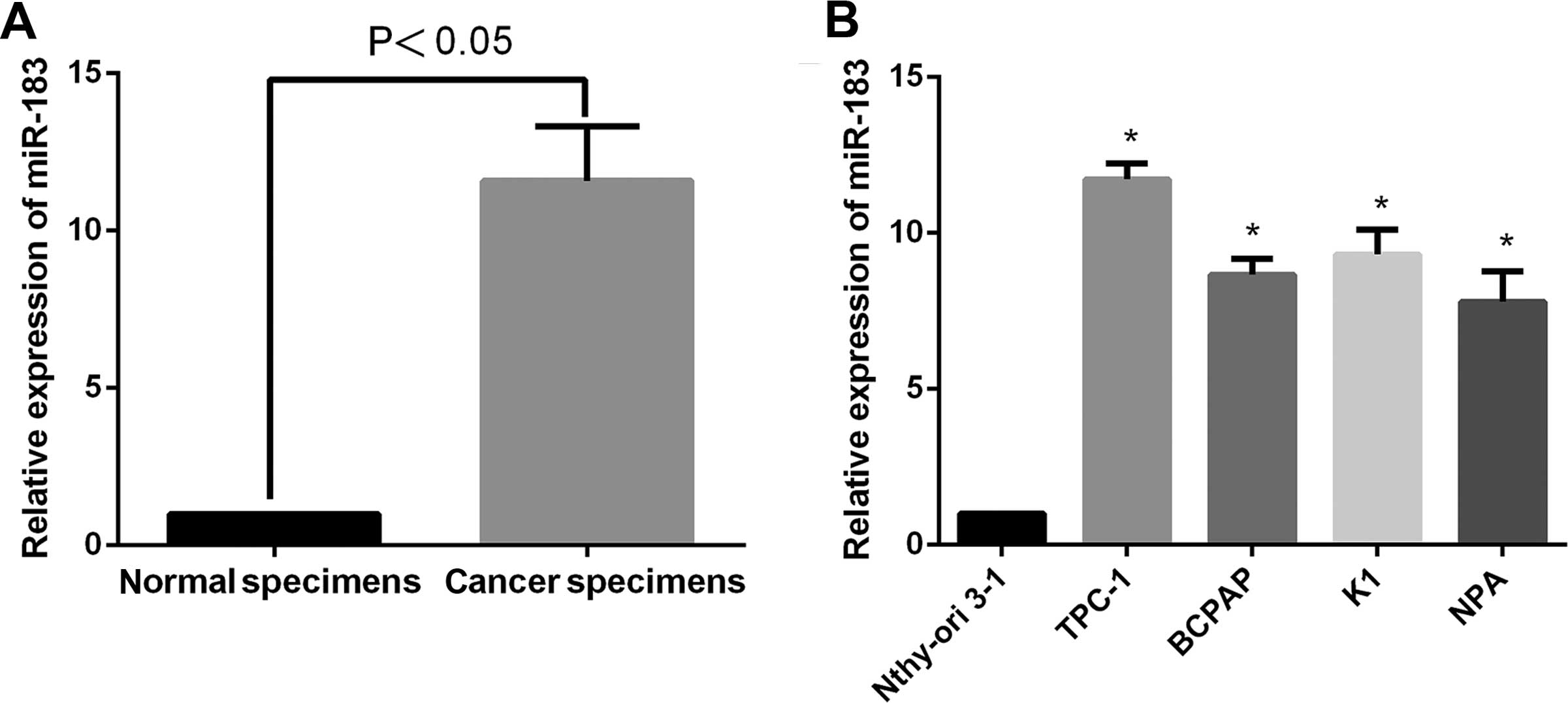
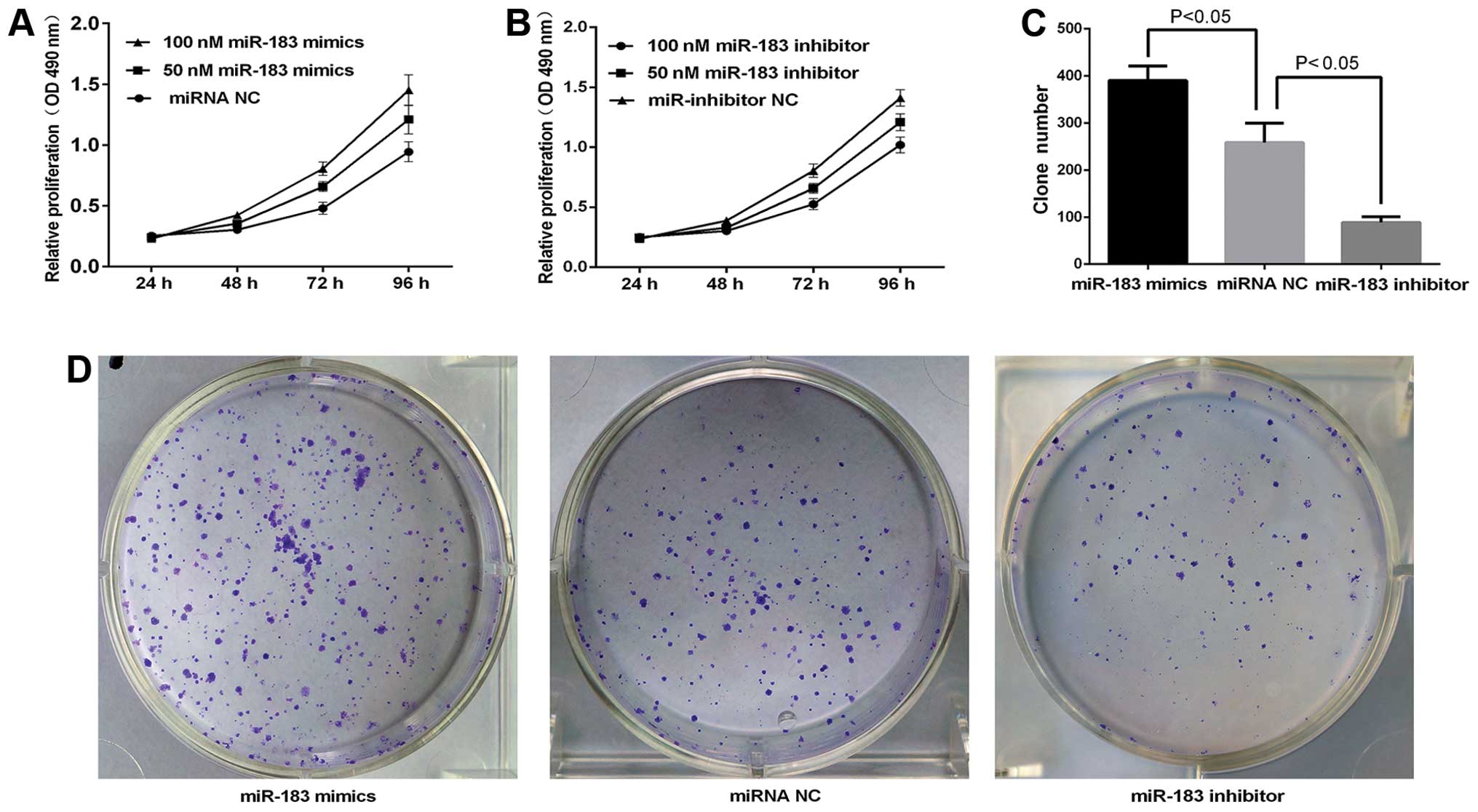
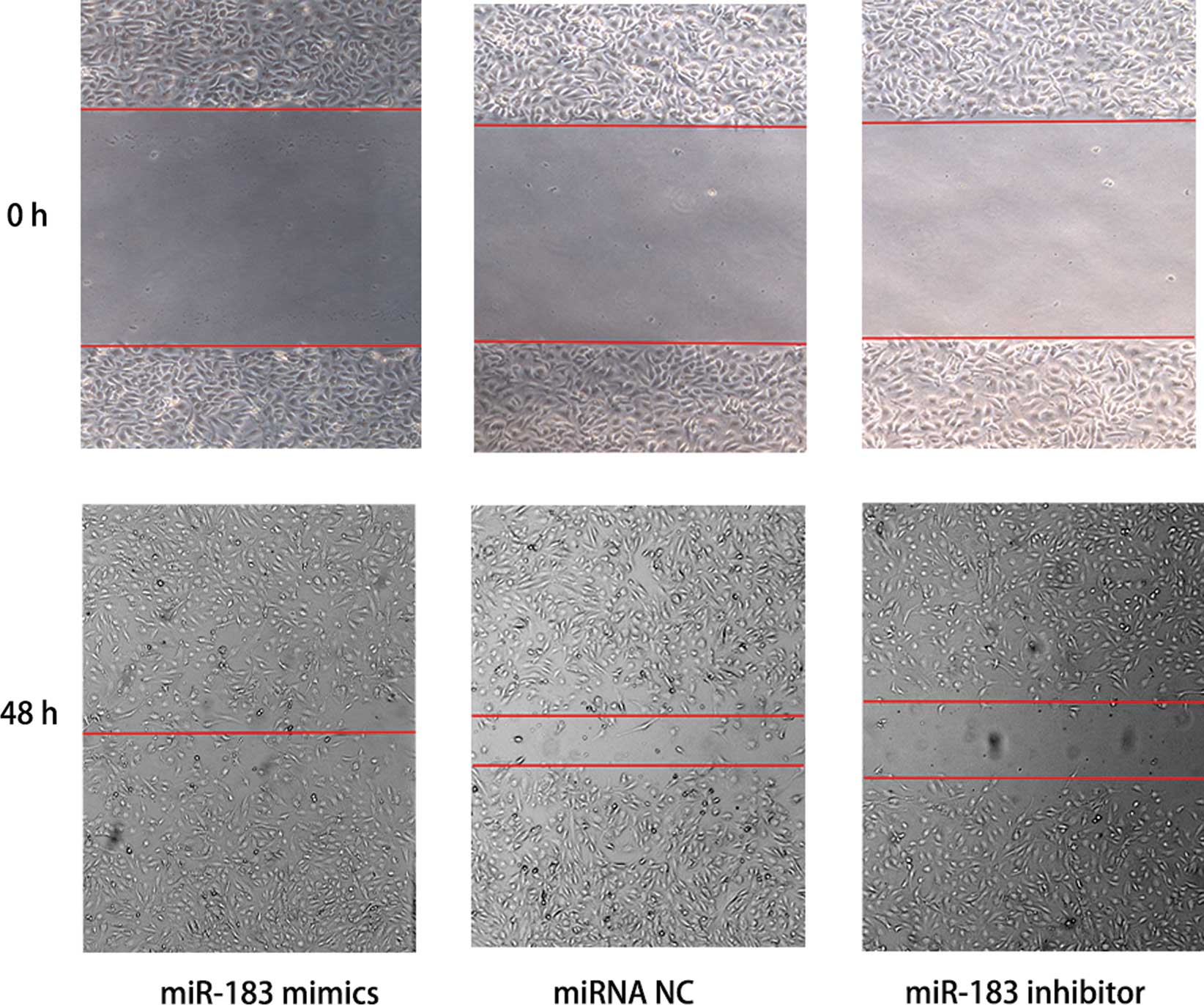
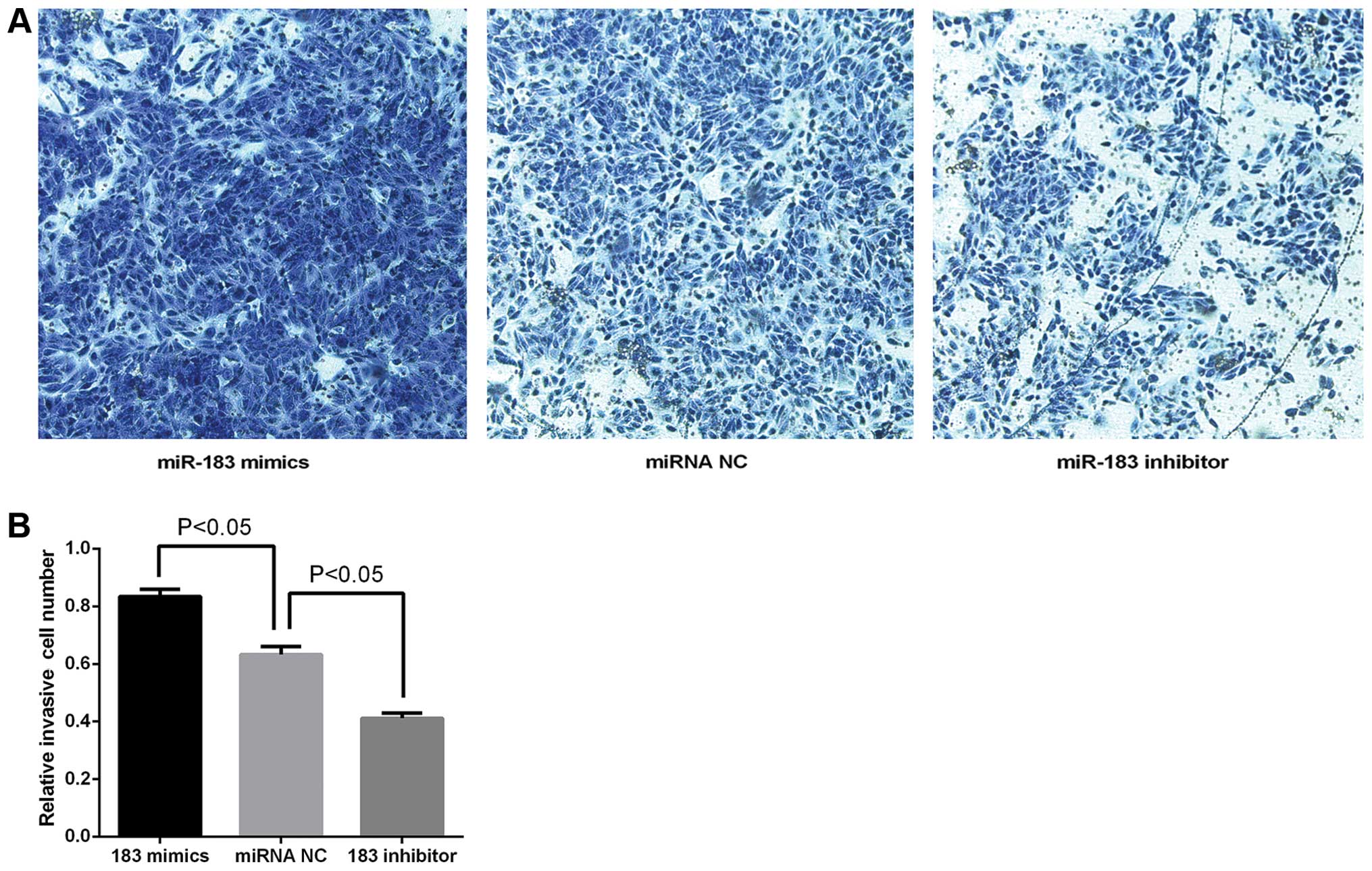
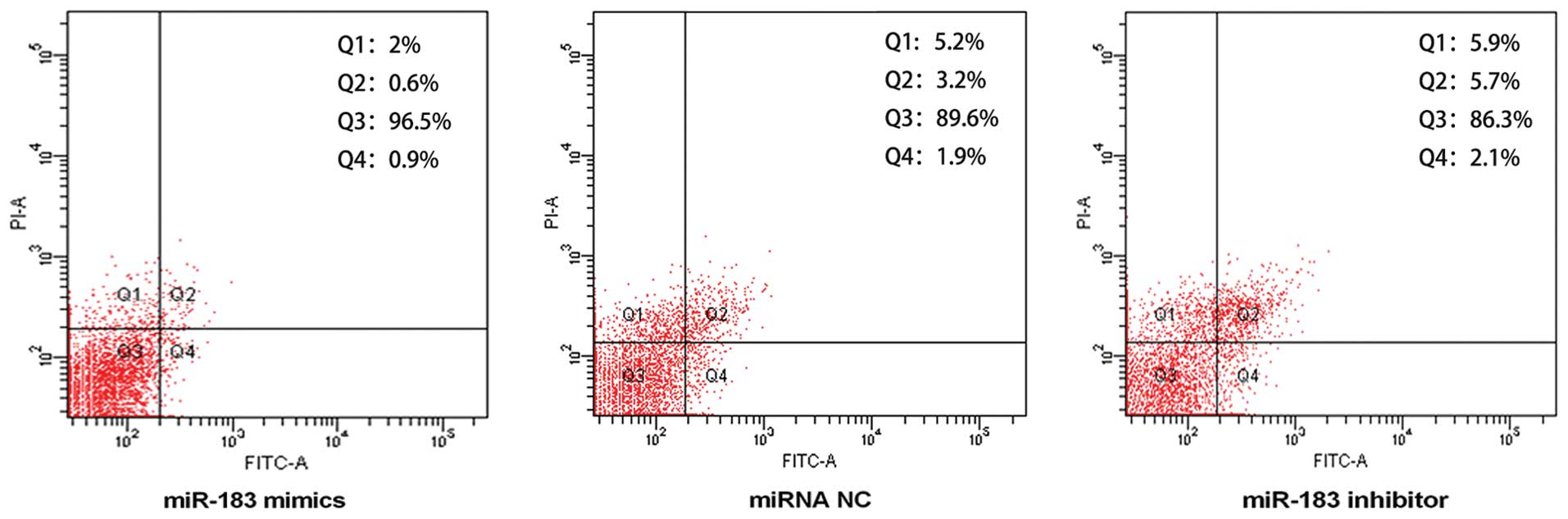
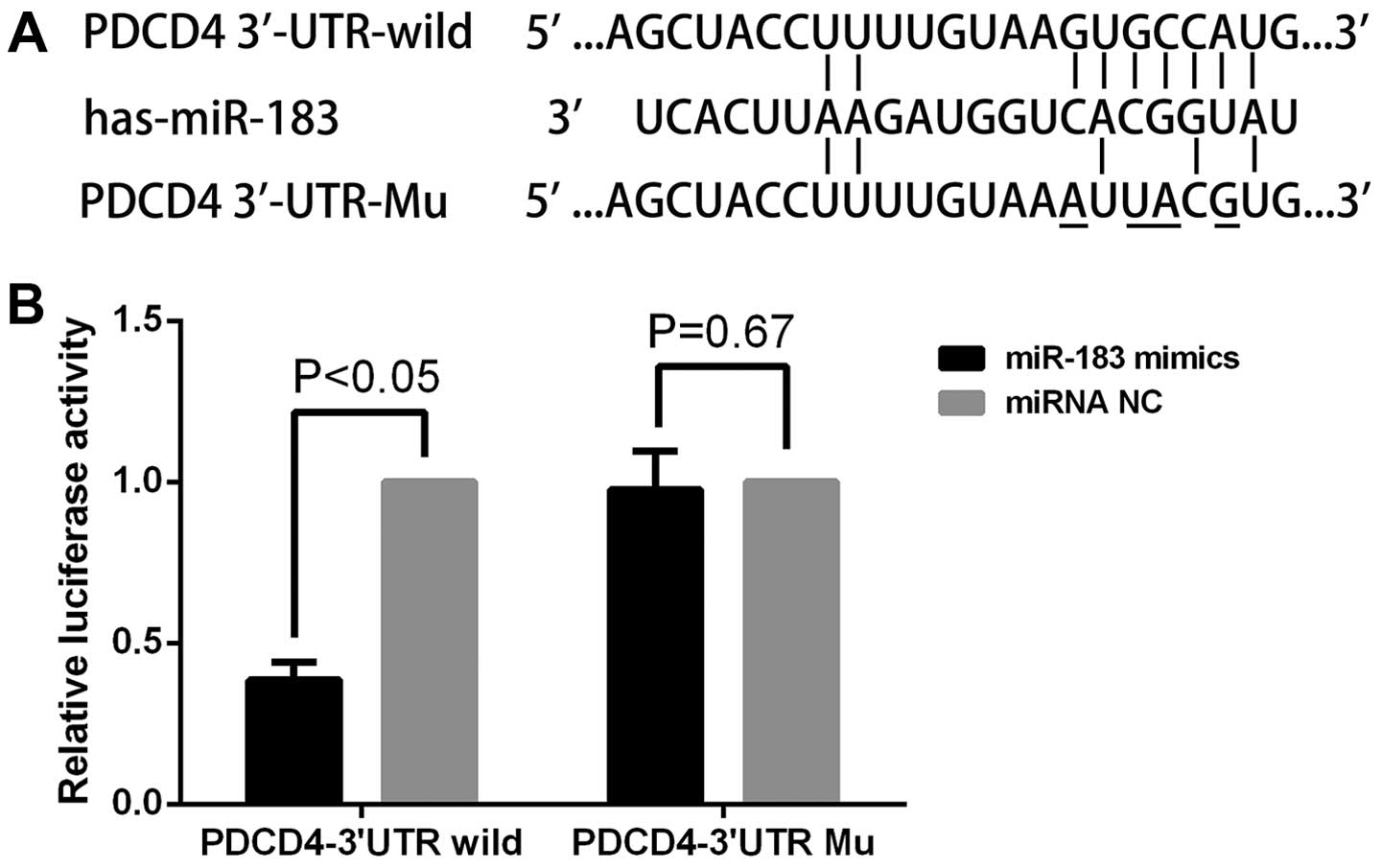
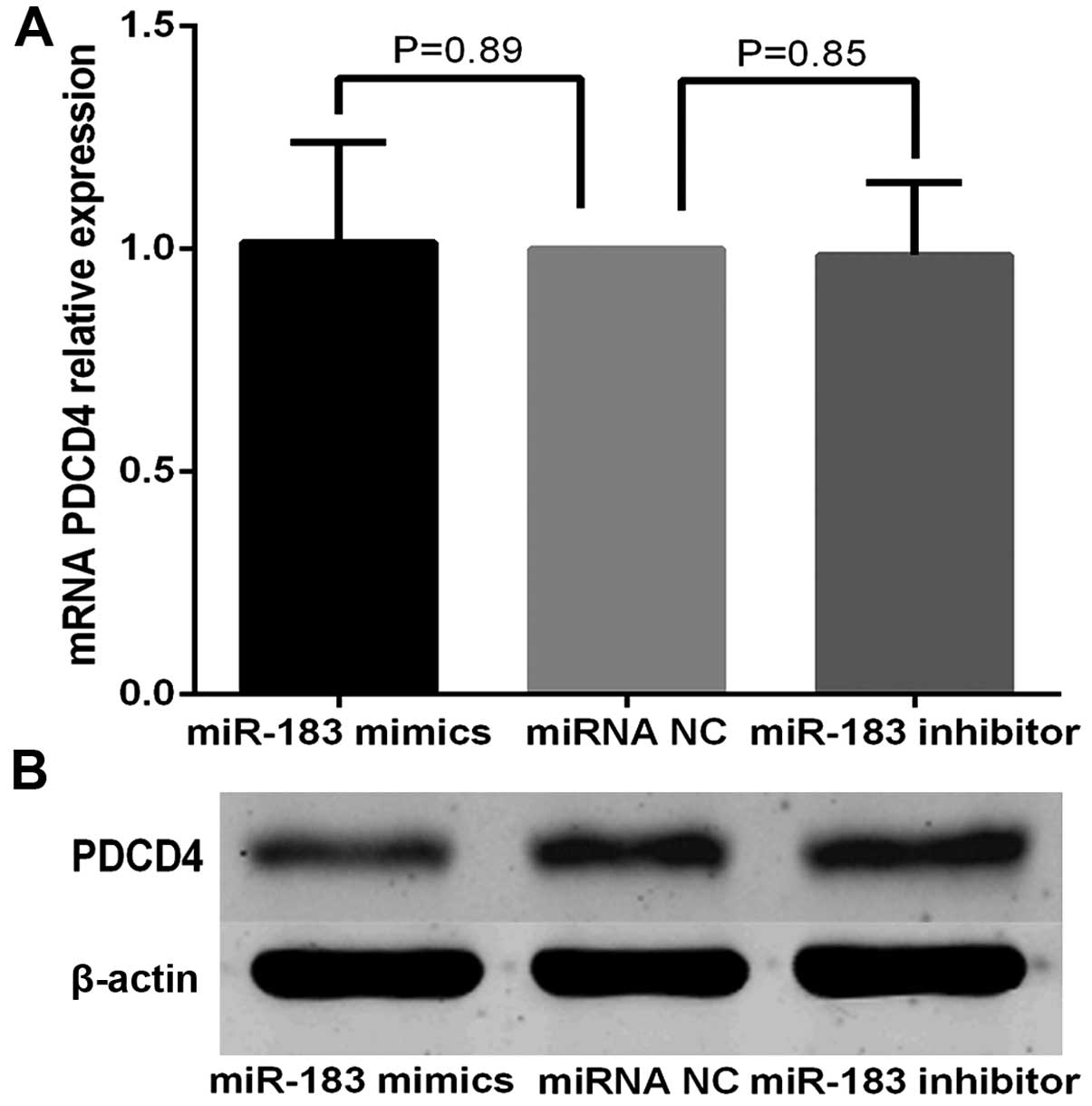
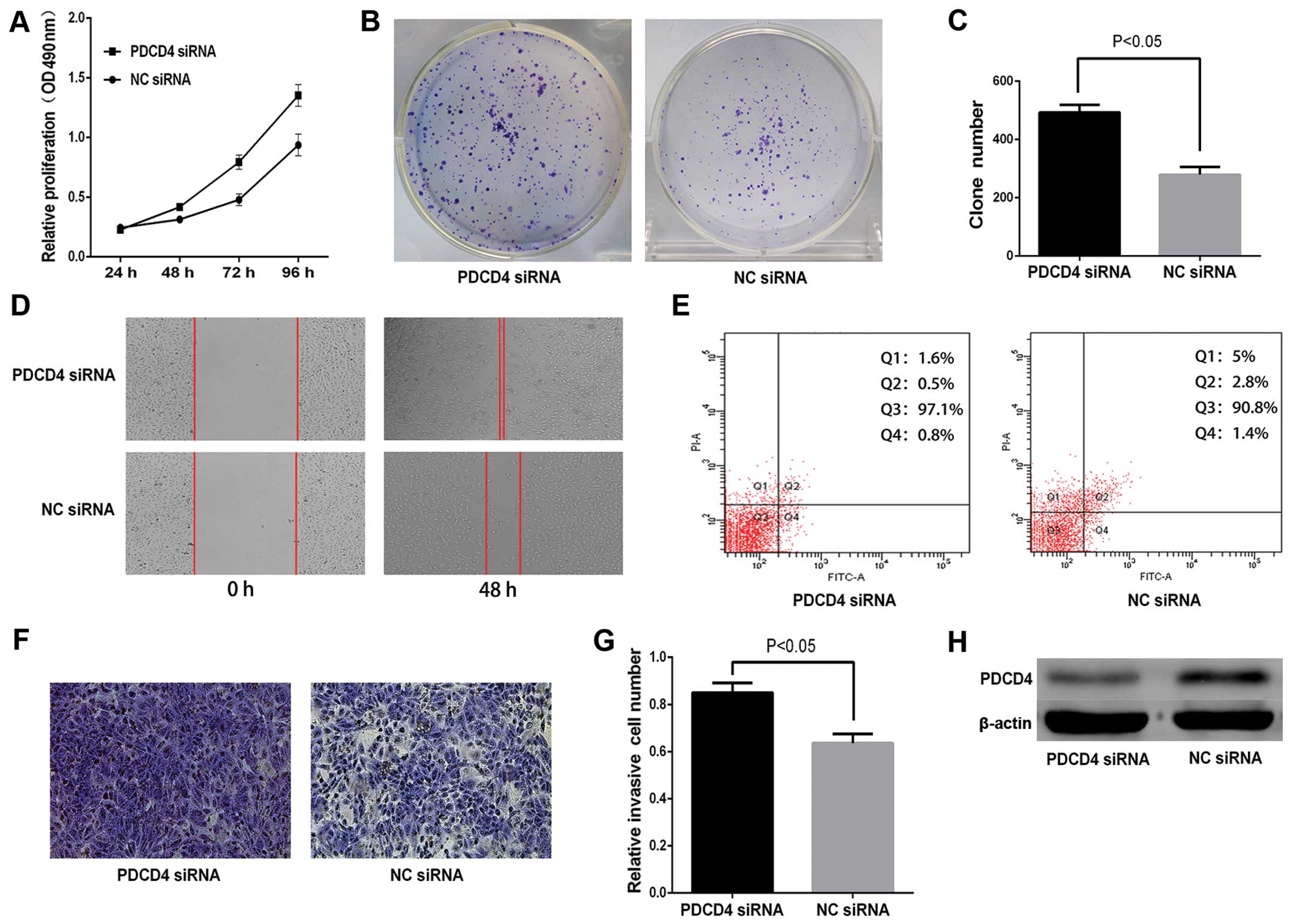
|
1
|
Leenhardt L, Grosclaude P and
Chérié-Challine L: Thyroid Cancer Committee: Increased incidence of
thyroid carcinoma in France: A true epidemic or thyroid nodule
management effects? Report from the French Thyroid Cancer
Committee. Thyroid. 14:1056–1060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Davies L and Welch HG: Increasing
incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973–2002. JAMA.
295:2164–2167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schmid KW: Molecular pathology of thyroid
tumors. Pathologe. 31(Suppl 2): 229–233. 2010.In German. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin.
62:283–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Loh KC, Greenspan FS, Gee L, Miller TR and
Yeo PP: Pathological tumor-node-metastasis (pTNM) staging for
papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas: A retrospective
analysis of 700 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82:3553–3562.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chi SW, Zang JB, Mele A and Darnell RB:
Argonaute HiTS-CLiP decodes microRNA-mRNA interaction maps. Nature.
460:479–486. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hale BJ, Yang CX and Ross JW: Small RNA
regulation of reproductive function. Mol Reprod Dev. 81:148–159.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vohradsky J, Panek J and Vomastek T:
Numerical modelling of microRNA-mediated mRNA decay identifies
novel mechanism of microRNA controlled mRNA downregulation. Nucleic
Acids Res. 38:4579–4585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chu C and Zhao Z: MicroRNA in the
molecular mechanism of the circadian clock in mammals. Front
Biosci. 18:441–446. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer.
94:776–780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dykxhoorn DM: MicroRNAs and metastasis:
Little RNAs go a long way. Cancer Res. 70:6401–6406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao Y, Wang C, Shan Z, Guan H, Mao J, Fan
C, Wang H, Zhang H and Teng W: miRNA expression in a human
papillary thyroid carcinoma cell line varies with invasiveness.
Endocr J. 57:81–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Menon MP and Khan A: Micro-RNAs in thyroid
neoplasms: Molecular, diagnostic and therapeutic implications. J
Clin Pathol. 62:978–985. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nikiforova MN, Chiosea SI and Nikiforov
YE: MicroRNA expression profiles in thyroid tumors. Endocr Pathol.
20:85–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Srivastava A, Goldberger H, Dimtchev A,
Ramalinga M, Chijioke J, Mrian C, Oermann EK, Uhm S, Kim JS, Chen
LN, et al: MicroRNA profiling in prostate cancer - the diagnostic
potential of urinary miR-205 and miR-214. PLoS One. 8:e769942013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Hodge LS, Elsawa SF, Grote DM,
Price-Troska TL, Asmann YW, Fonseca R, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Novak
AJ and Ansell SM: MicroRNA expression in tumor cells from
Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia reflects both their normal and
malignant cell counterparts. Blood Cancer J. 1:e242011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tetzlaff MT, Liu A, Xu X, Master SR,
Baldwin DA, Tobias JW, Livolsi VA and Baloch ZW: Differential
expression of miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinoma compared to
multinodular goiter using formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues.
Endocr Pathol. 18:163–173. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pallante P, Visone R, Ferracin M, Ferraro
A, Berlingieri MT, Troncone G, Chiappetta G, Liu CG, Santoro M,
Negrini M, et al: MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary
carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:497–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Stark C and
Colburn NH: Characterization of programmed cell death 4 in multiple
human cancers reveals a novel enhancer of drug sensitivity. Mol
Cancer Ther. 3:103–110. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Göke R, Barth P, Schmidt A, Samans B and
Lankat-Buttgereit B: Programmed cell death protein 4 suppresses
CDK1/cdc2 via induction of p21Waf1/Cip1. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 287:C1541–C1546. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vikhreva PN, Shepelev MV, Korobko EV and
Korobko IV: Pdcd4 tumor suppressor: Properties, functions, and
their application to oncology. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 2:3–11.
2010.In Russian.
|
|
27
|
Young MR, Santhanam AN, Yoshikawa N and
Colburn NH: Have tumor suppressor PDCD4 and its counteragent
oncogenic miR-21 gone rogue? Mol Interv. 10:76–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Allgayer H: Pdcd4, a colon cancer
prognostic that is regulated by a microRNA. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
73:185–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fassan M, Pizzi M, Battaglia G, Giacomelli
L, Parente P, Bocus P, Ancona E and Rugge M: Programmed cell death
4 (PDCD4) expression during multistep Barrett’s carcinogenesis. J
Clin Pathol. 63:692–696. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fassan M, Pizzi M, Giacomelli L, Mescoli
C, Ludwig K, Pucciarelli S and Rugge M: PDCD4 nuclear loss
inversely correlates with miR-21 levels in colon carcinogenesis.
Virchows Arch. 458:413–419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fassan M, Realdon S, Pizzi M, Balistreri
M, Battaglia G, Zaninotto G, Ancona E and Rugge M: Programmed cell
death 4 nuclear loss and miR-21 or activated Akt overexpression in
esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis. Dis Esophagus. 25:263–268.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Liu Y, Fan Y, Liu Z, Wang
X, Yuan Q, Yin Y, Yu J, Zhu M, et al: MicroRNA-21 regulates
biological behaviors in papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting
programmed cell death 4. J Surg Res. 189:68–74. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pennelli G, Fassan M, Mian C, Pizzi M,
Balistreri M, Barollo S, Galuppini F, Guzzardo V, Pelizzo M and
Rugge M: PDCD4 expression in thyroid neoplasia. Virchows Arch.
462:95–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li J, Fu H, Xu C, Tie Y, Xing R, Zhu J,
Qin Y, Sun Z and Zheng X: miR-183 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced
apoptosis by downregulation of PDCD4 expression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 10:3542010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ren LH, Chen WX, Li S, He XY, Zhang ZM, Li
M, Cao RS, Hao B, Zhang HJ, Qiu HQ, et al: MicroRNA-183 promotes
proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
by targeting programmed cell death 4. Br J Cancer. 111:2003–2013.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bastian BC, LeBoit PE, Hamm H, Bröcker EB
and Pinkel D: Chromosomal gains and losses in primary cutaneous
melanomas detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer
Res. 58:2170–2175. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sarver AL, Li L and Subramanian S:
MicroRNA miR-183 functions as an oncogene by targeting the
transcription factor EGR1 and promoting tumor cell migration.
Cancer Res. 70:9570–9580. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mihelich BL, Khramtsova EA, Arva N,
Vaishnav A, Johnson DN, Giangreco AA, Martens-Uzunova E, Bagasra O,
Kajdacsy-Balla A and Nonn L: miR-183-96-182 cluster is
overexpressed in prostate tissue and regulates zinc homeostasis in
prostate cells. J Biol Chem. 286:44503–44511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Deng G,
Tanaka Y, Tabatabai ZL and Hinoda Yand Dahiya R: microRNA-183 is an
oncogene targeting Dkk-3 and SMAD4 in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer.
108:1659–1667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang G, Mao W and Zheng S: MicroRNA-183
regulates Ezrin expression in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
582:3663–3668. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mu Y, Zhang H, Che L and Li K: Clinical
significance of microRNA-183/Ezrin axis in judging the prognosis of
patients with osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 31:8212014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhu J, Feng Y, Ke Z, Yang Z, Zhou J, Huang
X and Wang L: Down-regulation of miR-183 promotes migration and
invasion of osteosarcoma by targeting Ezrin. Am J Pathol.
180:2440–2451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Dwyer RM and Kerin
MJ: Dysregulated miR-183 inhibits migration in breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 10:5022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tsuchiyama K, Ito H, Taga M, Naganuma S,
Oshinoya Y, Nagano K, Yokoyama O and Itoh H: Expression of
microRNAs associated with Gleason grading system in prostate
cancer: miR-182-5p is a useful marker for high grade prostate
cancer. Prostate. 73:827–834. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner
I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F, Miller K, Lein M, Kristiansen G and Jung
K: Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010.
|
|
47
|
Larne O, Martens-Uzunova E, Hagman Z,
Edsjö A, Lippolis G, den Berg MS, Bjartell A, Jenster G and Ceder
Y: miQ - a novel microRNA based diagnostic and prognostic tool for
prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:2867–2875. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Goeppert B, Schmezer P, Dutruel C, Oakes
C, Renner M, Breinig M, Warth A, Vogel MN, Mittelbronn M, Mehrabi
A, et al: Down-regulation of tumor suppressor A kinase anchor
protein 12 in human hepatocarcinogenesis by epigenetic mechanisms.
Hepatology. 52:2023–2033. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu AM, Yao TJ, Wang W, Wong KF, Lee NP,
Fan ST, Poon RT, Gao C and Luk JM: Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b
in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular
carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2:e0008252012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liang Z, Gao Y, Shi W, Zhai D, Li S, Jing
L, Guo H, Liu T, Wang Y and Du Z: Expression and significance of
microRNA-183 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci World J.
2013:3818742013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Sarver AL, French AJ, Borralho PM,
Thayanithy V, Oberg AL, Silverstein KA, Morlan BW, Riska SM,
Boardman LA, Cunningham JM, et al: Human colon cancer profiles show
differential microRNA expression depending on mismatch repair
status and are characteristic of undifferentiated proliferative
states. BMC Cancer. 9:4012009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Takatsuno Y, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Uetake H, Sugihara K and Mori M: Over- and
under-expressed microRNAs in human colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
34:1069–1075. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Earle JS, Luthra R, Romans A, Abraham R,
Ensor J, Yao H and Hamilton SR: Association of microRNA expression
with microsatellite instability status in colorectal
adenocarcinoma. J Mol Diagn. 12:433–440. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li X, Zhang G, Luo F, Ruan J, Huang D,
Feng D, Xiao D, Zeng Z, Chen X and Wu W: Identification of
aberrantly expressed miRNAs in rectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 28:77–84.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mian C, Pennelli G, Fassan M, Balistreri
M, Barollo S, Cavedon E, Galuppini F, Pizzi M, Vianello F, Pelizzo
MR, et al: microRNA profiles in familial and sporadic medullary
thyroid carcinoma: Preliminary relationships with RET status and
outcome. Thyroid. 22:890–896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhao H, Guo M, Zhao G, Ma Q, Ma B, Qiu X
and Fan Q: miR-183 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma via
downregulation of the expression of Ezrin in F5M2 cells. Int J Mol
Med. 30:1013–1020. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li J, Liang SH and Lu X: Potential role of
ezrin and its related microRNA in ovarian cancer invasion and
metastasis. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 45:787–792. 2010.in
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang J, Wang X, Li Z, Liu H and Teng Y:
microRNA-183 suppresses retinoblastoma cell growth, invasion and
migration by targeting LRP6. FEBS J. 281:1355–1365. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Tanaka H, Sasayama T, Tanaka K, Nakamizo
S, Nishihara M, Mizukawa K, Kohta M, Koyama J, Miyake S, Taniguchi
M, et al: microRNA-183 upregulates HiF-1α by targeting isocitrate
dehydrogenase 2 (iDH2) in glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 111:273–283.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Li G, Luna C, Qiu J, Epstein DL and
Gonzalez P: Targeting of integrin beta1 and kinesin 2alpha by
microRNA 183. J Biol Chem. 285:5461–5471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Li J, Liang S, Jin H, Xu C, Ma D and Lu X:
Tiam1, negatively regulated by miR-22, miR-183 and miR-31, is
involved in migration, invasion and viability of ovarian cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1835–1842. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Soejima H, Miyoshi O, Yoshinaga H, Masaki
Z, Ozaki I, Kajiwara S, Niikawa N, Matsuhashi S and Mukai T:
Assignment of the programmed cell death 4 gene (PDCD4) to human
chromosome band 10q24 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell
Genet. 87:113–114. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Cmarik JL, Min H, Hegamyer G, Zhan S,
Kulesz-Martin M, Yoshinaga H, Matsuhashi S and Colburn NH:
Differentially expressed protein Pdcd4 inhibits tumor
promoter-induced neoplastic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:14037–14042. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Young MR, Yang HS and Colburn NH:
Promising molecular targets for cancer prevention: AP-1, NF-kappa B
and Pdcd4. Trends Mol Med. 9:36–41. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Afonja O, Juste D, Das S, matsuhashi S and
Samuels HH: Induction of PDCD4 tumor suppressor gene expression by
RAR agonists, antiestrogen and HER-2/neu antagonist in breast
cancer cells. Evidence for a role in apoptosis. Oncogene.
23:8135–8145. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Hamajima H,
Yasutake T, Eguchi Y, Ideguchi H, Yamamoto K and Matsuhashi S:
Involvement of programmed cell death 4 in transforming growth
factorbeta1-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncogene. 25:6101–6112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
Lindow M, Krogh A and Lund AH: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:1026–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S and mo
YY: MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and
metastasis. Cell Res. 18:350–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM,
Ramos KS, Colburn NH and Li Y: MicroRNA-21 promotes cell
transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene.
Oncogene. 27:4373–4379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R, Sato
N, Imamura Y, Nagai Y, Yoshida N, Toyama E, Hayashi N, Watanabe M,
et al: MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1915–1922.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Göke A, Göke R, Knolle A, Trusheim H,
Schmidt H, Wilmen A, Carmody R, Göke B and Chen YH: DUG is a novel
homologue of translation initiation factor 4G that binds eIF4A.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 297:78–82. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Komar AA, Zheng X,
Merrick WC, Costes S, Lockett SJ, Sonenberg N and Colburn NH: The
transformation suppressor Pdcd4 is a novel eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 4A binding protein that inhibits translation. Mol
Cell Biol. 23:26–37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Leupold JH, Yang HS, Colburn NH, Asangani
I, Post S and Allgayer H: Tumor suppressor Pdcd4 inhibits
invasion/intravasation and regulates urokinase receptor (u-PAR)
gene expression via Sp-transcription factors. Oncogene.
26:4550–4562. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lankat-Buttgereit B, Gregel C, Knolle A,
Hasilik A, Arnold R and Göke R: Pdcd4 inhibits growth of tumor
cells by suppression of carbonic anhydrase type II. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 214:149–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang WQ, Zhang H, Wang HB, Sun YG, Peng
ZH, Zhou G, Yang SM, Wang RQ and Fang DC: Programmed cell death 4
(PDCD4) enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Mol Diagn Ther. 14:155–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang Q, Sun Z and Yang HS: Downregulation
of tumor suppressor Pdcd4 promotes invasion and activates both
betacatenin/Tcf and AP-1-dependent transcription in colon carcinoma
cells. Oncogene. 27:1527–1535. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Zhang Z and DuBois RN: Detection of
differentially expressed genes in human colon carcinoma cells
treated with a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Oncogene. 20:4450–4456.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang Y, Meng H, Peng Q, Yang X, Gan R,
Zhao L, Chen Z, Lu J and Meng QH: Downregulation of microRNA-21
expression restrains non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation
and migration through upregulation of programmed cell death 4.
Cancer Gene Ther. 22:23–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Luo F, Ji J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zheng G, Jing J,
Wang B, Xu W, Shi L, Lu X, et al: MicroRNA-21, up-regulated by
arsenite, directs the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
enhances the invasive potential of transformed human bronchial
epithelial cells by targeting PDCD4. Toxicol Lett. 232:301–309.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|