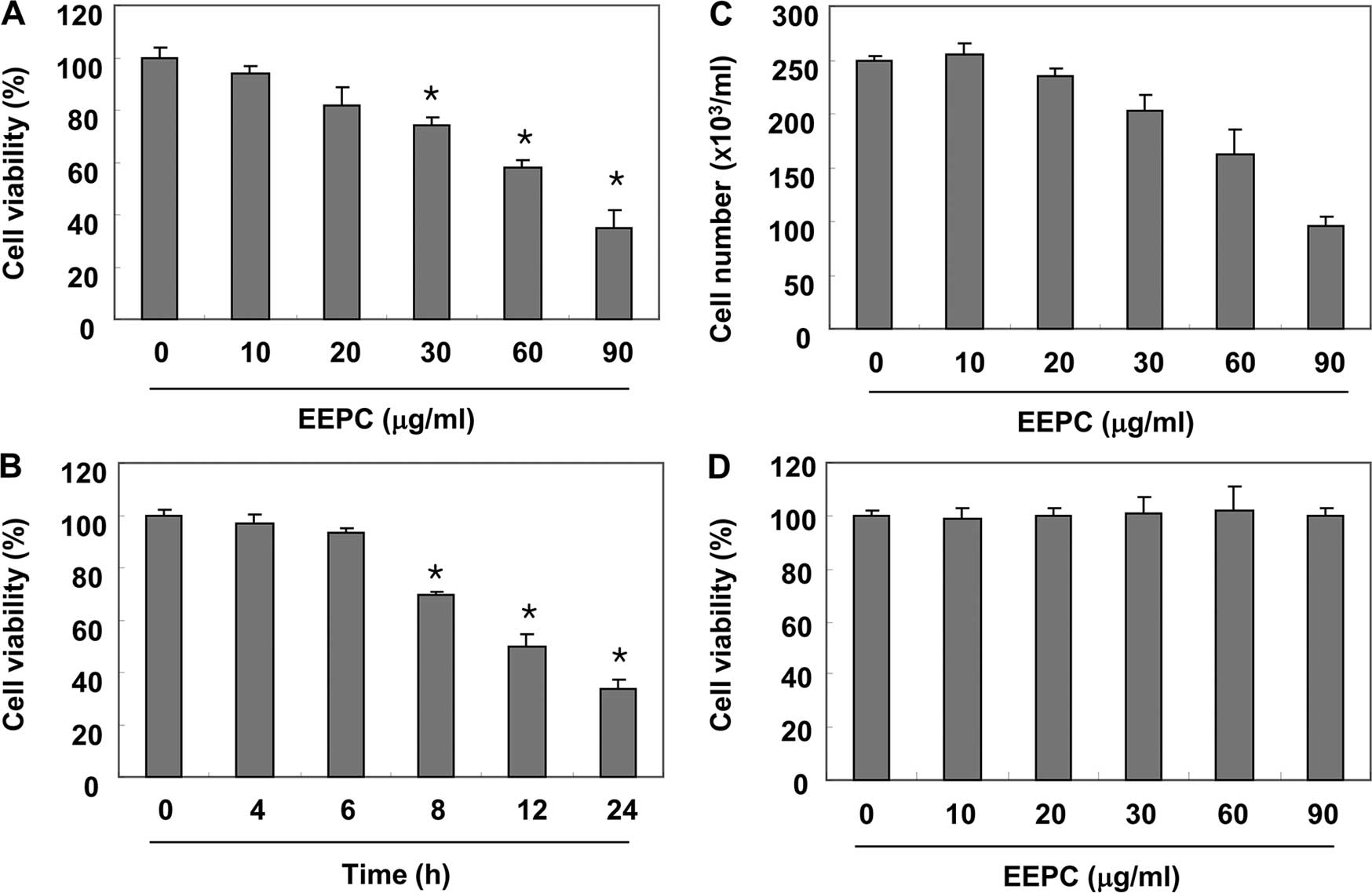
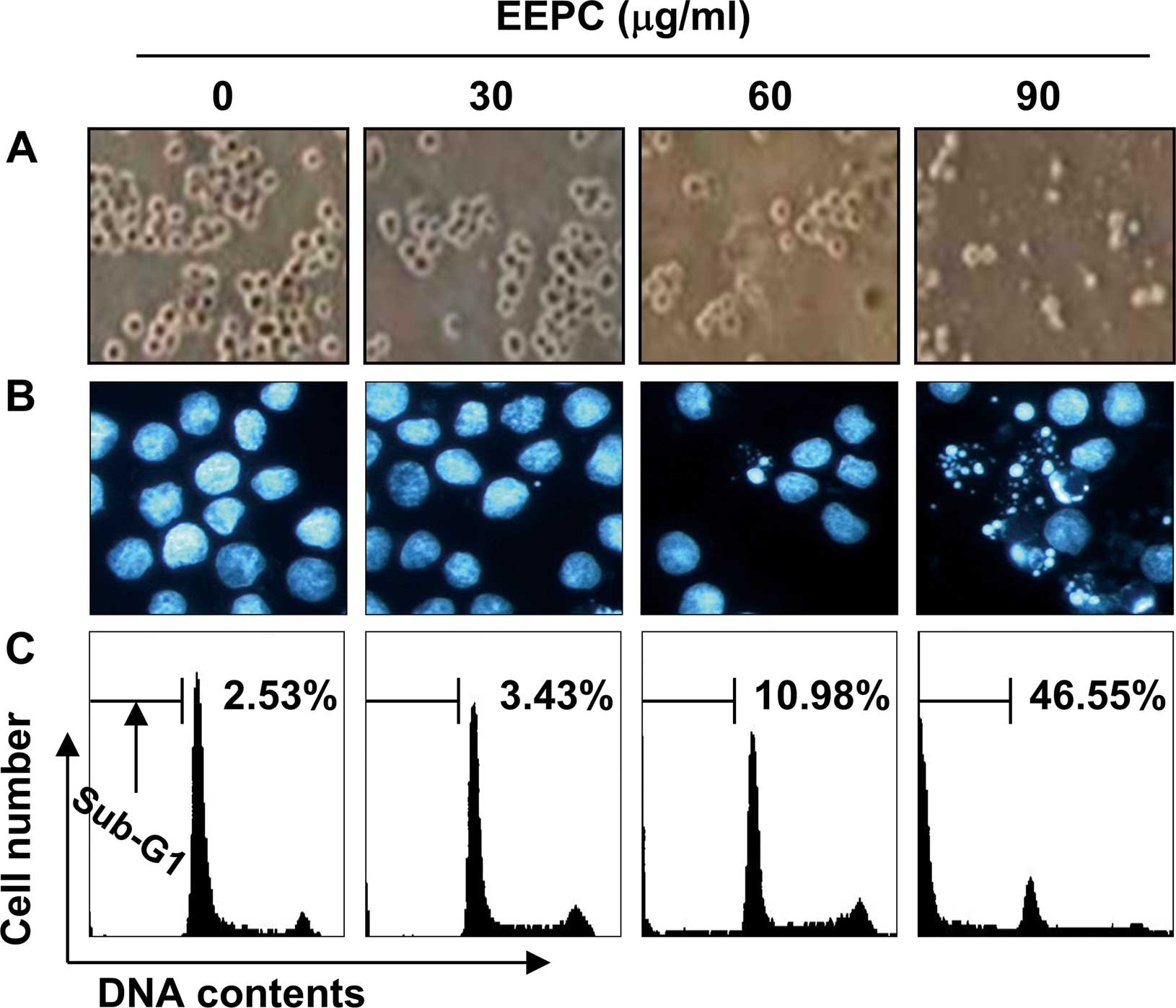
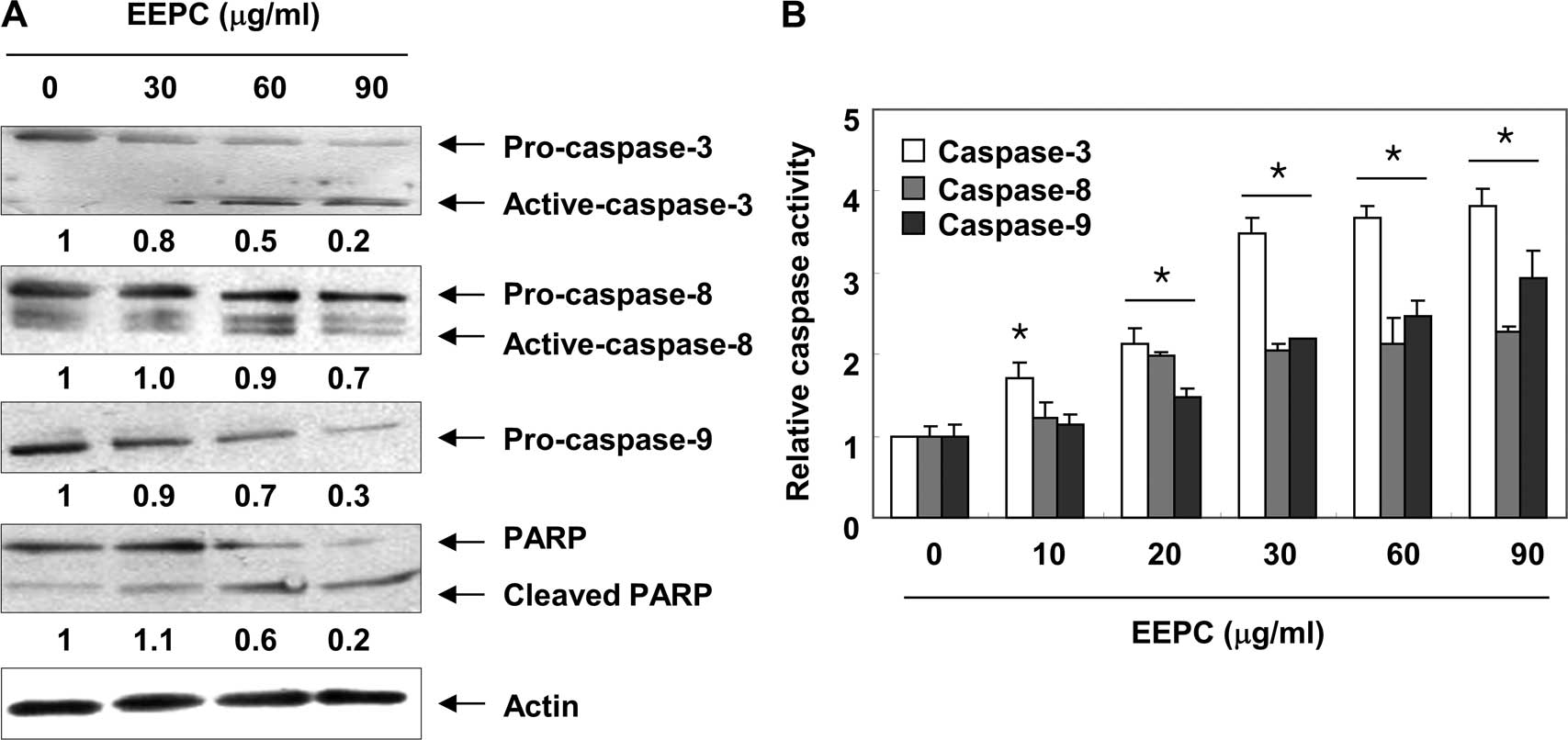
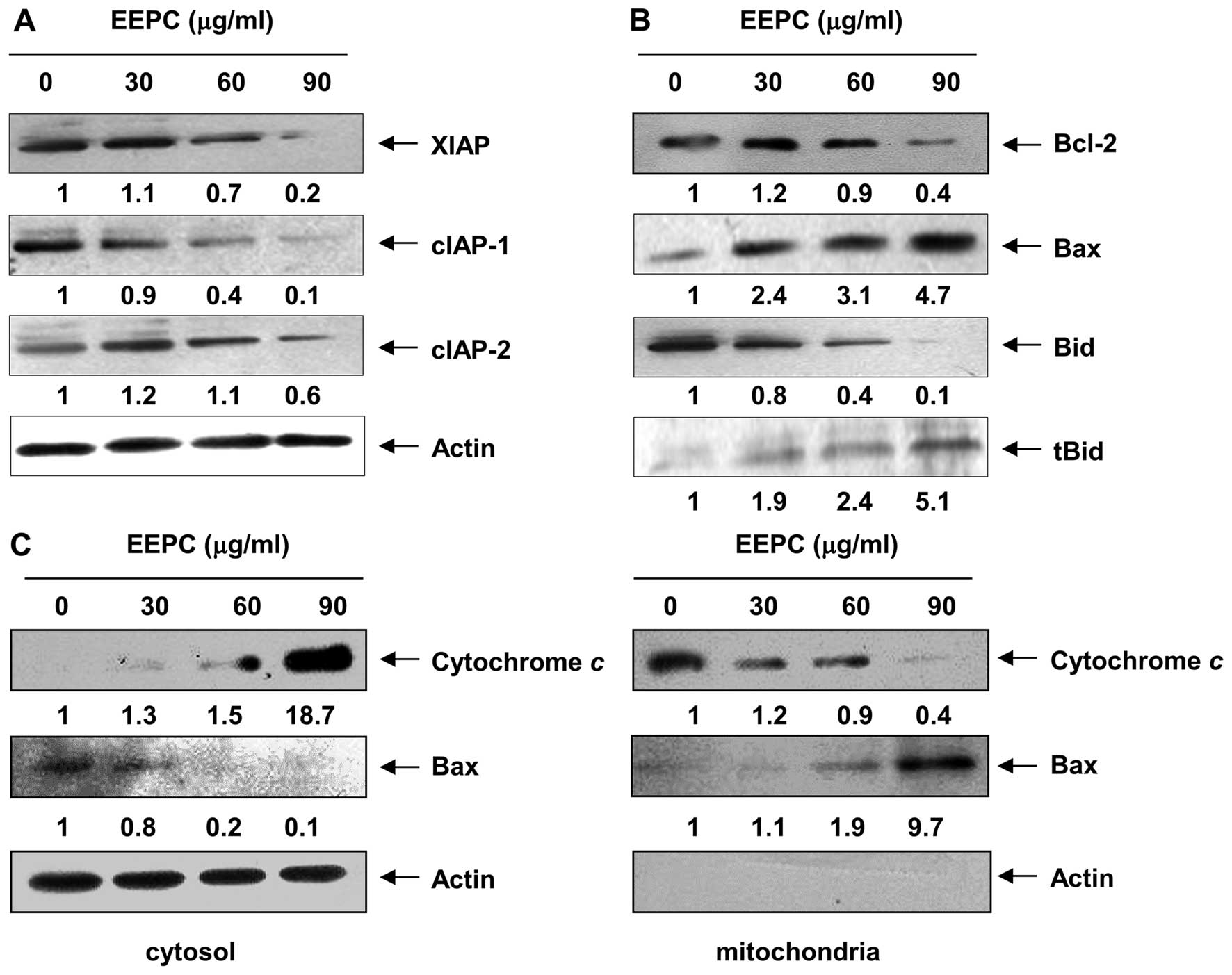
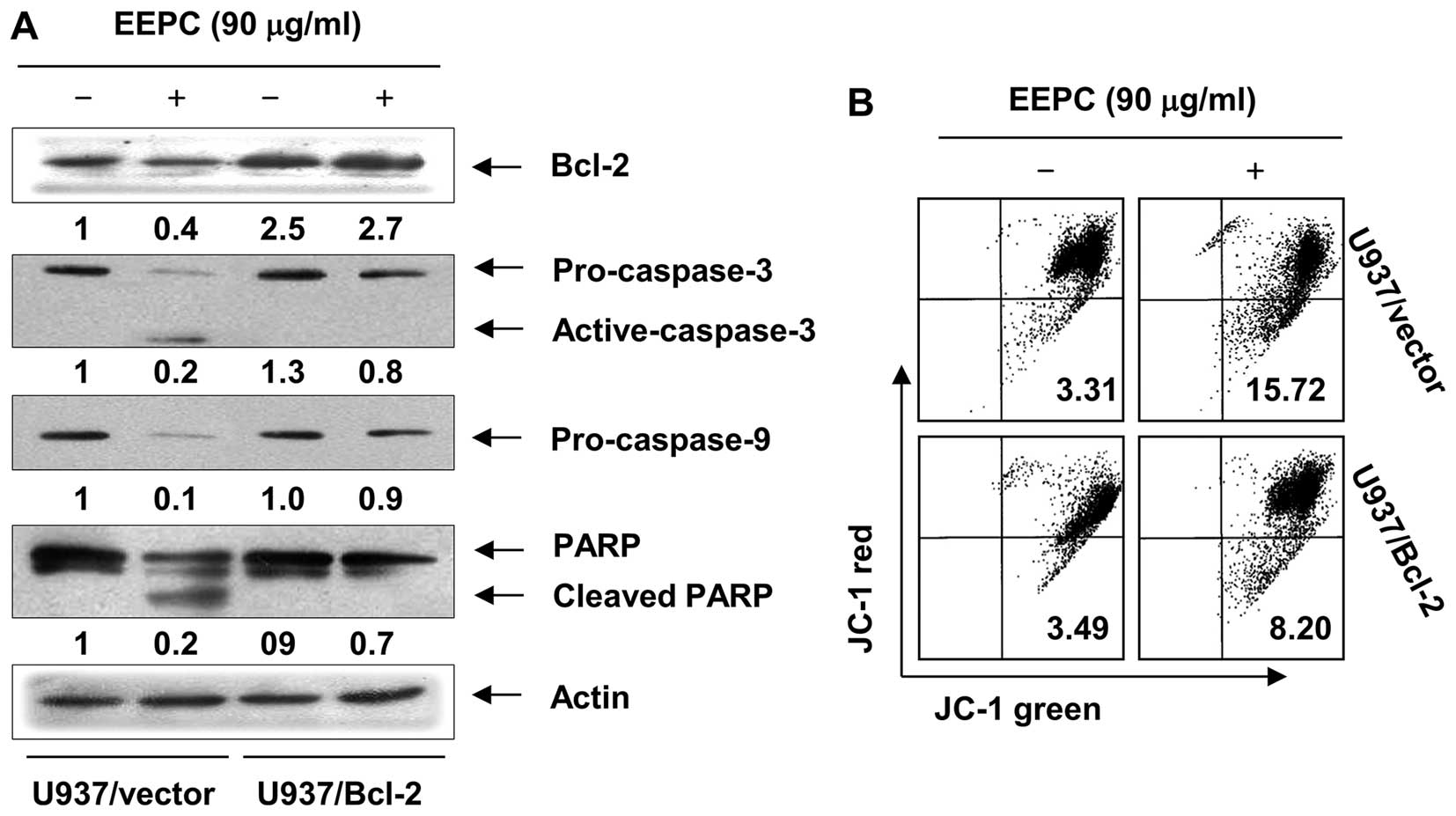
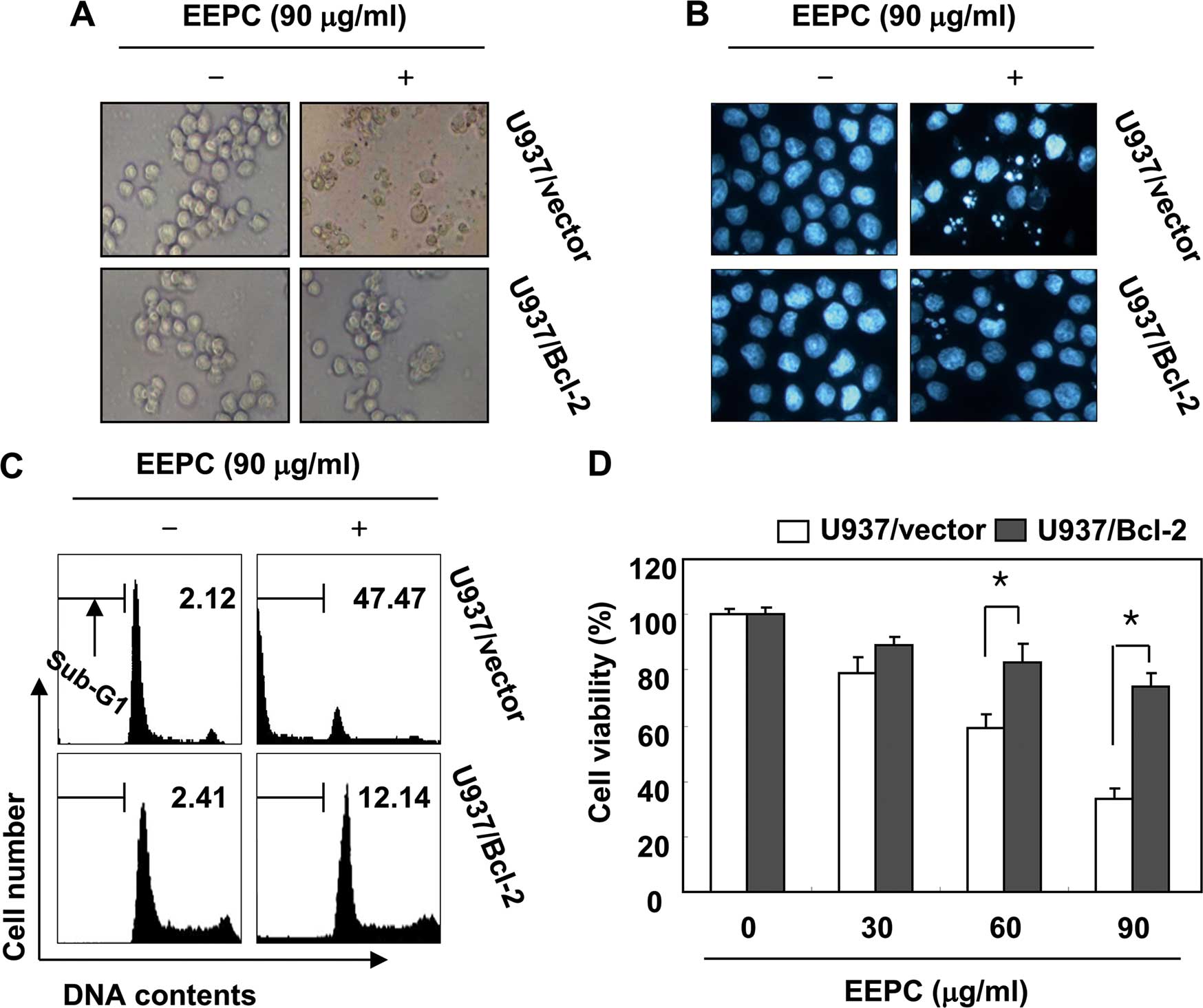
|
1
|
Lavrik IN: Systems biology of apoptosis
signaling networks. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 21:551–555. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karbowski M, Norris KL, Cleland MM, Jeong
SY and Youle RJ: Role of Bax and Bak in mitochondrial
morphogenesis. Nature. 443:658–662. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Khuda-Bukhsh AR, Das S and Saha SK:
Molecular approaches toward targeted cancer prevention with some
food plants and their products: Inflammatory and other signal
pathways. Nutr Cancer. 66:194–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bultman SJ: Emerging roles of the
microbiome in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 35:249–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Song FQ, Liu Y, Kong XS, Chang W and Song
G: Progress on understanding the anticancer mechanisms of medicinal
mushroom: Inonotus obliquus. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:1571–1578.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ríos JL: Chemical constituents and
pharmacological properties of Poria cocos. Planta Med. 77:681–691.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun Y: Biological activities and potential
health benefits of polysaccharides from Poria cocos and their
derivatives. Int J Biol Macromol. 68:131–134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Ravipati AS, Koyyalamudi SR,
Jeong SC, Reddy N, Bartlett J, Smith PT, de la Cruz M, Monteiro MC,
Melguizo A, et al: Anti-fungal and anti-bacterial activities of
ethanol extracts of selected traditional Chinese medicinal herbs.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:673–681. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park YH, Son IH, Kim B, Lyu YS, Moon HI
and Kang HW: Poria cocos water extract (PCW) protects PC12 neuronal
cells from beta-amyloid-induced cell death through antioxidant and
antiapoptotic functions. Pharmazie. 64:760–764. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Zhou L, Zhang Y, Gapter LA, Ling H,
Agarwal R and Ng KY: Cytotoxic and anti-oxidant activities of
lanostane-type triterpenes isolated from Poria cocos. Chem Pharm
Bull. 56:1459–1462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chung TW, Koo BS, Choi EG, Kim MG, Lee IS
and Kim CH: Neuroprotective effect of a chuk-me-sun-dan on neurons
from ischemic damage and neuronal cell toxicity. Neurochem Res.
31:1–9. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee SM, Lee YJ, Yoon JJ, Kang DG and Lee
HS: Effect of Poria cocos on hypertonic stress-induced water
channel expression and apoptosis in renal collecting duct cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 141:368–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cuellar MJ, Giner RM, Recio MC, Just MJ,
Mañez S and Rios JL: Effect of the basidiomycete Poria cocos on
experimental dermatitis and other inflammatory conditions. Chem
Pharm Bull. 45:492–494. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fuchs SM, Heinemann C, Schliemann-Willers
S, Härtl H, Fluhr JW and Elsner P: Assessment of anti-inflammatory
activity of Poria cocos in sodium lauryl sulphate-induced irritant
contact dermatitis. Skin Res Technol. 12:223–227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jeong JW, Lee HH, Han MH, Kim GY, Hong SH,
Park C and Choi YH: Ethanol extract of Poria cocos reduces the
production of inflammatory mediators by suppressing the NF-kappaB
signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7
macrophages. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:1012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yasukawa K, Kaminaga T, Kitanaka S, Tai T,
Nunoura Y, Natori S and Takido M: 3β-p-hydroxybenzoyldehydrotumul
osic acid from Poria cocos, and its anti-inflammatory effect.
Phytochemistry. 48:1357–1360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yance DR Jr and Sagar SM: Targeting
angiogenesis with integrative cancer therapies. Integr Cancer Ther.
5:9–29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sagar SM, Yance D and Wong RK: Natural
health products that inhibit angiogenesis: A potential source for
investigational new agents to treat cancer-Part 1. Curr Oncol.
13:14–26. 2006.
|
|
22
|
Lu YT, Kuan YC, Chang HH and Sheu F:
Molecular cloning of a Poria cocos protein that activates Th1
immune response and allays Th2 cytokine and IgE production in a
murine atopic dermatitis model. J Agric Food Chem. 62:2861–2871.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang HH, Yeh CH and Sheu F: A novel
immunomodulatory protein from Poria cocos induces Toll-like
receptor 4-dependent activation within mouse peritoneal
macrophages. J Agric Food Chem. 57:6129–6139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng S, Eliaz I, Lin J, Thyagarajan-Sahu
A and Sliva D: Triterpenes from Poria cocos suppress growth and
invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells through the downregulation
of MMP-7. Int J Oncol. 42:1869–1874. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kikuchi T, Uchiyama E, Ukiya M, Tabata K,
Kimura Y, Suzuki T and Akihisa T: Cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing
activities of triterpene acids from Poria cocos. J Nat Prod.
74:137–144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng YL, Lei P, Tian T, Yin L, Chen DQ,
Chen H, Mei Q, Zhao YY and Lin RC: Diuretic activity of some
fractions of the epidermis of Poria cocos. J Ethnopharmacol.
150:1114–1118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ling H, Zhang Y, Ng KY and Chew EH:
Pachymic acid impairs breast cancer cell invasion by suppressing
nuclear factor-κB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:609–620. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ling H, Zhou L, Jia X, Gapter LA, Agarwal
R and Ng KY: Polyporenic acid C induces caspase-8-mediated
apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells. Mol Carcinog.
48:498–507. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gapter L, Wang Z, Glinski J and Ng KY:
Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by pachymic acid
from Poria cocos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 332:1153–1161. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee SJ, Hwang SO, Noh EJ, Kim DU, Nam M,
Kim JH, Nam JH and Hoe KL: Transactivation of bad by
vorinostat-induced acetylated p53 enhances doxorubicin-induced
cytotoxicity in cervical cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 46:e762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim YS, Li XF, Kang KH, Ryu B and Kim SK:
Stigmasterol isolated from marine microalgae Navicula incerta
induces apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. BMB Rep.
47:433–438. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Park C, Park S, Chung YH, Kim GY, Choi YW,
Kim BW and Choi YH: Induction of apoptosis by a hexane extract of
aged black garlic in the human leukemic U937 cells. Nutr Res Pract.
8:132–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seo K, Ki SH and Shin SM: Methylglyoxal
induces mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in liver. Toxicol
Res. 30:193–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duriez PJ and Shah GM: Cleavage of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: A sensitive parameter to study cell
death. Biochem Cell Biol. 75:337–349. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Danson S, Dean E, Dive C and Ranson M:
IAPs as a target for anticancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
7:785–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
de Graaf AO, de Witte T and Jansen JH:
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: New therapeutic targets in
hematological cancer? Leukemia. 18:1751–1759. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kadenbach B, Arnold S, Lee I and Hüttemann
M: The possible role of cytochrome c oxidase in stress-induced
apoptosis and degenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1655:400–408. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ: Mechanisms of
cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:437–444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stankiewicz AR, Lachapelle G, Foo CP,
Radicioni SM and Mosser DD: Hsp70 inhibits heat-induced apoptosis
upstream of mitochondria by preventing Bax translocation. J Biol
Chem. 280:38729–38739. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Degli Esposti M and Dive C: Mitochondrial
membrane permeabilisation by Bax/Bak. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
304:455–461. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shamas-Din A, Brahmbhatt H, Leber B and
Andrews DW: BH3-only proteins: Orchestrators of apoptosis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1813:508–520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fennell DA and Chacko A: Exploiting BH3
only protein function for effective cancer therapy. Front Biosci.
13:6682–6692. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fiandalo MV and Kyprianou N: Caspase
control: Protagonists of cancer cell apoptosis. Exp Oncol.
34:165–175. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hensley P, Mishra M and Kyprianou N:
Targeting caspases in cancer therapeutics. Biol Chem. 394:831–843.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Walczak H and Krammer PH: The CD95
(APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems. Exp Cell Res.
256:58–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Asakura T and Ohkawa K: Chemotherapeutic
agents that induce mitochondrial apoptosis. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 4:577–590. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tomek M, Akiyama T and Dass CR: Role of
Bcl-2 in tumour cell survival and implications for pharmacotherapy.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 64:1695–1702. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jourdain A and Martinou JC: Mitochondrial
outer-membrane permeabilization and remodelling in apoptosis. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1884–1889. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|