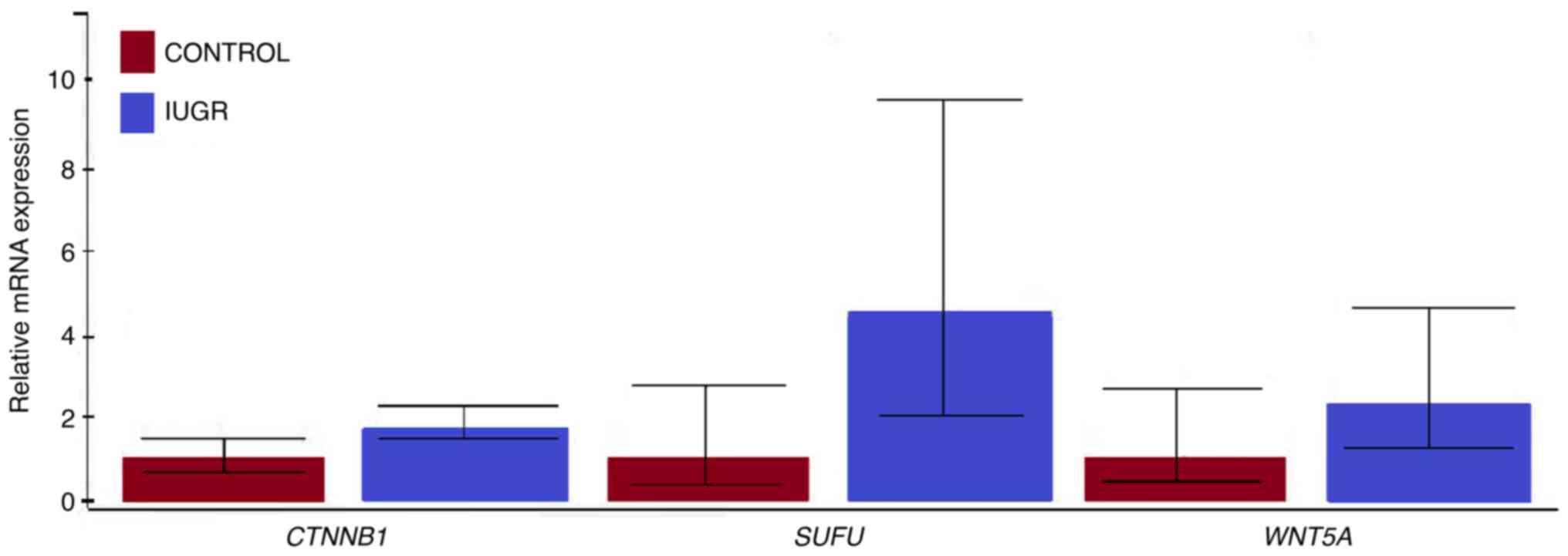
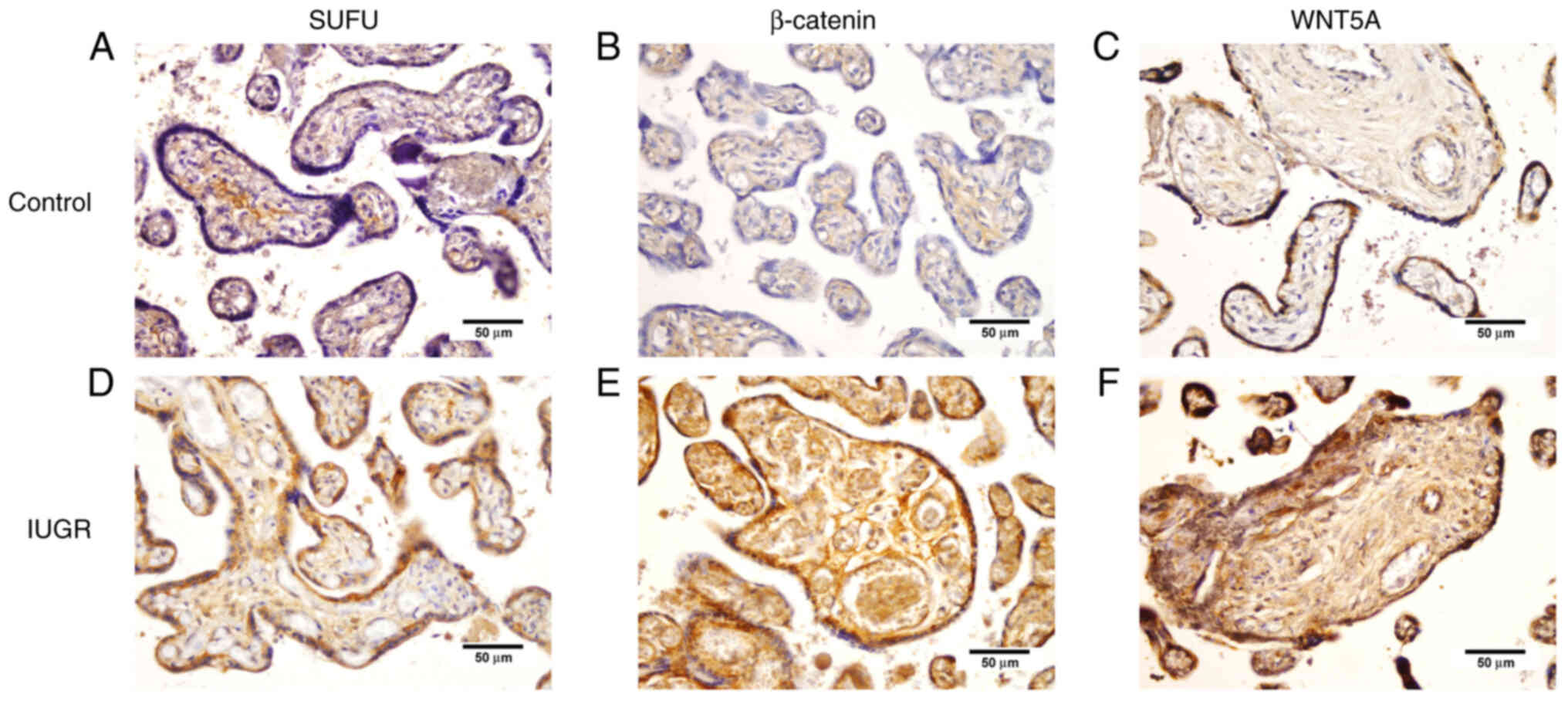
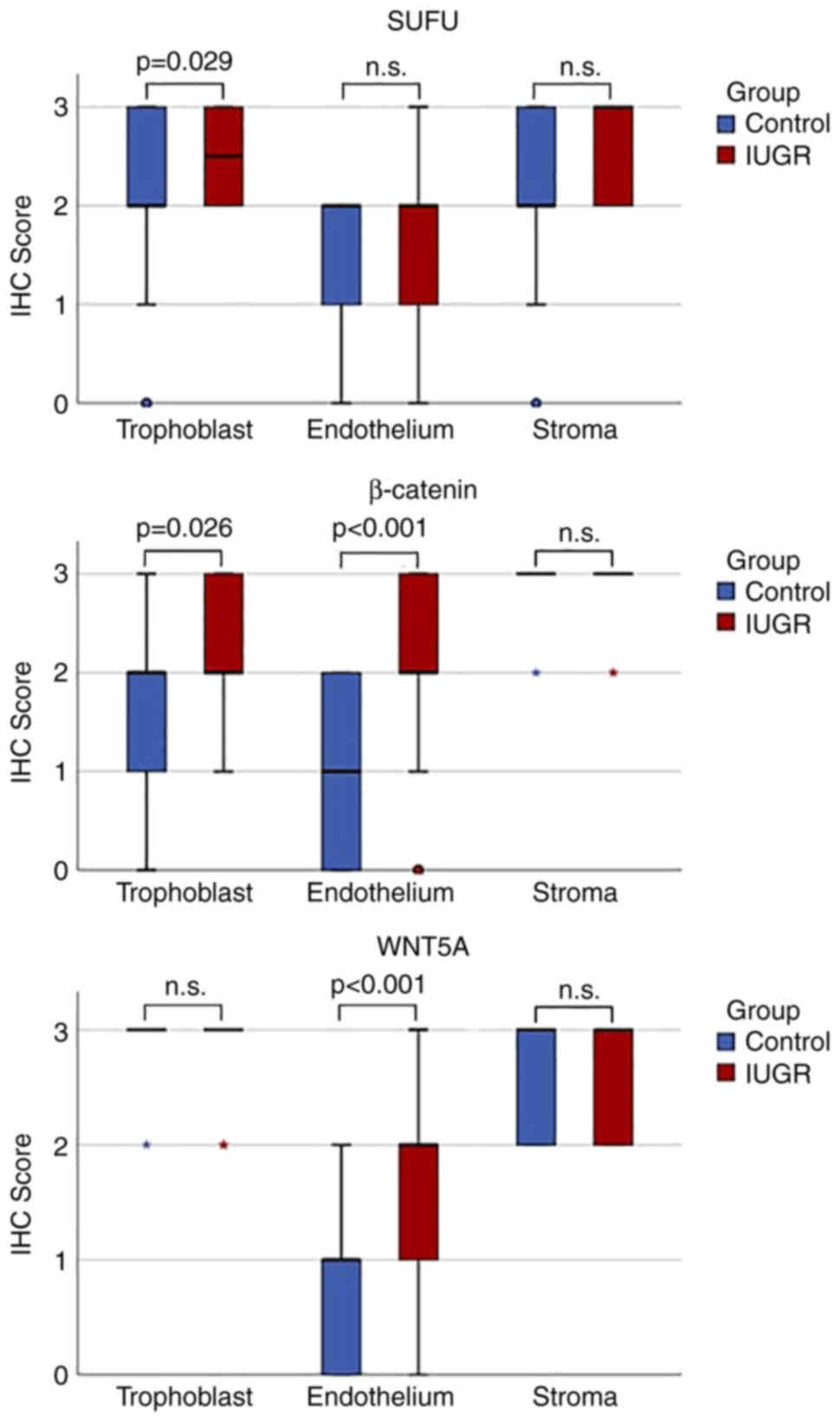
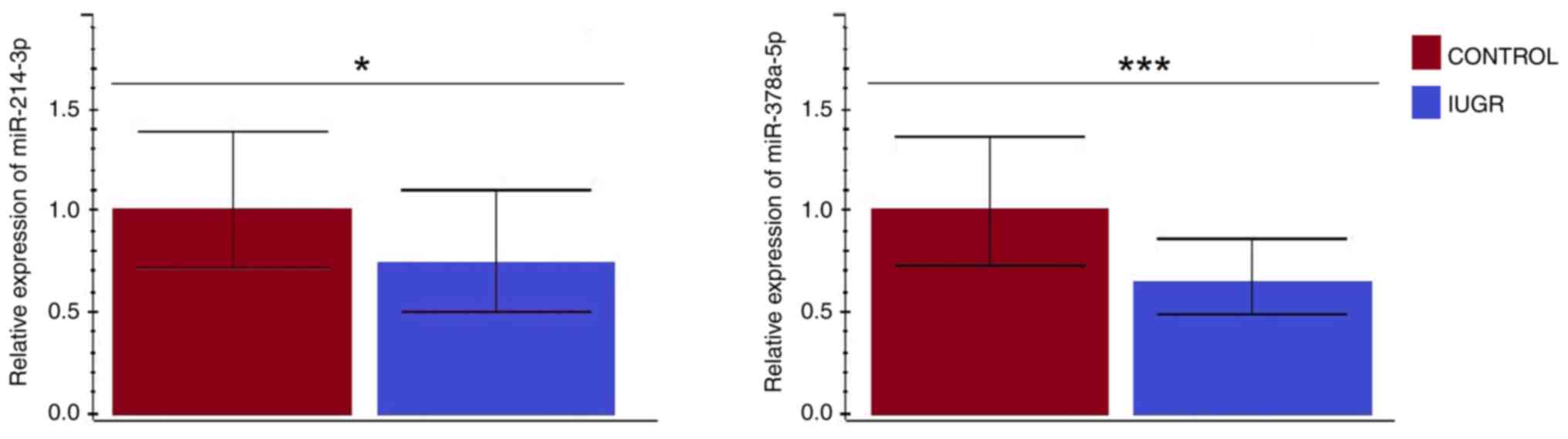
|
1
|
ACOG Practice bulletin no. 134, . Fetal
growth restriction. Obstet Gynecol. 121:1122–1133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hutter D, Kingdom J and Jaeggi E: Causes
and mechanisms of intrauterine hypoxia and its impact on the fetal
cardiovascular system: A review. Int J Pediatr. 2010:4013232010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krishna U and Bhalerao S: Placental
insufficiency and fetal growth restriction. J Obstet Gynaecol
India. 61:505–511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pollack RN and Divon MY: Intrauterine
growth retardation: Definition, classification, and etiology. Clin
Obstet Gynecol. 35:99–107. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guellec I, Lapillonne A, Renolleau S,
Charlaluk ML, Roze JC, Marret S, Vieux R, Monique K and Ancel PY;
EPIPAGE Study Group, : Neurologic outcomes at school age in very
preterm infants born with severe or mild growth restriction.
Pediatrics. 127:e883–e891. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sacchi C, Marino C, Nosarti C, Vieno A,
Visentin S and Simonelli A: Association of intrauterine growth
restriction and small for gestational age status with childhood
cognitive outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA
Pediatr. 174:772–781. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levine TA, Grunau RE, McAuliffe FM,
Pinnamaneni R, Foran A and Alderdice FA: Early childhood
neurodevelopment after intrauterine growth restriction: A
systematic review. Pediatrics. 135:126–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Latos PA and Hemberger M: From the stem of
the placental tree: Trophoblast stem cells and their progeny.
Development. 143:3650–3660. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hemberger M, Hanna CW and Dean W:
Mechanisms of early placental development in mouse and humans. Nat
Rev Genet. 21:27–43. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Knöfler M and Pollheimer J: Human
placental trophoblast invasion and differentiation: A particular
focus on Wnt signaling. Front Genet. 4:1902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matsuura K, Jigami T, Taniue K, Morishita
Y, Adachi S, Senda T, Nonaka A, Aburatani H, Nakamura T and Akiyama
T: Identification of a link between Wnt/β-catenin signalling and
the cell fusion pathway. Nat Commun. 2:5482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aoki M, Mieda M, Ikeda T, Hamada Y,
Nakamura H and Okamoto H: R-spondin3 is required for mouse
placental development. Dev Biol. 301:218–226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miller JR: The Wnts. Genome Biol.
3:Reviews30012002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cadigan KM and Peifer M: Wnt signaling
from development to disease: Insights from model systems. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0028812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van Amerongen R and Nusse R: Towards an
integrated view of Wnt signaling in development. Development.
136:3205–3214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaufmann P, Black S and Huppertz B:
Endovascular trophoblast invasion: Implications for the
pathogenesis of intrauterine growth retardation and preeclampsia.
Biol Reprod. 69:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sonderegger S, Pollheimer J and Knöfler M:
Wnt signalling in implantation, decidualisation and placental
differentiation-review. Placenta. 31:839–847. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma XR, Edmund Sim UH, Pauline B, Patricia
L and Rahman J: Overexpression of WNT2 and TSG101 genes in
colorectal carcinoma. Trop Biomed. 25:46–57. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Geng M, Cao YC, Chen YJ, Jiang H, Bi LQ
and Liu XH: Loss of Wnt5a and Ror2 protein in hepatocellular
carcinoma associated with poor prognosis. World J Gastroenterol.
18:1328–1338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bui TD, Zhang L, Rees MC, Bicknell R and
Harris AL: Expression and hormone regulation of Wnt2, 3, 4, 5a, 7a,
7b and 10b in normal human endometrium and endometrial carcinoma.
Br J Cancer. 75:1131–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ge JF, Xu YY, Qin G, Cheng JQ and Chen FH:
Resveratrol Ameliorates the anxiety- and depression-like behavior
of subclinical hypothyroidism rat: Possible involvement of the HPT
Axis, HPA Axis, and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 7:442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oishi I, Suzuki H, Onishi N, Takada R,
Kani S, Ohkawara B, Koshida I, Suzuki K, Yamada G, Schwabe GC, et
al: The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical
Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells. 8:645–654. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang Y, Gholamin S, Schubert S, Willardson
MI, Lee A, Bandopadhayay P, Bergthold G, Masoud S, Nguyen B, Vue N,
et al: Epigenetic targeting of Hedgehog pathway transcriptional
output through BET bromodomain inhibition. Nat Med. 20:732–740.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rubin LL and de Sauvage FJ: Targeting the
Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:1026–1033. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jia Y, Wang Y and Xie J: The Hedgehog
pathway: Role in cell differentiation, polarity and proliferation.
Arch Toxicol. 89:179–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jeng KS, Chang CF and Lin SS: Sonic
Hedgehog signaling in organogenesis, tumors, and tumor
microenvironments. Int J Mol Sci. 21:7582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Min TH, Kriebel M, Hou S and Pera EM: The
dual regulator Sufu integrates Hedgehog and Wnt signals in the
early Xenopus embryo. Dev Biol. 358:262–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koukoura O, Sifakis S and Spandidos DA:
DNA methylation in the human placenta and fetal growth (review).
Mol Med Rep. 5:883–889. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Serman L, Vlahović M, Sijan M, Bulić-Jakus
F, Serman A, Sincić N, Matijević R, Jurić-Lekić G and Katusić A:
The impact of 5-azacytidine on placental weight, glycoprotein
pattern and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in rat
placenta. Placenta. 28:803–811. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chelbi ST, Mondon F, Jammes H, Buffat C,
Mignot TM, Tost J, Busato F, Gut I, Rebourcet R, Laissue P, et al:
Expressional and epigenetic alterations of placental serine
protease inhibitors: SERPINA3 is a potential marker of
preeclampsia. Hypertension. 49:76–83. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ferreira JC, Choufani S, Grafodatskaya D,
Butcher DT, Zhao C, Chitayat D, Shuman C, Kingdom J, Keating S and
Weksberg R: WNT2 promoter methylation in human placenta is
associated with low birthweight percentile in the neonate.
Epigenetics. 6:440–449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dexheimer PJ and Cochella L: MicroRNAs:
From mechanism to organism. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:4092020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duchaine TF and Fabian MR: Mechanistic
insights into MicroRNA-Mediated gene silencing. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 11:a0327712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gebert LFR and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Paul P, Chakraborty A, Sarkar D, Langthasa
M, Rahman M, Bari M, Singha RS, Malakar AK and Chakraborty S:
Interplay between miRNAs and human diseases. J Cell Physiol.
233:2007–2018. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ciesla M, Skrzypek K, Kozakowska M, Loboda
A, Jozkowicz A and Dulak J: MicroRNAs as biomarkers of disease
onset. Anal Bioanal Chem. 401:2051–2061. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang W: MicroRNAs: Biomarkers,
diagnostics, and therapeutics. Methods Mol Biol. 1617:57–67. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kochhar P, Dwarkanath P, Ravikumar G,
Thomas A, Crasta J, Thomas T, Kurpad AV and Mukhopadhyay A:
Placental expression of miR-21-5p, miR-210-3p and miR-141-3p:
Relation to human fetoplacental growth. Eur J Clin Nutr.
76:730–738. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zarkovic M, Hufsky F, Markert UR and Marz
M: The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Human Placenta. Cells.
11:15882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu P, Ma Y, Wu H and Wang YL:
Placenta-Derived MicroRNAs in the pathophysiology of Human
pregnancy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6463262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Awamleh Z, Gloor GB and Han VKM: Placental
microRNAs in pregnancies with early onset intrauterine growth
restriction and preeclampsia: Potential impact on gene expression
and pathophysiology. BMC Med Genomics. 12:912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He S, Yang F, Yang M, An W, Maguire EM,
Chen Q, Xiao R, Wu W, Zhang L, Wang W and Xiao Q:
miR-214-3p-Sufu-GLI1 is a novel regulatory axis controlling
inflammatory smooth muscle cell differentiation from stem cells and
neointimal hyperplasia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:4652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH and Yang BB:
MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis
by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:20350–20355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hyun J, Wang S, Kim J, Rao KM, Park SY,
Chung I, Ha CS, Kim SW, Yun YH and Jung Y: MicroRNA-378 limits
activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by
suppressing Gli3 expression. Nat Commun. 7:109932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kardum V, Karin V, Glibo M, Skrtic A,
Martic TN, Ibisevic N, Skenderi F, Vranic S and Serman L:
Methylation-associated silencing of SFRP1 gene in high-grade serous
ovarian carcinomas. Ann Diagn Pathol. 31:45–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rizzardi AE, Johnson AT, Vogel RI,
Pambuccian SE, Henriksen J, Skubitz AP, Metzger GJ and Schmechel
SC: Quantitative comparison of immunohistochemical staining
measured by digital image analysis versus pathologist visual
scoring. Diagn Pathol. 7:422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vrsalovic MM, Korac P, Dominis M, Ostojic
S, Mannhalter C and Kusec R: T- and B-cell clonality and frequency
of human herpes viruses-6, −8 and Epstein Barr virus in
angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 22:169–177.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Paluszczak J, Wiśniewska D,
Kostrzewska-Poczekaj M, Kiwerska K, Grénman R, Mielcarek-Kuchta D
and Jarmuż-Szymczak M: Prognostic significance of the methylation
of Wnt pathway antagonists-CXXC4, DACT2, and the inhibitors of
sonic hedgehog signaling-ZIC1, ZIC4, and HHIP in head and neck
squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Oral Investig. 21:1777–1788. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sola IM, Serman A, Karin-Kujundzic V, Paic
F, Skrtic A, Slatina P, Kakarigi L, Vranic S and Serman L:
Dishevelled family proteins (DVL1-3) expression in intrauterine
growth restriction (IUGR) placentas. Bosn J Basic Med Sci.
21:447–453. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Julian CG, Wilson MJ, Lopez M, Yamashiro
H, Tellez W, Rodriguez A, Bigham AW, Shriver MD, Rodriguez C,
Vargas E and Moore LG: Augmented uterine artery blood flow and
oxygen delivery protect Andeans from altitude-associated reductions
in fetal growth. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
296:R1564–R1575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Williams LA, Evans SF and Newnham JP:
Prospective cohort study of factors influencing the relative
weights of the placenta and the newborn infant. BMJ. 314:1864–1868.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Thompson LP: Effects of chronic hypoxia on
fetal coronary responses. High Alt Med Biol. 4:215–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rashid CS, Bansal A and Simmons RA:
Oxidative stress, intrauterine growth restriction, and
developmental programming of type 2 diabetes. Physiology
(Bethesda). 33:348–359. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang C, Tannous E and Zheng JJ: Oxidative
stress upregulates Wnt signaling in human retinal microvascular
endothelial cells through activation of disheveled. J Cell Biochem.
120:14044–14054. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Funato Y, Michiue T, Asashima M and Miki
H: The thioredoxin-related redox-regulating protein nucleoredoxin
inhibits Wnt-beta-catenin signalling through dishevelled. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:501–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Vikram A, Kim YR, Kumar S, Naqvi A,
Hoffman TA, Kumar A, Miller FJ Jr, Kim CS and Irani K: Canonical
Wnt signaling induces vascular endothelial dysfunction via
p66Shc-regulated reactive oxygen species. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 34:2301–2309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Spillmann F, Van Linthout S, Miteva K,
Lorenz M, Stangl V, Schultheiss HP and Tschöpe C: LXR agonism
improves TNF-α-induced endothelial dysfunction in the absence of
its cholesterol-modulating effects. Atherosclerosis. 232:1–9. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bretón-Romero R, Feng B, Holbrook M, Farb
MG, Fetterman JL, Linder EA, Berk BD, Masaki N, Weisbrod RM,
Inagaki E, et al: Endothelial dysfunction in human diabetes is
mediated by Wnt5a-JNK signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
36:561–569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Caricasole A, Copani A, Caraci F, Aronica
E, Rozemuller AJ, Caruso A, Storto M, Gaviraghi G, Terstappen GC
and Nicoletti F: Induction of Dickkopf-1, a negative modulator of
the Wnt pathway, is associated with neuronal degeneration in
Alzheimer's brain. J Neurosci. 24:6021–6027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Alvarez AR, Godoy JA, Mullendorff K,
Olivares GH, Bronfman M and Inestrosa NC: Wnt-3a overcomes
beta-amyloid toxicity in rat hippocampal neurons. Exp Cell Res.
297:186–196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fan M, Xu Y, Hong F, Gao X, Xin G, Hong H,
Dong L and Zhao X: Rac1/β-Catenin signalling pathway contributes to
trophoblast cell invasion by targeting Snail and MMP9. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 38:1319–1332. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pennington KA, Schlitt JM, Jackson DL,
Schulz LC and Schust DJ: Preeclampsia: Multiple approaches for a
multifactorial disease. Dis Model Mech. 5:9–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu Q, Wu G and Li JX: Effect of hypoxia on
expression of placental trophoblast cells SATB1 and β-catenin and
its correlation with the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Asian Pac J
Trop Med. 9:567–571. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bischof P and Campana A: Molecular
mediators of implantation. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Obstet
Gynaecol. 14:801–814. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Nadeem L, Munir S, Fu G, Dunk C, Baczyk D,
Caniggia I, Lye S and Peng C: Nodal signals through activin
receptor-like kinase 7 to inhibit trophoblast migration and
invasion: Implication in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Am J
Pathol. 178:1177–1189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tang C, Mei L, Pan L, Xiong W, Zhu H, Ruan
H, Zou C, Tang L, Iguchi T and Wu X: Hedgehog signaling through
GLI1 and GLI2 is required for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human trophoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1850:1438–1448. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang Y and Zhang Y: Forkhead box C2
promotes the invasion ability of human trophoblast cells through
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 42:859–866. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu J, Heydeck W, Zeng H and Liu A: Dual
function of suppressor of fused in Hh pathway activation and mouse
spinal cord patterning. Dev Biol. 362:141–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tariki M, Wieczorek SA, Schneider P,
Bänfer S, Veitinger S, Jacob R, Fendrich V and Lauth M: RIO kinase
3 acts as a SUFU-dependent positive regulator of Hedgehog
signaling. Cell Signal. 25:2668–2675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Banister CE, Koestler DC, Maccani MA,
Padbury JF, Houseman EA and Marsit CJ: Infant growth restriction is
associated with distinct patterns of DNA methylation in human
placentas. Epigenetics. 6:920–927. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kimura AP, Liebhaber SA and Cooke NE:
Epigenetic modifications at the human growth hormone locus predict
distinct roles for histone acetylation and methylation in placental
gene activation. Mol Endocrinol. 18:1018–1032. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chuang HC, Chang CW, Chang GD, Yao TP and
Chen H: Histone deacetylase 3 binds to and regulates the GCMa
transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:1459–1469. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Fu G, Brkić J, Hayder H and Peng C:
MicroRNAs in Human placental development and pregnancy
complications. Int J Mol Sci. 14:5519–5544. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Higashijima A, Miura K, Mishima H,
Kinoshita A, Jo O, Abe S, Hasegawa Y, Miura S, Yamasaki K, Yoshida
A, et al: Characterization of placenta-specific microRNAs in fetal
growth restriction pregnancy. Prenat Diagn. 33:214–222. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pineles BL, Romero R, Montenegro D, Tarca
AL, Han YM, Kim YM, Draghici S, Espinoza J, Kusanovic JP, Mittal P,
et al: Distinct subsets of microRNAs are expressed differentially
in the human placentas of patients with preeclampsia. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 196:261.e1–e6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhu XM, Han T, Sargent IL, Yin GW and Yao
YQ: Differential expression profile of microRNAs in human placentas
from preeclamptic pregnancies vs normal pregnancies. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 200:661.e1–e7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Donker RB, Mouillet JF, Nelson DM and
Sadovsky Y: The expression of Argonaute2 and related microRNA
biogenesis proteins in normal and hypoxic trophoblasts. Mol Hum
Reprod. 13:273–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Peng Y, Qin Y, Zhang X, Deng S, Yuan Y,
Feng X, Chen W, Hu F, Gao Y, He J, et al: MiRNA-20b/SUFU/Wnt axis
accelerates gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and EMT.
Heliyon. 7:e066952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Alimirah F, Peng X, Gupta A, Yuan L, Welsh
J, Cleary M and Mehta RG: Crosstalk between the vitamin D receptor
(VDR) and miR-214 in regulating SuFu, a hedgehog pathway inhibitor
in breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 349:15–22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Peng Y, Zhang X, Ma Q, Yan R, Qin Y, Zhao
Y, Cheng Y, Yang M, Wang Q, Feng X, et al: MiRNA-194 activates the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer by targeting the
negative Wnt regulator, SUFU. Cancer Lett. 385:117–127. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Park M, Kim M, Hwang D, Park M, Kim WK,
Kim SK, Shin J, Park ES, Kang CM, Paik YK and Kim H:
Characterization of gene expression and activated signaling
pathways in solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of pancreas. Mod Pathol.
27:580–593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Long H, Wang Z, Chen J, Xiang T, Li Q,
Diao X and Zhu B: microRNA-214 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting the
suppressor-of-fused protein (Sufu). Oncotarget. 6:38705–38718.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ma L, Yang X, Wei R, Ye T, Zhou JK, Wen M,
Men R, Li P, Dong B, Liu L, et al: MicroRNA-214 promotes hepatic
stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing Sufu
expression. Cell Death Dis. 9:7182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Tupone MG, D'Aguanno S, Di Martile M,
Valentini E, Desideri M, Trisciuoglio D, Donzelli S, Sacconi A,
Buglioni S, Ercolani C, et al: microRNA-378a-5p iS a novel positive
regulator of melanoma progression. Oncogenesis. 9:222020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hua Z, Lv Q, Ye W, Wong CK, Cai G, Gu D,
Ji Y, Zhao C, Wang J, Yang BB and Zhang Y: MiRNA-directed
regulation of VEGF and other angiogenic factors under hypoxia. PLoS
One. 1:e1162006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Odibo AO, Nelson D, Stamilio DM, Sehdev HM
and Macones GA: Advanced maternal age is an independent risk factor
for intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Perinatol. 23:325–328.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Palatnik A, De Cicco S, Zhang L, Simpson
P, Hibbard J and Egede LE: The association between advanced
maternal age and diagnosis of small for gestational age. Am J
Perinatol. 37:37–43. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Vega J, Sáez G, Smith M, Agurto M and
Morris NM: Risk factors for low birth weight and intrauterine
growth retardation in Santiago, Chile. Rev Med Chil. 121:1210–1219.
1993.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kalinka J, Hanke W and Szymczak W: Risk
factors of intrauterine growth retardation: A study of an urban
population in Poland. Cent Eur J Public Health. 4:192–196.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Tierney-Gumaer R and Reifsnider E: Risk
factors for low birth weight infants of Hispanic, African American,
and White women in Bexar County, Texas. Public Health Nurs.
25:390–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yu SH, Mason J, Crum J, Cappa C and
Hotchkiss DR: Differential effects of young maternal age on child
growth. Glob Health Action. 9:311712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|