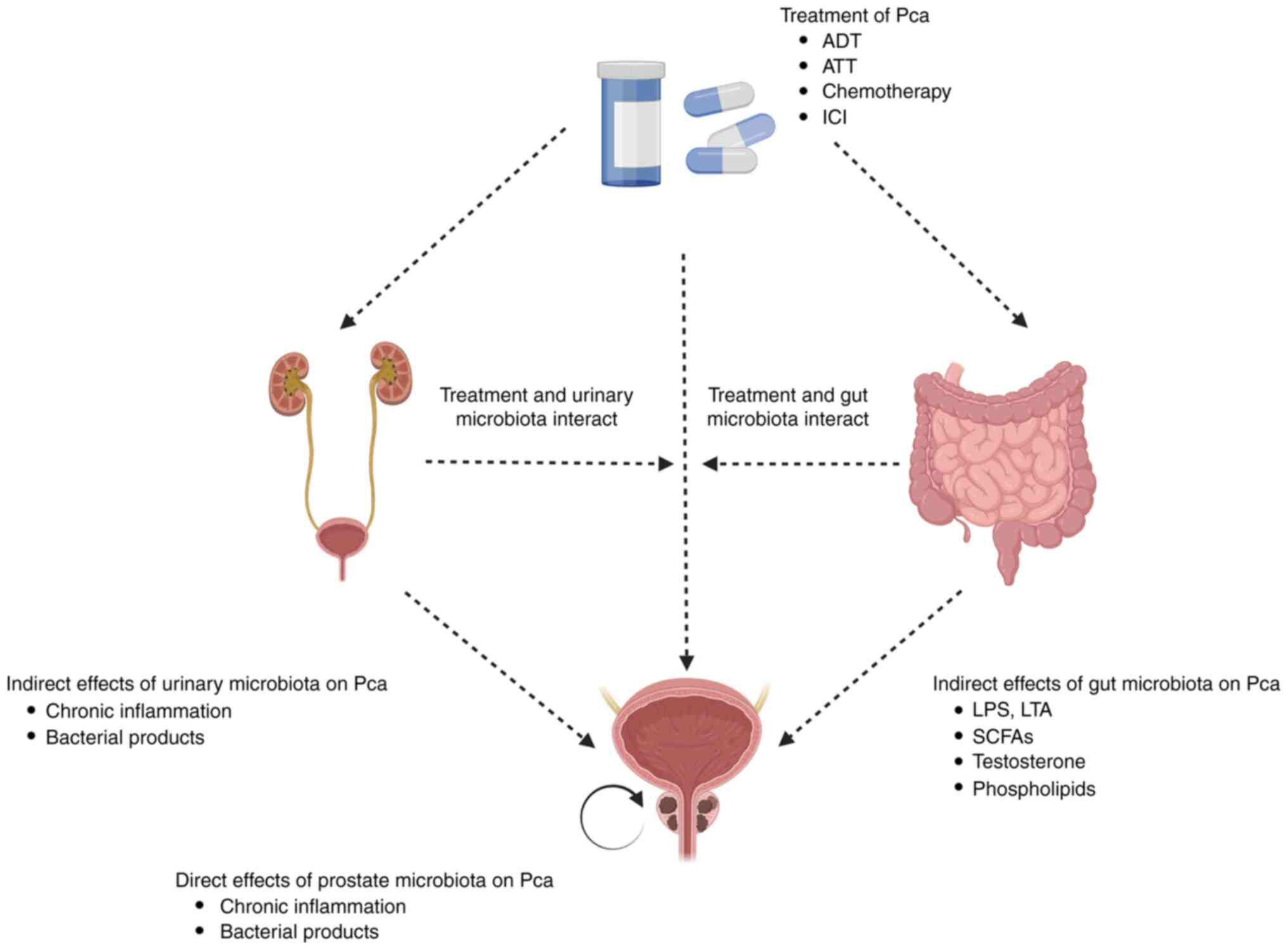
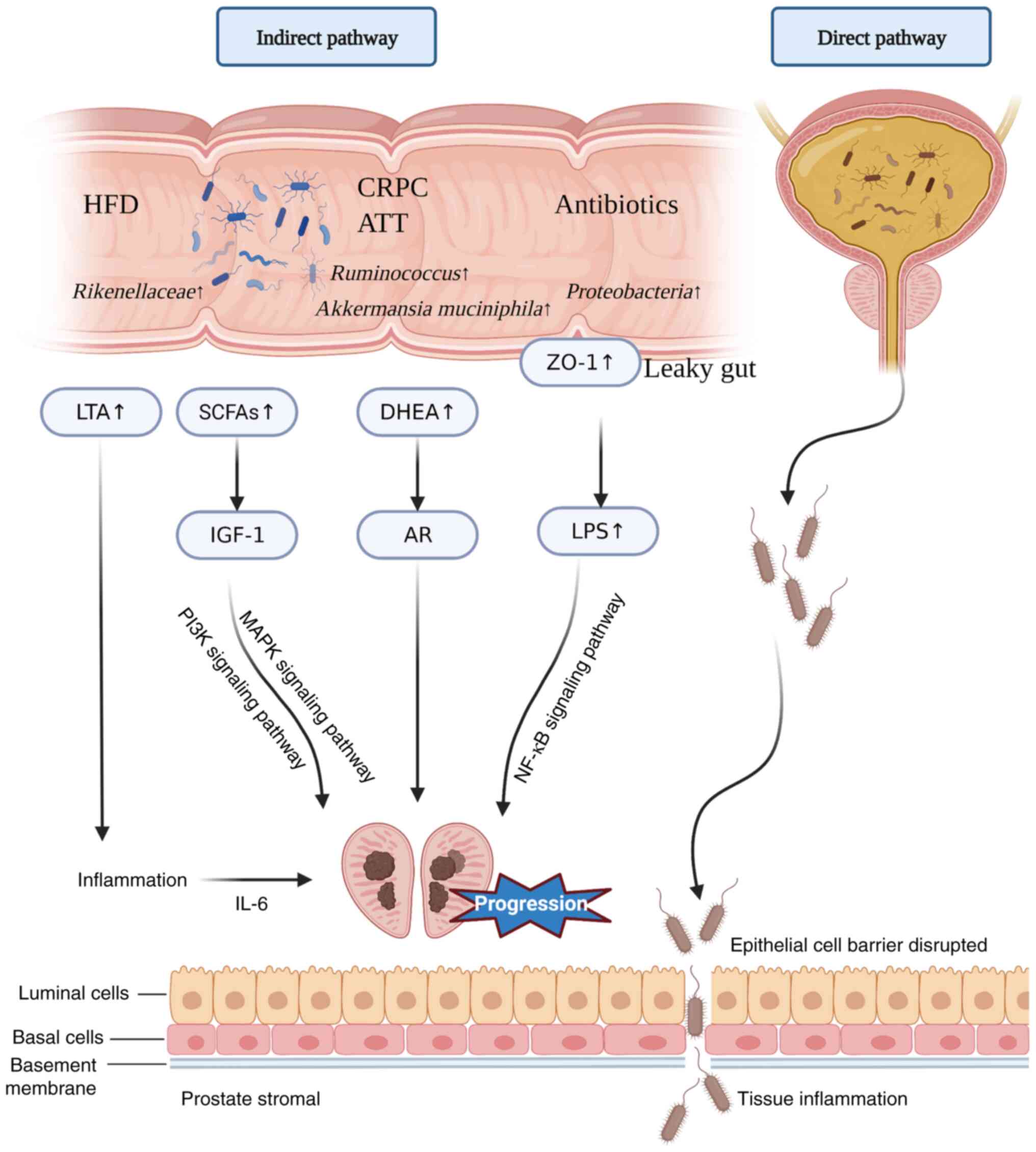
|
1
|
Sender R, Fuchs S and Milo R: Revised
estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body.
PLoS Biol. 14:e10025332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lynch SV and Pedersen O: The human
intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N Engl J Med.
375:2369–2379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marchesi JR, Adams DH, Fava F, Hermes GD,
Hirschfield GM, Hold G, Quraishi MN, Kinross J, Smidt H, Tuohy KM,
et al: The gut microbiota and host health: A new clinical frontier.
Gut. 65:330–339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xavier JB, Young VB, Skufca J, Ginty F,
Testerman T, Pearson AT, Macklin P, Mitchell A, Shmulevich I, Xie
L, et al: The cancer microbiome: Distinguishing direct and indirect
effects requires a systemic view. Trends Cancer. 6:192–204. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whisner CM and Aktipis CA: The role of the
microbiome in cancer initiation and progression: how microbes and
cancer cells utilize excess energy and promote one another's
growth. Curr Nutr Rep. 8:42–51. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davar D, Dzutsev AK, McCulloch JA,
Rodrigues RR, Chauvin JM, Morrison RM, Deblasio RN, Menna C, Ding
Q, Pagliano O, et al: Fecal microbiota transplant overcomes
resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients. Science.
371:595–602. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Litwin MS and Tan HJ: The diagnosis and
treatment of prostate cancer: A review. JAMA. 317:2532–2542. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chandrasekar T, Yang JC, Gao AC and Evans
CP: Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate
cancer (CRPC). Transl Androl Urol. 4:365–380. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bratt O, Folkvaljon Y, Eriksson MH, Akre
O, Carlsson S, Drevin L, Lissbrant IF, Makarov D, Loeb S and
Stattin P: Undertreatment of men in their seventies with high-risk
nonmetastatic prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 68:53–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Salachan PV and Sørensen KD: Dysbiotic
microbes and how to find them: A review of microbiome profiling in
prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alexander JL, Wilson ID, Teare J, Marchesi
JR, Nicholson JK and Kinross JM: Gut microbiota modulation of
chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:356–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Katongole P, Sande OJ, Joloba M, Reynolds
SJ and Niyonzima N: The human microbiome and its link in prostate
cancer risk and pathogenesis. Infect Agent Cancer. 15:532020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cohen RJ, Shannon BA, McNeal JE, Shannon T
and Garrett KL: Propionibacterium acnes associated with
inflammation in radical prostatectomy specimens: A possible link to
cancer evolution? J Urol. 173:1969–1974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sfanos KS, Sauvageot J, Fedor HL, Dick JD,
De Marzo AM and Isaacs WB: A molecular analysis of prokaryotic and
viral DNA sequences in prostate tissue from patients with prostate
cancer indicates the presence of multiple and diverse
microorganisms. Prostate. 68:306–320. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alexeyev O, Bergh J, Marklund I,
Thellenberg-Karlsson C, Wiklund F, Grönberg H, Bergh A and Elgh F:
Association between the presence of bacterial 16S RNA in prostate
specimens taken during transurethral resection of prostate and
subsequent risk of prostate cancer (Sweden). Cancer Causes Control.
17:1127–1133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yow MA, Tabrizi SN, Severi G, Bolton DM,
Pedersen J, Giles GG and Southey MC: Australian prostate cancer
bioresource: Characterisation of microbial communities within
aggressive prostate cancer tissues. Infect Agent Cancer. 12:42017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cavarretta I, Ferrarese R, Cazzaniga W,
Saita D, Lucianò R, Ceresola ER, Locatelli I, Visconti L, Lavorgna
G, Briganti A, et al: The microbiome of the prostate tumor
microenvironment. Eur Urol. 72:625–631. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eisenhofer R, Minich JJ, Marotz C, Cooper
A, Knight R and Weyrich LS: Contamination in low microbial biomass
microbiome studies: Issues and recommendations. Trends Microbiol.
27:105–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Achermann Y, Goldstein EJ, Coenye T and
Shirtliff ME: Propionibacterium acnes: From commensal to
opportunistic biofilm-associated implant pathogen. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 27:419–440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lloyd-Price J, Abu-Ali G and Huttenhower
C: The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 8:512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feng Y, Jaratlerdsiri W, Patrick SM, Lyons
RJ, Haynes AM, Collins CC, Stricker PD, Bornman MSR and Hayes VM:
Metagenomic analysis reveals a rich bacterial content in high-risk
prostate tumors from African men. Prostate. 79:1731–1738. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng Y, Ramnarine VR, Bell R, Volik S,
Davicioni E, Hayes VM, Ren S and Collins CC: Metagenomic and
metatranscriptomic analysis of human prostate microbiota from
patients with prostate cancer. BMC Genomics. 20:1462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Banerjee S, Alwine JC, Wei Z, Tian T, Shih
N, Sperling C, Guzzo T, Feldman MD and Robertson ES: Microbiome
signatures in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 40:749–764. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyake M, Ohnishi K, Hori S, Nakano A,
Nakano R, Yano H, Ohnishi S, Owari T, Morizawa Y, Itami Y, et al:
Mycoplasma genitalium infection and chronic inflammation in human
prostate cancer: Detection using prostatectomy and needle biopsy
specimens. Cells. 8:2122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma J, Gnanasekar A, Lee A, Li WT, Haas M,
Wang-Rodriguez J, Chang EY, Rajasekaran M and Ongkeko WM: Influence
of intratumor microbiome on clinical outcome and immune processes
in prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:25242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salachan PV, Rasmussen M, Fredsøe J, Ulhøi
B, Borre M and Sørensen KD: Microbiota of the prostate tumor
environment investigated by whole-transcriptome profiling. Genome
Med. 14:92022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stamey TA, Fair WR, Timothy MM and Chung
HK: Antibacterial nature of prostatic fluid. Nature. 218:444–447.
1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gatti G, Quintar AA, Andreani V, Nicola
JP, Maldonado CA, Masini-Repiso AM, Rivero VE and Maccioni M:
Expression of toll-like receptor 4 in the prostate gland and its
association with the severity of prostate cancer. Prostate.
69:1387–1397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sfanos KS, Yegnasubramanian S, Nelson WG
and De Marzo AM: The inflammatory microenvironment and microbiome
in prostate cancer development. Nat Rev Urol. 15:11–24. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weeber F, Ooft SN, Dijkstra KK and Voest
EE: Tumor organoids as a pre-clinical cancer model for drug
discovery. Cell Chem Biol. 24:1092–1100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guest C, Harris R, Sfanos KS, Shrestha E,
Partin AW, Trock B, Mangold L, Bader R, Kozak A, Mclean S, et al:
Feasibility of integrating canine olfaction with chemical and
microbial profiling of urine to detect lethal prostate cancer. PLoS
One. 16:e02455302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hilt EE, Putonti C, Thomas-White K, Lewis
AL, Visick KL, Gilbert NM and Wolfe AJ: Aerococcus urinae isolated
from women with lower urinary tract symptoms: In Vitro aggregation
and genome analysis. J Bacteriol. 202:e00170–e20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lewis DA, Brown R, Williams J, White P,
Jacobson SK, Marchesi JR and Drake MJ: The human urinary
microbiome; bacterial DNA in voided urine of asymptomatic adults.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 3:412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Adebayo AS, Ackermann G, Bowyer RCE, Wells
PM, Humphreys G, Knight R, Spector TD and Steves CJ: The urinary
tract microbiome in older women exhibits host genetic and
environmental influences. Cell Host Microbe. 28:298–305.e3. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shrestha E, White JR, Yu SH, Kulac I,
Ertunc O, De Marzo AM, Yegnasubramanian S, Mangold LA, Partin AW
and Sfanos KS: Profiling the urinary microbiome in men with
positive versus negative biopsies for prostate cancer. J Urol.
199:161–171. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma X, Chi C, Fan L, Dong B, Shao X, Xie S,
Li M and Xue W: The microbiome of prostate fluid is associated with
prostate cancer. Front Microbiol. 10:16642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu H, Meng H, Zhou F, Ni X, Shen S and Das
UN: Urinary microbiota in patients with prostate cancer and benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Arch Med Sci. 11:385–394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alanee S, El-Zawahry A, Dynda D, Dabaja A,
McVary K, Karr M and Braundmeier-Fleming A: A prospective study to
examine the association of the urinary and fecal microbiota with
prostate cancer diagnosis after transrectal biopsy of the prostate
using 16S RNA gene analysis. Prostate. 79:81–87. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsai KY, Wu DC, Wu WJ, Wang JW, Juan YS,
Li CC, Liu CJ and Lee HY: Exploring the association between gut and
urine microbiota and prostatic disease including benign prostatic
hyperplasia and prostate cancer using 16S rRNA sequencing.
Biomedicines. 10:26762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Worby CJ, Schreiber HL IV, Straub TJ, van
Dijk LR, Bronson RA, Olson BS, Pinkner JS, Obernuefemann CLP, Muñoz
VL, Paharik AE, et al: Longitudinal multi-omics analyses link gut
microbiome dysbiosis with recurrent urinary tract infections in
women. Nat Microbiol. 7:630–639. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jeney SES, Lane F, Oliver A, Whiteson K
and Dutta S: Fecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment of
refractory recurrent urinary tract infection. Obstet Gynecol.
136:771–773. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
de Vos WM, Tilg H, Van Hul M and Cani PD:
Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut. 71:1020–1032.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sepich-Poore GD, Zitvogel L, Straussman R,
Hasty J, Wargo JA and Knight R: The microbiome and human cancer.
Science. 371:eabc45522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dethlefsen L, Huse S, Sogin ML and Relman
DA: The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut
microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol.
6:e2802008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Boursi B, Mamtani R, Haynes K and Yang YX:
Recurrent antibiotic exposure may promote cancer formation-another
step in understanding the role of the human microbiota? Eur J
Cancer. 51:2655–2664. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhong W, Wu K, Long Z, Zhou X, Zhong C,
Wang S, Lai H, Guo Y, Lv D, Lu J and Mao X: Gut dysbiosis promotes
prostate cancer progression and docetaxel resistance via activating
NF-κB-IL6-STAT3 axis. Microbiome. 10:942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Amirian ES, Petrosino JF, Ajami NJ, Liu Y,
Mims MP and Scheurer ME: Potential role of gastrointestinal
microbiota composition in prostate cancer risk. Infect Agent
Cancer. 8:422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liss MA, White JR, Goros M, Gelfond J,
Leach R, Johnson-Pais T, Lai Z, Rourke E, Basler J, Ankerst D and
Shah DP: Metabolic biosynthesis pathways identified from fecal
microbiome associated with prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 74:575–582.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Golombos DM, Ayangbesan A, O'Malley P,
Lewicki P, Barlow L, Barbieri CE, Chan C, DuLong C, Abu-Ali G,
Huttenhower C and Scherr DS: The role of gut microbiome in the
pathogenesis of prostate cancer: A prospective, pilot study.
Urology. 111:122–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsushita M, Fujita K, Motooka D, Hatano
K, Fukae S, Kawamura N, Tomiyama E, Hayashi Y, Banno E, Takao T, et
al: The gut microbiota associated with high-Gleason prostate
cancer. Cancer Sci. 112:3125–3135. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hayashi T, Fujita K, Nojima S, Hayashi Y,
Nakano K, Ishizuya Y, Wang C, Yamamoto Y, Kinouchi T, Matsuzaki K,
et al: High-fat diet-induced inflammation accelerates prostate
cancer growth via IL6 signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 24:4309–4318.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Smith KS, Frugé AD, van der Pol W, Caston
NE, Morrow CD, Demark-Wahnefried W and Carson TL: Gut microbial
differences in breast and prostate cancer cases from two randomised
controlled trials compared to matched cancer-free controls. Benef
Microbes. 12:239–248. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu Y, Wu X and Jiang H: High dietary fat
intake lowers serum equol concentration and promotes prostate
carcinogenesis in a transgenic mouse prostate model. Nutr Metab
(Lond). 16:242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu Y, Wu X and Jiang H: Combined maternal
and post-weaning high fat diet inhibits male offspring's prostate
cancer tumorigenesis in transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate
model. Prostate. 79:544–553. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Moeller AH, Suzuki TA, Phifer-Rixey M and
Nachman MW: Transmission modes of the mammalian gut microbiota.
Science. 362:453–457. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Matsushita M, Fujita K, Hayashi T, Kayama
H, Motooka D, Hase H, Jingushi K, Yamamichi G, Yumiba S, Tomiyama
E, et al: Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids promote
prostate cancer growth via IGF1 signaling. Cancer Res.
81:4014–4026. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Matsushita M, Fujita K, Hatano K, Hayashi
T, Kayama H, Motooka D, Hase H, Yamamoto A, Uemura T, Yamamichi G,
et al: High-fat diet promotes prostate cancer growth through
histamine signaling. Int J Cancer. 151:623–636. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sato H, Narita S, Ishida M, Takahashi Y,
Mingguo H, Kashima S, Yamamoto R, Koizumi A, Nara T, Numakura K, et
al: Specific gut microbial environment in lard diet-induced
prostate cancer development and progression. Int J Mol Sci.
23:22142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Badgeley A, Anwar H, Modi K, Murphy P and
Lakshmikuttyamma A: Effect of probiotics and gut microbiota on
anti-cancer drugs: Mechanistic perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta
Rev Cancer. 1875:1884942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Routy B, Le Chatelier E, Derosa L, Duong
CPM, Alou MT, Daillère R, Fluckiger A, Messaoudene M, Rauber C,
Roberti MP, et al: Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based
immuno-therapy against epithelial tumors. Science. 359:91–97. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Matson V, Fessler J, Bao R, Chongsuwat T,
Zha Y, Alegre ML, Luke JJ and Gajewski TF: The commensal microbiome
is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma
patients. Science. 359:104–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
González- Mercado VJ, Lim J, Berk L, Esele
M, Rodríguez CS and Colón-Otero G: Gut microbiota differences in
Island Hispanic Puerto Ricans and mainland non-Hispanic whites
during chemoradiation for rectal cancer: A pilot study. Curr Probl
Cancer. 44:1005512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dai Z, Fu J, Peng X, Tang D and Song J:
Intestinal microbiota: The driving force behind advances in cancer
immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 14:47962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Watson PA, Arora VK and Sawyers CL:
Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors
in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:701–711. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu Y and Jiang H: Compositional
differences of gut microbiome in matched hormone-sensitive and
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Transl Androl Urol.
9:1937–1944. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li JKM, Wang LL, Wong CYP, Chiu PKF, Teoh
JYC, Kwok HSW, Leung SCH, Wong SH, Tsui SKW and Ng CF: A
cross-sectional study on gut microbiota in prostate cancer patients
with prostatectomy or androgen deprivation therapy. Prostate Cancer
Prostatic Dis. 24:1063–1072. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kure A, Tsukimi T, Ishii C, Aw W, Obana N,
Nakato G, Hirayama A, Kawano H, China T, Shimizu F, et al: Gut
environment changes due to androgen deprivation therapy in patients
with prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
13:10.1038/s41391–022-00536-3. 2022.
|
|
69
|
Pernigoni N, Zagato E, Calcinotto A,
Troiani M, Mestre RP, Calì B, Attanasio G, Troisi J, Minini M,
Mosole S, et al: Commensal bacteria promote endocrine resistance in
prostate cancer through androgen biosynthesis. Science.
374:216–224. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu Y, Yang C, Zhang Z and Jiang H: Gut
microbiota dysbiosis accelerates prostate cancer progression
through increased LPCAT1 expression and enhanced DNA repair
pathways. Front Oncol. 11:6797122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Huang PY, Yang YC, Wang CI, Hsiao PW,
Chiang HI and Chen TW: Increase in Akkermansiaceae in gut
microbiota of prostate cancer-bearing mice. Int J Mol Sci.
22:96262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wilson ID and Nicholson JK: Gut microbiome
interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl
Res. 179:204–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mohler JL, Gregory CW, Ford OH III, Kim D,
Weaver CM, Petrusz P, Wilson EM and French FS: The androgen axis in
recurrent prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:440–448. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Buttigliero C, Tucci M, Bertaglia V,
Vignani F, Bironzo P, Di Maio M and Scagliotti GV: Understanding
and overcoming the mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to
abiraterone and enzalutamide in castration resistant prostate
cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:884–892. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sfanos KS, Markowski MC, Peiffer LB, Ernst
SE, White JR, Pienta KJ, Antonarakis ES and Ross AE: Compositional
differences in gastrointestinal microbiota in prostate cancer
patients treated with androgen axis-targeted therapies. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 21:539–548. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Daisley BA, Chanyi RM, Abdur-Rashid K, Al
KF, Gibbons S, Chmiel JA, Wilcox H, Reid G, Anderson A, Dewar M, et
al: Abiraterone acetate preferentially enriches for the gut
commensal Akkermansia muciniphila in castrate-resistant prostate
cancer patients. Nat Commun. 11:48222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Vétizou M, Pitt JM, Daillère R, Lepage P,
Waldschmitt N, Flament C, Rusakiewicz S, Routy B, Roberti MP, Duong
CP, et al: Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on
the gut microbiota. Science. 350:1079–1084. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shaikh FY, White JR, Gills JJ, Hakozaki T,
Richard C, Routy B, Okuma Y, Usyk M, Pandey A, Weber JS, et al: A
uniform computational approach improved on existing pipelines to
reveal microbiome biomarkers of nonresponse to immune checkpoint
inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 27:2571–2583. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Terrisse S, Goubet AG, Ueda K, Thomas AM,
Quiniou V, Thelemaque C, Dunsmore G, Clave E, Gamat-Huber M,
Yonekura S, et al: Immune system and intestinal microbiota
determine efficacy of androgen deprivation therapy against prostate
cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0041912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Peiffer LB, White JR, Jones CB, Slottke
RE, Ernst SE, Moran AE, Graff JN and Sfanos KS: Composition of
gastrointestinal microbiota in association with treatment response
in individuals with metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer
progressing on enzalutamide and initiating treatment with anti-PD-1
(pembrolizumab). Neoplasia. 32:1008222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|