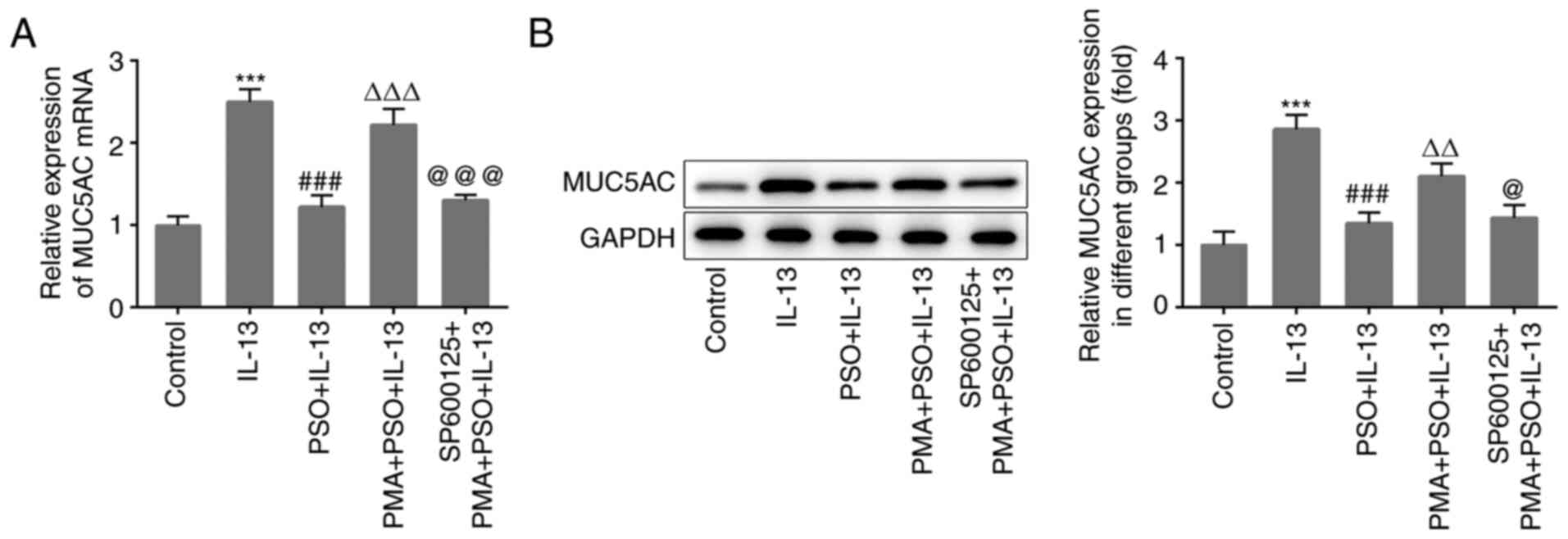
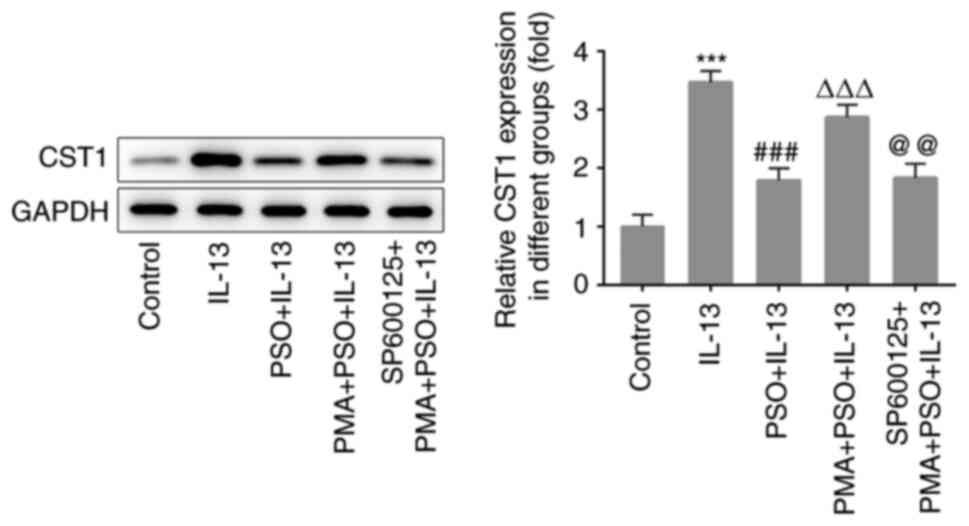
|
1
|
Kakli HA and Riley TD: Allergic rhinitis.
Prim Care. 43:465–475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ri H, Peiyan Z, Jianqi W, Yunteng Z, Gang
L and Baoqing S: Desmoglein 3 gene mediates epidermal growth
factor/epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway involved
in inflammatory response and immune function of anaphylactic
rhinitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1092142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Song CH, Bui TT, Piao CH, Shin HS, Shon
DH, Han EH, Kim HT and Chai OH: Rosae multiflorae fructus hot water
extract inhibits a murine allergic asthma via the suppression of
Th2 cytokine production and histamine release from mast cells. J
Med Food. 19:853–8539. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan DA: Allergic rhinitis and asthma:
Epidemiology and common pathophysiology. Allergy Asthma Proc.
35:357–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoyte FCL and Nelson HS: Recent advances
in allergic rhinitis. F1000Res. 7:F1000 Faculty Rev. 13332018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bernstein DI, Schwartz G and Bernstein JA:
Allergic rhinitis: Mechanisms and treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin
North Am. 36:261–278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seo E, Kang H, Oh YS and Jun HS: Psoralea
corylifolia L. Seed extract attenuates diabetic nephropathy by
inhibiting renal fibrosis and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic mice. Nutrients. 9:8282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Yu C, Hu Y, Xia X, Liao Y, Zhang J,
Chen H, Lu W, Zhou W and Song Z: New application of psoralen and
angelicin on periodontitis with Anti-bacterial, Anti-inflammatory,
and osteogenesis effects. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 8:1782018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du MY, Duan JX, Zhang CY, Yang HH, Guan
XX, Zhong WJ, Liu YZ, Li ZM, Cheng YR, Zhou Y and Guan CX: Psoralen
attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice through
inhibiting myofibroblast activation and collagen deposition. Cell
Biol Int. Jul 22–2019.doi: 10.1002/cbin.11205 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
10
|
Wang C, Al-Ani MK, Sha Y, Chi Q, Dong N,
Yang L and Xu K: Psoralen protects chondrocytes, exhibits
anti-inflammatory effects on synoviocytes, and attenuates
monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Int J Biol Sci.
15:229–238. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Trop-Steinberg S and Azar Y: AP-1
expression and its clinical relevance in immune disorders and
cancer. Am J Med Sci. 353:474–483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gazon H, Barbeau B, Mesnard JM and
Peloponese JM Jr: Hijacking of the AP-1 signaling pathway during
development of ATL. Front Microbiol. 8:26862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bejjani F, Evanno E, Zibara K, Piechaczyk
M and Jariel-Encontre I: The AP-1 transcriptional complex: Local
switch or remote command? Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1872:11–23. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi WJ: The heterochromatin-1
phosphorylation contributes to TPA-induced AP-1 expression. Biomol
Ther (Seoul). 22:308–313. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uluçkan Ö, Guinea-Viniegra J, Jimenez M
and Wagner EF: Signalling in inflammatory skin disease by AP-1
(Fos/Jun). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 33 (4 Suppl 92):S44–S49. 2015.
|
|
16
|
Liu X, Yin S, Chen Y, Wu Y, Zheng W, Dong
H, Bai Y, Qin Y, Li J, Feng S and Zhao P: LPSinduced
proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial
cells and macrophages via NFκB, STAT3 or AP1 activation. Mol Med
Rep. 17:5484–5491. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giovannini-Chami L, Marcet B, Moreilhon C,
Chevalier B, Illie MI, Lebrigand K, Robbe-Sermesant K, Bourrier T,
Michiels JF, Mari B, et al: Distinct epithelial gene expression
phenotypes in childhood respiratory allergy. Eur Respir J.
39:1197–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lei Y, Guo P, An J, Guo C, Lu F and Liu M:
Identification of pathogenic genes and upstream regulators in
allergic rhinitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 115:97–103.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chai L, Zhou K, Wang S, Zhang H, Fan N, Li
J, Tan X, Hu L and Fan X: Psoralen and bakuchiol ameliorate M-CSF
plus RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption
via inhibition of AKT and AP-1 pathways in vitro. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 48:2123–2133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsukura S, Stellato C, Georas SN,
Casolaro V, Plitt JR, Miura K, Kurosawa S, Schindler U and
Schleimer R: Interleukin-13 upregulates eotaxin expression in
airway epithelial cells by a STAT6-dependent mechanism. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 24:755–761. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wills-Karp M: Interleukin-13 in asthma
pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. 202:175–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chun HW, Kim SJ, Pham TH, Bak Y, Oh J, Ryu
HW, Oh SR, Hong JT and Yoon DY: Epimagnolin A inhibits IL-6
production by inhibiting p38/NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways in
PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells. Environ Toxicol. 34:796–803. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anuchapreeda S, Rungrojsakul M, Tima S,
Chiampanichayakul S and Krig SR: Co-activation of WT1 and AP-1
proteins on WT1 gene promoter to induce WT1 gene expression in K562
cells. Cell Signal. 53:339–347. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Lv Q, Song X, Jiang K and Zhang J:
ADRB2 suppresses IL-13-induced allergic rhinitis inflammatory
cytokine regulated by miR-15a-5p. Hum Cell. 32:306–315. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wills-Karp M, Luyimbazi J, Xu X, Schofield
B, Neben TY, Karp CL and Donaldson DD: Interleukin-13: Central
mediator of allergic asthma. Science. 282:2258–2261. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuperman DA, Huang X, Koth LL, Chang GH,
Dolganov GM, Zhu Z, Elias JA, Sheppard D and Erle DJ: Direct
effects of interleukin-13 on epithelial cells cause airway
hyperreactivity and mucus overproduction in asthma. Nat Med.
8:885–889. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao Y and Yu Z: MicroRNA16 inhibits
interleukin13induced inflammatory cytokine secretion and mucus
production in nasal epithelial cells by suppressing the IκB kinase
β/nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:4042–4050.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang B, Gao Y, Zheng G, Ren X, Sun B, Zhu
K, Luo H, Wang Z and Xu M: Platycodin D inhibits
interleukin-13-induced the expression of inflammatory cytokines and
mucus in nasal epithelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1108–1112.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li JP, Xie BP, Zhang WJ, Shi LY, Li WJ,
Zeng Y, Gan GX and Li YH: Psoralen inhibits RAW264.7
differentiation into osteoclasts and bone resorption by regulating
CD4+T cell differentiation. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
43:1228–1234. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin H, Wang L, Xu C, Li B, Luo Q, Wu J, Lv
Y, Wang G and Dong J: Effects of Psoraleae fructus and its major
component psoralen on Th2 response in allergic asthma. Am J Chin
Med. 42:665–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li K, Zhang F, Wei L, Han Z, Liu X, Pan Y,
Guo C and Han W: Recombinant human elafin ameliorates chronic
hyperoxia-induced lung injury by inhibiting nuclear Factor-Kappa B
signaling in neonatal mice. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 40:320–330.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu S, Dai J and Chen X: Vitamin D reduces
autophagy by regulating NF-κB resistance to Aspergillus fumigatus
infection. Gene. 753:1448192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu Q, Xu J, Zhang K, Zhong M, Cao H, Wei
R, Jin L and Gao Y: Study on the protective effect and mechanism of
Dicliptera chinensis (L.) Juss (Acanthaceae) polysaccharide on
immune liver injury induced by LPS. Biomed Pharmacother.
134:1111592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang D, Li Q, Kolosov VP and Zhou X: The
inhibition of aldose reductase on mucus production induced by
interleukin-13 in the human bronchial epithelial cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:588–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hong Z, Guo Z, Zhang R, Xu J, Dong W,
Zhuang G and Deng C: Airborne fine particulate matter induces
oxidative stress and inflammation in human nasal epithelial cells.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 239:117–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Khorasanizadeh M, Eskian M, Gelfand EW and
Rezaei N: Mitogen-activated protein kinases as therapeutic targets
for asthma. Pharmacol Ther. 174:112–1126. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|