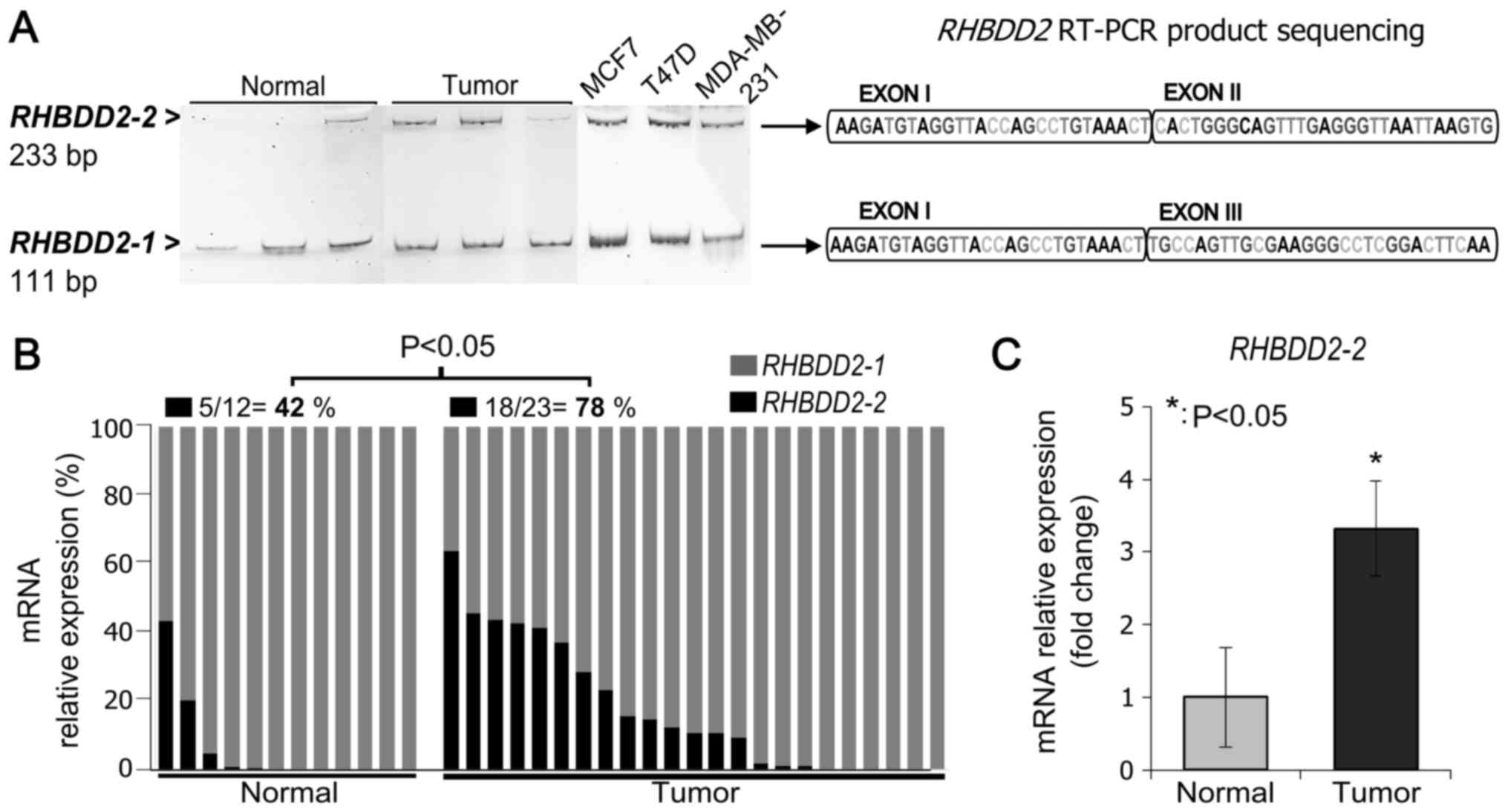
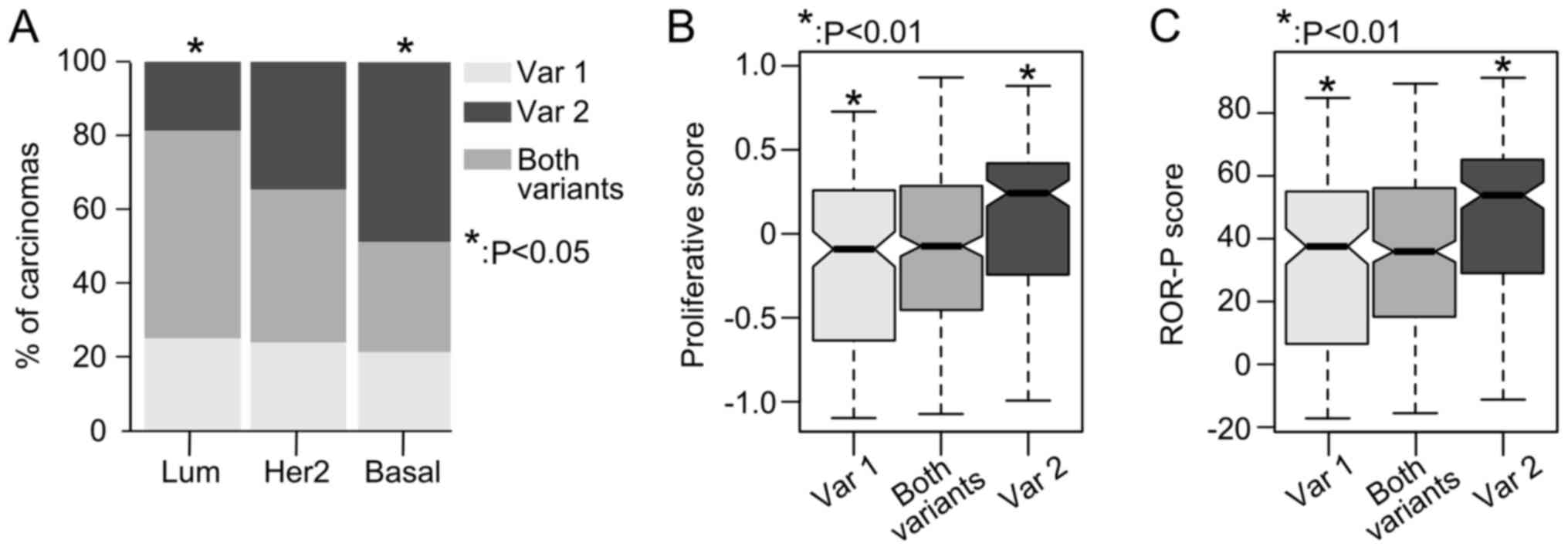
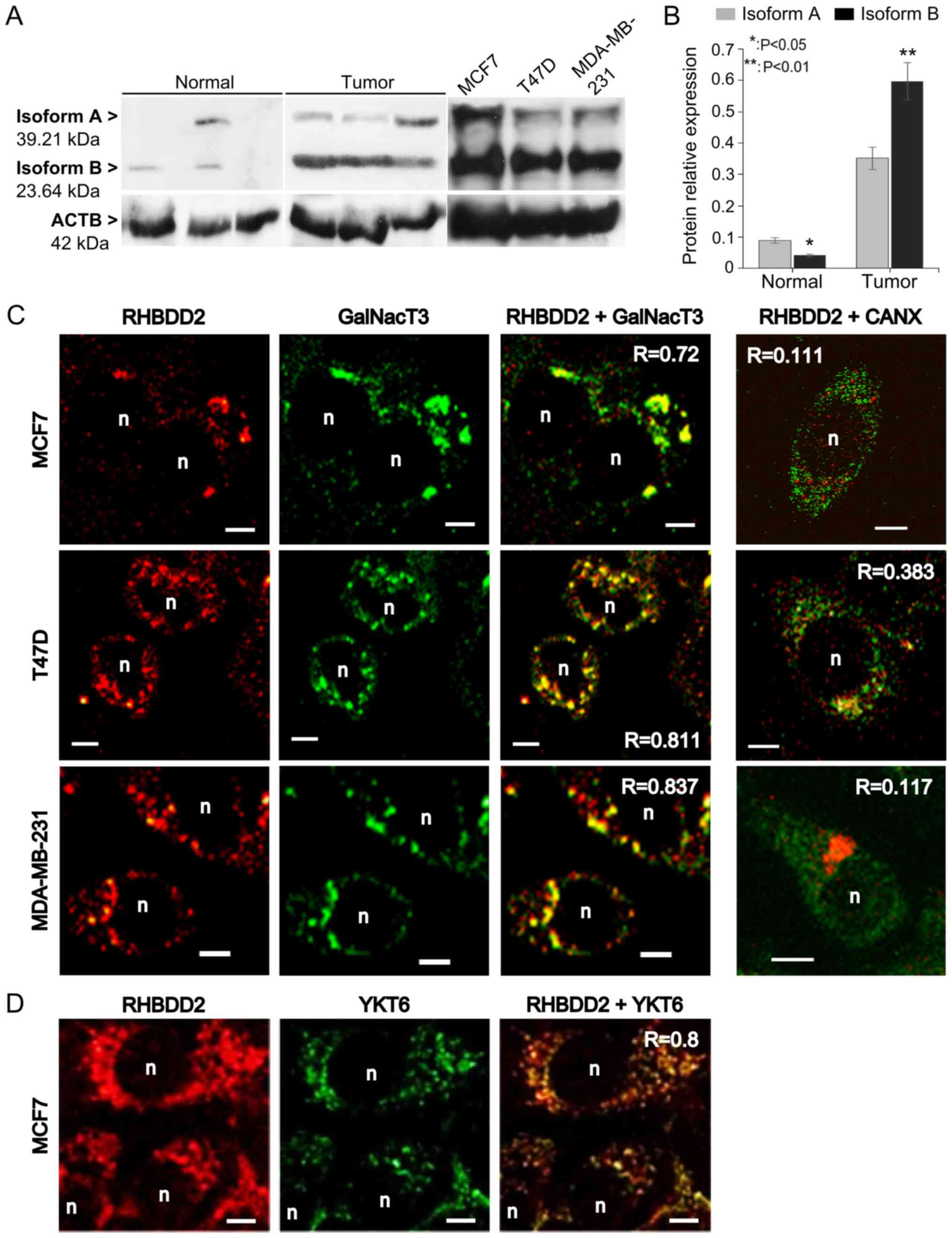
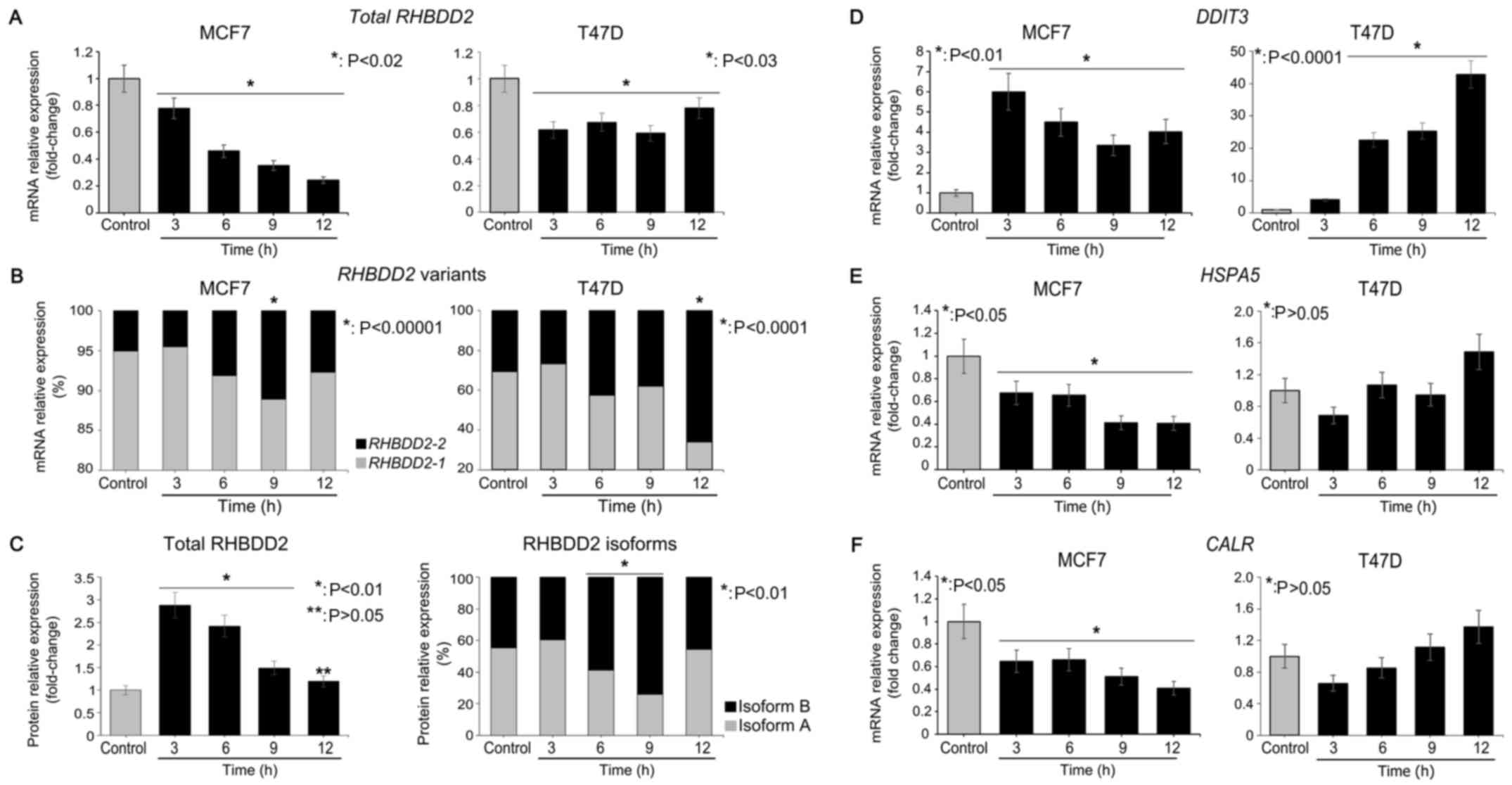
|
1
|
Freeman M: The rhomboid-like superfamily:
Molecular mechanisms and biological roles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
30:235–254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bergbold N and Lemberg MK: Emerging role
of rhomboid family proteins in mammalian biology and disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1828:2840–2848. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abba MC, Sun H, Hawkins KA, Drake JA, Hu
Y, Nunez MI, Gaddis S, Shi T, Horvath S, Sahin A and Aldaz CM:
Breast cancer molecular signatures as determined by SAGE:
Correlation with lymph node status. Mol Cancer Res. 5:881–890.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abba MC, Lacunza E, Nunez MI, Colussi A,
Isla-Larrain M, Segal-Eiras A, Croce MV and Aldaz CM: Rhomboid
domain containing 2 (RHBDD2): A novel cancer-related gene
over-expressed in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1792:988–997. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lacunza E, Canzoneri R, Rabassa ME,
Zwenger A, Segal-Eiras A, Croce MV and Abba MC: RHBDD2: A
5-fluorouracil responsive gene overexpressed in the advanced stages
of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 33:2393–2399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Canzoneri R, Lacunza E, Isla Larrain M,
Croce MV and Abba MC: Rhomboid family gene expression profiling in
breast normal tissue and tumor samples. Tumour Biol. 35:1451–1458.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lacunza E, Rabassa ME, Canzoneri R,
Pellon-Maison M, Croce MV, Aldaz CM and Abba MC: Identification of
signaling pathways modulated by RHBDD2 in breast cancer cells: A
link to the unfolded protein response. Cell Stress Chaperones.
19:379–388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Biamonti G, Catillo M, Pignataro D,
Montecucco A and Ghigna C: The alternative splicing side of cancer.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 32:30–36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Venables JP: Aberrant and alternative
splicing in cancer. Cancer Res. 64:7647–7654. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ghigna C, Valacca C and Biamonti G:
Alternative splicing and tumor progression. Curr Genomics.
9:556–570. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
David CJ and Manley JL: Alternative
pre-mRNA splicing regulation in cancer: Pathways and programs
unhinged. Genes Dev. 24:2343–2364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oltean S and Bates DO: Hallmarks of
alternative splicing in cancer. Oncogene. 33:5311–5318. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carlson SG, Fawcett TW, Bartlett JD,
Bernier M and Holbrook NJ: Regulation of the C/EPB-related gene
gadd153 by glucose deprivation. Mol Cell Biol. 13:4736–4744. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee AS: The ER chaperone and signalling
regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Methods. 35:373–381. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Michalak M, Groenendyk J, Szabo E, Gold LI
and Opas M: Calreticulin, a multi-process calcium-buffering
chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 417:651–666.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bergeron JJ, Brenner MB, Thomas DY and
Williams DB: Calnexin: A membrane-bound chaperone of the
endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 19:124–128. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Röttger S, White J, Wandall HH, Olivo JC,
Stark A, Bennett EP, Whitehouse C, Berger EG, Clausen H and Nilsson
T: Localization of three human polypeptide GalNAc-transferases in
HeLa cells suggests initiation of O-linked glycosylation throughout
the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Sci. 111:45–60. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang T and Hong W: Ykt6 forms a SNARE
complex with syntaxin 5, GS28, and Bet1 and participates in a late
stage in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi transport. J Biol Chem.
276:27480–27487. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bolte S and Cordelières FP: A guided tour
into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J
Microsc. 224:213–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S,
Voduc D, Vickery T, Davies S, Fauron C, He X, Hu Z, et al:
Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic
subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 27:1160–1167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai X, Li T, Bai Z, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhan J
and Shi B: Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical
use and future trends. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2929–2943.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He N, Kim N, Jeong E, Lu Y, Mills GB and
Yoon S: Glucose starvation induces mutation and lineage-dependent
adaptive responses in a large collection of cancer cell lines. Int
J Oncol. 48:67–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Amir-Ahmady B and Salati LM: Regulation of
the processing of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA by
nutritional status. J Biol Chem. 276:10514–10523. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hicks SW and Machamer CE: Golgi structure
in stress sensing and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1744:406–414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cyphert TJ, Suchanek AL, Griffith BN and
Salati LM: Starvation actively inhibits splicing of
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA via a bifunctional ESE/ESS
element bound by hnRNP K. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1829:905–915. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Yang N, Huang
W, Mohamed-Hadley A, Yao W, Benencia F and Coukos G: Different
effects of glucose starvation on expression and stability of VEGF
mRNA isoforms in murine ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 292:860–868. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Spriggs KA, Bushell M and Willis AE:
Translational regulation of gene expression during conditions of
cell stress. Mol Cell. 40:228–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Martínez-Salas E, Piñeiro D and Fernández
N: Alternative mechanisms to initiate translation in eukaryotic
mRNAs. Comp Funct Genomics. 2012:3915462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Barbosa C, Peixeiro I and Romão L: Gene
expression regulation by upstream open reading frames and human
disease. PLoS Genet. 9:e10035292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahmedli NB, Gribanova Y, Njoku CC, Naidu
A, Young A, Mendoza E, Yamashita CK, Ozgül RK, Johnson JE, Fox DA
and Farber DB: Dynamics of the rhomboid-like protein RHBDD2
expression in mouse retina and involvement of its human ortholog in
retinitis pigmentosa. J Biol Chem. 288:9742–9754. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ferretti VA, Canzoneri R, Barbeito CG,
Croce MV, Abba MC and Lacunza E: Spatiotemporal expression of
Rhomboid domain containing 2 (Rhbdd2) during rat development. Acta
Histochem. 117:635–641. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|