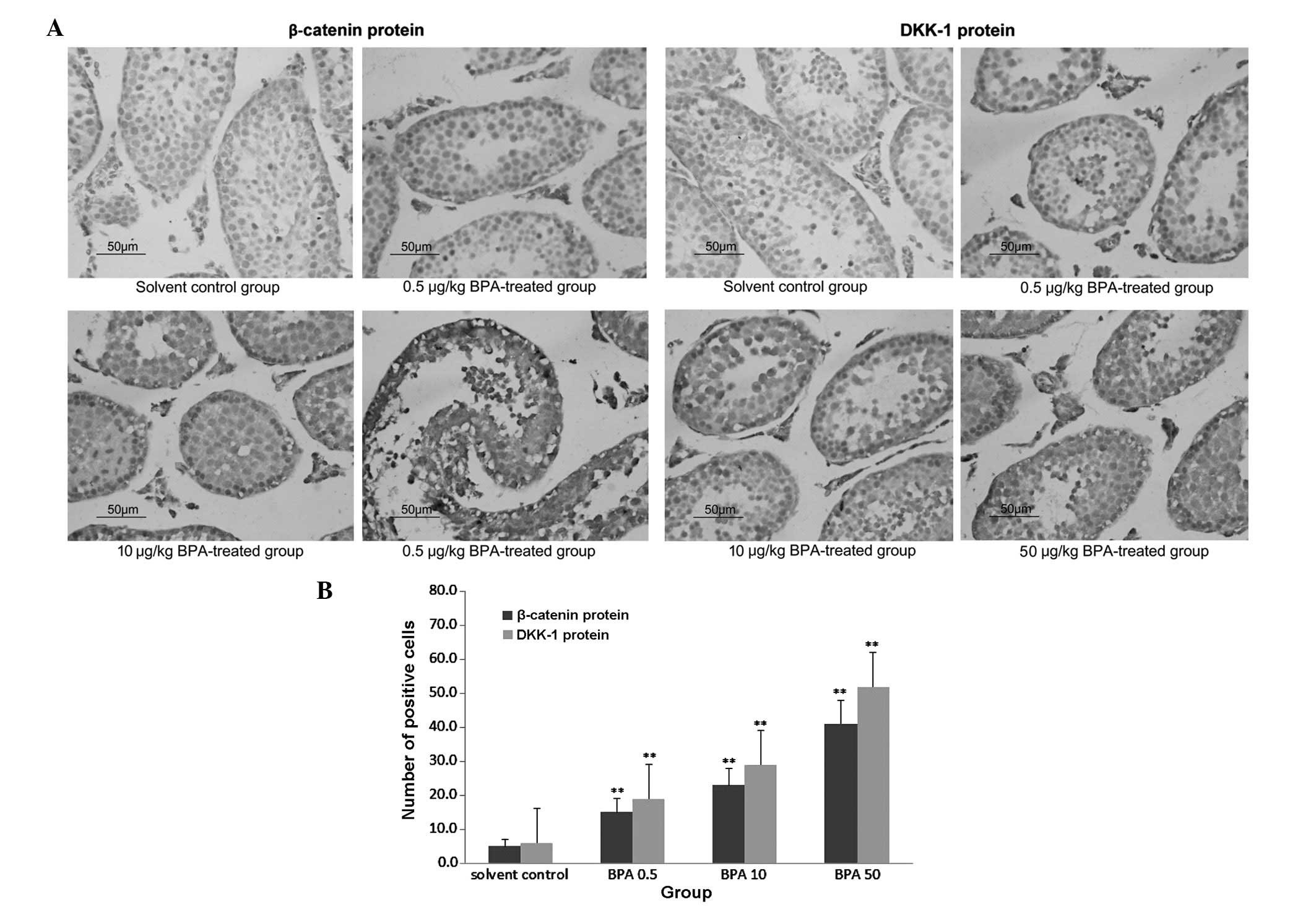
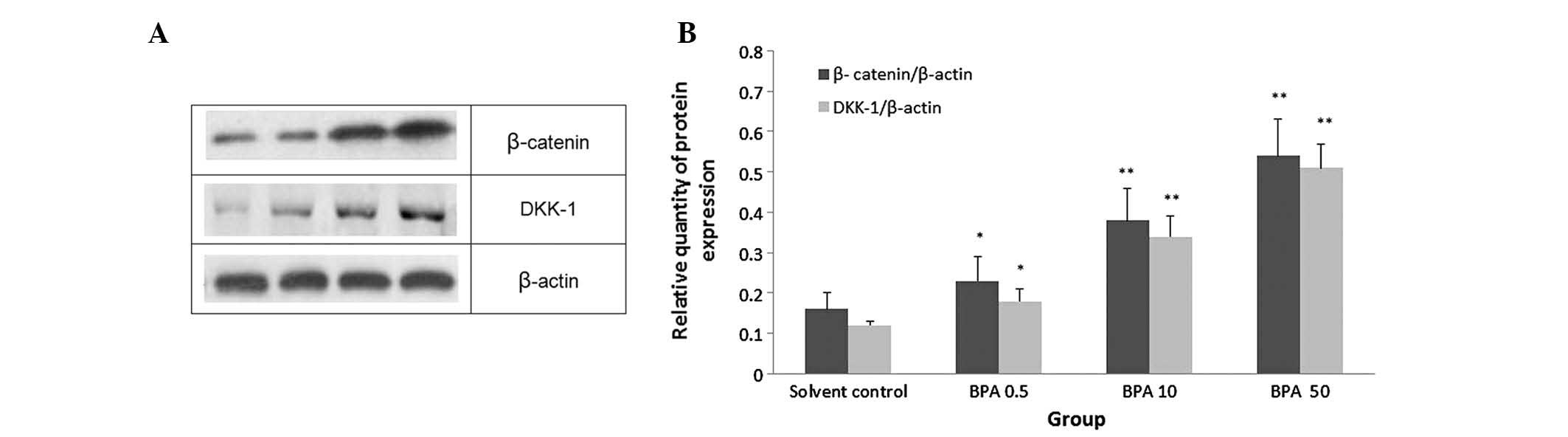
|
1
|
Yamamoto T, Yasuhara A, Shiraishi H and
Nakasugi O: Bisphenol A in hazardous waste landfill leachates.
Chemosphere. 42:415–418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ikezuki Y, Tsutsumi O, Takai Y, Kamei Y
and Taketani Y: Determination of bisphenol A concentrations in
human biological fluids reveals significant early prenatal
exposure. Hum Reprod. 17:2839–2841. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vandenberg LN, Hauser R, Marcus M, Olea N
and Welshons WV: Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod
Toxicol. 24:139–177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Michałowicz J: Bisphenol A - sources,
toxicity and biotransformation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
37:738–758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ouchi K and Watanabe S: Measurement of
bisphenol A in human urine using liquid chromatography with
multi-channel coulometric electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr B
Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 780:365–370. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pupo M, Pisano A, Lappano R, Santolla MF,
De Francesco EM, Abonante S, Rosano C and Maggiolini M: Bisphenol A
induces gene expression changes and proliferative effects through
GPER in breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Environ Health Perspect. 120:1177–1182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mattsson A, Mura E, Brunström B, Panzica G
and Halldin K: Selective activation of estrogen receptor alpha in
Japanese quail embryos affects reproductive organ differentiation
but not the male sexual behavior or the parvocellular vasotocin
system. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 159:150–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calafat AM, Ye X, Wong LY, Reidy JA and
Needham LL: Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and
4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect.
116:39–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagel SC, vom Saal FS, Thayer KA, Dhar MG,
Boechler M and Welshons WV: Relative binding affinity-serum
modified access (RBA-SMA) assay predicts the relative in vivo
bioactivity of the xenoestrogens bisphenol A and octylphenol.
Environ Health Perspect. 105:70–76. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khan SA, Ball RB and Hendry WJ III:
Effects of neonatal administration of diethylstilbestrol in male
hamsters: Disruption of reproductive function in adults after
apparently normal pubertal development. Biol Reprod. 58:137–142.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nagao T, Saito Y, Usumi K, Nakagomi M,
Yoshimura S and Ono H: Disruption of the reproductive system and
reproductive performance by administration of nonylphenol to
newborn rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 19:284–296. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McKinnell C, Atanassova N, Williams K,
Fisher JS, Walker M, Turner KJ, Saunders TK and Sharpe RM:
Suppression of androgen action and the induction of gross
abnormalities of the reproductive tract in male rats treated
neonatally with diethylstilbestrol. J Androl. 22:323–338.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Atanassova N, McKinnell C, Walker M,
Turner KJ, Fisher JS, Morley M, Millar MR, Groome NP and Sharpe RM:
Permanent effects of neonatal estrogen exposure in rats on
reproductive hormone levels, Sertoli cell number, and the
efficiency of spermatogenesis in adulthood. Endocrinology.
140:5364–5373. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kabuto H, Amakawa M and Shishibori T:
Exposure to bisphenol A during embryonic/fetal life and infancy
increases oxidative injury and causes underdevelopment of the brain
and testis in mice. Life Sci. 74:2931–2940. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taylor JA, Richter CA, Ruhlen RL and vom
Saal FS: Estrogenic environmental chemicals and drugs: Mechanisms
for effects on the developing male urogenital system. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 127:83–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Klapholz-Brown Z, Walmsley GG, Nusse YM,
Nusse R and Brown PO: Transcriptional program induced by Wnt
protein in human fibroblasts suggests mechanisms for cell
cooperativity in defining tissue microenvironments. PLoS One.
2:e9452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu T and Li C: Convergence between
Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol Cancer. 9:2362010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rexhepaj E, Agnarsdóttir M, Bergman J,
Edqvist PH, Bergqvist M, Uhlén M, Gallagher WM, Lundberg E and
Ponten F: A texture based pattern recognition approach to
distinguish melanoma from non-melanoma cells in histopathological
tissue microarray sections. PLoS One. 8:e620702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barrett ES and Sobolewski M: Polycystic
ovary syndrome: Do endocrine-disrupting chemicals play a role?
Semin Reprod Med. 32:166–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rochefort H: Bisphenol A and
hormone-dependent cancers: Potential risk and mechanism. Med Sci.
29:539–544. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Lee HR, Jeung EB, Cho MH, Kim TH, Leung PC
and Choi KC: Molecular mechanism(s) of endocrine-disrupting
chemicals and their potent oestrogenicity in diverse cells and
tissues that express oestrogen receptors. J Cell Mol Med. 17:1–11.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bonefeld-Jørgensen EC, Ghisari M, Wielsøe
M, Bjerregaard-Olesen C, Kjeldsen LS and Long M: Biomonitoring and
hormone-disrupting effect biomarkers of persistent organic
pollutants in vitro and ex vivo. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
115:118–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sultan C, Balaguer P, Terouanne B, Georget
V, Paris F, Jeandel C, Lumbroso S and Nicolas J: Environmental
xenoestrogens, anti-androgens and disorders of male sexual
differentiation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 178:99–105. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nagel SC, vom Saal FS, Thayer KA, Dhar MG,
Boechler M and Welshons WV: Relative binding affinity-serum
modified access (RBA-SMA) assay predicts the relative in vivo
bioactivity of the xenoestrogens bisphenol A and octylphenol.
Environ Health Perspect. 105:70–76. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
vom Saal FS, Cooke PS, Buchanan DL,
Palanza P, Thayer KA, Nagel SC, Parmigiani S and Welshons WV: A
physiologically based approach to the study of bisphenol A and
other estrogenic chemicals on the size of reproductive organs,
daily sperm production, and behavior. Toxicol Ind Health.
14:239–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gupta C: Reproductive malformation of the
male offspring following maternal exposure to estrogenic chemicals.
Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 224:61–68. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Toyama Y, Suzuki-Toyota F, Maekawa M, Ito
C and Toshimori K: Adverse effects of bisphenol A to spermiogenesis
in mice and rats. Arch Histol Cytol. 67:373–381. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Minamiyama Y, Ichikawa H, Takemura S,
Kusunoki H, Naito Y and Yoshikawa T: Generation of reactive oxygen
species in sperms of rats as an earlier marker for evaluating the
toxicity of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Free Radic Res.
44:1398–1406. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan PP, Pan XY, Wang HH, Li ZX, Wang XN,
Lai Q, Song WJ, Zhao HY and Dou ZH: Effects of bisphenol-A on
blastocyst development and implantation. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue
Yuan Xue Bao. 36:351–356. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu XL, Chen XY, Wang ZC, Shen T and Zhao
H: Effects of exposure to bisphenol A during pregnancy and
lactation on the testicular morphology and caspase-3 protein
expression of ICR pups. Biomed Rep. 1:420–424. 2013.
|
|
31
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Q, Cai J, Cai XH and Chen L: miR-346
regulates osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS
One. 8:e722662013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fujimaki S, Hidaka R, Asashima M, Takemasa
T and Kuwabara T: Wnt protein-mediated satellite cell conversion in
adult and aged mice following voluntary wheel running. J Biol Chem.
289:7399–7412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Li M, Zuo K, Li D, Ye M, Ding L,
Cai H, Fu D, Fan Y and Lv Z: Upregulated miR-155 in papillary
thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor growth by targeting APC and
activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:E1305–E1313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ye S, Wang J, Yang S, Xu W, Xie M, Han K,
Zhang B and Wu Z: Specific inhibitory protein Dkk-1 blocking
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway improve protective effect on the
extracellular matrix. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
31:657–662. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kong XB and Zhang C: Dickkopf (Dkk) 1
promotes the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells toward
neuroectoderm. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 45:185–193. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Esteve P, Sandonìs A, Ibañez C, Shimono A,
Guerrero I and Bovolenta P: Secreted frizzled-related proteins are
required for Wnt/β-catenin signalling activation in the vertebrate
optic cup. Development. 138:4179–4184. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Knobloch J, Schmitz I, Götz K,
Schulze-Osthoff K and Rüther U: Thalidomide induces limb anomalies
by PTEN stabilization, Akt suppression, and stimulation of
caspase-dependent cell death. Mol Cell Biol. 28:529–538. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ning B, Wang P, Pei X, Kang Y, Song J,
Wang D, Zhang W and Ma R: Dual function of β-catenin in articular
cartilage growth and degeneration at different stages of postnatal
cartilage development. Int Orthop. 36:655–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|