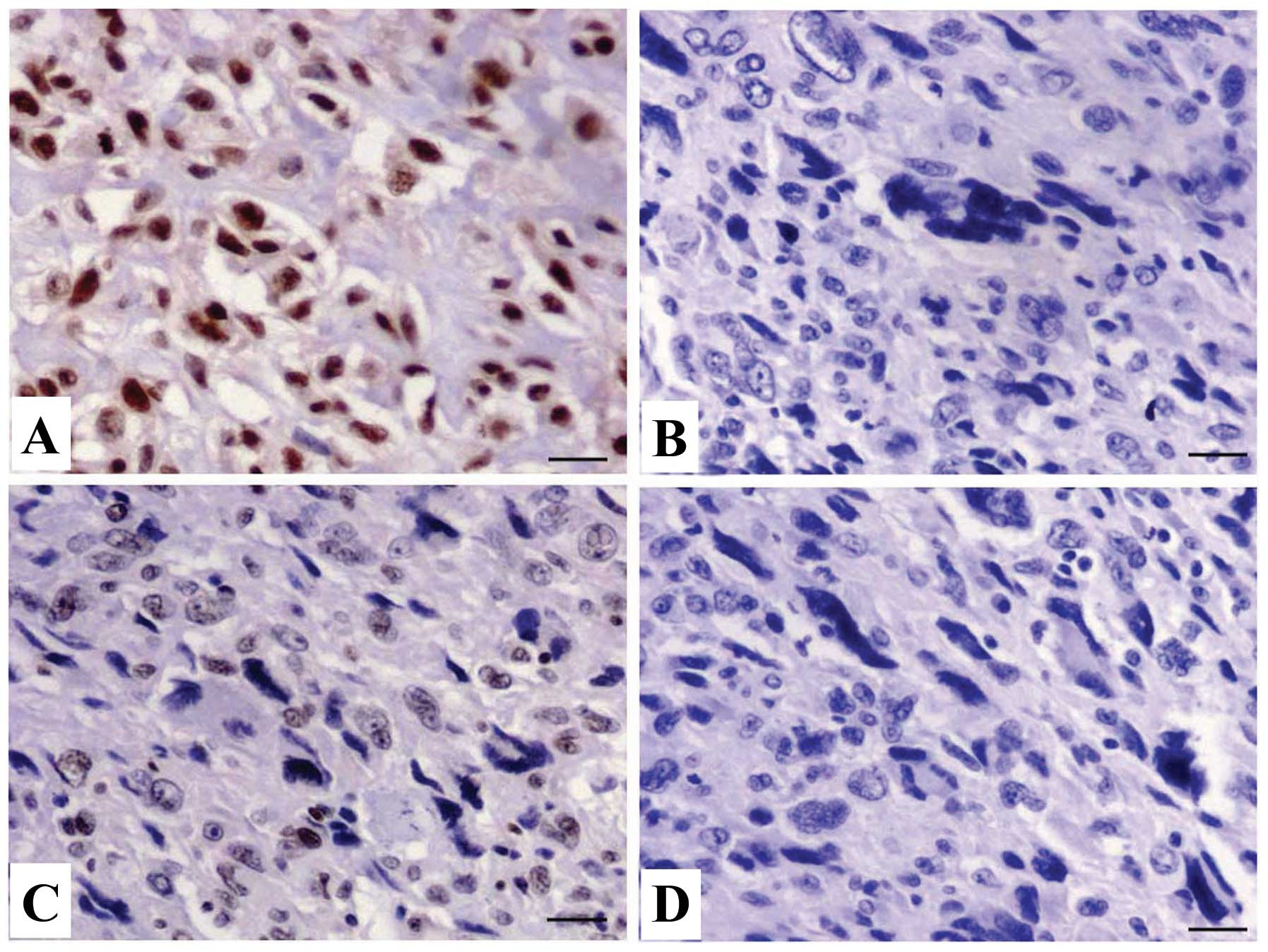
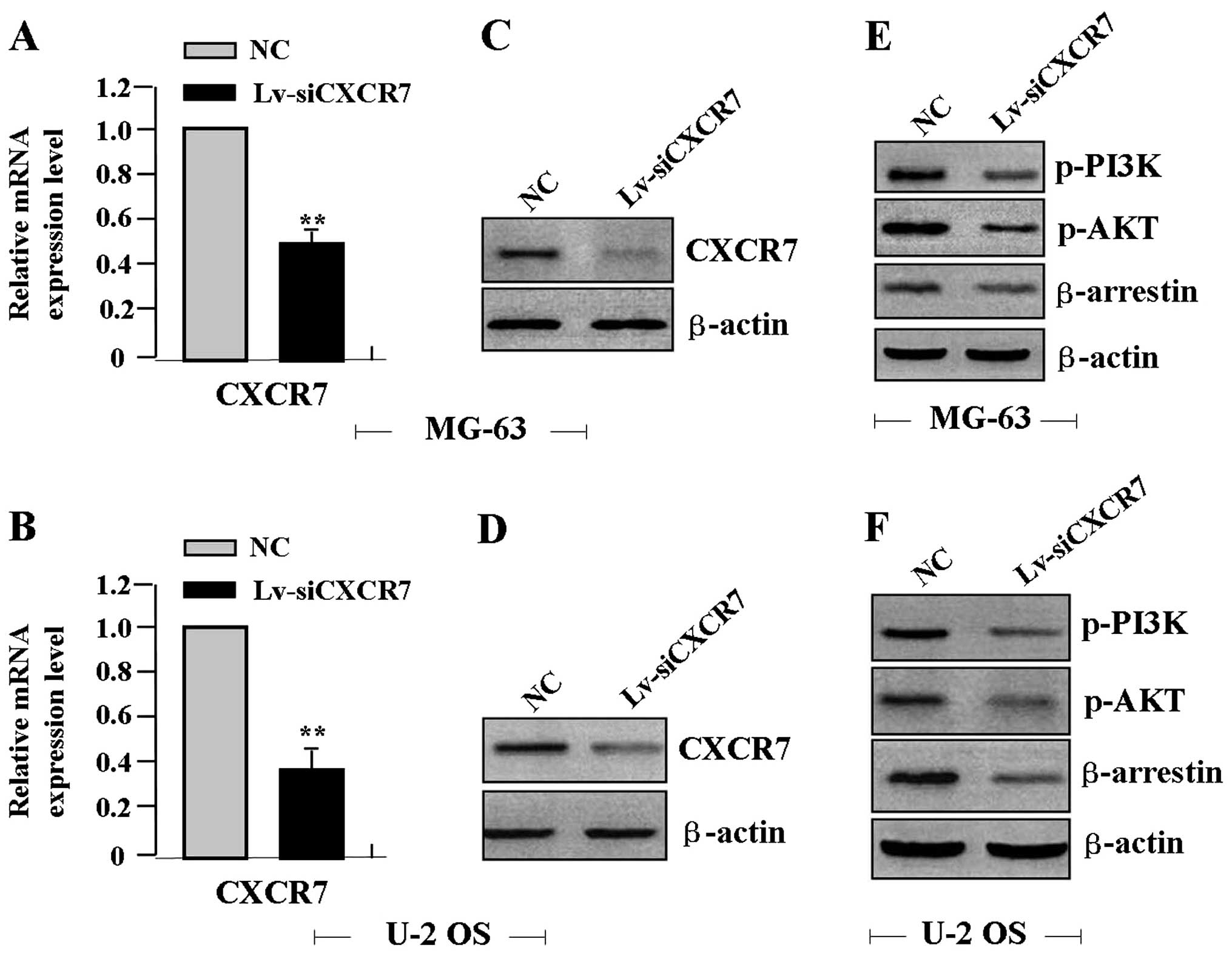
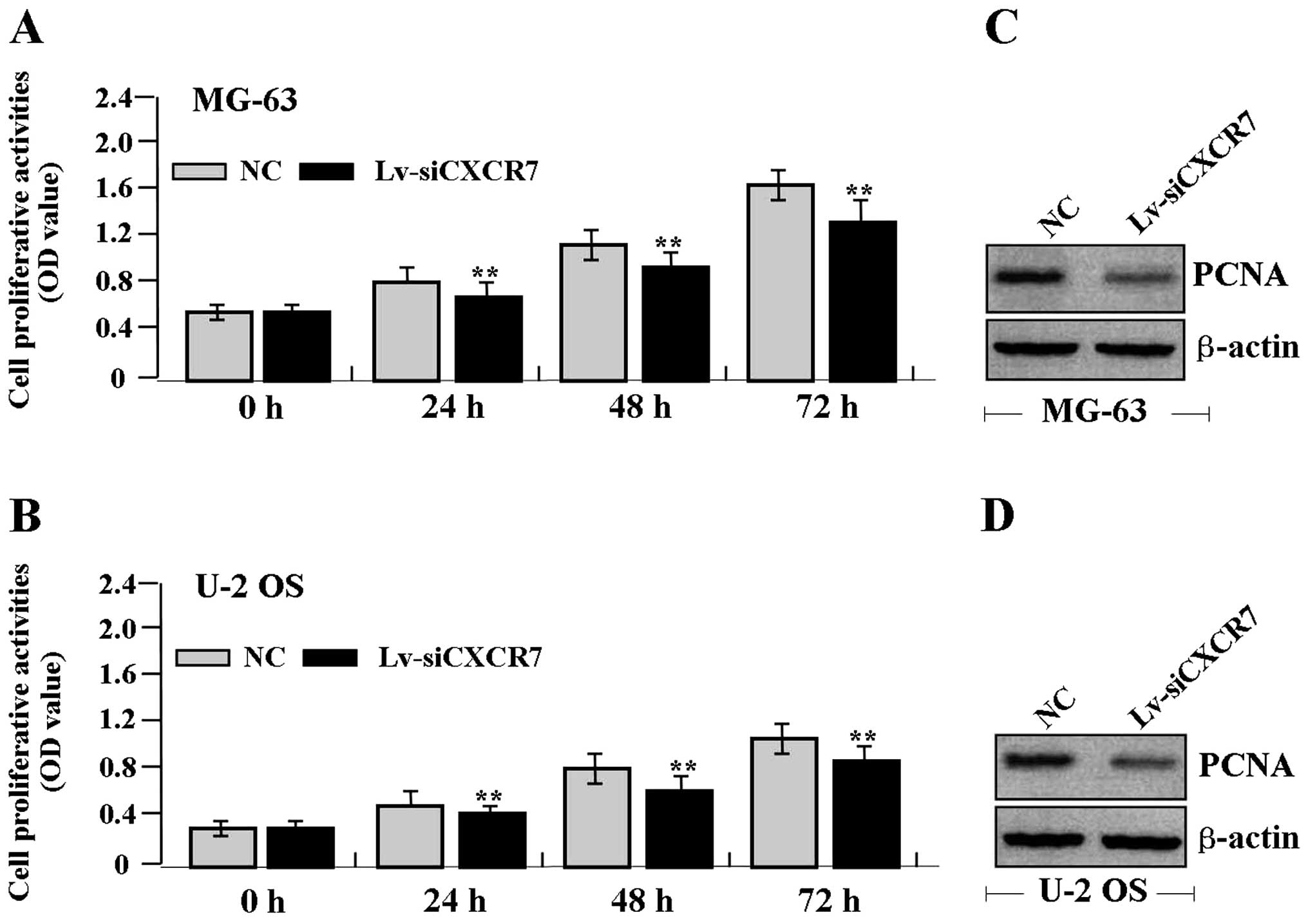
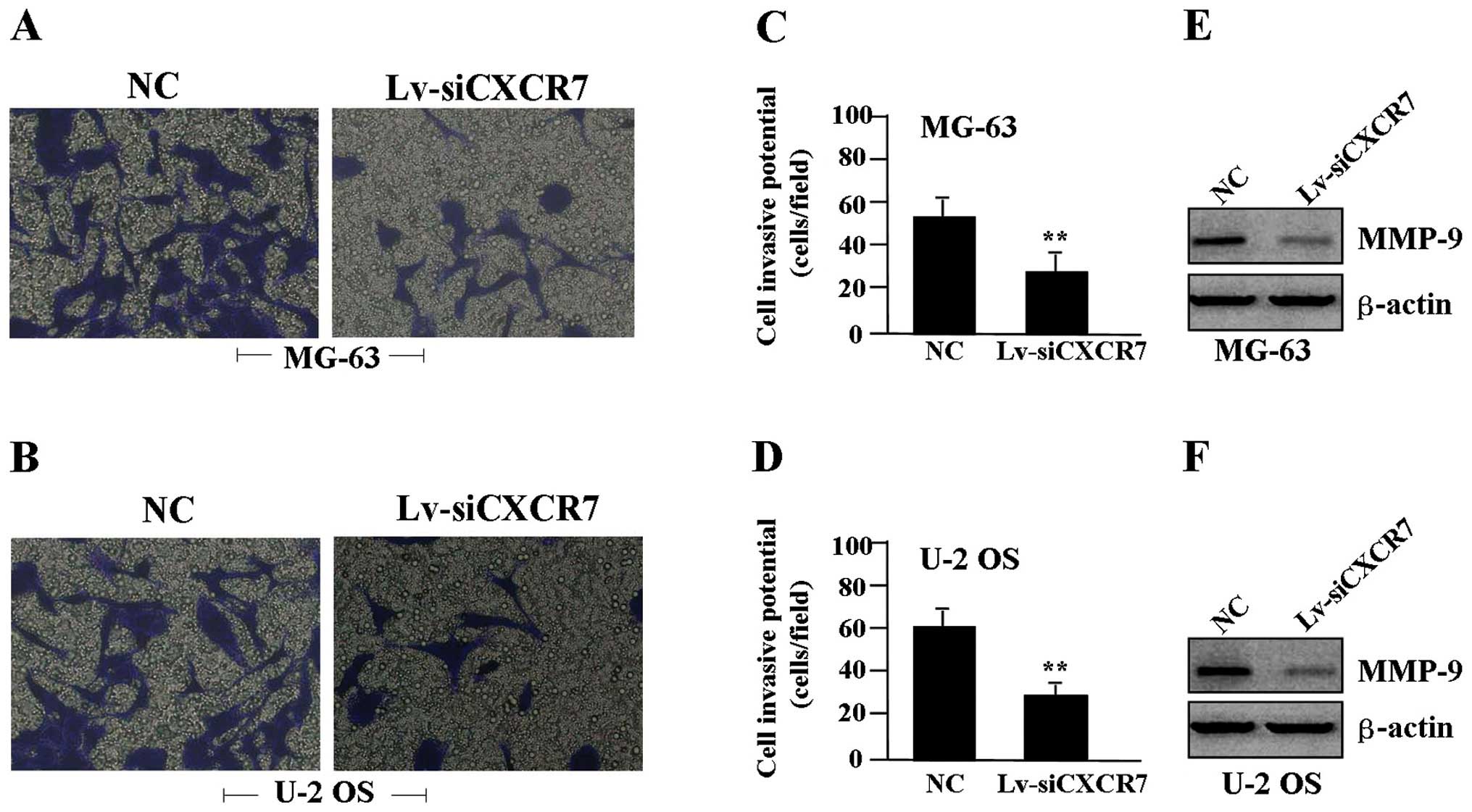
|
1
|
Chen X, Luther G, Zhang W, et al: The E-F
hand calcium-binding protein S100A4 regulates the proliferation,
survival and differentiation potential of human osteosarcoma cells.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:1083–1096. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roth M, Linkowski M, Tarim J, et al:
Ganglioside GD2 as a therapeutic target for antibody-mediated
therapy in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer. 120:548–554. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goguet-Surmenian E, Richard-Fiardo P,
Guillemot E, et al: CXCR7-mediated progression of osteosarcoma in
the lungs. Br J Cancer. 109:1579–1585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun X, Cheng G, Hao M, et al:
CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 29:709–722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hattermann K and Mentlein R: An infernal
trio: the chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 in
tumor biology. Ann Anat. 195:103–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh AK, Arya RK, Trivedi AK, et al:
Chemokine receptor trio: CXCR3, CXCR4 and CXCR7 crosstalk via
CXCL11 and CXCL12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:41–49. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Odemis V, Lipfert J, Kraft R, et al: The
presumed atypical chemokine receptor CXCR7 signals through
Gi/o proteins in primary rodent astrocytes and human
glioma cells. Glia. 60:372–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao X, Zhou L, Han S, et al: High
expression of CXCR4 and CXCR7 predicts poor survival in gallbladder
cancer. J Int Med Res. 39:1253–1264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hattermann K, Held-Feindt J, Lucius R, et
al: The chemokine receptor CXCR7 is highly expressed in human
glioma cells and mediates antiapoptotic effects. Cancer Res.
70:3299–3308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Chen W, Gao L, et al: High
expression of CXCR4, CXCR7 and SDF-1 predicts poor survival in
renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 10:2122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gebauer F, Tachezy M, Effenberger K, et
al: Prognostic impact of CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 104:140–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schrevel M, Karim R, ter Haar NT, et al:
CXCR7 expression is associated with disease-free and
disease-specific survival in cervical cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
106:1520–1525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Heinrich EL, Lee W, Lu J, et al: Chemokine
CXCL12 activates dual CXCR4 and CXCR7-mediated signaling pathways
in pancreatic cancer cells. J Transl Med. 10:682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gosalbez M, Hupe MC, Lokeshwar SD, et al:
Differential expression of stroma derived factor-1 isoforms in
bladder cancer. J Urol. Nov 26–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Sun DX, Teng XY, et al: Expression
of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and CXCR7 in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Endocr Pathol. 23:247–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tarnowski M, Liu R, Wysoczynski M, et al:
CXCR7: a new SDF-1-binding receptor in contrast to normal
CD34+ progenitors is functional and is expressed at
higher level in human malignant hematopoietic cells. Eur J
Haematol. 85:472–483. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hao M, Zheng J, Hou K, et al: Role of
chemokine receptor CXCR7 in bladder cancer progression. Biochem
Pharmacol. 84:204–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo JC, Li J, Yang YC, et al:
Oligonucleotide microarray identifies genes differentially
expressed during tumorigenesis of DMBA-induced pancreatic cancer in
rats. PLoS One. 8:e829102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Monnier J, Boissan M, L’Helgoualc’h A, et
al: CXCR7 is up-regulated in human and murine hepatocellular
carcinoma and is specifically expressed by endothelial cells. Eur J
Cancer. 48:138–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hattermann K, Mentlein R and Held-Feindt
J: CXCL12 mediates apoptosis resistance in rat C6 glioma cells.
Oncol Rep. 27:1348–1352. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xue TC, Han D, Chen RX, et al: High
expression of CXCR7 combined with alpha fetoprotein in
hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with extra-hepatic metastasis
to lung after hepatectomy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:657–663.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gahan JC, Gosalbez M, Yates T, et al:
Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in kidney tumors:
molecular profiling of histological subtypes and association with
metastasis. J Urol. 187:827–833. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guillemot E, Karimdjee-Soilihi B, Pradelli
E, et al: CXCR7 receptors facilitate the progression of colon
carcinoma within lung not within liver. Br J Cancer. 107:1944–1949.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang T, Xia QJ, Chen JB, et al: Expression
of the CXCL12/SDF-1 chemokine receptor CXCR7 in human brain
tumours. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5281–5286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zabel BA, Lewén S, Berahovich RD, et al:
The novel chemokine receptor CXCR7 regulates trans-endothelial
migration of cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng K, Li HY, Su XL, et al: Chemokine
receptor CXCR7 regulates the invasion, angiogenesis and tumor
growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Décaillot FM, Kazmi MA, Lin Y, et al:
CXCR7/CXCR4 heterodimer constitutively recruits β-arrestin to
enhance cell migration. J Biol Chem. 286:32188–32197.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu FY, Zhao ZJ, Li P, et al: NF-κB
participates in chemokine receptor 7-mediated cell survival in
metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oncol Rep.
25:383–391. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Yates TJ, Knapp J, Gosalbez M, et al:
C-X-C chemokine receptor 7: a functionally associated molecular
marker for bladder cancer. Cancer. 119:61–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Risio M: Cell proliferation in colorectal
tumor progression: an immunohistochemical approach to intermediate
biomarkers. J Cell Biochem (Suppl). 16G:79–87. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hornebeck W, Lambert E, Petitfrère E and
Bernard P: Beneficial and detrimental influences of tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in tumor progression.
Biochimie. 87:377–383. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dong S, Kong J, Kong F, et al:
Insufficient radiofrequency ablation promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through Akt and ERK signaling pathways. J Transl Med. 11:2732013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|