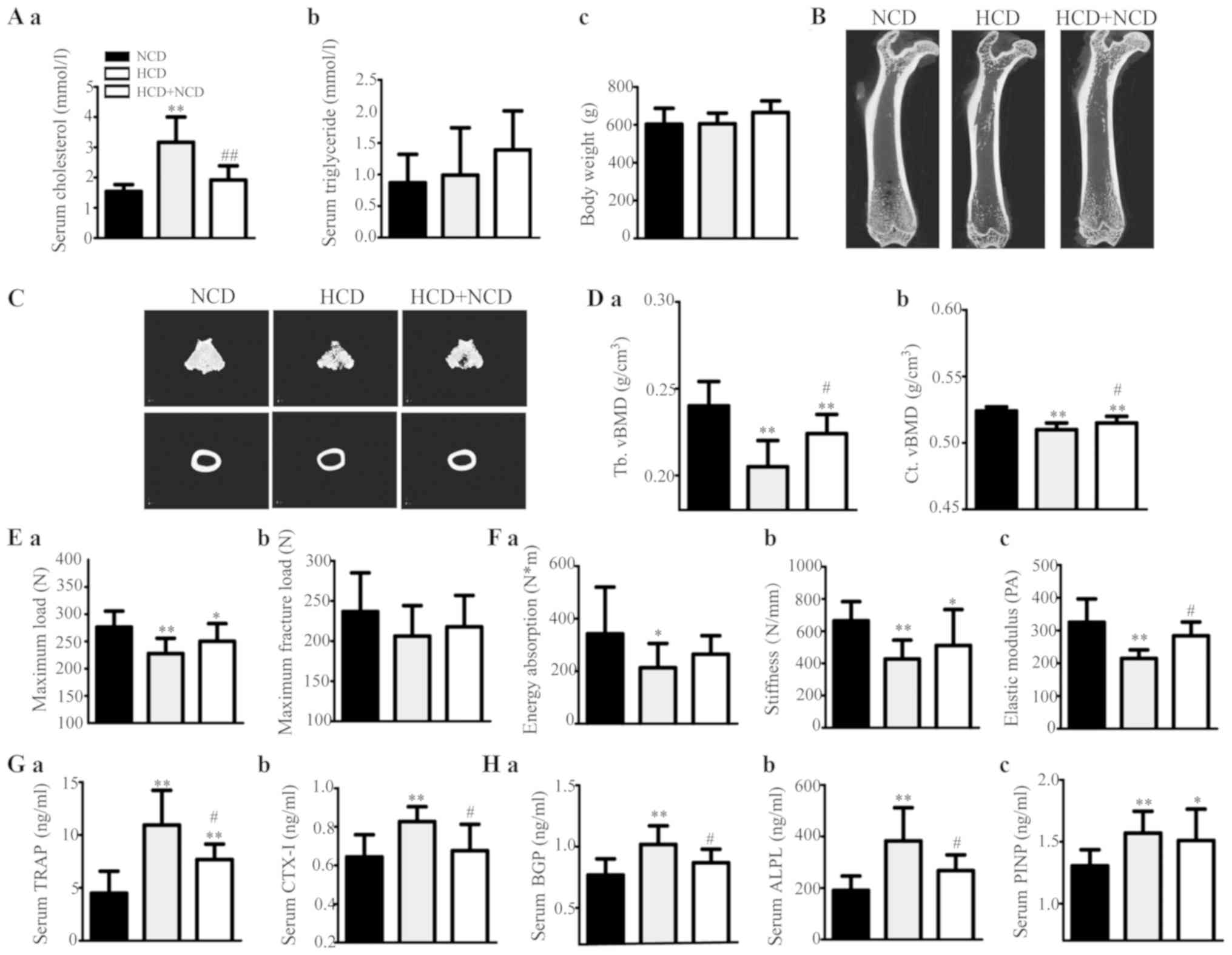
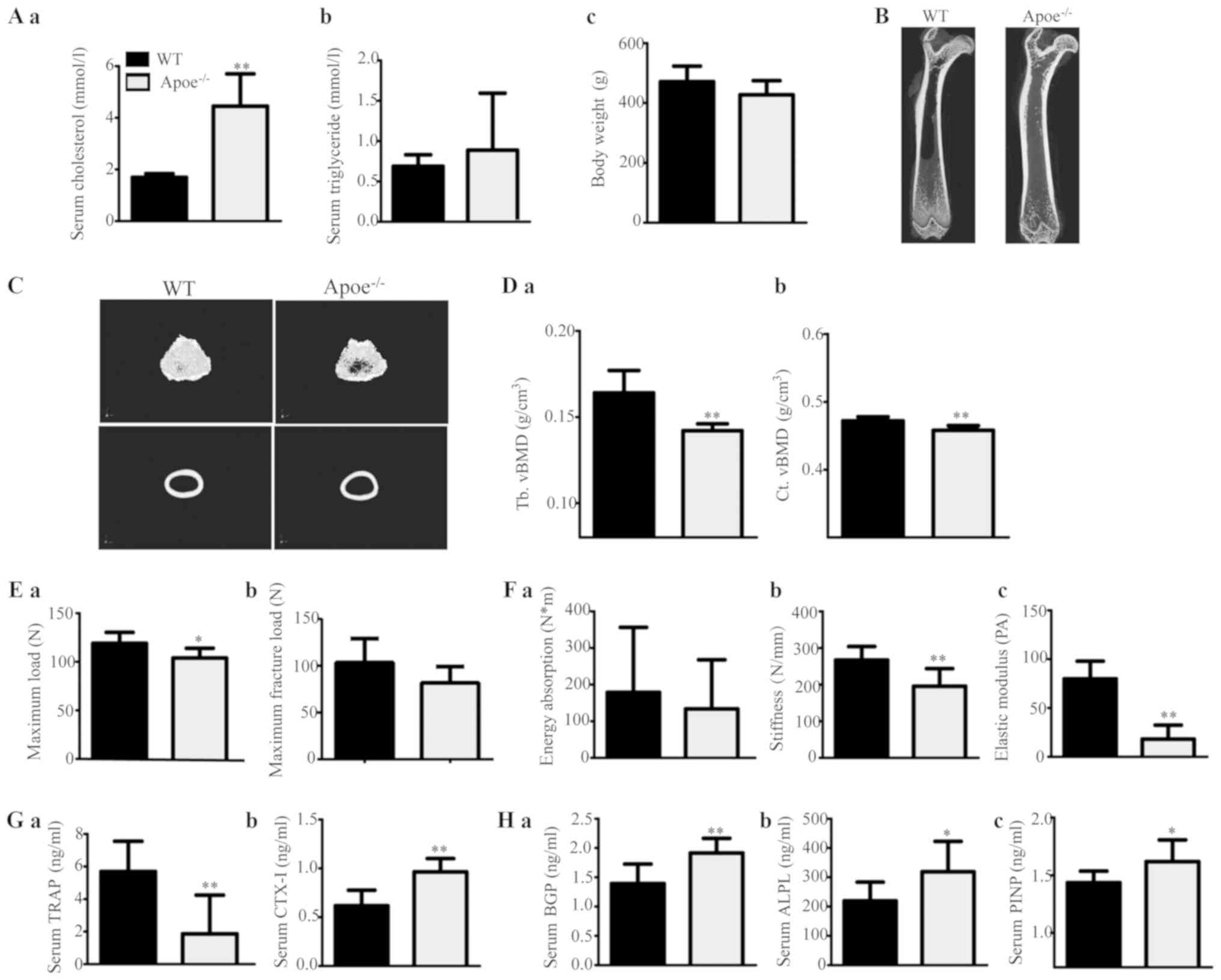
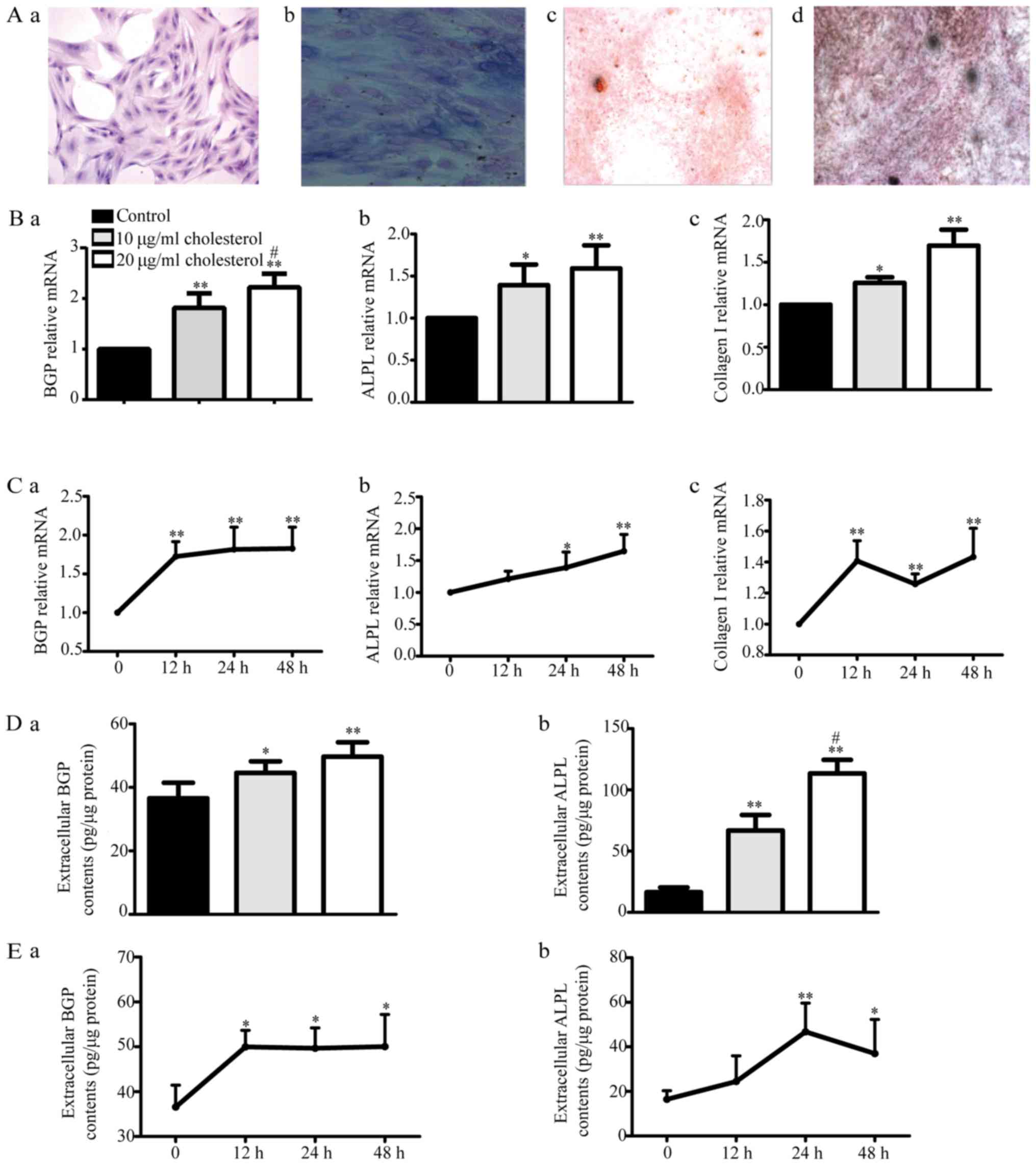
|
1
|
Osteoporosis, . Review of the evidence for
prevention, diagnosis and treatment and cost-effectiveness
analysis. Introduction. Osteoporos Int. 8 (Suppl 4):S7–S80. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Looker AC, Orwoll ES, Johnston CC Jr,
Lindsay RL, Wahner HW, Dunn WL, Calvo MS, Harris TB and Heyse SP:
Prevalence of low femoral bone density in older U.S. adults from
NHANES III. J Bone Miner Res. 12:1761–1768. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cummings SR and Melton LJ: Epidemiology
and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 359:1761–1767.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Trivedi DP and Khaw KT: Bone mineral
density at the hip predicts mortality in elderly men. Osteoporos
Int. 12:259–265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu LY, Yang TC, Kuo SW, Hsiao CF, Hung YJ,
Hsieh CH, Tseng HC, Hsieh AT, Chen TW, Chang JB, et al: Correlation
between bone mineral density and plasma lipids in Taiwan. Endocr
Res. 29:317–325. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Y, Gao L, Xie X and Tan SC:
Epidemiology of dyslipidemia in Chinese adults: Meta-analysis of
prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control. Popul Health Metr.
12:282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng G: Relevant Guidelines for the
management of abnormal lipids in 2016 and updated interpretation of
expert consensus. World Clinical Drugs. 7:441–444. 2017.
|
|
8
|
Turner CH and Burr DB: Basic biomechanical
measurements of bone: A tutorial. Bone. 14:595–608. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li XF, Zhao JM, Su W, et al: Primary
culture and identification of rat osteoblasts. J Clin Rehabil
Tissue Eng Res. 15:990–994. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Mooradian AD: Dyslipidemia in type 2
diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 5:150–159.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koshiyama H, Wada Y and Nakamura Y:
Hypercholesterolemia as a possible risk factor for osteopenia in
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 161:1678. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang N, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhang B, Wang
F, Wang C, Zhao M, Yu C, Gao L, Zhao J and Guan Q: The relationship
between endogenous testosterone and lipid profile in middle-aged
and elderly Chinese men. Eur J Endocrinol. 170:487–494. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wongdee K and Charoenphandhu N:
Osteoporosis in diabetes mellitus: Possible cellular and molecular
mechanisms. World J Diabetes. 2:41–48. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gaffney CD, Pagano MJ, Kuker AP, Stember
DS and Stahl PJ: Osteoporosis and low bone mineral density in men
with testosterone deficiency syndrome. Sex Med Rev. 3:298–315.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saad F, Röhrig G, von Haehling S and
Traish A: Testosterone deficiency and testosterone treatment in
older men. Gerontology. 63:144–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsourdi E, Rijntjes E, Köhrle J, Hofbauer
LC and Rauner M: Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism in male mice
and their effects on bone mass, bone turnover, and the Wnt
inhibitors sclerostin and Dickkopf-1. Endocrinology. 156:3517–3527.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reid IR: Relationships between fat and
bone. Osteoporos Int. 19:595–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murdolo G, Bartolini D, Tortoioli C,
Piroddi M, Iuliano L and Galli F: Lipokines and oxysterols: Novel
adipose-derived lipid hormones linking adipose dysfunction and
insulin resistance. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:811–820. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Verma S, Rajaratnam JH, Denton J, Hoyland
JA and Byers RJ: Adipocytic proportion of bone marrow is inversely
related to bone formation in osteoporosis. J Clin Pathol.
55:693–698. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Edwards CJ, Hart DJ and Spector TD: Oral
statins and increased bone-mineral density in postmenopausal women.
Lancet. 355:2218–2219. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meier CR, Schlienger RG, Kraenzlin ME,
Schlegel B and Jick H: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of
fractures. JAMA. 283:3205–3210. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Majima T, Shimatsu A, Komatsu Y, Satoh N,
Fukao A, Ninomiya K, Matsumura T and Nakao K: Increased bone
turnover in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Endocr J.
55:143–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Halade GV, Rahman MM, Williams PJ and
Fernandes G: High fat diet-induced animal model of age-associated
obesity and osteoporosis. J Nutr Biochem. 21:1162–1169. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tatsumi S, Ito M, Asaba Y, Tsutsumi K and
Ikeda K: Life-long caloric restriction reveals biphasic and
dimorphic effects on bone metabolism in rodents. Endocrinology.
149:634–641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen JR, Lazarenko OP, Wu X, Tong Y,
Blackburn ML, Shankar K, Badger TM and Ronis MJ: Obesity reduces
bone density associated with activation of PPARγ and suppression of
Wnt/β-catenin in rapidly growing male rats. PLoS One. 5:e137042010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
You L, Sheng ZY, Tang CL, Chen L, Pan L
and Chen JY: High cholesterol diet increases osteoporosis risk via
inhibiting bone formation in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
32:1498–1504. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan L, Prentice A, Zhou B, Zhang H, Wang
X, Stirling DM, Laidlaw A, Han Y and Laskey A: Age- and
gender-related differences in bone mineral status and biochemical
markers of bone metabolism in Northern Chinese men and women. Bone.
30:412–415. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khosla S, Melton LJ III and Riggs BL:
Osteoporosis: Gender differences and similarities. Lupus.
8:393–396. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ebbesen EN, Thomsen JS, Beck-Nielsen H,
Nepper-Rasmussen HJ and Mosekilde L: Age- and gender-related
differences in vertebral bone mass, density, and strength. J Bone
Miner Res. 14:1394–1403. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tintut Y, Morony S and Demer LL:
Hyperlipidemia promotes osteoclastic potential of bone marrow cells
ex vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:e6–e10. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei S, Zhang Y, Su L, He K, Wang Q, Zhang
Y, Yang D, Yang Y and Ma S: Apolipoprotein E-deficient rats develop
atherosclerotic plaques in partially ligated carotid arteries.
Atherosclerosis. 243:589–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ekuni D, Yoneda T, Endo Y, Kasuyama K,
Irie K, Mizutani S, Azuma T, Tomofuji T and Morita M: Occlusal
disharmony accelerates the initiation of atherosclerosis in apoE
knockout rats. Lipids Health Dis. 13:1442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luegmayr E, Glantschnig H, Wesolowski GA,
Gentile MA, Fisher JE, Rodan GA and Reszka AA: Osteoclast
formation, survival and morphology are highly dependent on
exogenous cholesterol/lipoproteins. Cell Death Differ. 11 (Suppl
1):S108–S118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li H, Guo H and Li H: Cholesterol loading
affects osteoblastic differentiation in mouse mesenchymal stem
cells. Steroids. 78:426–433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu S, Bertl K, Sun H, Liu ZH, Andrukhov O
and Rausch-Fan X: Effect of simvastatin on the osteogenetic
behavior of alveolar osteoblasts and periodontal ligament cells.
Hum Cell. 25:29–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|