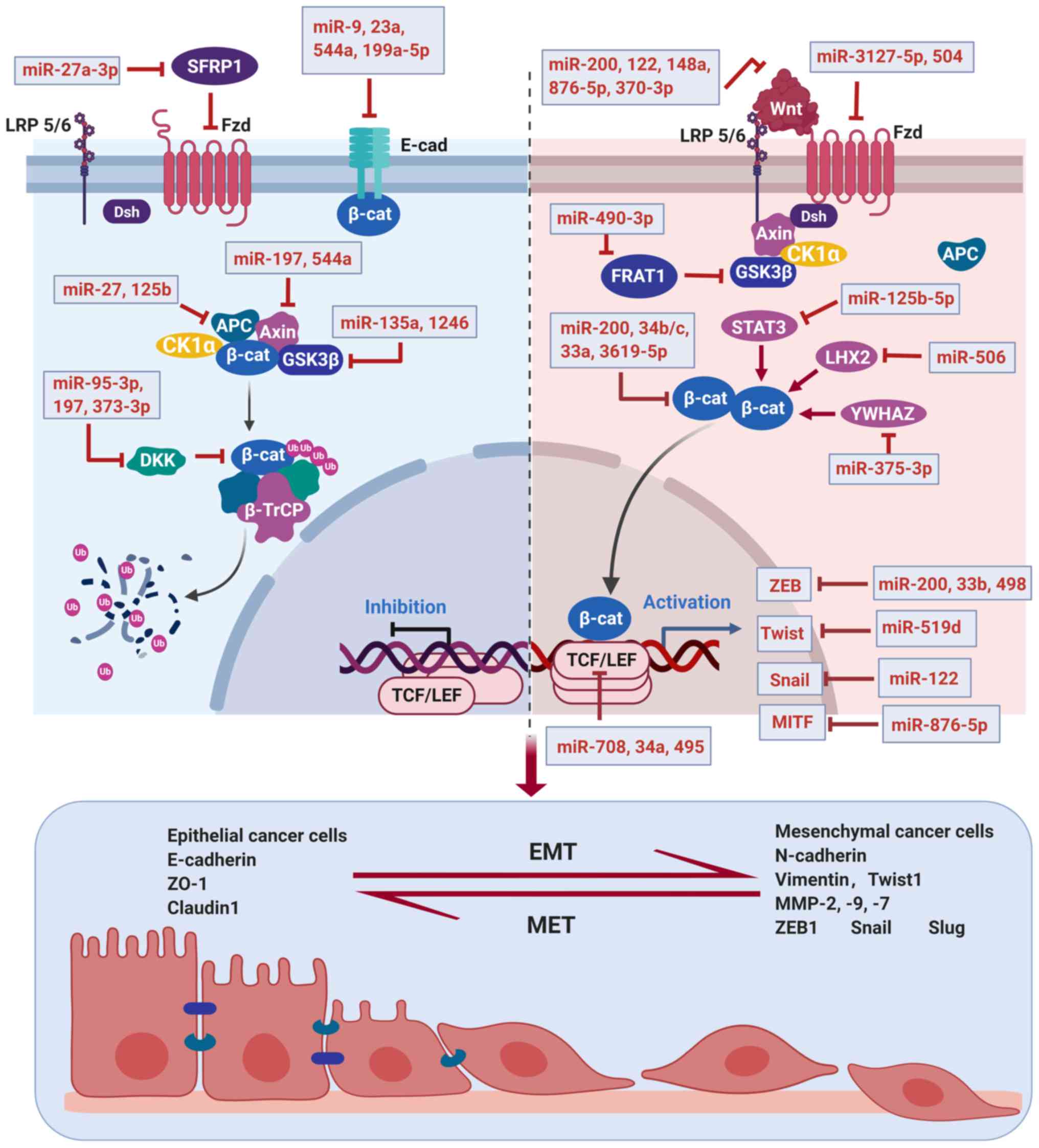
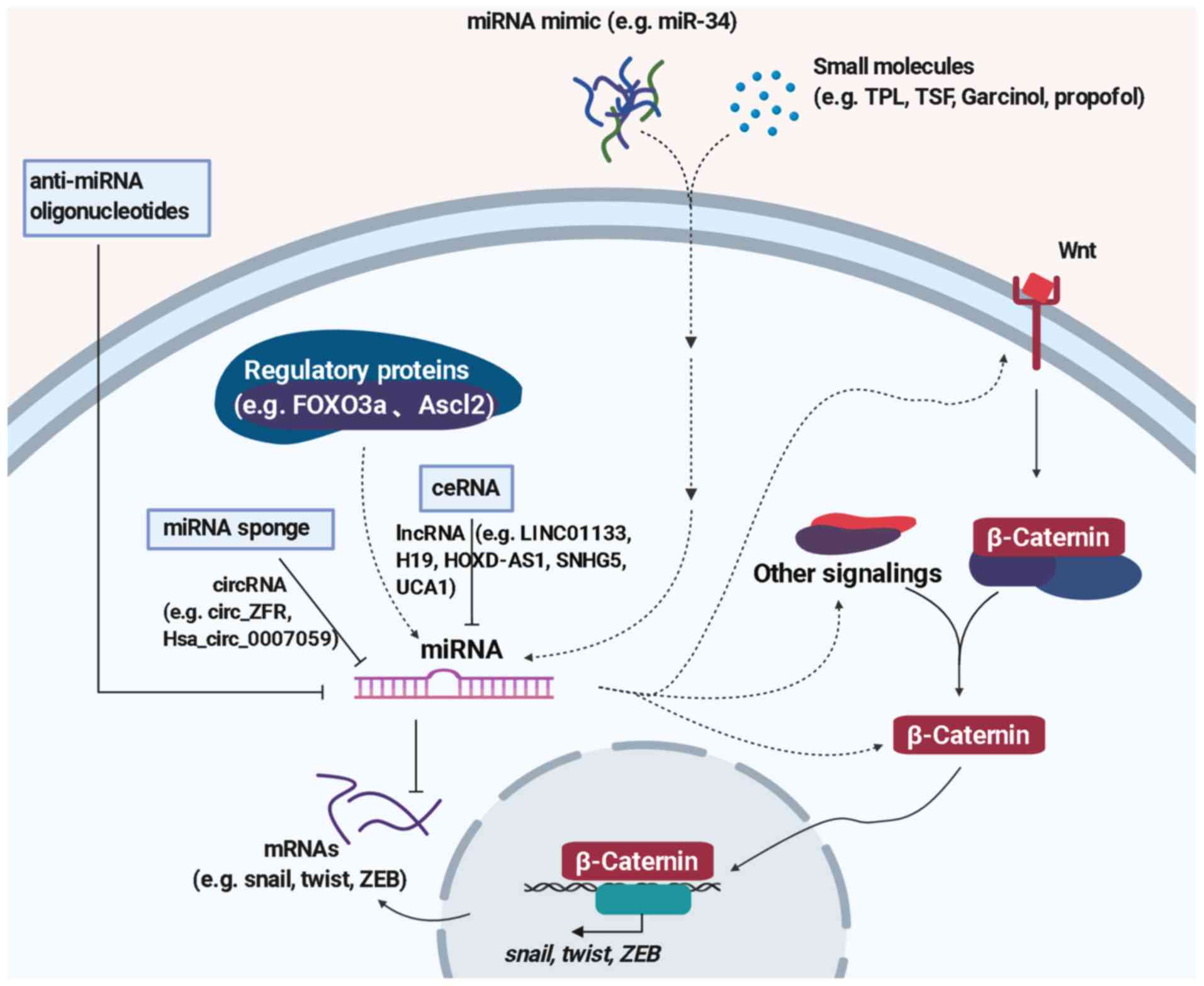
|
1
|
Pasquier J, Abu-Kaoud N, Al Thani H and
Rafii A: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in a clinical
perspective. J Oncol. 2015:7921822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okumura N, Kagami T, Fujii K, Nakahara M
and Koizumi N: Involvement of nectin-afadin in the adherens
junctions of the corneal endothelium. Cornea. 37:633–640. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsukita S, Furuse M and Itoh M:
Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:285–293. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takai Y, Miyoshi J, Ikeda W and Ogita H:
Nectins and nectin-like molecules: Roles in contact inhibition of
cell movement and proliferation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:603–615.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inagaki M, Irie K, Ishizaki H,
Tanaka-Okamoto M, Miyoshi J and Takai Y: Role of cell adhesion
molecule nectin-3 in spermatid development. Genes Cells.
11:1125–1132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okabe N, Shimizu K, Ozaki-Kuroda K,
Nakanishi H, Morimoto K, Takeuchi M, Katsumaru H, Murakami F and
Takai Y: Contacts between the commissural axons and the floor plate
cells are mediated by nectins. Dev Biol. 273:244–256. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heuberger J and Birchmeier W: Interplay of
cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0029152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coopman P and Djiane A: Adherens Junction
and E-Cadherin complex regulation by epithelial polarity. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 73:3535–3553. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo F, Parker Kerrigan BC, Yang D, Hu L,
Shmulevich I, Sood AK, Xue F and Zhang W: Post-transcriptional
regulatory network of epithelial-to-mesenchymal and
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions. J Hematol Oncol. 7:192014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dong C, Wu Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Kang T,
Rychahou PG, Chi YI, Evers BM and Zhou BP: Interaction with Suv39H1
is critical for Snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in breast
cancer. Oncogene. 32:1351–1362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo Q and Qin W: DKK3 blocked
translocation of β-catenin/EMT induced by hypoxia and improved
gemcitabine therapeutic effect in pancreatic cancer Bxpc-3 cell. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:2832–2841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao JH, Luo Y, Jiang YG, He DL and Wu CT:
Knockdown of β-Catenin through shRNA cause a reversal of EMT and
metastatic phenotypes induced by HIF-1α. Cancer Invest. 29:377–382.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai J, Guan H, Fang L, Yang Y, Zhu X, Yuan
J, Wu J and Li M: MicroRNA-374a activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling
to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 123:566–579.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu C, Zhuang Y, Jiang S, Liu S, Zhou J, Wu
J, Teng Y, Xia B, Wang R and Zou X: Interaction between
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and microRNAs regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer (Review). Int J
Oncol. 48:2236–2246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zaravinos A: The Regulatory Role of
MicroRNAs in EMT and Cancer. J Oncol. 2015:8658162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim DH, Xing T, Yang Z, Dudek R, Lu Q and
Chen YH: Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Embryonic
Development, Tissue Repair and Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview. J
Clin Med. 7:12017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang RR, Gui YH and Wang X: Role of the
canonical Wnt signaling pathway in heart valve development.
Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 17:757–762. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahsan K, Singh N, Rocha M, Huang C and
Prince VE: Prickle1 is required for EMT and migration of zebrafish
cranial neural crest. Dev Biol. 448:16–35. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Paolillo M, Serra M and Schinelli S:
Integrins in glioblastoma: Still an attractive target? Pharmacol
Res. 113:55–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Santoro R, Zanotto M, Carbone C, Piro G,
Tortora G and Melisi D: MEKK3 sustains EMT and stemness in
pancreatic cancer by regulating YAP and TAZ transcriptional
activity. Anticancer Res. 38:1937–1946. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu B, Tian X and Li Y, Yang T, Han Z, An
J, Kong L and Li Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition may be
involved in the immune evasion of circulating gastric tumor cells
via downregulation of ULBP1. Cancer Med. 9:2686–2697. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang H, Kim H, Lee S, Youn H and Youn B:
Role of Metabolic Reprogramming in Epithelial-Mesenchymal
Transition (EMT). Int J Mol Sci. 20:20422019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Garg M: Epithelial plasticity, autophagy
and metastasis: Potential modifiers of the crosstalk to overcome
therapeutic resistance. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen L, Mai W, Chen M, Hu J, Zhuo Z, Lei
X, Deng L, Liu J, Yao N, Huang M, et al: Arenobufagin inhibits
prostate cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by
down-regulating β-catenin. Pharmacol Res. 123:130–142. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Derynck R, Muthusamy BP and Saeteurn KY:
Signaling pathway cooperation in TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 31:56–66.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM,
Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, Rimm DL, Wong H, Rodriguez A,
Herschkowitz JI, et al: Residual breast cancers after conventional
therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13820–13825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Astudillo P: Wnt5a Signaling in Gastric
Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:1102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang M, Marco P, Capra V and Kibar Z:
Update on the Role of the Non-Canonical Wnt/Planar Cell Polarity
Pathway in Neural Tube Defects. Cells. 8:11982019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cici D, Corrado A, Rotondo C and Cantatore
FP: Wnt signaling and biological therapy in rheumatoid arthritis
and spondyloarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:55522019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Huang GR, Wei SJ, Huang YQ, Xing W, Wang
LY and Liang LL: Mechanism of combined use of vitamin D and
puerarin in anti-hepatic fibrosis by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin
signalling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4178–4185. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gay A and Towler DA: Wnt signaling in
cardiovascular disease: Opportunities and challenges. Curr Opin
Lipidol. 28:387–396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Villarroel A, Del Valle-Perez B, Fuertes
G, Curto J, Ontiveros N, Garcia de Herreros A and Duñach M: Src and
Fyn define a new signaling cascade activated by canonical and
non-canonical Wnt ligands and required for gene transcription and
cell invasion. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:919–935. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rao TP and Kuhl M: An updated overview on
Wnt signaling pathways: A prelude for more. Circ Res.
106:1798–1806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kawano Y and Kypta R: Secreted antagonists
of the Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci. 116:2627–2634. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A and
Aaronson SA: Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated
by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat Cell Biol.
3:683–686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brott BK and Sokol SY: Regulation of
Wnt/LRP signaling by distinct domains of Dickkopf proteins. Mol
Cell Biol. 22:6100–6110. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu W, Glinka A, Delius H and Niehrs C:
Mutual antagonism between dickkopf1 and dickkopf2 regulates
Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Curr Biol. 10:1611–1614. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mao B and Niehrs C: Kremen2 modulates
Dickkopf2 activity during Wnt/LRP6 signaling. Gene. 302:179–183.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cruciat CM and Niehrs C: Secreted and
transmembrane wnt inhibitors and activators. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0150812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Piccolo S, Agius E, Leyns L, Bhattacharyya
S, Grunz H, Bouwmeester T and De Robertis EM: The head inducer
Cerberus is a multifunctional antagonist of Nodal, BMP and Wnt
signals. Nature. 397:707–710. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Itasaki N, Jones CM, Mercurio S, Rowe A,
Domingos PM, Smith JC and Krumlauf R: Wise, a context-dependent
activator and inhibitor of Wnt signalling. Development.
130:4295–4305. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S and Brabletz T:
E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:151–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Talbot LJ, Bhattacharya SD and Kuo PC:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, the tumor microenvironment, and
metastatic behavior of epithelial malignancies. Int J Biochem Mol
Biol. 3:117–136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ghahhari NM and Babashah S: Interplay
between microRNAs and WNT/beta-catenin signalling pathway regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Eur J Cancer.
51:1638–1649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guo Y, Xiao L, Sun L and Liu F:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: A promising new target for fibrosis
diseases. Physiol Res. 61:337–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gebert LFR and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek
SH and Kim VN: MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
EMBO J. 23:4051–4060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Okada C, Yamashita E, Lee SJ, Shibata S,
Katahira J, Nakagawa A, Yoneda Y and Tsukihara T: A high-resolution
structure of the pre-microRNA nuclear export machinery. Science.
326:1275–1279. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dalmay T: Mechanism of miRNA-mediated
repression of mRNA translation. Essays Biochem. 54:29–38. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Thomson JM, Newman M, Parker JS,
Morin-Kensicki EM, Wright T and Hammond SM: Extensive
post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications
for cancer. Genes Dev. 20:2202–2207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Moyret-Lalle C, Ruiz E and Puisieux A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factors and miRNAs:
‘Plastic surgeons’ of breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:311–322.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zeng M, Zhu L, Li L and Kang C: miR-378
suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon
cancer cells by inhibiting SDAD1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 22:122017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tian L, Zhao Z, Xie L and Zhu J:
MiR-361-5p inhibits the mobility of gastric cancer cells through
suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Gene. 675:102–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Guo R, Wu Z, Wang J, Li Q, Shen S, Wang W,
Zhou L, Wang W, Cao Z and Guo Y: Development of a
Non-Coding-RNA-based EMT/CSC Inhibitory Nanomedicine for In Vivo
Treatment and Monitoring of HCC. Adv Sci (Weinh). 6:18018852019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Teague EM, Print CG and Hull ML: The role
of microRNAs in endometriosis and associated reproductive
conditions. Hum Reprod Update. 16:142–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt
L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS,
Borre M, et al: Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200
family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
128:1327–1334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tryndyak VP, Beland FA and Pogribny IP:
E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and
microRNA-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and
drug-resistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 126:2575–2583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Elson-Schwab I, Lorentzen A and Marshall
CJ: MicroRNA-200 family members differentially regulate
morphological plasticity and mode of melanoma cell invasion. PLoS
One. 5:e131762010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hu X, Macdonald DM, Huettner PC, Feng Z,
El Naqa IM, Schwarz JK, Mutch DG, Grigsby PW, Powell SN and Wang X:
A miR-200 microRNA cluster as prognostic marker in advanced ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 114:457–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shinozaki A, Sakatani T, Ushiku T, Hino R,
Isogai M, Ishikawa S, Uozaki H, Takada K and Fukayama M:
Downregulation of microRNA-200 in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 70:4719–4727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A,
Kim HR and Sarkar FH: miR-200 regulates PDGF-D-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion, and invasion of
prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells. 27:1712–1721. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Saydam O, Shen Y, Wurdinger T, Senol O,
Boke E, James MF, TannousB A, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Yi M, Stephens
RM, et al: Downregulated microRNA-200a in meningiomas promotes
tumor growth by reducing E-cadherin and activating the
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5923–5940.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sanchez-Tillo E, Lazaro A, Torrent R,
Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A, Engel P and Postigo A: ZEB1
represses E-cadherin and induces an EMT by recruiting the SWI/SNF
chromatin-remodeling protein BRG1. Oncogene. 29:3490–3500. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cong N, Du P, Zhang A, Shen F, Su J, Pu P,
Wang T, Zjang J, Kang C and Zhang Q: Downregulated microRNA-200a
promotes EMT and tumor growth through the wnt/β-catenin pathway by
targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1/ZEB2 in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:1579–1587. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Su J, Zhang A, Shi Z, Ma F, Pu P, Wang T,
Zhang J, Kang C and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-200a suppresses the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by interacting with β-catenin. Int
J Oncol. 40:1162–1170. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Tian Y, Pan Q, Shang Y, Zhu R, Ye J, Liu
Y, Zhong X, Li S, He Y, Chen L, et al: MicroRNA-200 (miR-200)
cluster regulation by achaete scute-like 2 (Ascl2): Impact on the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 289:36101–36115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liu J, Ruan B, You N, Huang Q, Liu W, Dang
Z, Xu W, Zhou T, Ji R, Cao Y, et al: Downregulation of miR-200a
induces EMT phenotypes and CSC-like signatures through targeting
the beta-catenin pathway in hepatic oval cells. PLoS One.
8:e794092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Suliman MA, Zhang Z, Na H, Ribeiro AL,
Zhang Y, Niang B, Hamid AS, Zhang H, Xu L and Zuo Y: Niclosamide
inhibits colon cancer progression through downregulation of the
Notch pathway and upregulation of the tumor suppressor miR-200
family. Int J Mol Med. 38:776–784. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Feng B, Wang R, Song HZ and Chen LB:
MicroRNA-200b reverses chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant human
lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting E2F3. Cancer. 118:3365–3376.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Qu J, Li M, An J, Zhao B, Zhong W, Gu Q,
Cao L, Yang H and Hu C: MicroRNA-33b inhibits lung adenocarcinoma
cell growth, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
suppressing Wnt/β-catenin/ZEB1 signaling. Int J Oncol.
47:2141–2152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang X, Xu X, Ge G, Zang X, Shao M, Zou
S, Zhang Y, Mao Z, Zhang J, Mao F, et al: miR498 inhibits the
growth and metastasis of liver cancer by targeting ZEB2. Oncol Rep.
41:1638–1648. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Yue H, Tang B, Zhao Y, Niu Y, Yin P, Yang
W, Zhang Z and Yu P: MIR-519d suppresses the gastric cancer
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Twist1 and inhibits
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 9:3654–3664.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jin Y, Wang J, Han J, Luo D and Sun Z:
MiR-122 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting Snail1 and Snail2 and
suppressing WNT/β-cadherin signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res.
360:210–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Song XF, Wang QH and Huo R: Effects of
microRNA-708 on epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell
proliferation and apoptosis in melanoma cells by targeting lef1
through the wnt signaling pathway. Pathol Oncol Res. 25:377–389.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Liang J, Li Y, Daniels G, Sfanos K, De
Marzo A, Wei J, Li X, Chen W, Wang J, Zhong X, et al: LEF1
Targeting EMT in Prostate Cancer Invasion Is Regulated by miR-34a.
Mol Cancer Res. 13:681–688. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chen J, Luo Q, Yuan Y, Huang X, Cai W, Li
C, Wei T, Zhang L, Yang M, Liu Q, et al: Pygo2 associates with MLL2
histone methyltransferase and GCN5 histone acetyltransferase
complexes to augment Wnt target gene expression and breast cancer
stem-like cell expansion. Mol Cell Biol. 30:5621–5635. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chi Y, Wang F, Zhang T, Xu H, Zhang Y,
Shan Z, Wu S, Fan Q and Sun Y: miR-516a-3p inhibits breast cancer
cell growth and EMT by blocking the Pygo2/Wnt signalling pathway. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:6295–6307. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zheng HE, Wang G, Song J, Liu Y, Li YM and
Du WP: MicroRNA-495 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung
cancer by targeting TCF4 and inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:7750–7759. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xu Z, Yu Z, Tan Q, Wei C, Tang Q, Wang L
and Hong Y: MiR-876-5p regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation,
apoptosis and migration through targeting WNT5A and MITF. Biosci
Rep. 39:BSR201900662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang X, Gan L, Yu G,
Chen Y, Liu K, Li P, Pan J, Wang J and Qin S: Inhibition of LDH-A
by lentivirus-mediated small interfering RNA suppresses
intestinal-type gastric cancer tumorigenicity through the
downregulation of Oct4. Cancer Lett. 321:45–54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Iida H, Suzuki M, Goitsuka R and Ueno H:
Hypoxia induces CD133 expression in human lung cancer cells by
up-regulation of OCT3/4 and SOX2. Int J Oncol. 40:71–79.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ling DJ, Chen ZS, Zhang YD, Liao QD, Feng
JX, Zhang XY and Shi TS: MicroRNA-145 inhibits lung cancer cell
metastasis. Mol Med Rep. 11:3108–3114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Liu H, Yin J, Wang H, Jiang G, Deng M,
Zhang G, Bu X, Cai S, Du J and He Z: FOXO3a modulates
WNT/beta-catenin signaling and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in prostate cancer cells. Cell Signal. 27:510–518. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhang Q, Miao S, Han X, Li C, Zhang M, Cui
K, Xiong T, Chen Z, Wang C and Xu H: MicroRNA-3619-5p suppresses
bladder carcinoma progression by directly targeting β-catenin and
CDK2 and activating p21. Cell Death Dis. 9:9602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liang C, Wang Z, Li YY, Yu BH, Zhang F and
Li HY: miR-33a suppresses the nuclear translocation of beta-catenin
to enhance gemcitabine sensitivity in human pancreatic cancer
cells. Tumour Biol. 36:9395–9403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang N, Wang Q, Shen D, Sun X, Cao X and
Wu D: Downregulation of microRNA-122 promotes proliferation,
migration, and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther.
9:2035–2047. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yan H, Dong X, Zhong X, Ye J, Zhou Y, Yang
X, Shen J and Zhang J: Inhibitions of epithelial to mesenchymal
transition and cancer stem cells-like properties are involved in
miR-148a-mediated anti-metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Carcinog. 53:960–969. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Peng L, Liu Z, Xiao J, Tu Y, Wan Z, Xiong
H, Li Y and Xiao W: MicroRNA-148a suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting
Wnt10b and inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 38:301–308. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Huang X, Zhu H, Gao Z, Li J, Zhuang J,
Dong Y, Shen B, Li M, Zhou H, Guo H, Huang R and Yan J: Wnt7a
activates canonical Wnt signaling, promotes bladder cancer cell
invasion, and is suppressed by miR-370-3p. J Biol Chem.
293:6693–6706. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yang Y, Sun Y, Wu Y, Tang D, Ding X, Xu W,
Su B and Gao W: Downregulation of miR-3127-5p promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via FZD4 regulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 57:842–853. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu Q, Guan Y, Li Z and Wang Y, Liu Y, Cui
R and Wang Y: miR-504 suppresses mesenchymal phenotype of
glioblastoma by directly targeting the FZD7-mediated Wnt-β-catenin
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jin R, Liu W, Menezes S, Yue F, Zheng M,
Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR: The metastasis suppressor NDRG1
modulates the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of
β-catenin through mechanisms involving FRAT1 and PAK4. J Cell Sci.
127:3116–3130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zheng K, Zhou X, Yu J, Li Q, Wang H, Li M,
Shao Z, Zhang F, Luo Y, Shen Z, et al: Epigenetic silencing of
miR-490-3p promotes development of an aggressive colorectal cancer
phenotype through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Cancer Lett. 376:178–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Cui Y, Yang Y, Ren L, Yang J, Wang B, Xing
T, Chen H and Chen M: miR-15a-3p Suppresses Prostate Cancer Cell
Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting SLC39A7 Via Downregulating
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
34:472–479. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Nimmanon T, Ziliotto S, Morris S, Flanagan
L and Taylor KM: Phosphorylation of zinc channel ZIP7 drives MAPK,
PI3K and mTOR growth and proliferation signalling. Metallomics.
9:471–481. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhao X, Lu Y, Nie Y and Fan D: MicroRNAs
as critical regulators involved in regulating epithelial-
mesenchymal transition. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:935–944. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Huang H, Wang C, Liu F, Li HZ, Peng G, Gao
X, Dong KQ, Wang HR, Kong DP, Qu M, et al: Reciprocal network
between cancer stem-like cells and macrophages facilitates the
progression and androgen deprivation therapy resistance of prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:4612–4626. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Arai K, Eguchi T, Rahman MM, Sakamoto R,
Masuda N, Nakatsura T, Calderwood SK, Kozaki K and Itoh M: A Novel
high-throughput 3D screening system for EMT inhibitors: A pilot
screening discovered the EMT inhibitory activity of CDK2 Inhibitor
SU9516. PLoS One. 11:e01623942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wang X and Chen Z: Knockdown of CUL4B
Suppresses the Proliferation and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung
Cancer Cells. Oncol Res. 24:271–277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhang JQ, Chen S, Gu JN, Zhu Y, Zhan Q,
Cheng DF, Chen H, Deng XX, Shen BY and Peng CH: MicroRNA-300
promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway by targeting CUL4B in pancreatic cancer cells. J
Cell Biochem. 119:1027–1040. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yu R, Cai L, Chi Y, Ding X and Wu X:
miR377 targets CUL4A and regulates metastatic capability in ovarian
cancer. Int J Mol Med. 41:3147–3156. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Paraiso KH, Das Thakur M, Fang B, Koomen
JM, Fedorenko IV, John JK, Tsao H, Flaherty KT, Sondak VK, Messina
JL, et al: Ligand-independent EPHA2 signaling drives the adoption
of a targeted therapy-mediated metastatic melanoma phenotype.
Cancer Discov. 5:264–273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Huang J, He Y, McLeod HL, Xie Y, Xiao D,
Hu H, Chen P, Shen L, Zeng S, Yin X, et al: miR-302b inhibits
tumorigenesis by targeting EphA2 via Wnt/β-catenin/EMT signaling
cascade in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 17:8862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Song B, Lin HX, Dong LL, Ma JJ and Jiang
ZG: MicroRNA-338 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of
gastric cancer cells by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1290–1296. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhou F, Gou S, Xiong J, Wu H, Wang C and
Liu T: Oncogenicity of LHX2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Mol Biol Rep. 41:8163–8167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Liang TS, Zheng YJ, Wang J, Zhao JY, Yang
DK and Liu ZS: MicroRNA-506 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the inactivation of the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by down-regulating LHX2. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Chen J, Rajasekaran M, Xia H, Zhang X,
Kong SN, Sekar K, Seshachalam VP, Deivasigamani A, Goh BK, Ooi LL,
et al: The microtubule-associated protein PRC1 promotes early
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Gut. 65:1522–1534. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Tang H, Zhao H, Yu ZY, Feng X, Fu BS, Qiu
CH and Zhang JW: MicroRNA-194 inhibits cell invasion and migration
in hepatocellular carcinoma through PRC1-mediated inhibition of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Dig Liver Dis. 51:1314–1322. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Chen CH, Chuang SM, Yang MF, Liao JW, Yu
SL and Chen JJ: A novel function of YWHAZ/beta-catenin axis in
promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung cancer
metastasis. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1319–1331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Guo F, Gao Y, Sui G, Jiao D, Sun L, Fu Q
and Jin C: miR-375-3p/YWHAZ/β-catenin axis regulates migration,
invasion, EMT in gastric cancer cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
46:144–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Shi L, Huo JW, Chen SS, Xue JX, Gao WY, Li
XY, Song YH, Xu HT, Zhu XW and Chen K: MicroRNA-22 targets FMNL2 to
inhibit melanoma progression via the regulation of the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:5332–5342.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wang JJ, Li ZF, Li XJ, Han Z, Zhang L and
Liu ZJ: Effects of microRNA-136 on melanoma cell proliferation,
apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targetting PMEL
through the Wnt signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201707432017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang JX, Mai SJ, Huang XX, Wang FW, Liao
YJ, Lin MC, Kung HF, Zeng YX and Xie D: MiR-29c mediates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal carcinoma
metastasis via PTP4A and GNA13 regulation of β-catenin signaling.
Ann Oncol. 25:2196–2204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Zhang Z, Yang Y and Zhang X: MiR-770
inhibits tumorigenesis and EMT by targeting JMJD6 and regulating
WNT/β-catenin pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Life Sci.
188:163–171. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Yanaka Y, Muramatsu T, Uetake H, Kozaki K
and Inazawa J: miR-544a induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through the activation of WNT signaling pathway in gastric cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 36:1363–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hu Z, Wang P, Lin J, Zheng X, Yang F,
Zhang G, Chen D, Xie J, Gao Z, Peng L and Xie C: MicroRNA-197
Promotes Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 51:470–486. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Gebert LF, Rebhan MA, Crivelli SE, Denzler
R, Stoffel M and Hall J: Miravirsen (SPC3649) can inhibit the
biogenesis of miR-122. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:609–621. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Petrova YI, Schecterson L and Gumbiner BM:
Roles for E-cadherin cell surface regulation in cancer. Mol Biol
Cell. 27:3233–3244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Xu XZ, Li XA, Luo Y, Liu JF, Wu HW and
Huang G: MiR-9 promotes synovial sarcoma cell migration and
invasion by directly targeting CDH1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
112:61–71. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Ma F, Li W, Liu C, Li W, Yu H, Lei B, Ren
Y, Li Z, Pang D and Qian C: MiR-23a promotes TGF-β1-induced EMT and
tumor metastasis in breast cancer cells by directly targeting CDH1
and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 8:69538–69550.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhao X, He L, Li T, Lu Y, Miao Y, Liang S,
Guo H, Bai M, Xie H, Luo G, et al: SRF expedites metastasis and
modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition by regulating
miR-199a-5p expression in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Differ.
21:1900–1913. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R and Zhao G: miR-27
promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204:486–491.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Mao XW, Xiao JQ, Li ZY, Zheng YC and Zhang
N: Effects of microRNA-135a on the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by
targeting GSK3β through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp
Mol Med. 50:e4292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Yang F, Xiong H, Duan L, Li Q, Li X and
Zhou Y: MiR-1246 Promotes Metastasis and Invasion of A549 cells by
Targeting GSK-3betaMediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cancer Res
Treat. 51:1420–1429. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin
O and Woodgett JR: Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta
in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature. 406:86–90. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Liu WY, Yang Z, Sun Q, Yang X, Hu Y, Xie
H, Gao HJ, Guo LM, Yi JY, Liu M and Tang H: miR-377-3p drives
malignancy characteristics via upregulating GSK-3β expression and
activating NF-κB pathway in hCRC cells. J Cell Biochem.
119:2124–2134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Nie J, Jiang HC, Zhou YC, Jiang B, He WJ,
Wang YF and Dong J: MiR-125b regulates the proliferation and
metastasis of triple negative breast cancer cells via the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway and EMT. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
83:1062–1071. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Barrantes Idel B, Montero-Pedrazuela A,
Guadano-Ferraz A, Obregon MJ, Martinez de Mena R, Gailus-Durner V,
Fuchs H, Franz TJ, Kalaydjiev S, Klempt M, et al: Generation and
characterization of dickkopf3 mutant mice. Mol Cell Biol.
26:2317–2326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Hoang BH, Kubo T, Healey JH, Yang R,
Nathan SS, Kolb EA, Mazza B, Meyers PA and Gorlick R: Dickkopf 3
inhibits invasion and motility of Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells by
modulating the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway. Cancer Res. 64:2734–2739.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Xi M, Cheng L, Hua W, Zhou YL, Gao QL,
Yang JX and Qi SY: MicroRNA-95-3p promoted the development of
prostatic cancer via regulating DKK3 and activating Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:1002–1011. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Weng J, Zhang H, Wang C, Liang J, Chen G,
Li W, Tang H and Hou J: miR-373-3p Targets DKK1 to promote
EMT-induced metastasis via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in tongue
squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2017:60109262017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Elzi DJ, Song M, Hakala K, Weintraub ST
and Shiio Y: Wnt antagonist SFRP1 functions as a secreted mediator
of senescence. Mol Cell Biol. 32:4388–4399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Qiao B, He BX, Cai JH, Tao Q and King-Yin
Lam A: MicroRNA-27a-3p modulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral
squamous carcinoma stem cells by targeting SFRP1. Sci Rep.
7:446882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Zebisch M, Xu Y, Krastev C, MacDonald BT,
Chen M, Gilbert RJ, He X and Jones EY: Structural and molecular
basis of ZNRF3/RNF43 transmembrane ubiquitin ligase inhibition by
the Wnt agonist R-spondin. Nat Commun. 4:27872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Qiao G, Dai C, He Y, Shi J and Xu C:
Effects of miR106b3p on cell proliferation and
epithelialmesenchymal transition, and targeting of ZNRF3 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 43:1817–1829.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Deng X, Wu B, Xiao K, Kang J, Xie J, Zhang
X and Fan Y: MiR-146b-5p promotes metastasis and induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer by targeting
ZNRF3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:71–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Zhang W, Chen X, Kato Y, Evans PM, Yuan S,
Yang J, Rychahou PG, Yang VW, He X, Evers BM and Liu C: Novel cross
talk of Kruppel-like factor 4 and beta-catenin regulates normal
intestinal homeostasis and tumor repression. Mol Cell Biol.
26:2055–2064. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Chen E, Li Q, Wang H, Yang F, Min L and
Yang J: MiR-92a promotes tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer, a
transcriptomic and functional based study. Biomed Pharmacother.
106:1370–1377. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Parenti S, Montorsi L, Fantini S, Mammoli
F, Gemelli C, Atene CG, Losi L, Frassineti C, Calabretta B,
Tagliafico E, et al: KLF4 Mediates the Effect of 5-ASA on the
β-Catenin Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
11:503–510. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Fan D, Lin X, Zhang F, Zhong W, Hu J, Chen
Y, Cai Z, Zou Y, He X, Chen X, et al: MicroRNA 26b promotes
colorectal cancer metastasis by downregulating phosphatase and
tensin homolog and wingless-type MMTV integration site family
member 5A. Cancer Sci. 109:354–362. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Tan M, Wu J and Cai Y: Suppression of Wnt
signaling by the miR-29 family is mediated by demethylation of
WIF-1 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
438:673–679. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Tokarz P and Blasiak J: The role of
microRNA in metastatic colorectal cancer and its significance in
cancer prognosis and treatment. Acta Biochim Pol. 59:467–474. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Garzon R, Marcucci G and Croce CM:
Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and
challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 9:775–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Bader AG: miR-34-a microRNA replacement
therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet. 3:1202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Slaby O, Laga R and Sedlacek O:
Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem J.
474:4219–4251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Trang P, Wiggins JF, Daige CL, Cho C,
Omotola M, Brown D, Weidhaas JB, Bader AG and Slack FJ: Systemic
delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid
emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol Ther. 19:1116–1122.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Zhang L, Liao Y and Tang L: MicroRNA-34
family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Gallant-Behm CL, Piper J, Dickinson BA,
Dalby CM, Pestano LA and Jackson AL: A synthetic microRNA-92a
inhibitor (MRG-110) accelerates angiogenesis and wound healing in
diabetic and nondiabetic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 26:311–323.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Qi Y and Li J: Triptolide inhibits the
growth and migration of colon carcinoma cells by down-regulation of
miR-191. Exp Mol Pathol. 107:23–31. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Wang G, Huang YX, Zhang R, Hou LD, Liu H,
Chen XY, Zhu JS and Zhang J: Toosendanin suppresses oncogenic
phenotypes of human gastric carcinoma SGC7901 cells partly via
miR200amediated downregulation of β-catenin pathway. Int J Oncol.
51:1563–1573. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Ahmad A, Sarkar SH, Bitar B, Ali S,
Aboukameel A, Sethi S, Li Y, Bao B, Kong D, Banerjee S, et al:
Garcinol regulates EMT and Wnt signaling pathways in vitro and in
vivo, leading to anticancer activity against breast cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2193–2201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Du Q, Zhang X, Zhang X, Wei M, Xu H and
Wang S: Propofol inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of MCF-7 cells by suppressing miR-21 expression. Artif
Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:1265–1271. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Zhao M, Xu P, Liu Z, Zhen Y, Chen Y, Liu
Y, Fu Q, Deng X, Liang Z, Li Y, et al: Dual roles of miR-374a by
modulated c-Jun respectively targets CCND1-inducing PI3K/AKT signal
and PTEN-suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Sathyanarayanan A, Chandrasekaran KS and
Karunagaran D: microRNA-145 downregulates SIP1-expression but
differentially regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and Wnt
signaling in SW480 and SW620 cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:2022–2035.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Li D, Tian B and Jin X: miR-630 Inhibits
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) by Regulating the
Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncol Res. 27:9–17.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Chien AJ, Moore EC, Lonsdorf AS,
Kulikauskas RM, Rothberg BG, Berger AJ, Major MB, Hwang ST, Rimm DL
and Moon RT: Activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in melanoma is
associated with decreased proliferation in patient tumors and a
murine melanoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1193–1198. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Ha TY: MicroRNAs in human diseases: From
cancer to cardiovascular disease. Immune Netw. 11:135–154. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Wang HY, Liu YN, Wu SG, Hsu CL, Chang TH,
Tsai MF, Lin YT and Shih JY: MiR-200c-3p suppression is associated
with development of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR mutant non-small
cell lung cancer via a mediating epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) process. Cancer Biomark. 28:351–363. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Howe EN,
Nordeen SK and Richer JK: MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and
restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic
agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1055–1066. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Gao S, Yu Y, Liu L, Meng J and Li G:
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007059 restrains proliferation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via
inhibiting microRNA-378. Life Sci. 233:1166922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Yang XZ, Cheng TT, He QJ, Lei ZY, Chi J,
Tang Z, Liao QX, Zhang H, Zeng LS and Cui SZ: LINC01133 as ceRNA
inhibits gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-106a-3p to
regulate APC expression and the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Mol
Cancer. 17:1262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Ding D, Li C, Zhao T, Li D, Yang L and
Zhang B: LncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN axis promoted
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by
acting on wnt signaling. Mol Cells. 41:423–435. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Zhang Y, Dun Y, Zhou S and Huang XH:
LncRNA HOXD-AS1 promotes epithelial ovarian cancer cells
proliferation and invasion by targeting miR-133a-3p and activating
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:1216–1221.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Li Y, Guo D, Zhao Y, Ren M, Lu G, Wang Y,
Zhang J, Mi C, He S and Lu X: Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 promotes
human hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating
miR-26a-5p/GSK3β signal pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:8882018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Chen X, Gao J, Yu Y, Zhao Z and Pan Y:
Long non-coding RNA UCA1 targets miR-185-5p and regulates cell
mobility by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melanoma
via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Gene. 676:298–305. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Taube JH, Malouf GG, Lu E, Sphyris N,
Vijay V, Ramachandran PP, Ueno KR, Gaur S, Nicoloso MS, Rossi S, et
al: Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 is required for EMT and
cancer stem cell properties. Sci Rep. 3:26872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Strillacci A, Valerii MC, Sansone P,
Caggiano C, Sgromo A, Vittori L, Fiorentino M, Poggioli G, Rizzello
F, Campieri M and Spisni E: Loss of miR-101 expression promotes
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway activation and malignancy in colon
cancer cells. J Pathol. 229:379–389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Huang Z, Li Q, Luo K, Zhang Q, Geng J,
Zhou X, Xu Y, Qian M, Zhang JA, Ji L and Wu J: miR-340-FHL2 axis
inhibits cell growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 10:3722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Liu P, Chen B, Gu Y and Liu Q: PNMA1,
regulated by miR-33a-5p, promotes proliferation and EMT in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 108:492–499. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Han S, Cao C, Tang T, Lu C, Xu J, Wang S,
Xue L, Zhang X and Li M: ROBO3 promotes growth and metastasis of
pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 366:61–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Li Y, Lv Z, He G, Wang J, Zhang X, Lu G,
Ren X, Wang F, Zhu X, Ding Y, et al: The SOX17/miR-371-5p/SOX2 axis
inhibits EMT, stem cell properties and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:9099–9112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Xu W, Ji J, Xu Y, Liu Y, Shi L, Liu Y, Lu
X, Zhao Y, Luo F, Wang B, et al: MicroRNA-191, by promoting the EMT
and increasing CSC-like properties, is involved in neoplastic and
metastatic properties of transformed human bronchial epithelial
cells. Mol Carcinog. 54 (Suppl 1):E148–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Li Y, Sun D, Gao J, Shi Z, Chi P, Meng Y,
Zou C and Wang Y: MicroRNA-373 promotes the development of
endometrial cancer by targeting LATS2 and activating the
Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018.
|
|
186
|
Yang Z, Wang XL, Bai R, Liu WY, Li X, Liu
M and Tang H: miR-23a promotes IKKα expression but suppresses ST7L
expression to contribute to the malignancy of epithelial ovarian
cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 115:731–740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Wang C, Wang X, Su Z, Fei H, Liu X and Pan
Q: MiR-25 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth, migration
and invasion by inhibiting RhoGDI1. Oncotarget. 6:36231–36244.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Hao J, Jin X, Shi Y and Zhang H: miR-93-5p
enhance lacrimal gland adenoid cystic carcinoma cell tumorigenesis
by targeting BRMS1L. Cancer Cell Int. 18:722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Tang J, Li L, Huang W, Sui C, Yang Y, Lin
X, Hou G, Chen X, Fu J, Yuan S, et al: MiR-429 increases the
metastatic capability of HCC via regulating classic Wnt pathway
rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett.
364:33–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Song Q, Xu Y, Yang C, Chen Z, Jia C, Chen
J, Zhang Y, Lai P, Fan X, Zhou X, et al: miR-483-5p promotes
invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting RhoGDI1
and ALCAM. Cancer Res. 74:3031–3042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Wang H, Yan B, Zhang P, Liu S, Li Q, Yang
J, Yang F and Chen E: MiR-496 promotes migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting RASSF6 in colorectal
cancer. J Cell Physiol. 235:1469–1479. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Liu L, Tian YC, Mao G, Zhang YG and Han L:
MiR-675 is frequently overexpressed in gastric cancer and enhances
cell proliferation and invasion via targeting a potent anti-tumor
gene PITX1. Cell Signal. 62:1093522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Zhang X, Peng Y, Huang Y, Yang M, Yan R,
Zhao Y, Cheng Y, Liu X, Deng S, Feng X, et al: SMG-1 inhibition by
miR-192/-215 causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric
carcinogenesis via activation of Wnt signaling. Cancer Med.
7:146–156. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Pei YF, Yin XM and Liu XQ: TOP2A induces
malignant character of pancreatic cancer through activating
β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:197–207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Guo YH, Wang LQ, Li B, Xu H, Yang JH,
Zheng LS, Yu P, Zhou AD, Zhang Y, Xie SJ, et al: Wnt/β-catenin
pathway transactivates microRNA-150 that promotes EMT of colorectal
cancer cells by suppressing CREB signaling. Oncotarget.
7:42513–42526. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Liang H, Wang C, Gao K, Li J and Jia R:
MuicroRNA-421 promotes the progression of nonsmall cell lung cancer
by targeting HOPX and regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 20:151–161. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Listing H, Mardin WA, Wohlfromm S, Mees ST
and Haier J: MiR-23a/-24-induced gene silencing results in
mesothelial cell integration of pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer.
112:131–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|