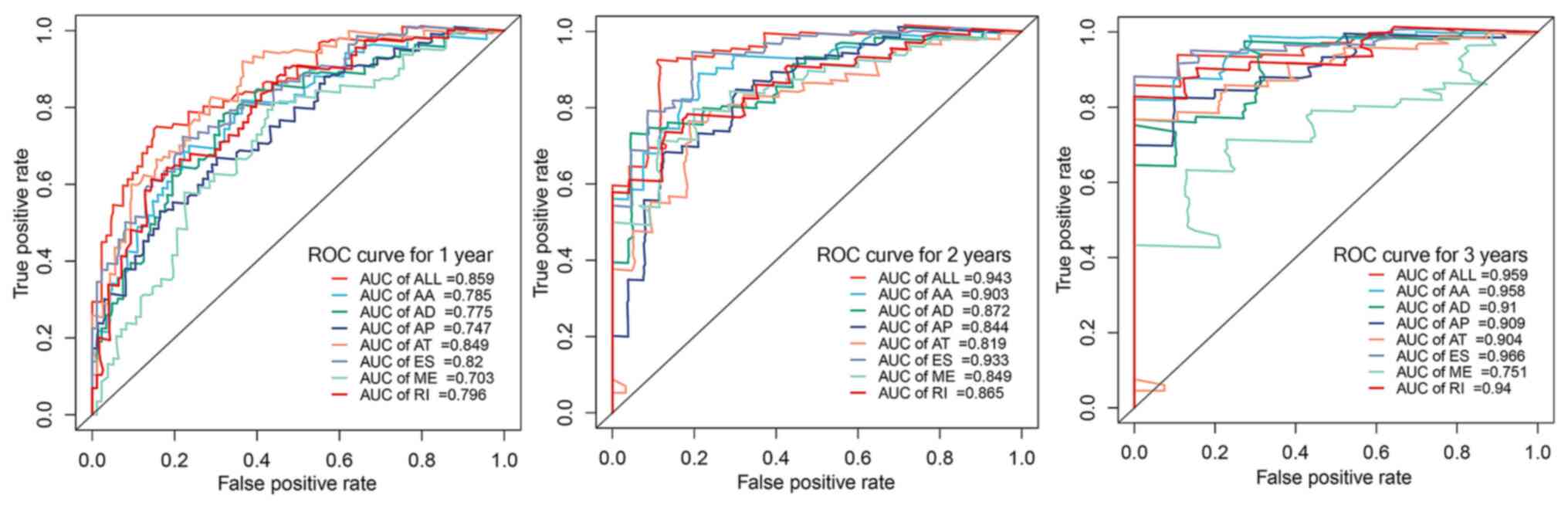
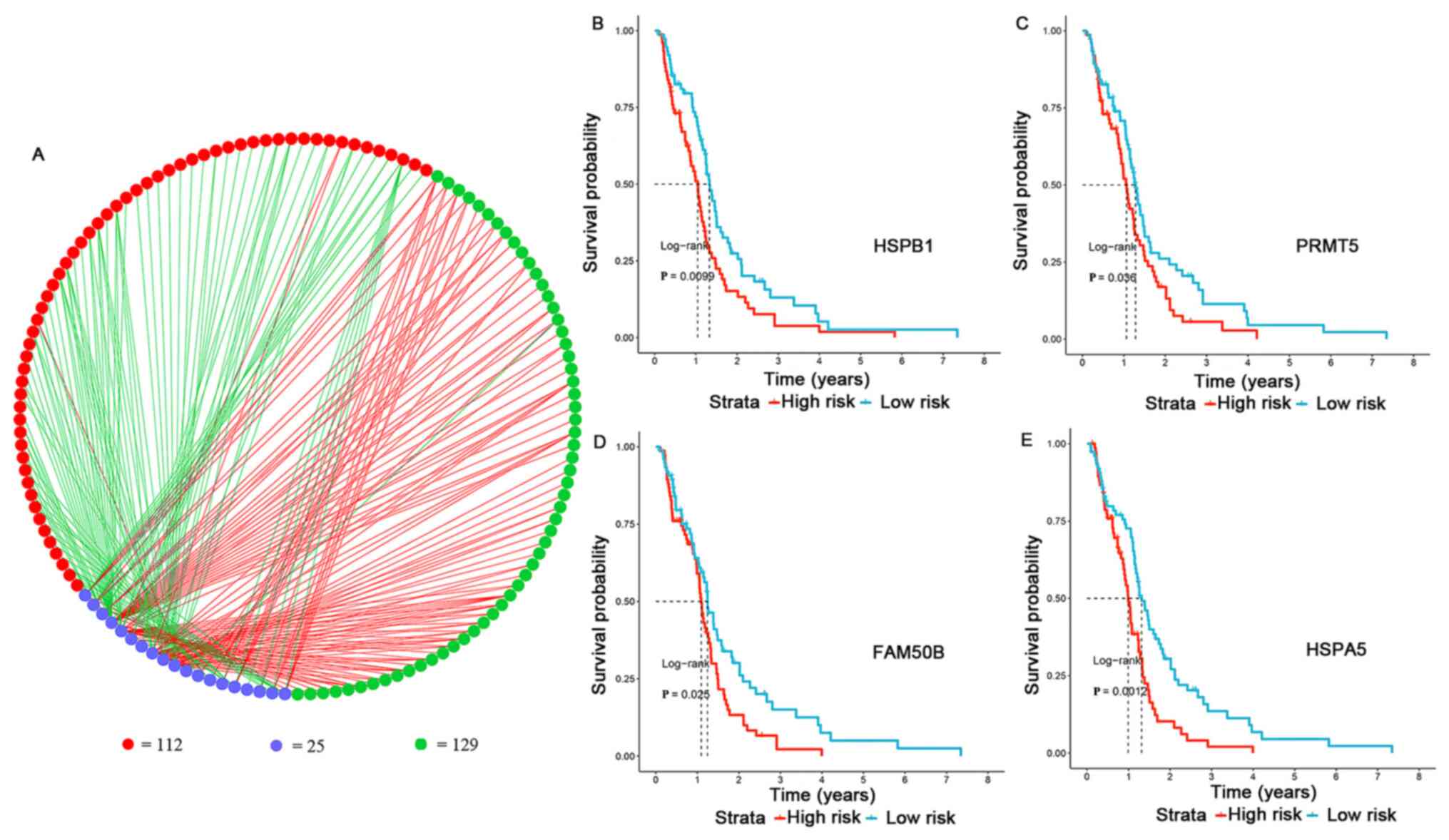
|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek
A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y, Stroup NE, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS:
CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system
tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro Oncol. 15
(Suppl 2):ii1–ii56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Binabaj MM, Bahrami A, ShahidSales S,
Joodi M, Joudi Mashhad M, Hassanian SM, Anvari K and Avan A: The
prognostic value of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma: A
meta-analysis of clinical trials. J Cell Physiol. 233:378–386.
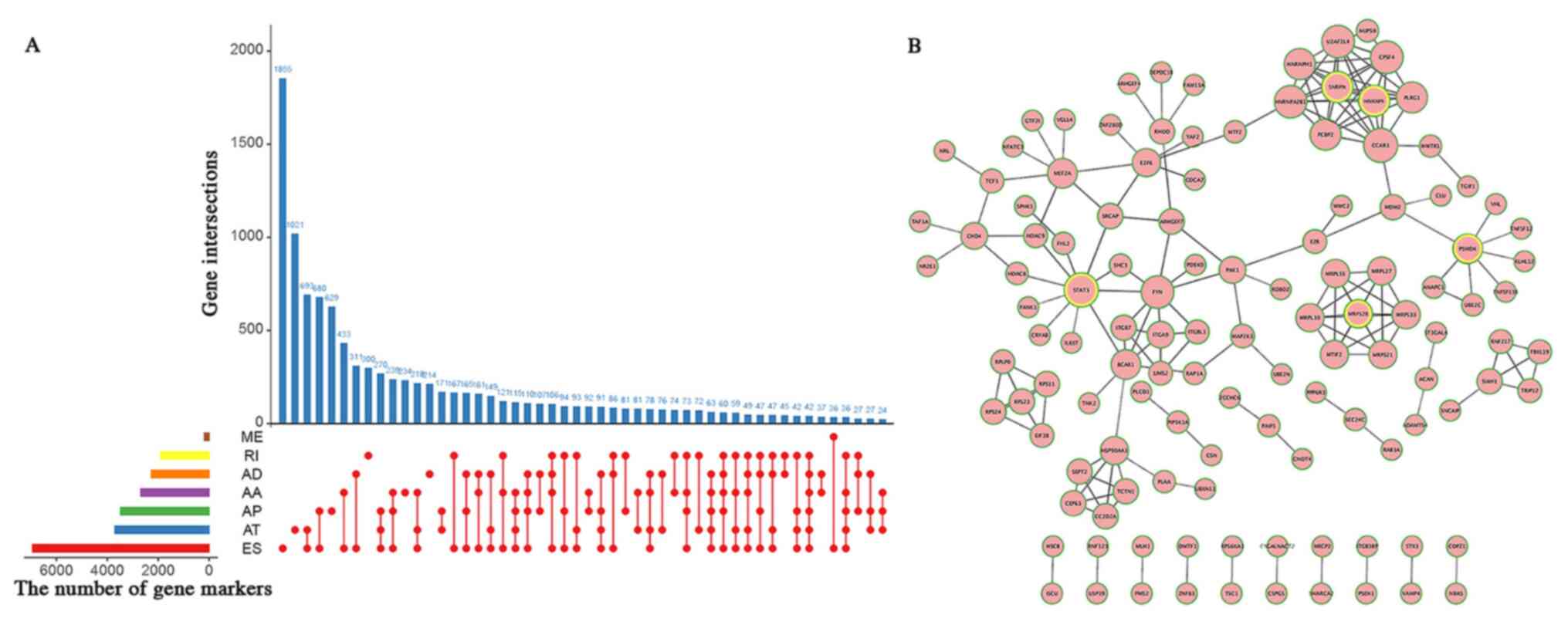
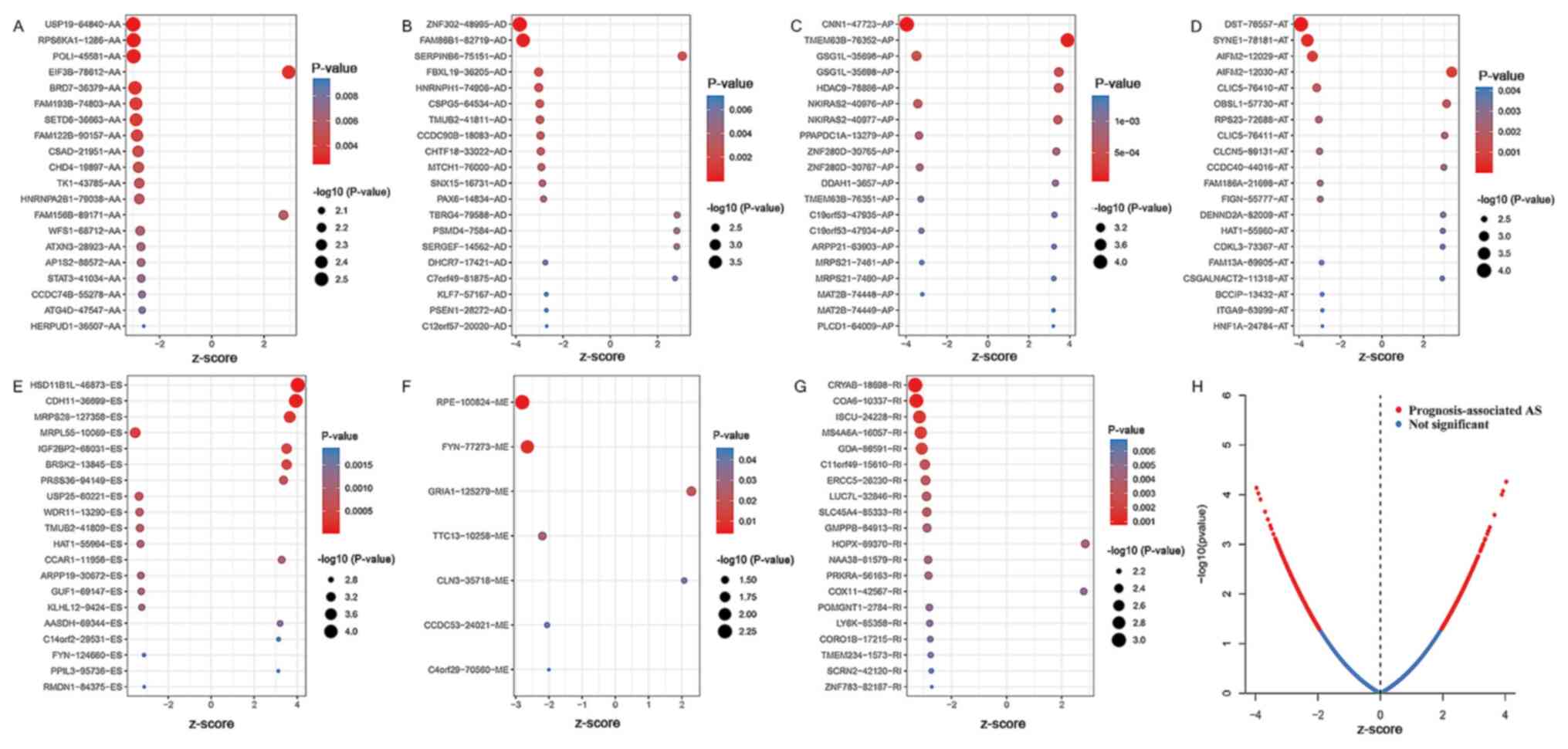
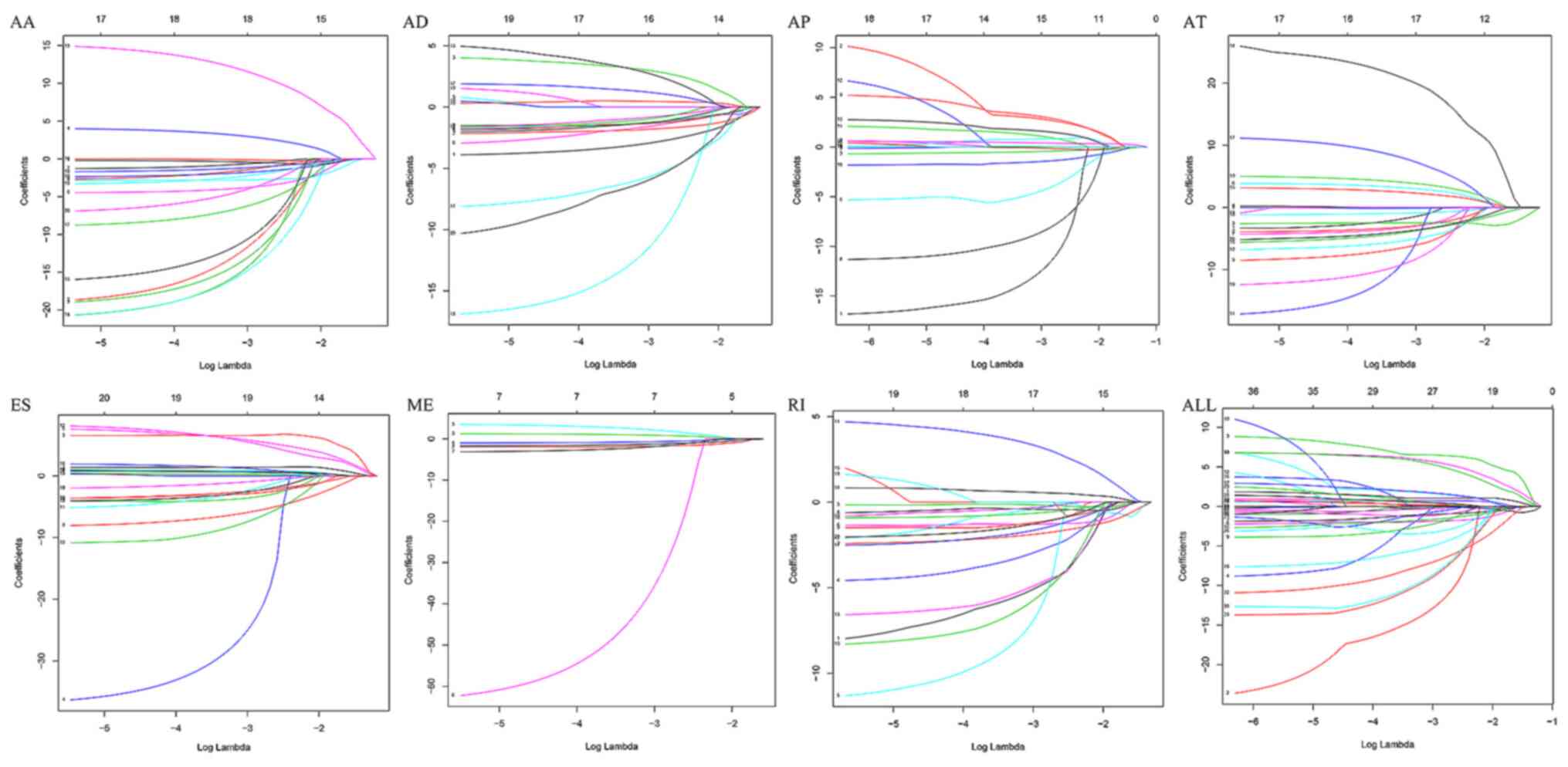
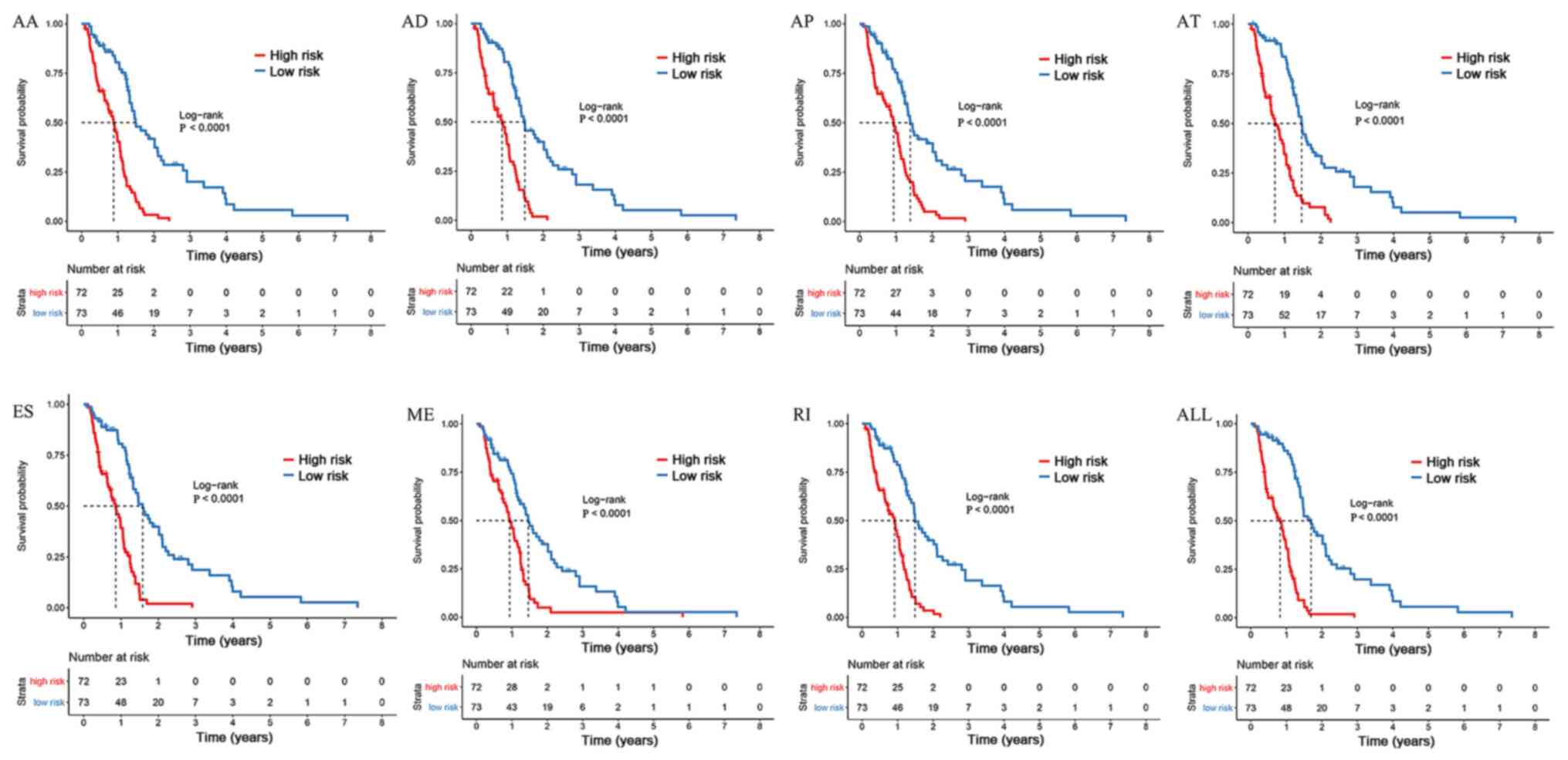
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao W, Li J, Chen MM, Luo Y, Ju Z, Nesser
NK, Johnson-Camacho K, Boniface CT, Lawrence Y, Pande NT, et al:
Large-scale characterization of drug responses of clinically
relevant proteins in cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell. Oct
2–2020.doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.10.008 (Online ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singh B and Eyras E: The role of
alternative splicing in cancer. Transcription. 8:91–98. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Y, Shi N, Regev A, He S and Hemann MT:
Integrated regulatory models for inference of subtype-specific
susceptibilities in glioblastoma. Mol Syst Biol. 16:e95062020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Du J, Yan X, Mi S, Li Y, Ji H, Hou K, Ma
S, Ba Y, Zhou P, Chen L, et al: Identification of prognostic model
and biomarkers for cancer stem cell characteristics in glioblastoma
by network analysis of multi-omics data and stemness indices. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 8:5589612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bao ZS, Li MY, Wang JY, Zhang CB, Wang HJ,
Yan W, Liu YW, Zhang W, Chen L and Jiang T: Prognostic value of a
nine-gene signature in glioma patients based on mRNA expression
profiling. CNS Neurosci Ther. 20:112–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin W, Tang G, Zhou Q, Cao Y, Li H, Fu X,
Wu Z and Jiang X: Expression profile analysis identifies a novel
five-gene signature to improve prognosis prediction of
glioblastoma. Front Genet. 10:4192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carpenter S, Ricci EP, Mercier BC, Moore
MJ and Fitzgerald KA: Post-transcriptional regulation of gene
expression in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:361–376. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nilsen TW and Graveley BR: Expansion of
the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature.
463:457–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Antonopoulou E and Ladomery M: Targeting
splicing in prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:12872018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim HK, Pham MHC, Ko KS, Rhee BD and Han
J: Alternative splicing isoforms in health and disease. Pflugers
Arch. 470:995–1016. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brosseau JP, Lucier JF, Nwilati H,
Thibault P, Garneau D, Gendron D, Durand M, Couture S, Lapointe E,
Prinos P, et al: Tumor microenvironment-associated modifications of
alternative splicing. RNA. 20:189–201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dvinge H, Kim E, Abdel-Wahab O and Bradley
RK: RNA splicing factors as oncoproteins and tumour suppressors.
Nat Rev Cancer. 16:413–430. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee Y and Rio DC: Mechanisms and
regulation of alternative Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem.
84:291–323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martinez-Montiel N, Rosas-Murrieta NH,
Anaya Ruiz M, Monjaraz-Guzman E and Martinez-Contreras R:
Alternative splicing as a target for cancer treatment. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:5452018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Suñé-Pou M, Prieto-Sánchez S,
Boyero-Corral S, Moreno-Castro C, El Yousfi Y, Suñé-Negre JM,
Hernández-Munain C and Suñé C: Targeting splicing in the treatment
of human disease. Genes (Basel). 8:872017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Noushmehr H, Weisenberger DJ, Diefes K,
Phillips HS, Pujara K, Berman BP, Pan F, Pelloski CE, Sulman EP,
Bhat KP, et al: Identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype
that defines a distinct subgroup of glioma. Cancer Cell.
17:510–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ryan M, Wong WC, Brown R, Akbani R, Su X,
Broom B, Melott J and Weinstein J: TCGASpliceSeq a compendium of
alternative mRNA splicing in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:D1018–D1022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ryan MC, Cleland J, Kim R, Wong WC and
Weinstein JN: SpliceSeq: A resource for analysis and visualization
of RNA-Seq data on alternative splicing and its functional impacts.
Bioinformatics. 28:2385–2387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lex A, Gehlenborg N, Strobelt H, Vuillemot
R and Pfister H: UpSet: Visualization of intersecting sets. IEEE
Trans Vis Comput Graph. 20:1983–1992. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu G, Feng X and Stein L: A human
functional protein interaction network and its application to
cancer data analysis. Genome Biol. 11:R532010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tibshirani R: The lasso method for
variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med. 16:385–395. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Heagerty PJ, Lumley T and Pepe MS:
Time-dependent ROC curves for censored survival data and a
diagnostic marker. Biometrics. 56:337–344. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Szopa W, Burley TA, Kramer-Marek G and
Kaspera W: Diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers in glioblastoma:
Current status and future perspectives. Bio Res Int.
2017:80135752017.
|
|
27
|
Taal W, Oosterkamp HM, Walenkamp AM,
Dubbink HJ, Beerepoot LV, Hanse MC, Buter J, Honkoop AH, Boerman D,
de Vos FY, et al: Single-agent bevacizumab or lomustine versus a
combination of bevacizumab plus lomustine in patients with
recurrent glioblastoma (BELOB trial): A randomised controlled phase
2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:943–953. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aldape K, Zadeh G, Mansouri S,
Reifenberger G and von Deimling A: Glioblastoma: Pathology,
molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 129:829–848.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng Y, Zhang P, Wang X, Wang K, Zhou M,
Long H, Lin J, Wu Z, Gao L and Song Y: Identification of prognostic
signatures. 2020.
|
|
30
|
Xie ZC, Wu HY, Dang YW and Chen G: Role of
alternative splicing signatures in the prognosis of glioblastoma.
Cancer Med. 8:7623–7636. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Zhao C, Guo B, Zhao Z, Wang H and
Fang Z: Systematic profiling of alternative mRNA splicing signature
for predicting glioblastoma prognosis. Front Oncol. 9:9282019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Ren Z, Peng Y, Li K, Wang X, Huang
G, Qi S and Liu Y: Classification of glioma based on prognostic
alternative splicing. BMC Med Genomics. 12:1652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J and Manley JL: Misregulation of
pre-mRNA alternative splicing in cancer. Cancer Discov.
3:1228–1237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qi Z, Shen L, Zhou H, Jiang Y, Lan L, Luo
L and Yin Z: Phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 antagonizes
TNF-α induced HeLa cell apoptosis via regulating TAK1
ubiquitination and activation of p38 and ERK signaling. Cell
Signal. 26:1616–1625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Banasavadi-Siddegowda YK, Russell L, Frair
E, Karkhanis VA, Relation T, Yoo JY, Zhang J, Sif S, Imitola J,
Baiocchi R and Kaur B: PRMT5-PTEN molecular pathway regulates
senescence and self-renewal of primary glioblastoma neurosphere
cells. Oncogene. 36:263–274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Banasavadi-Siddegowda YK, Welker AM, An M,
Yang X, Zhou W, Shi G, Imitola J, Li C, Hsu S, Wang J, et al: PRMT5
as a druggable target for glioblastoma therapy. Neuro Oncol.
20:753–763. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jia D, Lin W, Tang H, Cheng Y, Xu K, He Y,
Geng W and Dai Q: Integrative analysis of DNA methylation and gene
expression to identify key epigenetic genes in glioblastoma. Aging
(Albany NY). 11:5579–5592. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cerezo M and Rocchi S: New anti-cancer
molecules targeting HSPA5/BIP to induce endoplasmic reticulum
stress, autophagy and apoptosis. Autophagy. 13:216–217. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|