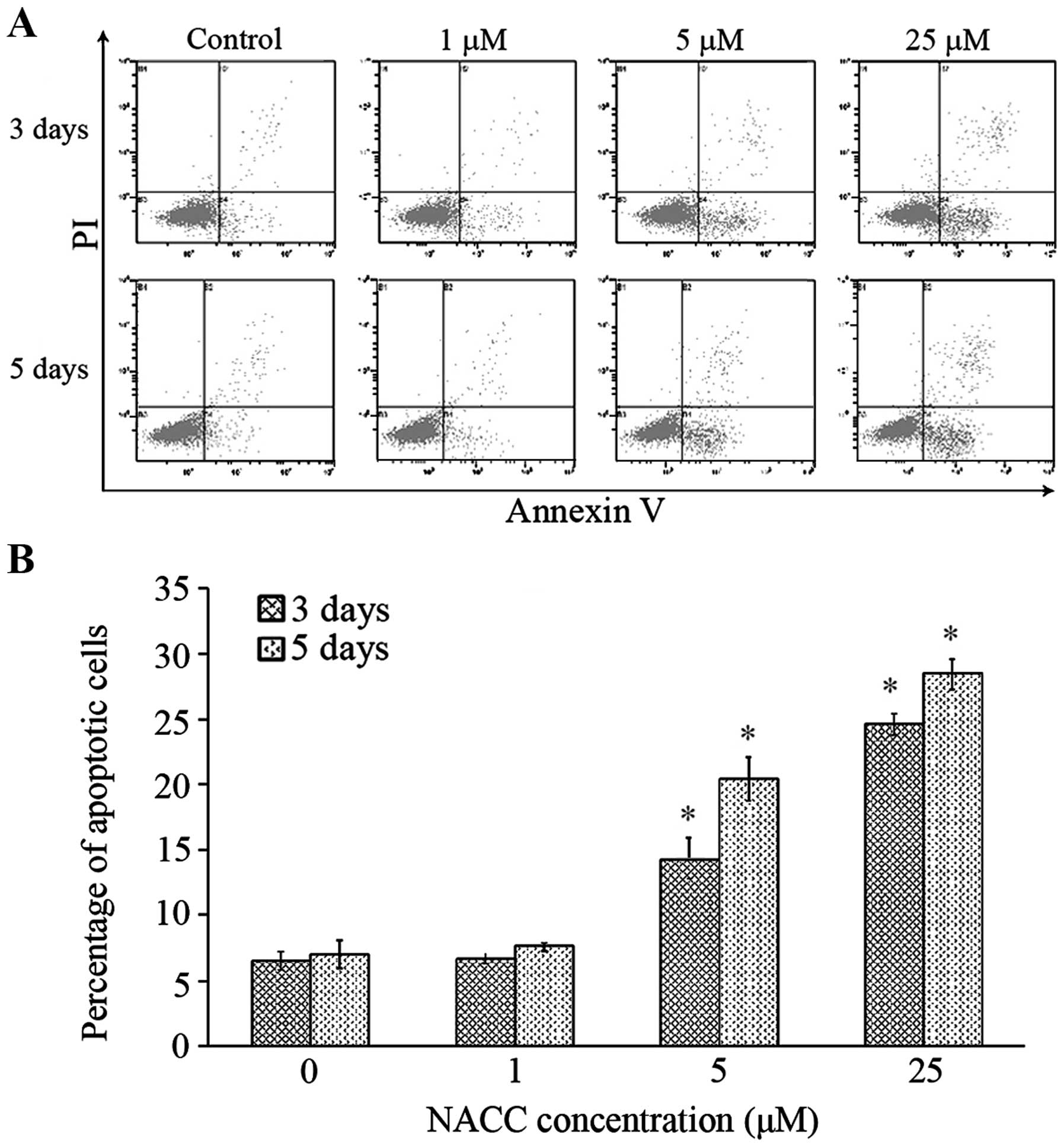
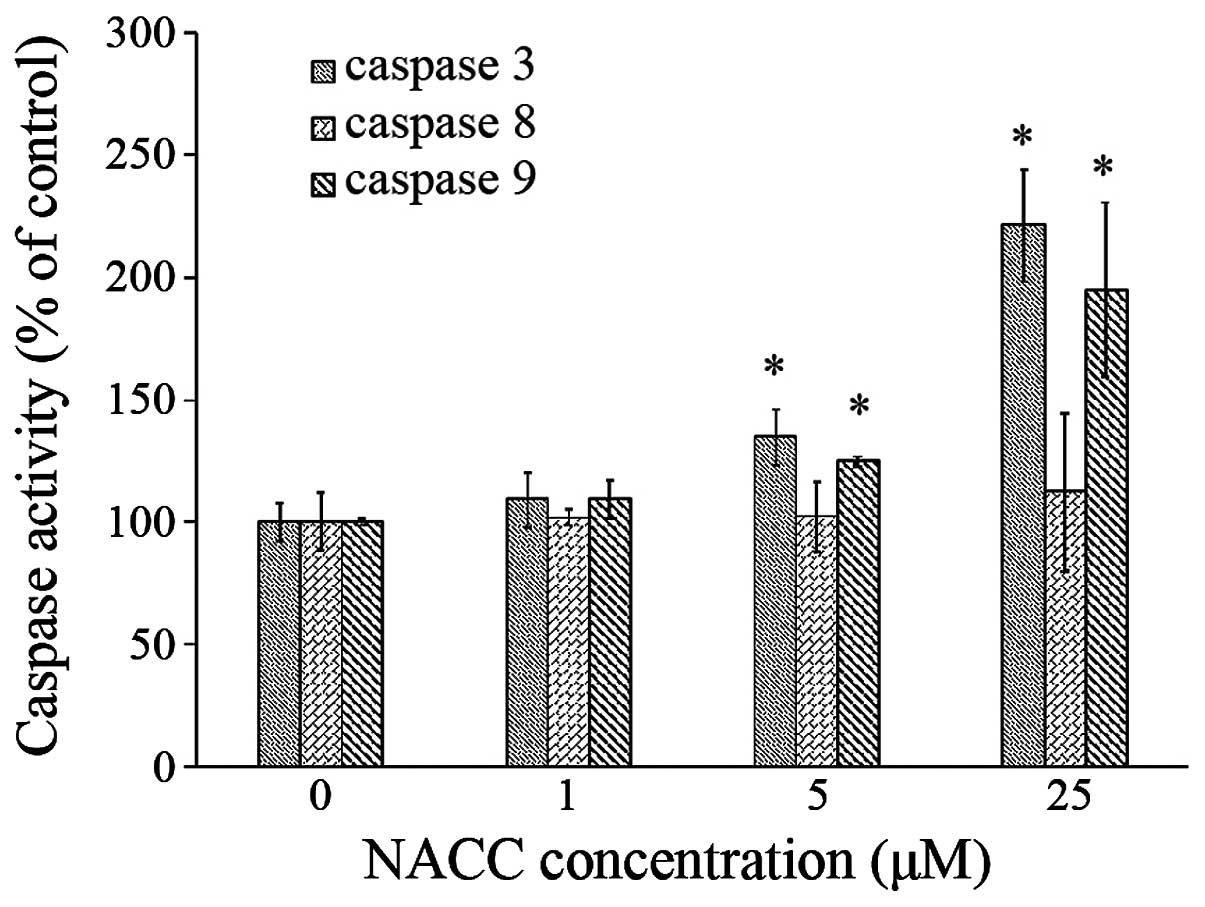
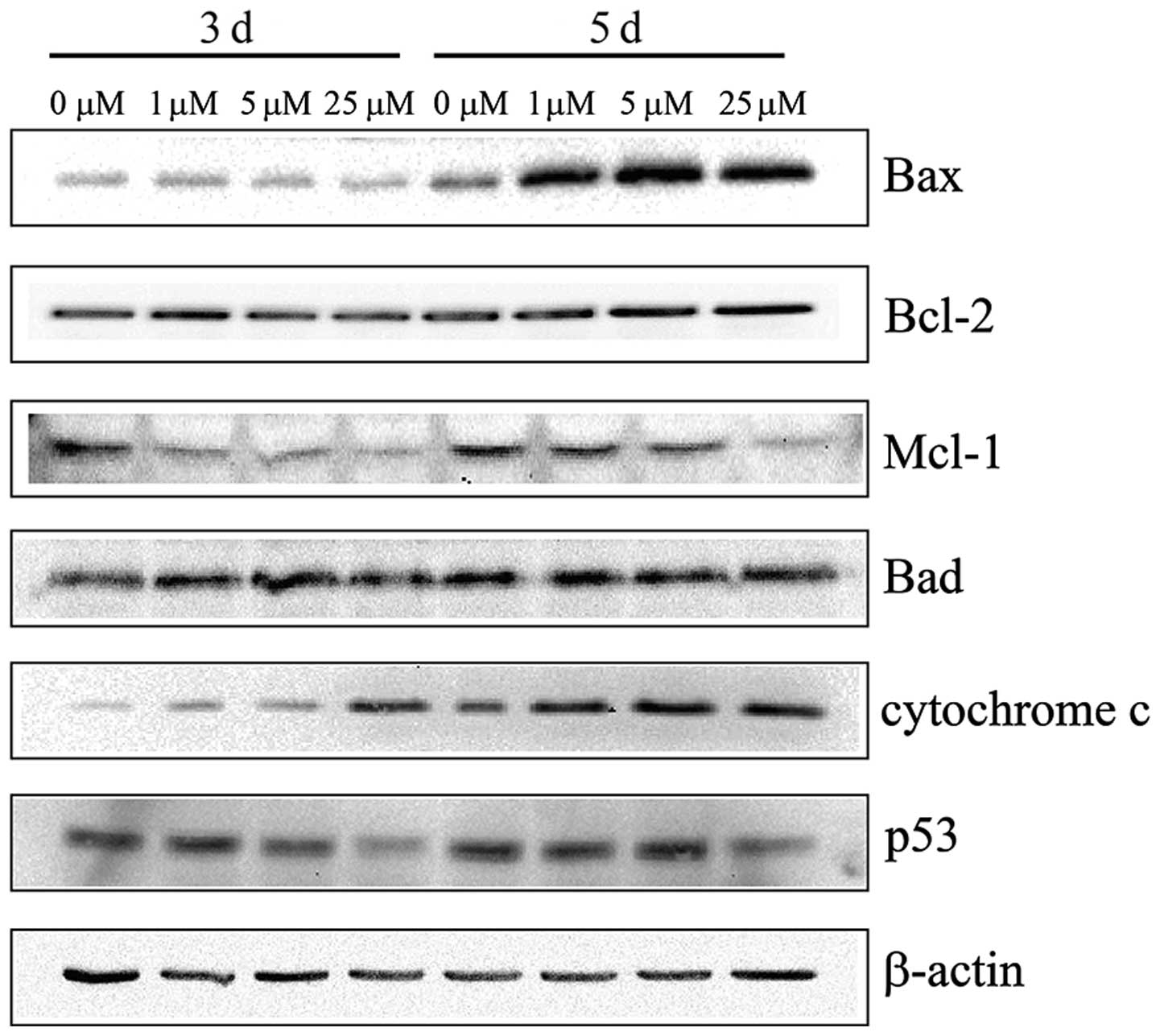
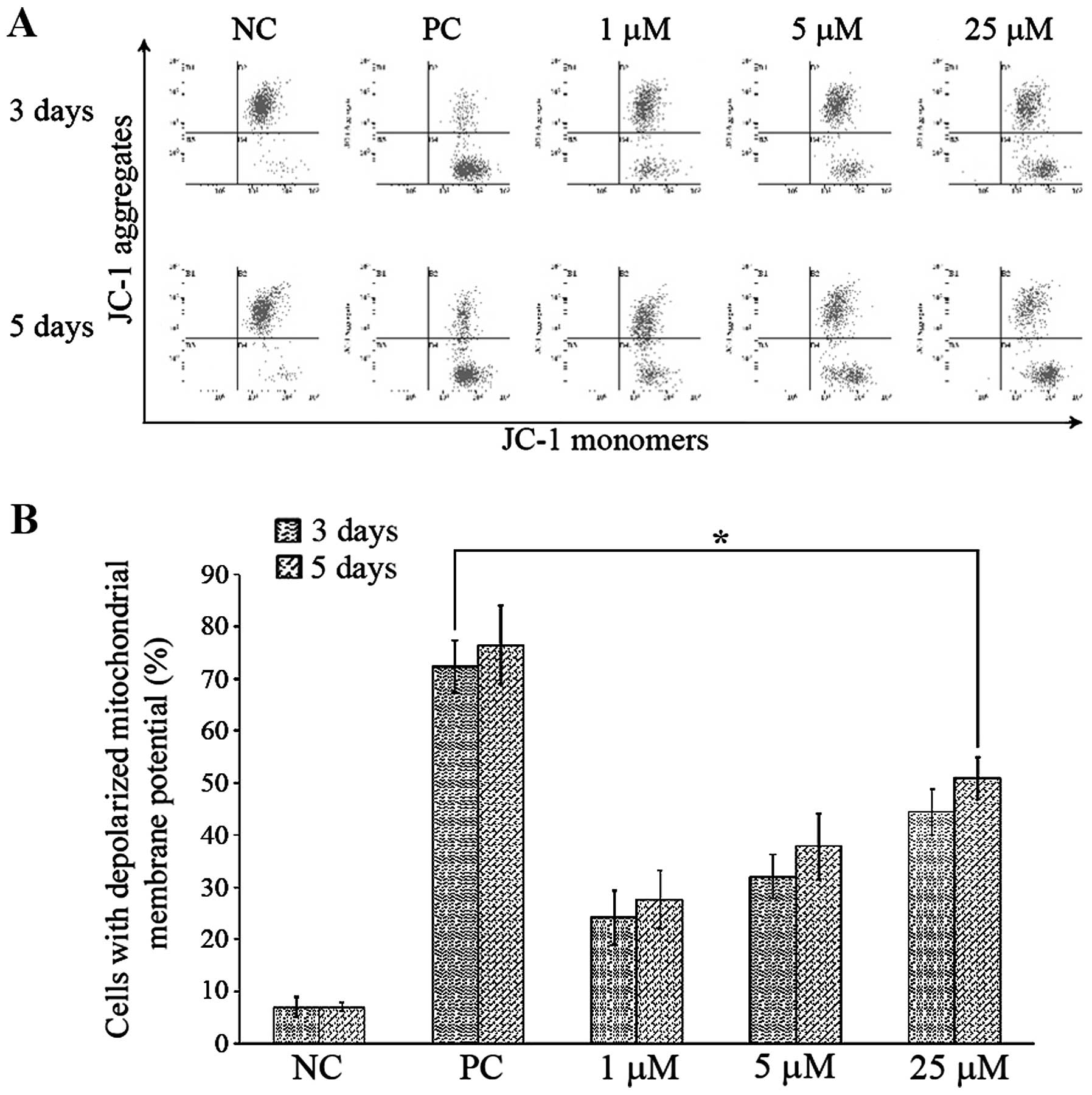
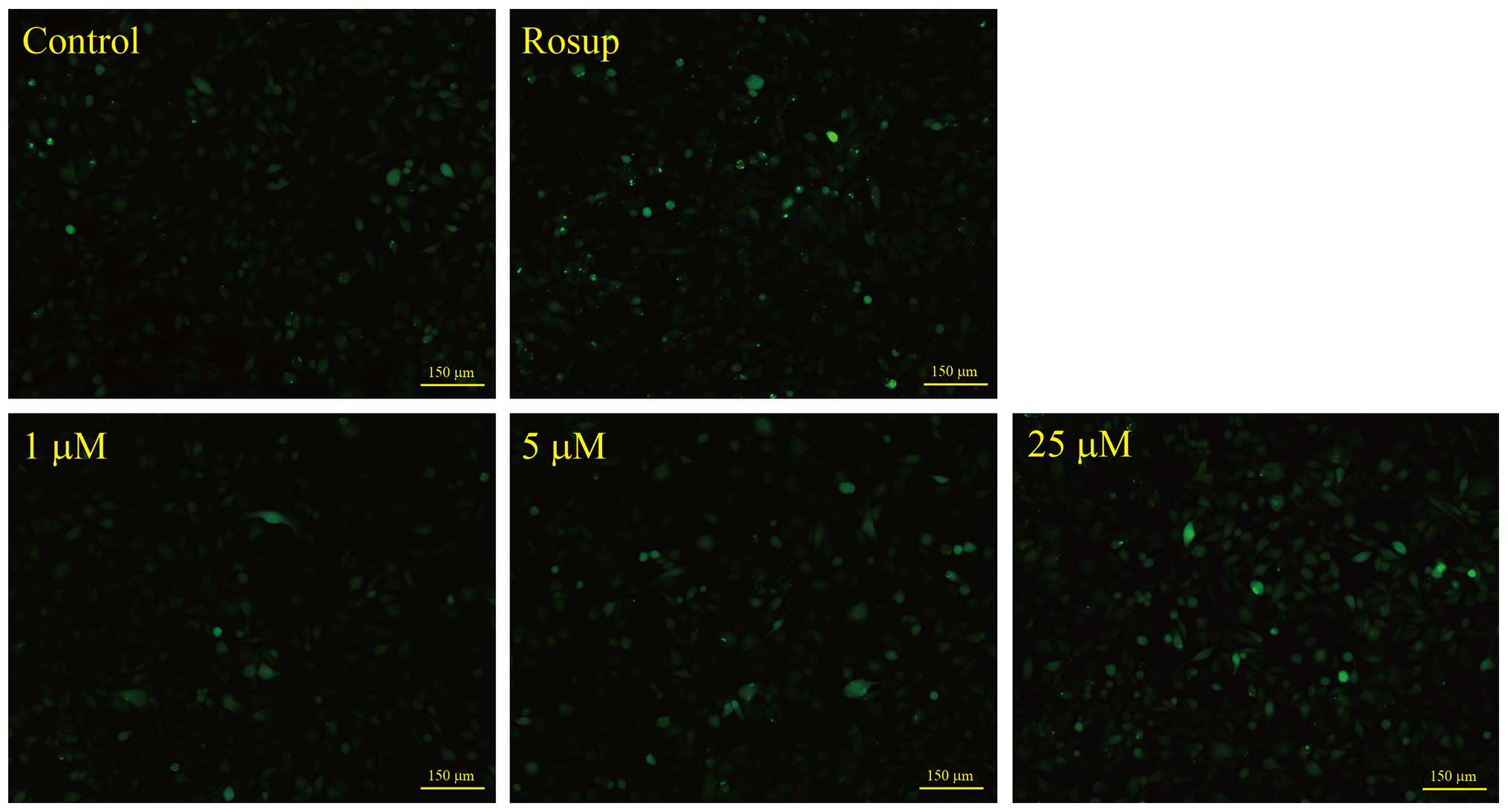
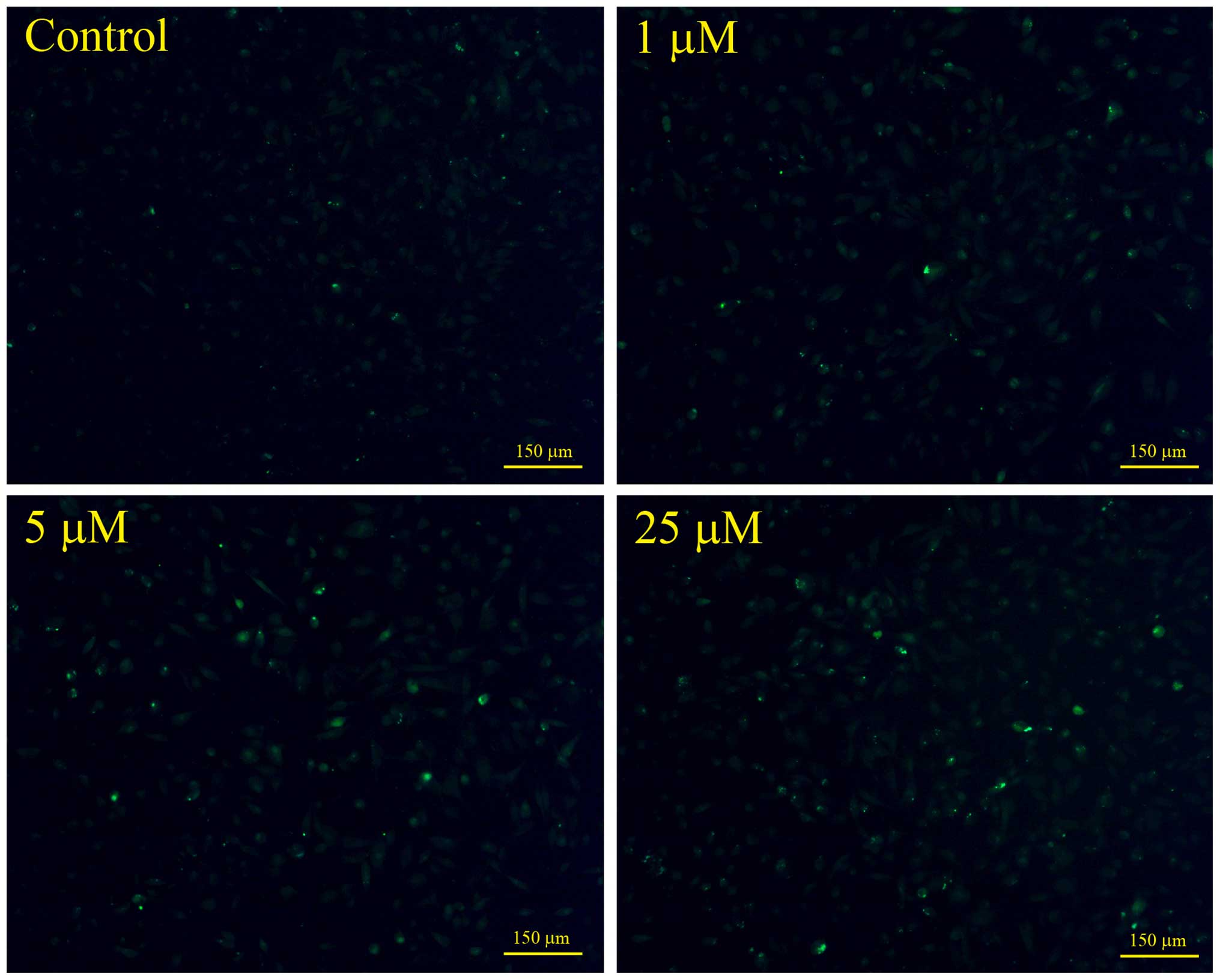
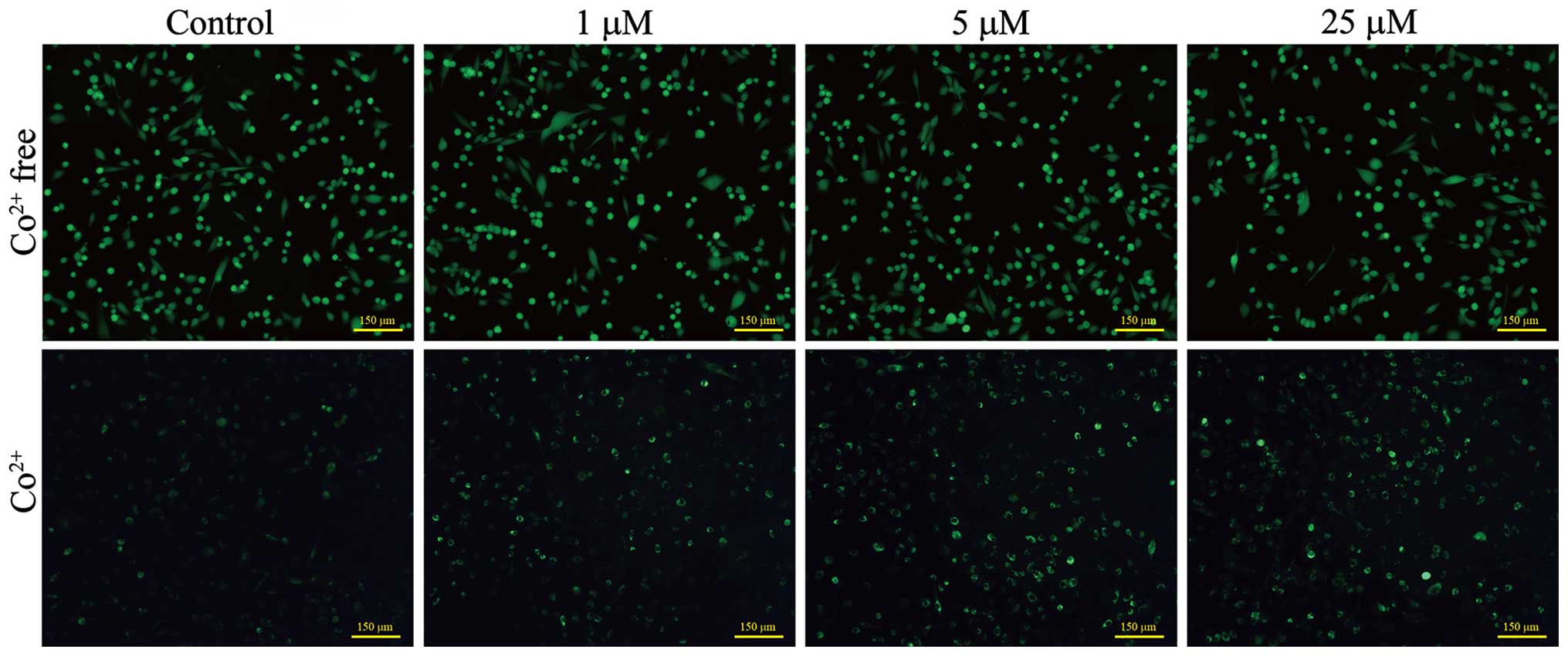
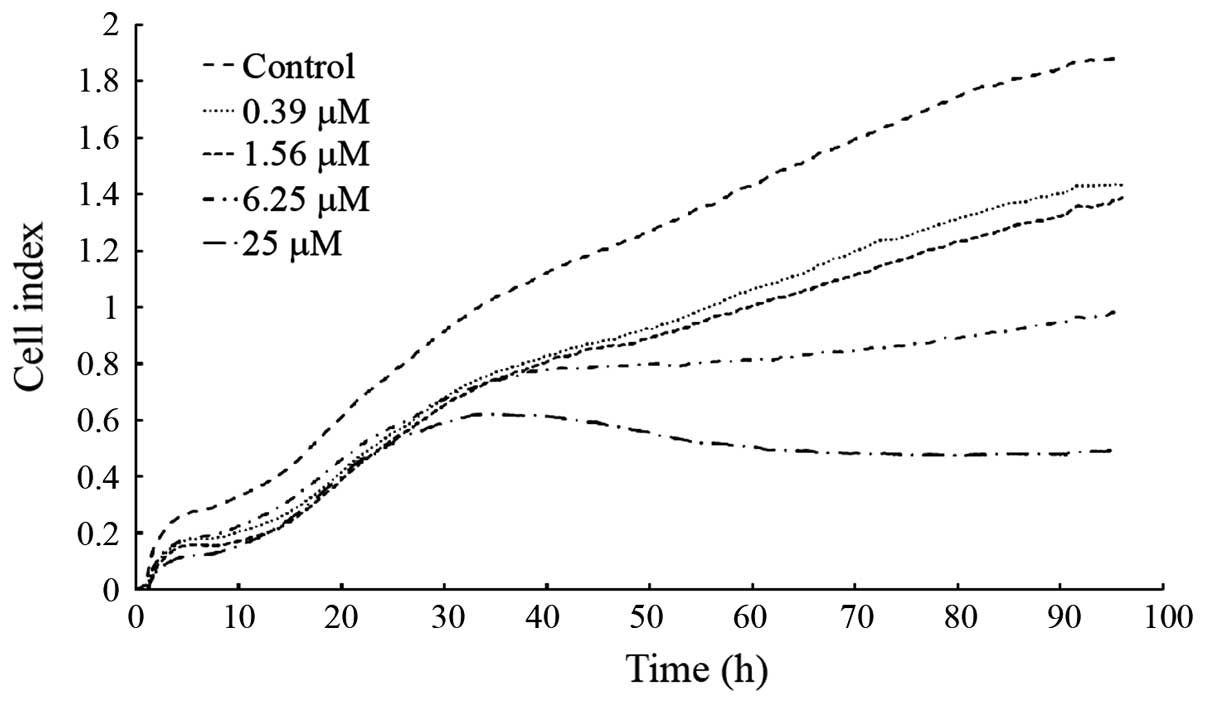
|
1
|
Markovic SN, Erickson LA, Rao RD, Weenig
RH, Pockaj BA, Bardia A, Vachon CM, Schild SE, McWilliams RR, Hand
JL, et al Melanoma Study Group of the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center:
Malignant melanoma in the 21st century, part 1: Epidemiology, risk
factors, screening, prevention, and diagnosis. Mayo Clin Proc.
82:364–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gogas HJ, Kirkwood JM and Sondak VK:
Chemotherapy for metastatic melanoma: Time for a change? Cancer.
109:455–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bergomi M, Pellacani G, Vinceti M,
Bassissi S, Malagoli C, Alber D, Sieri S, Vescovi L, Seidenari S
and Vivoli R: Trace elements and melanoma. J Trace Elem Med Biol.
19:69–73. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Vries E, Houterman S, Janssen-Heijnen
ML, Nijsten T, van de Schans SA, Eggermont AM and Coebergh JW:
Up-to-date survival estimates and historical trends of cutaneous
malignant melanoma in the south-east of The Netherlands. Ann Oncol.
18:1110–1116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang J, Amiri KI, Burke JR, Schmid JA and
Richmond A: BMS-345541 targets inhibitor of kappaB kinase and
induces apoptosis in melanoma: Involvement of nuclear factor kappaB
and mitochondria pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 12:950–960. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu WP, Yu HS, Sung PJ, Tsai FY, Shen YK,
Chang LS and Wang JJ: DC-81-Indole conjugate agent induces
mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human melanoma A375 cells. Chem
Res Toxicol. 20:905–912. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim R: Recent advances in understanding
the cell death pathways activated by anticancer therapy. Cancer.
103:1551–1560. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jana S, Paul S and Swarnakar S: Curcumin
as anti-endometriotic agent: Implication of MMP-3 and intrinsic
apoptotic pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:797–804. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang X and Wang X: Cytochrome c-mediated
apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:87–106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL and
Mignotte B: The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 942:157–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rizzuto R, Pinton P, Ferrari D, Chami M,
Szabadkai G, Magalhães PJ, Di Virgilio F and Pozzan T: Calcium and
apoptosis: Facts and hypotheses. Oncogene. 22:8619–8627. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen W, Seefeldt T, Young A, Zhang X and
Guan X: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of
N-acetyl-S-(p-chloro phenylcarbamoyl)cysteine and its analogs as a
novel class of anticancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 19:287–294.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Cheng J, Tang W, Su Z, Guo J, Tong L and
Wei Q: Calcineurin subunit B promotes TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis
by binding to mitochondria and causing mitochondrial
Ca2+ overload. Cancer Lett. 321:169–178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong YY, Si XM, Lin L and Lu J: Mechanisms
of cholecystokinin-induced calcium mobilization in gastric antral
interstitial cells of Cajal. World J Gastroenterol. 18:7184–7193.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gautier CA, Giaime E, Caballero E, Núñez
L, Song Z, Chan D, Villalobos C and Shen J: Regulation of
mitochondrial permeability transition pore by PINK1. Mol
Neurodegener. 7:222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eisenberg MC, Kim Y, Li R, Ackerman WE,
Kniss DA and Friedman A: Mechanistic modeling of the effects of
myoferlin on tumor cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:20078–20083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ichas F and Mazat JP: From calcium
signaling to cell death: Two conformations for the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. Switching from low- to
high-conductance state. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1366:33–50. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE,
Didelot C and Kroemer G: Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from
mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 13:1423–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Petronilli V, Miotto G, Canton M, Colonna
R, Bernardi P and Di Lisa F: Imaging the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore in intact cells. Biofactors. 8:263–272. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hüser J, Rechenmacher CE and Blatter LA:
Imaging the permeability pore transition in single mitochondria.
Biophys J. 74:2129–2137. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsao H, Chin L, Garraway LA and Fisher DE:
Melanoma: From mutations to medicine. Genes Dev. 26:1131–1155.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li X, Wu D, Shen J, Zhou M and Lu Y:
Rapamycin induces autophagy in the melanoma cell line M14 via
regulation of the expression levels of Bcl-2 and Bax. Oncol Lett.
5:167–172. 2013.
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Yu CH, Zhao XL, Wang Y, Jiang SG
and Gong XF: Econazole nitrate induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells via
mitochondrial and caspase pathways. Iran J Pharm Res. 13:1327–1334.
2014.
|
|
24
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bi MC, Rosen R, Zha RY, McCormick SA, Song
E and Hu DN: Zeaxanthin induces apoptosis in human uveal melanoma
cells through Bcl-2 family proteins and intrinsic apoptosis
pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2050822013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsumoto A, Isomoto H, Nakayama M,
Hisatsune J, Nishi Y, Nakashima Y, Matsushima K, Kurazono H, Nakao
K, Hirayama T, et al: Helicobacter pylori VacA reduces the cellular
expression of STAT3 and pro-survival Bcl-2 family proteins, Bcl-2
and Bcl-XL, leading to apoptosis in gastric epithelial cells. Dig
Dis Sci. 56:999–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Robertson JD and Orrenius S: Molecular
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by cytotoxic chemicals. Crit Rev
Toxicol. 30:609–627. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Xie M, Song T, Sheng H, Yu X and
Zhang Z: A novel BH3 mimetic efficiently induces apoptosis in
melanoma cells through direct binding to anti-apoptotic Bcl-2
family proteins, including phosphorylated Mcl-1. Pigment Cell
Melanoma Res. 28:161–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Amaral JD, Xavier JM, Steer CJ and
Rodrigues CM: The role of p53 in apoptosis. Discov Med. 9:145–152.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bykov VJ, Issaeva N, Selivanova G and
Wiman KG: Mutant p53-dependent growth suppression distinguishes
PRIMA-1 from known anticancer drugs: A statistical analysis of
information in the National Cancer Institute database.
Carcinogenesis. 23:2011–2018. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pradelli LA, Bénéteau M and Ricci JE:
Mitochondrial control of caspase-dependent and -independent cell
death. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1589–1597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luo Y, Li X, Huang X, Wong YS, Chen T,
Zhang Y and Zheng W: 1,4-Diselenophene-1,4-diketone triggers
caspase-dependent apoptosis in human melanoma A375 cells through
induction of mitochondrial dysfunction. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
59:1227–1232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M,
Decaudin D, Macho A, Hirsch T, Susin SA, Petit PX, Mignotte B and
Kroemer G: Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane
potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early
programmed cell death. J Exp Med. 182:367–377. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Su YT, Chang HL, Shyue SK and Hsu SL:
Emodin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells through
a reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:229–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kagan VE, Tyurin VA, Jiang J, Tyurina YY,
Ritov VB, Amoscato AA, Osipov AN, Belikova NA, Kapralov AA, Kini V,
et al: Cytochrome c acts as a cardiolipin oxygenase required for
release of proapoptotic factors. Nat Chem Biol. 1:223–232. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rogalska A, Koceva-Chyła A and Jóźwiak Z:
Aclarubicin-induced ROS generation and collapse of mitochondrial
membrane potential in human cancer cell lines. Chem Biol Interact.
176:58–70. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen W, Jiang Z, Lin N, Zheng Z, Chen Z,
Zhang X and Guan X: Evaluation of
N-acetyl-S-(p-chlorophenylcarbamoyl)cysteine as an irreversible
inhibitor of mammalian thioredoxin reductase1. J Enzyme Inhib Med
Chem. 17:1–7. 2015.
|
|
39
|
Fang J, Lu J and Holmgren A: Thioredoxin
reductase is irreversibly modified by curcumin: A novel molecular
mechanism for its anticancer activity. J Biol Chem.
280:25284–25290. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guan X, Hoffman BN, McFarland DC,
Gilkerson KK, Dwivedi C, Erickson AK, Bebensee S and Pellegrini J:
Glutathione and mercapturic acid conjugates of sulofenur and their
activity against a human colon cancer cell line. Drug Metab Dispos.
30:331–335. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Phelps PC, Jain PT, Berezesky IK, Boder GB
and Trump BF: Sulofenur cytotoxicity and changes in cytosolic
calcium and mitochondrial membrane potential in human colon
adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 88:27–35. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gerasimenko JV, Gerasimenko OV, Palejwala
A, Tepikin AV, Petersen OH and Watson AJ: Menadione-induced
apoptosis: Roles of cytosolic Ca(2+) elevations and the
mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J Cell Sci.
115:485–497. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nakagawa T, Shimizu S, Watanabe T,
Yamaguchi O, Otsu K, Yamagata H, Inohara H, Kubo T and Tsujimoto Y:
Cyclophilin D-dependent mitochondrial permeability transition
regulates some necrotic but not apoptotic cell death. Nature.
434:652–658. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Suh DH, Kim MK, Kim HS, Chung HH and Song
YS: Mitochondrial permeability transition pore as a selective
target for anti-cancer therapy. Front Oncol. 3:412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Marzo I, Brenner C, Zamzami N,
Jürgensmeier JM, Susin SA, Vieira HL, Prévost MC, Xie Z, Matsuyama
S, Reed JC, et al: Bax and adenine nucleotide translocator
cooperate in the mitochondrial control of apoptosis. Science.
281:2027–2031. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chipuk JE, Bouchier-Hayes L and Green DR:
Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: The
innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ. 13:1396–1402. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Toriumi K, Oma Y, Mimoto A, Futai E,
Sasagawa N, Turk B and Ishiura S: Polyalanine tracts directly
induce the release of cytochrome c, independently of the
mitochondrial permeability transition pore, leading to apoptosis.
Genes Cells. 14:751–757. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bonaventure J, Domingues MJ and Larue L:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling the migration of
melanocytes and melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
26:316–325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mahmood DF, Abderrazak A, El Hadri K,
Simmet T and Rouis M: The thioredoxin system as a therapeutic
target in human health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal.
19:1266–1303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Arnér ES and Holmgren A: The thioredoxin
system in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:420–426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|