|
1
|
World Health Organization: http://www.who.int/media-centre/factsheets/fs117/en/
Accessed July 8, 2015.
|
|
2
|
Morens DM: Antibody-dependent enhancement
of infection and the pathogenesis of viral disease. Clin Infect
Dis. 19:500–512. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization: Dengue
Hemorrhagic Fever: Diagnosis, Treatment and Control. 2nd edition.
World Health Organization; Geneva: 1997
|
|
4
|
Sakudo A, Onodera T, Shintani H and Ikuta
K: Dengue virus presence and surveillance in Okinawa (Review). Exp
Ther Med. 3:15–17. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hotta S: Experimental studies on dengue.
I. Isolation, identification and modification of the virus. J
Infect Dis. 90:1–9. 1952. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare:
http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/kekkaku-kansenshou19/dengue_fever.html
Accessed July 8, 2015.
|
|
7
|
Roth WK, Weber M and Seifried E:
Feasibility and efficacy of routine PCR screening of blood
donations for hepatitis C virus, hepatitis B virus, and HIV-1 in a
blood-bank setting. Lancet. 353:359–363. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamelin C and Lussier G: Concentration of
human cytomegalovirus from large volumes of tissue culture fluids.
J Gen Virol. 42:193–197. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Novotný J, Svobodová J, Ransnäs LA and
Kubistová K: A method for the preparation of purified antigens of
coxsackievirus B3 from a large volume of cell culture supernatant.
Acta Virol. 36:483–487. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Safarikova M and Safarik I: The
application of magnetic techniques in biosciences. Magn Elect Sep.
10:223–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK and
Dobson J: Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J
Phys D Appl Phys. 36:R167–R181. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Saraswati TE, Ogino A and Nagatsu M:
Plasma-activated immobilization of biomolecules onto
graphite-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. Carbon. 50:1253–1261.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Poplawska M, Bystrzejewski M, Grudziński
IP, Cywińska MA, Ostapko J and Cieszanowski A: Immobilization of
gamma globulins and polyclonal antibodies of class IgG onto
carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles functionalized with various
surface linkers. Carbon. 74:180–194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Saraswati TE, Matsuda T, Ogino A and
Nagatsu M: Surface modification of graphite encapsulated iron
nanoparticles by plasma processing. Diam Relat Mater. 20:359–363.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Saraswati TE, Tsumura S and Nagatsu M:
High-efficiency plasma surface modification of
graphite-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles using a pulsed
particle explosion technique. Jpn J Appl Phys. 53:0102052014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sakudo A, Chou H and Nagatsu M:
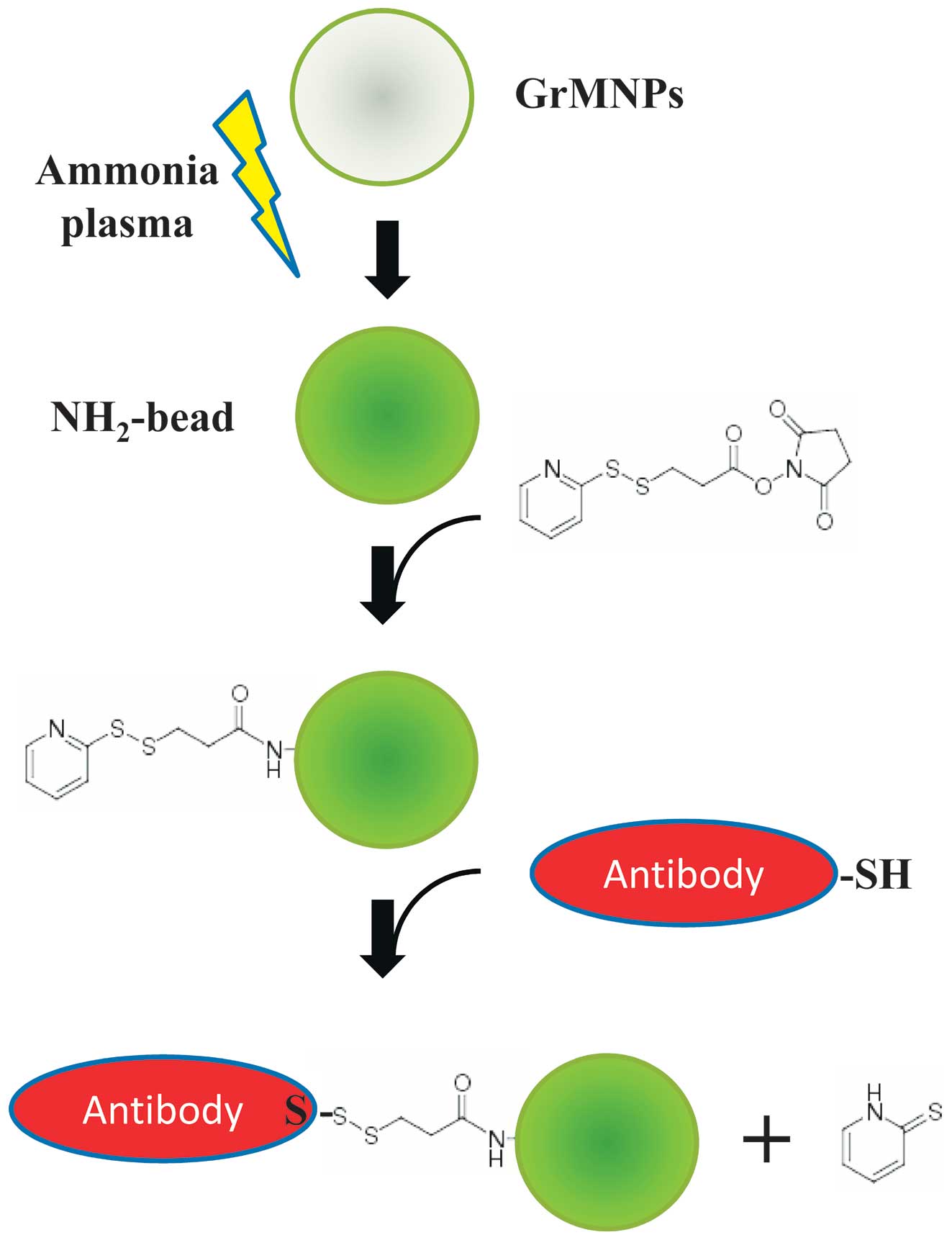
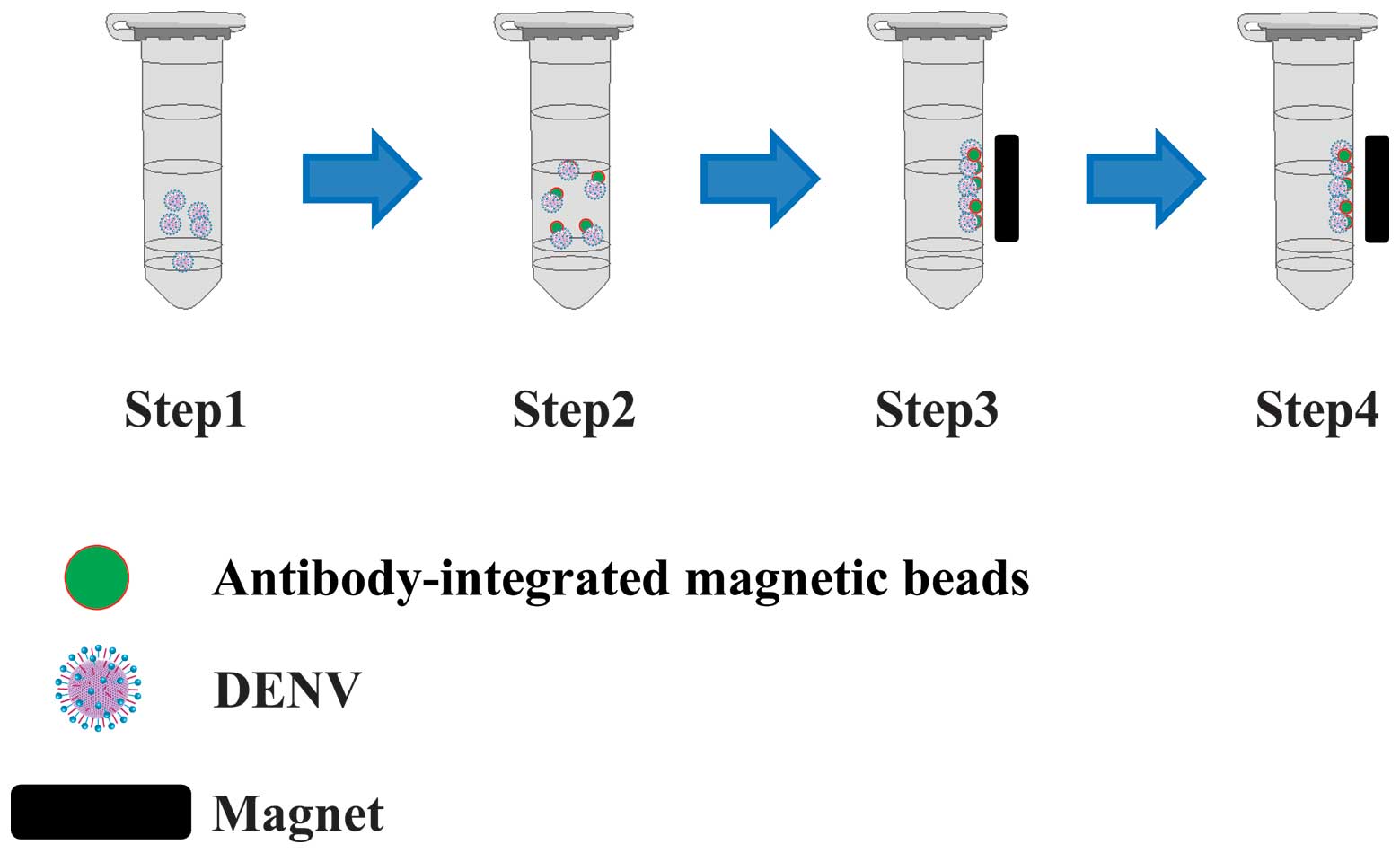
Antibody-integrated and functionalized graphite-encapsulated
magnetic beads, produced using ammonia gas plasma technology, for
capturing Salmonella. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:1012–1016. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sakudo A, Chou H, Ikuta K and Nagatsu M:
Integration of antibody by surface functionalization of
graphite-encapsulated magnetic beads using ammonia gas plasma
technology for capturing influenza A virus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
25:1876–1879. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagatsu M, Yoshida T, Mesko M, et al:
Narrow multi-walled carbon nanotubes produced by chemical vapor
deposition using graphene layer encapsulated catalytic metal
particles. Carbon. 44:3336–3341. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Saito Y, Yoshikawa T, Okuda M, et al: Iron
particles nesting in carbon cages grown by arc discharge. Chem Phys
Lett. 212:379–383. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Setthapramote C, Sasaki T, Puiprom O,
Limkittikul K, Pita ksajja kul P, Pipattanaboon C, Sasayama M,
Leuangwutiwong P, Phumratanaprapin W, Chamnachanan S, et al: Human
monoclonal antibodies to neutralize all dengue virus serotypes
using lymphocytes from patients at acute phase of the secondary
infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:867–872. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masrinoul P, Diata MO, Pambudi S,
Limkittikul K, Ikuta K and Kurosu T: Highly conserved region
141–168 of the NS1 protein is a new common epitope region of dengue
virus. Jpn J Infect Dis. 64:109–115. 2011.
|
|
22
|
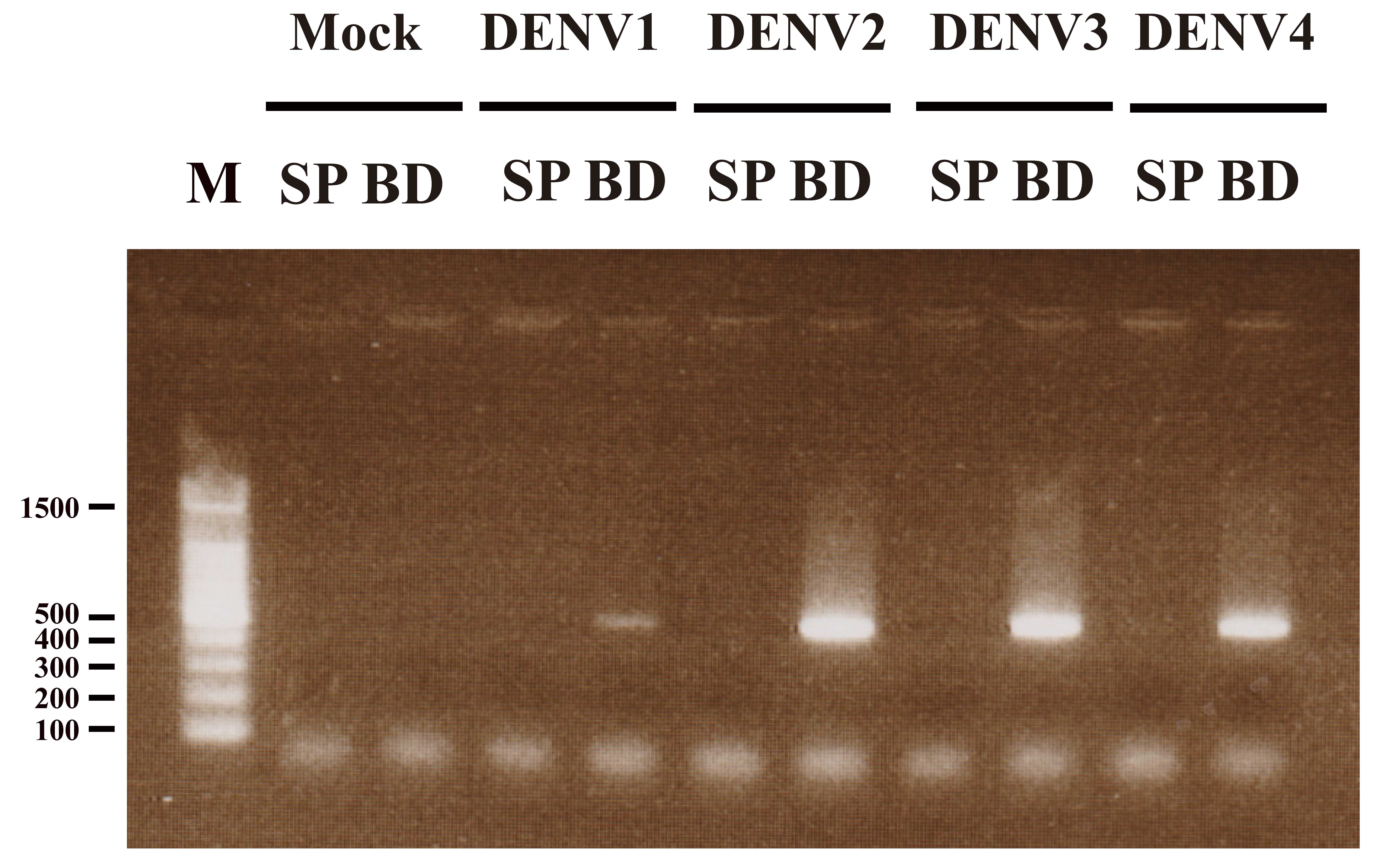
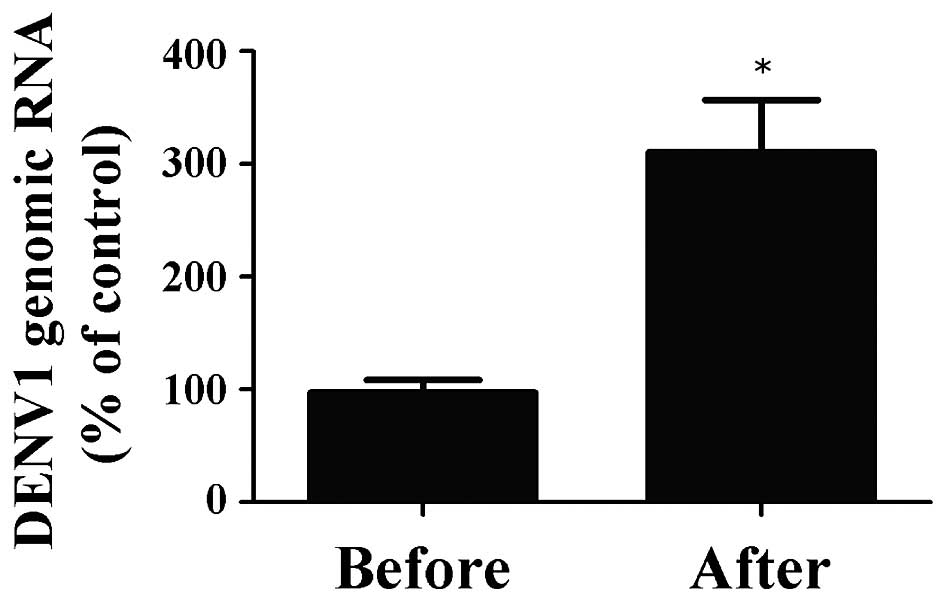
Paudel D, Jarman R, Limkittikul K,
Klungthong C, Chamnanchanunt S, Nisalak A, Gibbons R and
Chokejindachai W: Comparison of real-time SYBR green dengue assay
with real-time taqman RT-PCR dengue assay and the conventional
nested PCR for diagnosis of primary and secondary dengue infection.
N Am J Med Sci. 3:478–485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen X and Wang J: A sequential injection
fluorometric procedure for rapid determination of total protein in
human serum. Talanta. 69:681–685. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Plapp BV, Moore S and Stein WH: Activity
of bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease A with modified amino
groups. J Biol Chem. 246:939–945. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Safaríková M and Safarík I: Immunomagnetic
separation of Escherichia coli O26, O111 and O157 from vegetables.
Lett Appl Microbiol. 33:36–39. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Safarík I, Safaríková M and Forsythe SJ:
The application of magnetic separations in applied microbiology. J
Appl Bacteriol. 78:575–585. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kobayashi S, Natori K, Takeda N and Sakae
K: Immunomagnetic capture rt-PCR for detection of norovirus from
foods implicated in a foodborne outbreak. Microbiol Immunol.
48:201–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clavet CR, Margolin AB and Regan PM:
Herpes simplex virus type-2 specific glycoprotein G-2
immunomagnetically captured from HEp-2 infected tissue culture
extracts. J Virol Methods. 119:121–128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jothikumar N, Cliver DO and Mariam TW:
Immunomagnetic capture PCR for rapid concentration and detection of
hepatitis A virus from environmental samples. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 64:504–508. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Satoh K, Iwata A, Murata M, Hikata M,
Hayakawa T and Yamaguchi T: Virus concentration using
polyethyleneimine-conjugated magnetic beads for improving the
sensitivity of nucleic acid amplification tests. J Virol Methods.
114:11–19. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Uchida E, Sato K, Iwata A, Ishii-Watabe A,
Mizuguchi H, Hikata M, Murata M, Yamaguchi T and Hayakawa T: An
improved method for detection of replication-competent retrovirus
in retrovirus vector products. Biologicals. 32:139–146. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uchida E, Kogi M, Oshizawa T, Furuta B,
Satoh K, Iwata A, Murata M, Hikata M and Yamaguchi T: Optimization
of the virus concentration method using
polyethyleneimine-conjugated magnetic beads and its application to
the detection of human hepatitis A, B and C viruses. J Virol
Methods. 143:95–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iwata A, Satoh K, Murata M, Hikata M,
Hayakawa T and Yamaguchi T: Virus concentration using sulfonated
magnetic beads to improve sensitivity in nucleic acid amplification
tests. Biol Pharm Bull. 26:1065–1069. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hatano B, Kojima A, Sata T and Katano H:
Virus detection using Viro-Adembeads, a rapid capture system for
viruses and plaque assay in intentionally virus-contaminated
beverages. Jpn J Infect Dis. 63:52–54. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sakudo A and Ikuta K: A technique for
capturing broad subtypes and circulating recombinant forms of HIV-1
based on anionic polymer-coated magnetic beads. Int J Mol Med.
30:437–442. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sakudo A and Onodera T: Virus capture
using anionic polymer-coated magnetic beads. Int J Mol Med. 30:3–7.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sakudo A, Masrinoul P, Tanaka Y and Ikuta
K: Capture of dengue virus type 3 using anionic polymer-coated
magnetic beads. Int J Mol Med. 28:625–628. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sakudo A, Tanaka Y and Ikuta K: Capture of
infectious borna disease virus using anionic polymer-coated
magnetic beads. Neurosci Lett. 494:237–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sakudo A, Baba K, Tsukamoto M and Ikuta K:
Use of anionic polymer, poly(methyl vinyl ether-maleic
anhydride)-coated beads for capture of respiratory syncytial virus.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:4488–4491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sakudo A, Baba K, Tsukamoto M, Sugimoto A,
Okada T, Kobayashi T, Kawashita N, Takagi T and Ikuta K: Anionic
polymer, poly(methyl vinyl ether-maleic anhydride)-coated
beads-based capture of human influenza A and B virus. Bioorg Med
Chem. 17:752–757. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sakudo A and Ikuta K: Efficient capture of
infectious H5 avian influenza virus utilizing magnetic beads coated
with anionic polymer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:85–88. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sakudo A, Baba K and Ikuta K: Capturing
and concentrating adenovirus using magnetic anionic nanobeads. Int
J Nanomedicine. 11:1847–1857. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|